Accounting
Olga Yakushina
Tax expert-journalist
Current as of March 20, 2020
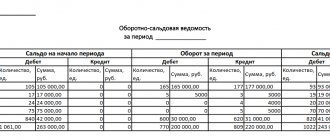
An accounting register called “Turnover balance sheet for account 70” (SALV) helps to summarize information about settlements with employees regarding wages. We will talk about the data reflected in this statement, as well as how to use SALT in account 70.
General description of the balance sheet for account 70
This register groups information about balances at the beginning and end of the period, turnover for the reporting period in account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”. Data in the statement must be disclosed for each employee. The procedure for recording transactions on account 70 is regulated by Section VI of the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On approval of the chart of accounts for accounting…” dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n:
| Transactions reflected in the debit of the account. 70: | Operations reflected on the credit account. 70: |
|
|
*The “Salary Deposit” operation is becoming less and less common these days. Its meaning is to close the payroll compiled for a group of employees when paying wages in cash. Since currently most organizations use non-cash forms of payment to pay wages, the formation of a unified payroll is losing relevance.
Moreover, as of November 30, 2020, the Bank of Russia’s directive No. 5587-U dated October 5, 2020 eliminated the rule about reflecting in the payroll the deposit of wages that were not paid on time.
ConsultantPlus experts told us what other innovations in the procedure for recording cash transactions came into effect on November 30, 2020. Get trial access to the K+ system and go to the review material for free. In K+ you can also check whether you are processing salary payments correctly. If you do not have access to the K+ system, sign up for a trial demo access and study the material for free.
The balance can be anything: active, passive and active-passive. Basically the balance of the account. 70 can be passive, this is due to the fact that wages are calculated on the last day of the reporting (worked) month, and are issued to the employee in the subsequent month. An active or active-passive balance can be when an excessive payment of wages to an employee exceeds their accrual, for example, when an erroneous transfer is made to a salary account.
An example of filling out a statement of accounts. 70 you can look at on our website. follow the link below.
Corresponds with accounts
Account 70 can correspond with the following accounts:
From the debit of account 70 to the credit of accounts:
- Account 50 - when paying wages in cash from the cash register;
- Account 51 – when paying wages by transfer from a current account;
- Account 52 – when paying wages by transfer from a foreign currency account;
- Account 55 – when paying wages by transfer from a special account;
- Account 68 - regarding tax withholding from wages;
- Account 69 - when withholding funds not covered by the social insurance fund (for example, when paying for a voucher);
- Account 71 - when withholding unpaid accountable amounts;
- Account 73 - when withholding funds in favor of the company (for example, when covering damage or defects);
- Account 76 - when depositing unpaid wages, or deductions under writs of execution;
- Account 79 - for settlements between the parent company and the branch;
- Account 94 - for a one-time recovery of the deficiency from the guilty person.
According to the credit of the account, it corresponds with the debit of the following accounts:
- Account 08 - regarding the calculation of wages to employees involved in the creation or preparation for operation of a non-current asset;
- Account 20 - when calculating wages to the main employees of the workshop;
- Account 23 – when calculating wages for employees of the auxiliary workshop;
- Account 25 – when calculating salaries for managerial or technical personnel;
- Account 26 - when calculating salaries for administrative staff;
- Account 28 - when calculating wages for employees who are constantly engaged in correcting defects;
- Account 29 – when calculating wages to employees of service farms;
- Account 44 - when calculating wages for employees engaged in trade;
- Account 69 - when calculating payments made from social funds;
- Account 76 - when calculating payments from third parties in favor of a specific employee;
- Account 79 – for settlements between the parent company and the branch;
- Account 84 - when accruing income based on the results of activities to the founders, members of the company, etc.;
- Account 91 - when calculating wages to employees who are not engaged in their main activities;
- Account 96 - in case of accrual of payments made at the expense of a previously created reserve;
- Account 97 - when calculating payments that will actually be taken into account in the following periods;
- Account 99 - when calculating payment for work to eliminate the consequences of force majeure.
Practical use of the balance sheet for account 70
In the balance sheet, the credit balance from the account statement. 70 as of the reporting date is reflected in the “Short-term liabilities” section in the line “Accounts payable” (clause 20 of PBU 4/99).
If there is an active-passive balance on the account. 70 data from the register is reflected in both the asset and liability of the balance sheet. Reducing assets and liabilities between themselves by offset is prohibited (clause 34 of PBU 4/99). At the same time, the active balance on the account. 70 is reflected in section II “Current assets” in the “Accounts receivable” line of the balance sheet.
It must be remembered that if the report indicators are of a significant level, then the data on them must be reflected separately.
Our article “What requirements should accounting reporting satisfy?” will help you understand the definition of the concept of “materiality level.”
In this case, you need to highlight a separate line in the balance sheet:
- in the liabilities side of the balance sheet in the “Short-term liabilities” section, the line “Debt to the organization’s personnel”
or
- in the balance sheet asset in the “Current assets” section, the line “Advances issued to employees.”
There are some difficulties in the practical application of the balance sheet for account 70. Thus, detailed information about the nature of settlement transactions with employees may be useful for interested users, such as:
- type of accrual;
- source of financing (cost, net profit, reserve, etc.);
- method of repaying debt to an employee (cash payment, deduction based on a writ of execution, deduction of personal income tax, use of non-monetary forms of payment, etc.).
SALT on account 70 does not provide users with such information. It only answers questions such as: “How much was accrued and issued to the employee? What is the balance of mutual settlements with him? To obtain more complete information on account 70, it is advisable to use other registers: payroll, summary of accrued wages, account turnover, etc.
More details about the payroll statement are described in the material “Unified Form No. T-49 - Form and Sample”.
Is it possible to pay part of the salary in kind on a time frame that is different from the time period for payment of the daily salary? The answer to this question was explained by the State Counselor of Justice of the Russian Federation, 2nd class of the State Labor Inspectorate in the Perm Territory, Yu. A. Dotsenko. Study the official’s point of view by getting trial access to the ConsultantPlus system for free.
Main characteristics and general structure
In order to initially get rid of all questions regarding what account 70 is, active or passive, it is necessary to analyze in detail its general structure. Loan debt is a direct source of cash generation.
In this case, wages (employee wages) is a short-term loan debt for any enterprise.
Since account 70 has a credit balance, it is a passive synthetic account. Thus, if the account has a passive structure, then it must generalize the transaction of crediting funds as a credit transaction. In this case, the debit transaction will be considered a debit transaction.
At the end of the period for drawing up reports, the accountant must calculate the financial turnover of money in credit and debit, and also highlight the final balance. The organization's report will indicate the amount required to be paid for the labor of employees. Each employee of the organization must open a personal account to maintain analytical records.
In addition, the accountant must additionally maintain the following information about each employee of the organization:
- Tax accounting of personal income.
- Statements of payment transactions.
- A document indicating all payment and settlement transactions.
- Statements of settlement transactions.
Every organization that conducts financial activities is required to use account 70 in accounting.
Results
SALT for account 70 is one of the possible registers for grouping data on settlements with employees. The data from this report is used to generate financial statements. Balance sheet according to the account. 70 provides information on accrued and paid wages and balances as of reporting dates for each employee of the organization. In order to obtain more detailed information on settlements with personnel, it is necessary to use other forms of accounting registers.
Sources: Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Structure of salary deductions
If material damage was caused due to the fault of an employee of the enterprise, then the administration has every right to deduct the cost of damage from the salary. He pays the amount, like any responsible person from the material side, according to the terms of the concluded contract - either the full cost or partial. It all depends on the damage caused to the enterprise.
If the contract with an individual states that the individual is obliged to fully repay the cost of damage caused to an object that was in storage, then the employee of the enterprise is obliged in this case to pay the full cost of the expenses. In this case, the following employees bear financial responsibility: cash registers, warehouse managers, as well as persons accepting money.
In the case of partial repayment of the cost of the damage caused, it is implied that the amount will be paid within the limit that was previously specified in the contract. In this case, the cost should not exceed the average monthly salary. The amount is subtracted based on the losses received at the enterprise, in accordance with the analytical accounting data.
Defect retention
The defect may be correctable, or it may be irreparable. It all depends on the severity of the marriage. If the defect is correctable, then it may involve the organization in the costs of carrying out restoration work. As a rule, the employee of the enterprise must reimburse them.
In the case where the defect is irreparable, the cost of compensation for the damage caused consists of the expenses that were incurred for the manufacture of the defective product, excluding the benefits received upon completion of the seizure. The costs that are paid in connection with the resulting irreparable defect are based on the difference between debit and credit turnover. The established total cost of losses due to detected defects must be recorded in the debit of account 70.
One of the mandatory payments is personal income tax (NDFL), which is deducted from the amount of remuneration received for the work of an enterprise employee.
It is worth noting that tax is calculated in certain cases - such rules apply in tax policy. In this case, if these rules are taken into account, tax deductions apply to certain income. Such income may include the following:
- The minimum value of income that is not subject to taxes.
- Deductions based on social status or charitable activities.
- Deductions based on skill.
- Deductions based on ownership of certain property.
For most tax payers, the rate has not changed and remains 13%.
As a conclusion, it is worth saying that in accounting (analytical) accounting, account 70 is capable of simultaneously combining several operations that are carried out at the enterprise every month. At the end of the reporting period, the accountant is required to calculate the balance and include it in the liability item of the account.
The displayed remaining balance indicates that the company has a loan debt to the company's employees. In this case, it remains important to keep records of salary payment obligations, because account 70 of the accounting also summarizes the accrual of settlements in the budget.
Keeping accounting records for wages is quite difficult, and the accountant must know about all the nuances. On account 70, settlements are made with employees, regardless of whether they are full-time or not. Any accountant should be aware that wages must include salaries or piecework earnings, bonuses, insurance payments, vacation pay, and so on.
Each employee undertakes to enter into an employment contract, the clauses of which he must familiarize himself with in detail, since all working conditions are indicated there. The contract specifies tariffs for the volume of work performed. In addition, the employment contract defines the relationship between the employer and the employee. The contract also stipulates the employee’s responsibilities in the event of disruption of work activity or damage, in accordance with regulations.
If an employee violates the terms of the contract, causing damage to the enterprise, then he must pay an amount that will cover the expenses of the enterprise. Accounting records all financial transactions. If damage has been caused, then the expenses are deducted from the employee’s salary, and this is recorded in account 70 of the accounting.
The employee pays expenses to the company for the damage caused based on the difference in debit and credit turnover. If the total amount of losses from the damage caused is determined, then it is entered into debit. All this will be very difficult to understand without certain knowledge, so if you are not involved in auditing or accounting, then this topic will be difficult to understand.
So, in fact, our SALT is ready!
Having generated the report with our own hands, we already clearly understand where the numbers come from and what significance they have. Thus, we can easily analyze movements and balances in any area of accounting.
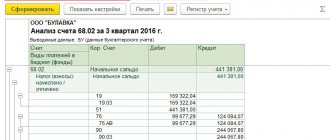
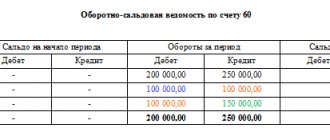
So, for example, from the SALT you can clearly see how much money was received into the company’s current account during the reporting period, how much we paid and what reserve we can still use. We can check the remaining goods or materials in the warehouse. As you can see, in our case, we have materials worth 25,000 in the warehouse, but all the goods have been written off. An analysis of the “creditor” showed that at the end of the period, LLC “Sfera” had a debt to suppliers in the amount of 29,500 rubles, and an advance payment from buyers on Kt 62 invoices was also “hanging” - 87,600 rubles. In addition, wages to employees have not been paid - the organization’s debt according to the Account Code. 70 – 217,500 rub. The turnover on account 90.1 shows the company’s revenue, it amounted to 212,400 rubles, including VAT, which is reflected in the Dt account. 90.3, etc.
In order to obtain detailed information on a specific accounting area, a SALT is generated for a specific account.
As you can see, the balance sheet is simply necessary for every accountant; it accumulates information about all the company’s operations.
Thus
But this is a completely different story, which you can learn from the course “Accounting and Taxation + 1C8.3. Analysis and audit of enterprise activities"
Why do I recommend this course?
First, you will realize that accounting is easy to master.
Secondly, you will receive ready-made practical cases for almost all working situations from the company’s economic activities.
Thirdly, you will test yourself and make sure of the knowledge you have acquired.
Fourthly, you choose a convenient way of learning: face-to-face or remotely.
Well, fifthly, it's really interesting!!!!
Try it!
Accounting for accrual and payment of wages in accounting
Benefits for temporary disability of the employee himself or him to care for his loved ones, leave to care for a child up to 1.5 years old, maternity benefits, financial assistance from the Social Insurance Fund are accrued by posting: D 69.1 K70 - benefits accrued If the organization provides for the creation of a reserve for certain types of expenses, then the calculation of wages from these amounts is reflected by the posting: D 96 K 70 - salary accrued from the reserve It is rare, but this happens when wages are paid from the reserve for future expenses: D 97 K 70 - wages are accrued from the reserve for future expenses Accrual of vacation pay or compensation for unused vacation is reflected in exactly the same transactions. Payments on account 70. Postings Payments of income to employees of the organization are reflected in the debit of account 70.