In order to calculate the account balance, you need to decide whether the account is active, passive or active-passive.
Active accounts are accounts where information on assets is stored (51,10,41), passive accounts are those accounts where the sources of funds in active accounts are reflected. (60,66) For example, settlements with suppliers. Since one method of calculation, calculating the balance (balance), is not suitable for all accounts, since all accounts are different in characteristics, we will consider 3 types of calculation:
- For active accounts;
- For passive accounts;
- For active-passive accounts;
- Calculation of the expanded balance.
Below (At the end of the article there will be a link to download the file (Excel) where, having scattered the amounts from the transactions, the Balance (Balance) will be calculated automatically.
Description of account 60
Account 60 is active-passive, so it can have both a credit and a debit balance.
IMPORTANT! The balance must be reflected in detail, since the debit balance of account 60 is the prepayment paid, and the credit balance is the debt to the supplier for material assets, work, and services received but not paid for.
It is convenient to conduct analytical accounting for this account both in the context of subaccounts and for each supplier. Many accounting programs allow you to support such analytics. As a result, turnover is formed for the entire account, for sub-accounts of the account, and if necessary, you can always generate SALT separately for each supplier. The latest report can serve as the basis for drawing up a statement of reconciliation of settlements with the counterparty.
Express accounting check
An express check of accounting in the 1C Accounting 8 program helps to obtain summary or detailed information about the state of the information base data at any time.
An express check is a set of checks grouped by accounting sections. Each check ensures that there are no errors in the infobase data. Control may consist in compliance of credentials with certain provisions of the law or in compliance of data with internal algorithms embedded in the program.
As a result of the express check, a report is generated that shows the total number of checks performed and the number of checks during which errors were detected. The report can be printed or saved to a file.
The results of the express check can be displayed with details up to the accounting section or before each check. The report can show comments for each check performed:
- subject of control - what exactly the current inspection checks;
- the result of the check - whether errors were found during the check;
- possible causes of errors;
- recommendations for troubleshooting.
The list of checks performed can be limited ( Show/hide settings ). To prevent a check or check section from being performed, you need to uncheck the box.
Formation of the statement: rules
The SALT must reflect absolutely all procurement documents, as well as all settlement documents:
- Credit turnover. The loan reflects all transactions related to the purchase of material assets, work, services, equipment, and fixed assets. All documents issued by suppliers and contractors: invoices, certificates of completed work, invoices must be reflected in the credit of account 60. This is how the organization’s accounts payable are formed. If an organization does not use account 15 when purchasing materials, then uninvoiced supplies are also reflected in the credit of account 60. It also shows the return of the advance payment from the supplier for a delivery that was not made by him.
How the work completion certificate should be filled out is described in detail here.
- Debit turnover. All operations related to payment to the supplier are processed through it. This includes repayment of the company’s debt reflected in the credit of account 60 and prepayment transactions. The debit must reflect all payment orders and cash documents on the basis of which the payment was made. This also includes data on offset transactions and return of goods to the supplier.
About the restrictions that exist for cash payments between legal entities, read the material “What is the limit for cash payments between legal entities?”
Report “Tax Audit Risk Assessment”.
The form contains report management commands, a “quick” user settings field, and a report result field.
When opened, the “quick” user settings field displays the current list of parameters (the current settings option) by which data can be selected for generating a report. The list of “quick” user settings includes only those parameters that are defined for this during configuration, as well as those for which the “ Quick access ” mode is specified in the user settings of each such parameter. By checking or unchecking options, and changing comparison conditions and comparison values, you can quickly obtain different slices of data.
To edit the full list of current settings, execute the “ Settings ” command. In the form that opens, the selection conditions for generating the report are created. The list may contain additional parameters.
To use existing settings, execute the command “ All actions - Select setting ”. In the list, select the desired setting and click the “ Select ” button. The selection command is present only if the report or configuration has the “ Storage of custom report settings ” property set.
The report may contain several options for report settings defined during configuration. To select the desired option, use the “ Select Option ” command. In the list, select the desired option and click the “ Select ” button. The list will contain those settings that were previously saved by the “ All actions - Save settings ” command.
If the values of all parameter settings are intended to be used to build a report in the future (possibly if the user has the “ Save user data ” right), then a version of these settings can be saved. To do this, execute the command “ All actions - Save option ”. In the form that opens, specify the name of the option and click the “ Save ” button.
If you need to change an existing option, run the command “ All actions - Change option ”. In the form that opens, select an option and click the “ Select ” button. Make the required changes and save the result.
If changes have been made to the “quick” user settings field and you want to return to the “standard” values (values that are saved for the current settings option), run the command “ All actions - Set standard settings ”.
To build a report, click the “ Generate ” button.
The result is displayed in the field of the spreadsheet document. In the upper part of which the values of the selection parameters used for this construction are indicated.
The report result can be saved in the 1C Accounting 8 program and also printed.
Next Previous
These features are available to both users of local versions and cloud solutions, for example 1C:Fresh, 1C:Ready Workplace (WWW) . To purchase boxed versions or rent the 1C:Accounting 8 program in the cloud, please call +7(499)390-31-58, or e-mail: [email protected]
We recommend that you read the sections
Sales of products, works and services. Settlements with customers
| Purchase of goods and materials and settlements with suppliers |
| Setting up functionality in the 1C Accounting 8.3 program |
| How to create a user with “Administrator” rights in 1C Accounting 8.3 |
| Personnel accounting. Calculation of wages, taxes and contributions from salary |
Formation of a statement: example
Let's start compiling the SALT. As mentioned above, the balance in the statement must be expanded. There are certain subtleties associated with this when creating the statement.
Let's look at an example.
Organization A entered into an agreement with organization B to perform work and transferred it an advance payment in the amount of 12,000 rubles. (including VAT 2,000 rubles) in October. In November, organization B completed the scope of work specified in the contract. The organizations signed a certificate of completion of work in the amount of 12,000 rubles. (including VAT 2,000 rubles), on the basis of which organization B issued an invoice to organization A.
Postings in the accounting records of organization A:
| Dt | CT | Sum | Description | Primary document |
| October | ||||
| 60 "Advances" | 51 | 11 800 | An advance payment was made to organization B under the contract | Payment order |
| 68 “Calculations for VAT” | 76 “Calculations for VAT on advances issued” | 1 800 | Accepted for deduction of VAT on advance payment | Invoice for advance payment from supplier |
| November | ||||
| 20 | 60 “Calculations for work performed” | 10 000 | The cost of work performed is reflected in the accounting without VAT | Certificate of completion |
| 19 | 60 “Calculations for work performed” | 1 800 | VAT reflected | Invoice for work |
| 60 “Calculations for work performed” | 60 "Advances" | 11 800 | Prepayment under the contract has been credited | Accounting information |
| 76 “Calculations for VAT on advances issued” | 68 “Calculations for VAT” | 1 800 | VAT accepted for deduction from advance payment has been restored | Sales ledger entry |
| 68 “Calculations for VAT” | 19 | 1 800 | Accepted for deduction of VAT on work performed | Purchase ledger entry |
As a rule, advances are taken into account in the account. 60 subaccount 02, and the remaining mutual settlements under subaccount 01.
For a sample registration of SALT for account 60 broken down by subaccounts, see the typical situation from ConsultantPlus. The rules for preparing accounting registers are also described here. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
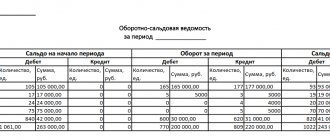
SALT for November on account 60 “Advances”
| Balance at the beginning | Period transactions | Closing balance | |||
| Dt | CT | Turnover by debit | Loan turnover | Dt | CT |
| 11 800 | — | — | 11 800 | — | — |
SALT for November on account 60 “Calculations for work performed”
| Balance at the beginning | Period transactions | Closing balance | |||
| Dt | CT | Turnover by debit | Loan turnover | Dt | CT |
| — | — | 11 800 | 11 800 | — | — |
SALT for November on account 60 (synthetic)
| Balance at the beginning | Period transactions | Closing balance | |||
| Dt | CT | Turnover by debit | Loan turnover | Dt | CT |
| 11 800 | — | 11 800 | 23 600 | — | — |
If no postings were made between the subaccounts of account 60, then the SALT will look like this:
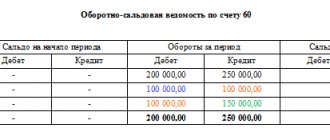
SALT for November on account 60 “Advances”
| Balance at the beginning | Period transactions | Closing balance | |||
| Dt | CT | Turnover by debit | Loan turnover | Dt | CT |
| 11 800 | — | — | — | 11 800 | — |
SALT for November on account 60 “Calculations for work performed”
| Balance at the beginning | Period transactions | Closing balance | |||
| Dt | CT | Turnover by debit | Loan turnover | Dt | CT |
| — | — | 11 800 | — | 11 800 | |
SALT for November on account 60 (synthetic)
| Balance at the beginning | Period transactions | Closing balance | |||
| Dt | CT | Turnover by debit | Loan turnover | Dt | CT |
| 11 800 | — | — | 11 800 | 11 800 | 11 800 |
Report “Analysis of the state of tax accounting for income tax”
The report is intended to identify possible errors in tax accounting data and take into account differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities.
The report contains an analytical analysis of the state of tax accounting and accounting for differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities, which is carried out by comparing data from accounting, tax accounting and accounting for differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities.
The report needs to be generated only after performing routine month-end closing operations.
The report indicators are grouped by economic content and presented in the form of graphic diagrams (block diagrams). Connections between blocks are reflected by arrows. The arrows illustrate the “transition” of value from one accounting object to another. The arrows come from blocks symbolizing objects being written off (their value decreases) and enter blocks symbolizing objects whose value is increasing.
Connections between circuits are indicated in two ways:
- using automatic transitions from one scheme to another;
- on the general diagram.
The transition from one scheme to another is made by double-clicking on the block with the indicators of interest. If the decoding of the requested indicator does not imply a transition to another scheme, then a transaction report opens, containing all the accounts for which this indicator was generated. Each account can be detailed by documents. To do this, you need to select the Expand by command panel documents checkbox. The document can be opened directly from the report and adjusted if necessary.
A general picture of the location of the schemes and the connections between the schemes can be found in the section “Structure of the tax base”. The structure of the tax base is available when opening a report and using the button of the same name on the command panel of any scheme and decoding table. Using the structure of the tax base, you can go to the accounting section of interest.
The “Production” diagram reflects production costs for the production of finished products and services provided to third-party customers. Expenses attributed to the cost of services provided to in-house production units are not reflected in the report.
In the “Cost of Assets” diagram, in the block “Cost of goods, RBP, written off as expenses and depreciation”, the value of assets written off for reasons other than sales (write-off for own needs, write-off for other expenses, returns to suppliers, etc.) is reflected. .
On the “Expenses for ordinary activities” diagram, in the block “Cost of goods, RBP, written off as expenses and depreciation”, the cost of assets written off as expenses for ordinary activities is reflected.
In the “Expenses for ordinary activities” diagram and in the “Production” diagram, a discrepancy between the data in the “Direct costs” block for multi-process production is allowed if at some production stage the reclassification of costs from direct to indirect and vice versa is allowed. The same rule applies to the “Indirect costs” block.
In the “Tax” diagram, the analysis of the state of tax accounting is carried out by comparing the amount of income tax according to tax accounting data (profit statement) and according to accounting data, taking into account the recognition and write-off of permanent and deferred tax assets and liabilities (profit and loss statement). If the amount of income tax according to accounting data coincides with the amount of income tax according to tax accounting data, then tax accounting is regarded as correct.
The blocks illustrate the value of the organization's assets, liabilities, income and expenses according to the following data:
- accounting (yellow background),
- tax accounting (blue background),
- accounting for permanent differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities (pink background),
- accounting for temporary differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities (green background).
If for the indicators of one block the rule “ Value assessment according to accounting data = Value assessment according to tax accounting data + Permanent and temporary differences ” is not followed, then the block is surrounded by a red frame. This is a signal of accounting errors. It is recommended to consider the history of the formation of block indicators, find out the reason for non-compliance with the rule and eliminate it.
The report is not intended to analyze data on income and expenses related to activities with a special taxation procedure. With the exception of those expenses that are classified as activities with a special taxation procedure, as a result of distribution according to income received. The report is not intended to analyze income that is not taken into account when determining the tax base (Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
SALT and balance sheet indicators
In accounting, the debit balance of account 60 is included in the balance sheet asset (in accounts receivable), and the credit balance is included in the balance sheet liability (in accounts payable). This is directly stated in paragraph 73 of the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n.
As can be seen from the example, if you do not make postings between subaccounts, then the balance of account 60 will be overstated in both debit and credit. And this in turn will lead to distortion of balance sheet lines.
For information on what other accounts are involved in the formation of receivables and payables, read the article “How are settlements with debtors and creditors carried out?”
An example of filling out a balance sheet based on data from the balance sheet as of December 31 is given in the ConsultantPlus system. Get trial access to the system for free and proceed to the example.
Additionally
Treatise on Accounts and Records (Luca Pacioli)
An accounting account is an accounting unit that is used for accounting information about homogeneous assets, liabilities, and capital.
The debit side of the ledger account is the left side of the ledger account. Derived from the Latin debet, meaning "he must."
A chart of accounts is a document that contains a list of accounting accounts and the procedure for their application.
Chart of accounts (Document)
| » | Kazakhstan Accounting Forum www.balans.kz |
Results
The meaning of such an accounting register as SALT is quite simple: this statement shows the balance at the beginning of the period, all turnover for the period, and the balance at the end of the period. Account balance 60 must be expanded, since it affects the indicators of the balance sheet line: debit - on the amount of accounts receivable, and credit - on the amount of accounts payable.
When an organization works with suppliers on the principle of “money first, chairs later,” the prepayment must be reflected in a separate subaccount. And after the obligations fulfilled by the supplier are recorded in accounting, it is necessary to make entries within the account. These turnovers also need to be reflected in the SALT. Then the account balance will be reliable and the correct information will appear in the corresponding balance lines.
Sources: Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 N 34n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Subconto card
The “Subconto Card” report is intended to present a sample of invoice correspondences, ordered by date, that relate to the selected time period and in which the selected type of subconto was used.
The structure of the report is similar to the Account Card report.
Each line of the report corresponds to one account correspondence. The report displays summary information: the initial balance of the selected account, as well as the final balance and total turnover.
Data can be displayed with an additional breakdown by time periods: month, year, etc.
What does balance mean?
At the beginning of the article it was already mentioned that literally translated from Italian the word “balance” means “balance”. The term also appears in the following contexts:
- balance (incoming or outgoing balance);
- calculation result;
- the difference between income and expenses, etc.
Surely many have heard about “balance and bulldo”. In simple words, “buldo” means an approximate or incorrect, erroneous balance. This word is slang in nature and is not found in official terminology.
Application
Now let's look in more detail at how balance indicators are used in the state and global economy. In particular, in trading, for forecasting, fundamental analysis is carried out on individual companies that arouse the interest of investors and on states in general. This is done to determine the direction of investment. An important indicator is the trade balance.
In the trade balance
As we already know, the trade balance is calculated using the formula:
STB=EX-IMP, where:
EKS – the amount of goods sent for export;
IMP is the sum of imported goods.
A positive STB value indicates that the goods of a given state are in demand in other countries. It should be noted that there are some negative aspects of a positive trade balance:
- goods that are needed within the country are exported;
- An increase in exports leads to a strengthening of the national currency. We have already mentioned Switzerland, where the government artificially restrains the franc exchange rate, taking into account the interests of exporters who do not benefit from the growth of the national currency.
A negative balance is typical for economically underdeveloped countries. However, there are exceptions. For example, in the United States, a significant portion of production has been transferred to other countries. The same thing happens in Japan. Thus, the trade balance is negative, while the economy is at a high level.
A professional trader should be aware of such nuances and use more detailed data in the context of economic sectors and individual companies.
In the balance of payments
The balance of payments reflects not only monetary payments for goods and services, but also the movement of capital between countries. These parameters are calculated separately. The current balance of payments for foreign trade transactions cannot be considered separately from other indicators. For example, a positive balance may arise as a result of the fact that at the end of the period an advance was received for goods whose shipment is planned for the next quarter or year. Therefore, data over several periods should be taken into account. As for the balance of capital flows, this indicator reflects the influx of foreign investment and the volume of investments in the economies of other countries.
If capital inflows increase, this is a positive trend indicating the interest of foreign investors.
The balance of payments indicators are influenced by the following factors:
- inflation;
- crises in the global economy;
- improvement of technologies;
- fluctuations in the exchange rate of the national currency;
- sanctions of other states, etc.
Due to many external factors, the balance of payments balance is often not a stable value.
In international trade
The country's position in the international market is largely determined by the indicators of the foreign trade balance. These indicators also influence the exchange rate of the national currency. If an increase in demand for government products is predicted, the exchange rate will rise. In other words, if an analysis of the trade balance showed that products are in demand, then demand is expected for the currency.
To maintain a positive trade balance, states sometimes resort to measures such as levying various fees on imports, motivating these actions to protect the interests of domestic producers. Having learned about this, foreign partners take retaliatory measures. This policy is called a trade war.
A negative balance of trade can be offset by a positive balance of payments. This situation is possible for developing countries with an influx of capital from foreign investors.
Balance in foreign trade relations
When analyzing the foreign economic activity of the state, the amounts of export and import transactions are taken into account. This takes into account both shipment and payment. To do this, the trade balance and the balance of payments balance are calculated.
Trade balance
The trade balance is the relationship between exports and imports. If exports exceed imports, this means that the government sells more goods abroad than it buys. This balance is called a positive balance and indicates that goods produced in a given country are in demand among consumers in other countries. A striking example is Switzerland, where there is a constant trade surplus. Swiss pharmaceutical products, household appliances and, of course, watches are in demand all over the world.
In general, the excess of exports over imports is characterized as a favorable factor for the economy. However, here you should pay attention to the structure of exports and imports. Thus, in Switzerland, food and industrial goods are exported. In Russia, a positive balance is achieved through the export of raw materials and energy resources, which leads to a reduction in natural resources. At the same time, the number of jobs in non-export-oriented areas is not increasing. As a result, only exporters, who are disadvantaged by a strong ruble, are in the black, and the majority of the population loses income due to the weakening of the national currency.
A negative trade balance occurs when imports exceed exports. This factor is considered negative, because The largest share of consumption is made up of imported goods, and the development of domestic production suffers. Accordingly, unemployment arises, the income of the population is highly dependent on the exchange rates of other countries, and money is withdrawn from the country.
Balance of payments
The balance of payments is the difference between the receipt of funds from other countries and payments abroad. The indicator is used in the analysis of mutual settlements between states and can also have a positive and negative value.
How to understand when there is a positive or negative balance of payments?
There can be a positive balance of payments in the following cases:
- if in the country as a whole, exports exceed imports (positive trade balance), accordingly, money receipts exceed expenses;
- public debt is growing due to the budget deficit - there are not enough funds to pay foreign creditors.
A negative balance occurs when imports exceed exports, as well as when the debt of other countries for the supply of goods in past periods increases. An increase in accounts receivable is possible, for example, if there is a recession in the economies of key partner countries.