The tradition of receiving and giving gifts on New Year's holidays and Christmas has become an integral part of our lives. For companies that present such pleasant surprises to their employees and their family members, business partners or other organizations, the correct management of these expenses causes a lot of trouble. If your company does not want to bypass documenting these costs and keeps accounting of gifts according to all the rules, then we advise you to read our article. We have prepared some useful tips for those who want to know what kind of taxation New Year's gifts are subject to and how to record the expenses incurred in accounting documents.
Who can I give a gift to?
Most commercial organizations in their activities are faced with the need for gifts for their employees, business partners, and third parties. But according to the law, a company cannot make a gift to any person; there are certain restrictions in this matter.
You cannot give anything:
- state and municipal employees;
- commercial enterprises;
- employees of medical and educational institutions, enterprises providing social services;
- other categories of recipients in accordance with Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Contributions to funds
Insurance premiums are not charged for gifts transferred under a gift agreement (Part 3, Article 7 of Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009). Gifts worth less than RUB 3,000 can also be given without concluding a written agreement. However, we still recommend that you formalize it, since in practice inspectors often equate gifts for which a gift agreement has not been formalized with bonuses and payments under an employment contract and charge additional insurance premiums. You can do without a written contract if the recipient is not an employee of the organization. In this case, insurance premiums are not charged.
How to properly formalize a donation
Before purchasing anything to give as a gift, you should make a list of people for whom the gift is planned. Gifts for employees of an organization will differ from gifts intended for business partners or clients of the company. Therefore, the next step will be to draw up a cost estimate for gifts, which will reflect the types and costs of all gifts.
After the preliminary expenses for this item have been calculated, the head of the organization must issue an order with the obligatory indication in it:
- persons responsible for organizing gifts;
- delivery deadlines;
- cost of gifts.
The purchase of gifts is formalized by a sales contract with the seller. The purchase must be confirmed by primary documents such as invoice, check, acceptance certificate.
Do I need to reflect New Year's gifts in accounting and tax accounting?
In order not to forget anything, and most importantly, anyone during this troublesome and worry-filled pre-New Year period, the first step is to make a list of all the people significant to your company and business. Next, the resulting list should be divided into separate categories, which imply gifts of different prices: for employees, for main business partners, for small counterparty companies, etc.
According to the created list, we will draw up a cost estimate. This document can and should be adjusted to optimize all costs. For example, ordering the production of your company’s logo to place it on a gift will only be necessary for contractors or representatives of government organizations, but it is not at all necessary to give souvenirs with the logo to your own staff.
When the cost estimate is completed, it is necessary to prepare and approve a document (usually an internal order of the company), which indicates:
- Responsible employees.
- Accounting for the timing of donations.
- An allocated budget for the purchase of gifts.
Before ordering New Year's souvenirs and accounting for them, do not forget to formalize your relationship with the selling company with an appropriate agreement. In this document, track the conditions in the paragraphs containing information about the possibility of returning the goods, the payment procedure, and the list of related accounting documents, which include:
- Checks.
- Invoices.
- Acceptance and transfer acts.
Confirmation of delivery of the gift can be made verbally or in writing. Agree, it is unlikely that your company will present a branded souvenir to a tax employee against signature. Remember that if the cost of the gift is equal to or more than 3,000 rubles, then its transfer must be recorded in writing by a gift agreement (clause 2 of Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). So, to avoid unwanted accounting bureaucracy, buy inexpensive souvenirs.
In large companies with a large staff of employees, accounting for the issuance of New Year's packages to employees and/or their children is carried out against signature in the statement, which greatly facilitates the accounting of gifts in accounting.
Such a pleasant event as the presentation of a souvenir is reflected in the legislation and is subject to certain rules. In particular, Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation contains the following nuances: if the value of a gift exceeds 3,000 rubles, its donation is prohibited:
- On behalf of minors and citizens declared incompetent, their legal representatives;
- Employees of educational organizations, medical organizations, organizations providing social services, and similar organizations, including organizations for orphans and children without parental care, citizens receiving treatment, maintenance or upbringing there, spouses and relatives of these citizens ;
- Persons holding government positions in the Russian Federation, government positions in constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal positions, civil servants, municipal employees, employees of the Bank of Russia in connection with their official position or in connection with the performance of their official duties;
- In relations between commercial organizations.
As you understand, giving a present to a tax representative or a municipal employee is a violation of the law. However, often the pre-New Year mood and the power of traditions erase this prohibition, and some are happy to give gifts, while others happily accept them.
Next, we’ll take a closer look at how New Year’s gifts included in different categories can be reflected in accounting and tax accounting.
Tax accounting of expenses for gifts
Let's look at the procedure for tax accounting for expenses on gifts using a conditional example. The company purchased 200 notebooks depicting its symbols for a total amount of 23,600 rubles (including VAT 3,600 rubles) to hand them over to its clients. How to reflect these transactions in tax accounting?
From a legal point of view, the provision of gifts by a commercial enterprise to its customers is regarded as a gratuitous transfer . Therefore, VAT in the amount of 3,600 rubles is charged on the cost of the gift, which is subsequently subject to offset. It should be noted that the cost of gifts (20,000 rubles) cannot be recognized as an expense to determine the amount of income tax. It does not matter to whom the gifts were given.
When calculating income tax, it is necessary to take into account the need to tax income in the form of a gift, the value of which exceeds 4,000 rubles. Exceeding the value of the gift entails the obligation of the donor company to submit a declaration f. to the tax service. 2-NDFL.
Personal income tax accrual
A gift is an employee's income received in kind. It is subject to personal income tax from the moment when the total amount of gifts received during the tax period (year) exceeds 4,000 rubles (clause 28 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For example, an organization gave an employee five gifts over the course of a year, each worth 2,000 rubles. Personal income tax is calculated starting from the third gift. The tax rate is 13% for resident donees and 30% for non-residents. The basis for calculating personal income tax on the value of a gift is its market value including VAT (clause 1 of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
Personal income tax = (cost of gifts – 4,000 ₽) × personal income tax rate
For monetary gifts, personal income tax is withheld upon issuance and transferred to the budget on the same day; for non-monetary gifts, personal income tax is withheld on the day of the next salary payment.
How to account for gifts to employees in the form of alcoholic beverages and food packages
Many domestic employers practice giving alcoholic beverages (champagne or stronger versions) to their employees on holidays, such as the New Year. The costs of their acquisition can be documented as expenses for organizing an official reception, i.e. entertainment expenses. The presentation of such gifts requires the execution of an order and an estimate for the reception.
The amount of such expenses is limited and cannot exceed 4% of labor costs in the reporting period.
Gifts for company employees may include food products, such as tea, coffee, and sweets. In this case, the costs of their acquisition can be reflected in different ways. If it is possible to personalize the recipient of the gift, then in this case the employer becomes obligated to withhold personal income tax.
The economic benefit of recipients, if they cannot be identified, cannot be determined, therefore, income tax on gifts in the form of food baskets cannot be withheld. However, such a situation may lead to a dispute with the tax authorities during an audit. Costs incurred when purchasing food products for gifts to employees can be taken into account as expenses for their food.
Accounting for New Year's gifts for employees' children
On New Year's holidays, it is customary to give gifts to both employees of the organization and their family members. In most companies, children of employees under 14 years old receive souvenirs. To properly document such New Year’s gifts in accounting, you need to prepare:
- Order from the head of a commercial organization.
- List of employees with children, indicating their ages.
- Statement for accounting of children's gifts issued.
The order and statement can be drawn up in free form. There is an opinion that in order to justify this accounting transaction it is necessary to prepare gift agreements for each child of employees on the staff of the organization, but in practice almost no one does this.
When an organization gives gifts to employees or their children for the New Year, accounting sometimes reflects this operation on 10, 41 and/or 012 accounts, but according to the principles of the methodology, this is not correct. Materials and inventory items are assets that generate profit, which cannot be said about traditional New Year's children's souvenirs. Therefore, it would be more correct to reflect them on account 91.02. Here's what it looks like in accounting software:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Confirmation document |
| Other expenses - children's New Year's gifts | 91-2 | 60 | Director's order |
| Input VAT | 19 | 60 | Invoice |
| Payment has been made to the supplier | 60 | 51 | Bank statement by account |
| VAT is accepted for deduction | 68-VAT | 19 | Invoice |
| The value of children's gifts is reflected in the off-balance sheet account | 012 | Consignment note, Receipt order | |
| Gifts were given to employees | 012 | List of gifts received | |
| VAT is charged when transferring a gift | 91-2 | 68-VAT | Invoice |
When calculating income tax and the simplified tax system, expenses for the purchase of gifts cannot be accepted for accounting purposes, because they are economically unjustified. These costs are incurred directly from the company's net profit.
regarding the calculation of VAT on the value of gifts. On the one hand, tax supervision believes that the delivery of New Year's souvenirs should be subject to VAT according to the rules set out in paragraph 1 of Article 39, subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 146, paragraph 2 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 22, 2009 No. 03-07-11/16. In this case, you can deduct the input VAT on the invoice. On the other hand, representatives of the judiciary consider children's gifts as a type of incentive for employees, which does not entail the payment of value added tax (FAS NWO in Resolution No. A26-12427/2009 of September 13, 2010, Resolution of FAS Central District of June 2, 2009 No. A62-5424/2008 and FAS UO dated February 20, 2008 No. F09-514/08-S2).
Accounting practice tends to favor first opinions. Companies charge VAT on the cost of gifts and issue invoices in a single copy without indicating the consignee, buyer or address. This is followed by registration of the presentation of gifts in the sales books. Those companies that are inclined to take the second point of view in this matter should be prepared for questions from the tax inspectorate and, most likely, will prove their case in court.
When documenting a donation transaction, accounting calculations and transfer of personal income tax are carried out in accordance with the requirements defined in paragraph 1 of Article 210 and subparagraph 2 of paragraph
2 of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a detailed description of which has already been given in our article.
Gifts for business partners
Accounting for expenses for gifts to business partners depends on the method of documenting them and the sources from which they were financed. Gifts can be formalized as a gratuitous transfer at the expense of the net profit of the donor legal entity. The cost of purchasing gifts is not included in income tax expenses.
Since a gratuitous transfer is considered a sale under the law, the cost of gifts is subject to VAT. You can formalize the delivery of a gift to partners by deed. You can reflect the costs of gifts to partners as entertainment expenses if the following conditions are met:
- during the period when the gifts were given, the donor actually held some official receptions;
- documents for holding receptions and making entertainment expenses are drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the law.
Obligation to pay VAT
The organization can deduct the input VAT indicated in the invoice of the gift seller on a general basis, regardless of the amount or the recipient.
For VAT payers, the transfer of a gift is recognized as a sale and is subject to VAT at a rate of 18% (Clause 1, Article 39, Paragraph 2, Clause 1, Clause 1, Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The invoice is drawn up in a single copy and registered in the organization's sales book. The basis for calculating VAT is the cost of purchasing a gift (excluding VAT) or, if the gift is a product of the organization, its cost.
For “simplified” recipients, the transfer of a gift to an individual is taxed in accordance with the applicable taxation system. There is no obligation to subject this transaction to VAT and to issue an invoice.
How to record gifts to clients in accounting
The good and kind tradition of giving various little things to your clients on New Year’s Eve is not entirely pleasant for the donating organization itself from the point of view of paying taxes. Let us consider the reflection of this operation in accounting in more detail using a specific example.
purchased 500 notebooks with its corporate logo for a total amount of 17,700 rubles (including VAT 2,700 rubles) as gifts for its customers. How does a souvenir reflect accounting and tax accounting for a client?
It has already been said that for the tax authorities, a gift is a transfer of ownership without payment, and its value is subject to VAT (subclause 1 of clause 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the tax paid to the seller of gifts is also subject to credit.
For income tax, expenses aimed at purchasing gifts are not taken into account for tax purposes (clause 16 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and cannot be accepted to reduce the tax base.
If we talk about personal income tax, then souvenirs whose price is equal to or more than 2,000 rubles are subject to it (clause 28 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, the tax office will expect your company to provide information about the income of the client partner (accounting certificate form 2-NDFL). Otherwise, a 50 ruble fine will be charged for each missing certificate, plus officials may suffer from the imposition of penalties.
We will give some useful tips on what to do in this case and avoid unnecessary losses when accounting for New Year's souvenirs.
The first thing you can do is to record the purchase of gifts as expenses for materials for the needs of the company. That is, primary documents should not contain the words “gift”, “souvenir” and others. So the company will have the right to reduce taxable income by the amount of money spent on purchasing New Year's gifts (excluding input VAT).
In our case, accounting for 500 notebooks as a company’s need does not seem likely to be true, so let’s consider another option. Its meaning is that purchased gifts can be decorated as an attribute of a promotion. This must be accompanied by an order from the director and an act approved by the persons responsible for the promotional event and its associated expenses.
This method can significantly reduce the organization’s costs for tax payments, which must be reflected in the accounting entries:
- In this case, the organization is not obliged to pay VAT (goods distributed during the promotional campaign are not sales, but are classified as advertising expenses).
- Input VAT can be deducted, and advertising costs can be taken into account when calculating the tax base. True, we should not forget that these costs are standardized, which means that the organization has the right to take into account these costs in the amount of no more than 1% of revenue for the reporting period minus VAT (clause 4 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Of course, the company will incur additional costs for paying advertising tax, but since it is noticeably less than VAT, the company will, one way or another, benefit by using this option for reflecting costs.
Situation 2. Souvenirs - for entertainment or advertising expenses
When distributing gifts bearing the symbols of the organization (for example, pens, notepads, calendars, flash drives, T-shirts, etc.), it is important for tax accounting whether the circle of recipients is known in advance.
After all, if souvenirs with a company logo are intended for an indefinite number of people, then their cost can be recognized as part of advertising expenses in an amount not exceeding 1% of sales revenue.
If souvenirs are given to representatives of counterparty companies during negotiations, then in this case the cost of the gifts, due to the certainty of the persons receiving them, cannot be taken into account as advertising expenses. At the same time, the tax authorities allowed it to be recognized as entertainment expenses. However, the Ministry of Finance has a different opinion. It is impossible to include such expenses in entertainment expenses, since they are not mentioned in paragraph 2 of Art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Payment of taxes on gifts from organizations
The tax payment deadline is no later than the day following the day of delivery of the gift in cash.
But if a gift worth more than 4,000 rubles is given by an organization in kind (for example, in the form of souvenirs, jewelry, expensive bouquets, etc.), the tax must be withheld on the day of payment of the next salary (clause 4 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
If for some reason the organization was unable to withhold and transfer personal income tax on the value of the gift over 4,000 rubles, then the income thus received is declared and paid by the personal income tax by the recipient himself, and not by the donor organization.
This is possible, in particular, in cases where an organization gave an expensive gift to an individual, but subsequently did not make any payments (salaries, bonuses, etc.) in his favor during the tax period.
In such situations, the organization will have to notify the Federal Tax Service and the taxpayer in writing about the impossibility of withholding personal income tax and the amount of tax payable on the gift given.
To do this, a 2-NDFL certificate with attribute 2 is sent to the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate and the individual. The deadline for sending such a certificate is no later than March 1 of the year following the expired tax period in which the relevant circumstances arose (clause 5 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If, before the end of the tax period, the organization nevertheless pays the taxpayer any money, it will be obliged to withhold tax from it, taking into account amounts not previously withheld. After the end of the tax period and a written notification of the impossibility of withholding personal income tax, the obligation to pay is assigned to the individual (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated August 22, 2014 No. SA-4-7/16692).
That is, by sending a 2-NDFL certificate with sign 2, the organization is relieved of the duties of a tax agent in terms of withholding and paying personal income tax on a gift given to an individual. Personal income tax will be paid by the taxpayer who received the gift, based on the notification sent to him by the Federal Tax Service. In this case, the individual will have to pay personal income tax no later than July 15 of the year that follows the year the gift was received (clause 4 of article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let's sum it up
- Methods of giving include both direct and veiled gifts. In the second case, either advertising or hospitality expenses can be recorded. Each donation option has its own limits that limit the possibility of its use.
- The set of documents for each of the selected options will be different. What they all have in common is the need to complete part of the documents before the event, and the second part after the event.
Prize - differences
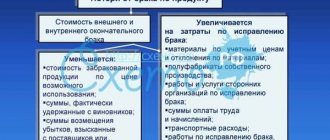
The concept of “gift” includes the entire group of items that are given on occasion, on a certain date. For example, March 8, February 23, New Year, employee’s birthday. The concept of “prize” is found mainly in cultural institutions and companies that work in the field of organizing cultural events. And the prize is awarded for winning any competition. It is awarded for certain merits. So “gifts” appear much more often in the documentation. Moreover, they are officially divided into valuable and non-valuable. They differ in price at 3 thousand rubles.
Registration of gifts in 1C: Accounting 8 ed. 3.0
The organization LLC "AvtoRemont" purchased gifts for the New Year for the most significant representatives (employees) of its business partners: Xiaomi thermal mugs in the amount of 50 pieces for a total amount of 59,000.00 rubles, including VAT 18% 9,000.00 rubles . Gifts were presented on December 24, 2021. The cost of one gift was 1,180 rubles, including VAT 18% 180.00 rubles.
According to the organization’s accounting policy, gifts for holidays are recorded in account 10.01 “Materials” before they are issued to recipients.
AvtoRemont LLC uses the general taxation system (GTS), the accrual method and PBU 18/02 (as amended).
| № | date | Operation | Dt | CT | Sum | Document 1C Create based on | Package of documents Incoming Outgoing Interior |
| 1 | Receipt of gifts to the warehouse | ||||||
| 1.1 | 03.12.2018 | Purchased gifts for business partners | 10.01 | 60.01 | 50 000,00 | Receipt (act, invoice) | Consignment note TORG-12 |
| 1.2 | 03.12.2018 | Input VAT included | 19.03 | 60.01 | 9 000,00 | ||
| 1.3 | 03.12.2018 | Input VAT is accepted for deduction | 68.02 | 19.03 | 9 000,00 | Invoice received Receipt (act, invoice) | Invoice |
| 2 | Presentation of gifts | ||||||
| 2.1 | 24.12.2018 | The cost of gifts issued is reflected in expenses | 91.02 BU - PR | 10.01 BU NU — | 50 000,00 50 000,00 50 000,00 | Free transfer Receipt (act, invoice) | Order (instruction) on the delivery of a gift Statement of accounting and transfer of gifts Accounting information |
| 2.2 | 24.12.2018 | VAT has been calculated on the gratuitous transfer of gifts | 91.02 BU PR | 68.02 BU - | 9 000,00 9 000,00 | ||
| 2.3 | 24.12.2018 | Invoice issued | — | — | 59 000,00 | Invoice issued | Invoice |
| 3 | Recognition of a permanent tax liability (PNO) | ||||||
| 3.1 | 31.12.2018 | A permanent tax liability (PNO) has been recognized in relation to the cost of gifts given (RUB 50,000.00 + RUB 9,000.00) x 20% | 99.02.3 | 68.04.2 | 11 800,00 | Regular operation “Calculation of income tax” as part of the “Month Closing” processing | Accounting information |
| 4 | Formation of tax reporting | ||||||
| 4.1 | 31.12.2018 | VAT declaration | — | — | — | Tax return for value added tax | VAT return |
| 5 | Formation of accounting (financial) statements | ||||||
| 5.1 | 31.12.2018 | Income statement | — | — | — | Financial statements | Financial statements |
Receipt of gifts to the warehouse
1.1. Gifts were purchased for business partners.
1.2. Input VAT included.
Document Receipt (act, invoice)
(Fig. 1):
- Section: Purchases – Receipts (acts, invoices)
. - Receipt
button .
Document transaction type – Goods (invoice)
. - Fill out the document:
- Specify the counterparty, agreement, warehouse, check the accounting accounts and settlement terms using the link in the “Settlements” field.
- Fill out the tabular part of the document using the Add
: - in the Nomenclature
, select incoming gifts; when creating new elements, select the type of nomenclature “Materials” (if gifts are taken into account in account 10 “Materials”); - in the Accounting Account
and
VAT Account
, check that account 10.01 “Raw materials and materials” and account 19.03 “VAT on purchased inventories” are indicated; - fill in the remaining columns (quantity, price, amount, rate and VAT amount).
button .
Rice. 1
Click the button to see the result of document processing (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2
1.3. Input VAT is accepted for deduction.
Document Invoice received
(Fig. 3):
- In the receipt document, fill in the fields Invoice No.
and
from
, then click the
Register
(Fig. 1).
Invoice received
will be automatically created , the fields of the document will be filled with data from the base document, and a link to the created document will appear in the form of the base document. - Click the link to open the document Invoice received
.
Check that the document fields are filled in and the Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt
.
If you clear the checkbox, the deduction is reflected in the regulatory document Formation of purchase ledger entries
.
Rice. 3
Click the button to see the result of document processing (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4
Presentation of gifts.
2.1. The cost of gifts issued is reflected in expenses.
2.2. VAT has been calculated on the gratuitous transfer of gifts.
Document Free transfer
(Fig. 5–6):
- The document can be:
- create on the basis of the document Receipt (deed, invoice)
, in this case, information about the transferred gifts, their quantity and accounting accounts will be automatically transferred to the document from the base document; - create as a new document (section Sales - Free transfer
).
.
button .
- the Recipient
field blank. - Specify the Warehouse
from which gifts are issued. - On the Products
, fill out the tabular part using the
Add
(Fig. 5): - in the Nomenclature
, select the gifts to be transferred; - indicate the number and price of gifts, VAT rate, and account.
(Fig. 6):
- in the fields Cost account
,
VAT account,
check the accounting account (account 91.02 “Other expenses” is entered by default); - in the Other income and expenses
field, the item of other income and expenses “Expenses for the transfer of goods (work, services) free of charge and for one’s own needs” is automatically indicated by default with the item type of the same name and the
Accepted for tax accounting
(Fig. 7).
- Carry out
button . - To print a request invoice for the release of gifts from the warehouse (form M-11) and an invoice for gratuitous transfer, use the Print
.
Rice. 5
Rice. 6
Rice. 7
Click the button to see the result of document processing (Fig. 8).
The cost of gifts and VAT calculated on the transfer of gifts are not included in expenses for the purposes of calculating income tax.
Postings to the debit of account HE.01.9 are for informational purposes only. On subaccounts NOT
“Income and expenses not taken into account for tax purposes” when posting some documents, amounts of expenses that are not accepted for tax accounting are reflected.
Rice. 8
2.3. An invoice has been issued.
Document Invoice issued
(Fig. 9):
- Click the Issue an invoice
in the
Gratuitous transfer
(Fig. 5).
Invoice issued
will be automatically created , its fields will be filled with data from the base document, and a link to the created document will appear in the form of the base document. - Using the link, open the document Invoice issued
and check the completion of its fields. - Operation type code
field is filled in automatically with the value “10”, which corresponds to the shipment (transfer) of goods (performance of work, provision of services), property rights free of charge in accordance with the Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] - To print the invoice, use the Print
.
In the consolidated invoice for the gratuitous transfer of gifts, dashes will be placed in lines 6 “Buyer”, 6a “Address”, 6b “TIN/KPP of the buyer”. The invoice will be reflected in the sales book (section Reports – Sales book
). - The document does not generate transactions.
Rice. 9
Recognition of a permanent tax liability (PNO)
Processing Closing the month
(Fig. 10):
- Section Operations – Month Closing
. - Set the closing month (December 2021).
- Button Perform month closing
.
Rice. 10
3.1. A permanent tax liability (PNO) has been recognized in relation to the value of gifts given.
Regular operation “Calculation of income tax” as part of the processing “Closing the month” (Fig. 11): follow the link with the name of the regulatory operation Calculation of income tax
(Fig. 10) select
Show postings
and see the result of its execution (Fig. 11).
A permanent tax liability (PNO) has been recognized on the value of gifts and VAT calculated on gratuitous transfers (not included in expenses for calculating income tax) in the amount of 11,800.00 rubles: (50,000.00 rubles + 9,000.00 rubles. ) * tax rate 20% = RUB 11,800.00.
Rice. eleven
Formation of tax reporting
4.1. VAT declaration.
Report Tax return for value added tax
(Fig. 12):
- Section Reports – Regulated reports
. - The period for which the report is generated is the 4th quarter of 2018.
Line 010 of Section 3 of the VAT return reflects the tax base and the amount of tax calculated from the value of the gifts given.
Rice. 12