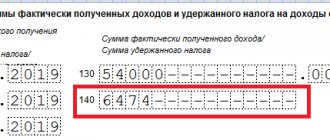
To account for the movement of funds invested by an organization in bank and other deposits, the Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for the financial and economic activities of organizations (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 N 94n) propose using subaccount 3 “Deposit accounts” of account 55 “Special bank accounts." The amount of funds deposited into the deposit account is at the same time recognized as a financial investment (clause 3 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for Financial Investments” (PBU 19/02), approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 10, 2002 N 126n) . To account for financial investments, the specified Instruction prescribes the use of account 58 “Financial investments”. With this option, to account for deposits, it is logical to open a special sub-account 5 “Bank deposit (deposit)”. It is advisable to consolidate the use of a specific account in the accounting policy of the organization (clauses 4, 7 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting Policy of Organizations” (PBU 1/2008), approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06.10.2008 N 106n). Financial investments are accounted for at their original cost (clauses 8, 9, 21 PBU 19/02), which in this case is equal to the amount of funds contributed to the deposit. Thus, when placing funds on a deposit account in a bank, the following posting is made: Debit 58-5 (55-3) Credit 51 - funds are transferred to the deposit account. Regardless of which accounting account the deposits are reflected in, information about them should be shown in the balance sheet as part of financial investments. Let us remind you that: - line 1170 “Financial investments” of the balance sheet indicates the cost of long-term financial investments, the circulation (repayment) period of which exceeds 12 months (clause 19 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting Statements of an Organization” (PBU 4/99), approved By Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 6, 1999 N 43n, clause 41 PBU 19/02); — line 1240 “Financial investments (except for cash equivalents)” shows information about the organization’s financial investments, the circulation (maturity) period of which does not exceed 12 months. Demand deposits are classified as highly liquid financial investments that can be easily converted into a predetermined amount funds and which are subject to an insignificant risk of changes in value (clause 5 of PBU 23/2011).
Such assets are reflected in line 1250 “Cash and cash equivalents”. Interest on the deposit receivable is other income of the organization. They are recognized in accounting for each reporting period in accordance with the terms of the bank deposit agreement during its validity period (clause 34 PBU 19/02, clauses 7, 10. 1, 16 of the Accounting Regulations “Organizational Income” PBU 9 /99, approved
By Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 N 32n).
Article: Accounting for deposits (Mitrich O.) (“Practical Accounting”, 2012, No. 10) IMHO, it is ambiguous. however, in 1C Bukhia I still did not find the concept of “Deposits on demand”.
Interest receivable (line code 2320)
Added by: Upload Does the published material violate your copyright?
Let us know. University: Subject: File: KL_Technol comp. accounting report_Strygina_2014.docx Downloads: 17 Added: 06/01/2015 Size: 161 Kb ☆ 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 < Previous Page 15 of 25 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Indicate the turnover on the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, sub-account “Other income”, in correspondence with the accounts of accrued interest on bonds, deposits, government securities, etc., on loans issued, for use bank of available funds in the organization’s account, for example 58, 76, 51, 52, etc.
Interest payable (line code 2330)
The turnover is reflected in the debit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, sub-account “Other expenses”, in correspondence with the accounts recording the amounts due for interest on bonds, shares, received loans, loans, for example 76, 66, 67, etc.
Other income (line code 2340)
This is the turnover under the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount “Other income”, in terms of other income received.
Other expenses (line code 2350)
This is the turnover in the debit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount “Other expenses”, in terms of other expenses incurred.
Profit (loss) before tax (line code 2300)
This is a calculated indicator, which is determined as follows:
The sum of lines 2200 “Profit (loss) from sales”, 2310 “Income from participation in other organizations”, 2320 “Interest receivable” and 2340 “Other income” and subtracting from the resulting amount the indicators of lines 2330 “Interest payable” and 2350 “ Other expenses". If as a result the organization received a negative value (loss), then it is shown in the Statement of Financial Results in parentheses.
The line is obtained as the difference between debit and credit turnover in account 99 “Profit and Loss” in correspondence with accounts 90 “Sales”, subaccount 90-9 “Profit/loss from sales”, and 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount 91-9 “Balance of other income and expenses.” The credit balance of account 99, the analytical account for accounting profit (loss), means that the organization has made a profit, and the debit balance means a loss.
Rules and procedure for filling out the Other income and expenses section
The conditional income tax expense (income) is equal to the value determined as the product of the accounting profit generated in the reporting period by the profit tax rate in effect on the reporting date, and is taken into account in accounting in a separate subaccount of account 99 for accounting for conditional expenses (conditional income) for income tax. Under the item “Interest receivable” (line 060)
income is reflected in the amount of interest due in accordance with agreements on bonds, deposits, government securities, etc., for the provision of funds to the organization for use, for the use by a credit organization of funds held in the organization’s account with this credit organization. If errors were discovered in previous reporting periods that do not affect the current income tax of the reporting period, then the amounts of adjustments should be reflected in a separate item in the income statement after the current income tax item. No changes are made to the accounting data of previous periods. At the same time, the tax return is adjusted for the amount of such errors.
It is clarified for the period to which the identified errors relate, that is, changes are made to the declaration for the previous period. Subject to the foregoing, the amount of income tax adjustments associated with the discovery of errors relating to prior reporting periods does not affect the current income tax. Line amount 100
income statement is equal to the debit turnover of account 91. 2 “Other expenses” for the corresponding items of analytical sections.
This should also include the amounts of valuation reserves created by the organization, which are accounted for in accounts 14 “Reserves for the reduction in the value of material assets”, 59 “Reserves for the impairment of investments in securities” and 63 “Reserves for doubtful debts”.
“Change in deferred tax liabilities” (line code 2430)
The difference between credit and debit turnover on account 77 “Deferred tax liabilities” for the reporting period is reflected without taking into account the debit turnover on account 77 in correspondence with account 99 “Profits and losses”. If the difference turns out to be negative, this means that more deferred tax liabilities were written off for the reporting period than accrued.
The positive difference between credit and debit turnover in account 77 (increase in deferred tax liabilities) must be subtracted from the accounting profit indicator on line 2300 “Profit (loss) before tax”, and the negative difference (decrease in deferred tax liabilities) must be added to the accounting profit indicator, those. a positive difference should be reported in line 2430, “Change in deferred tax liabilities,” in parentheses, and a negative difference should not be reported.
4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 < Previous Page 15 of 25 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Adjacent files in an item
- # 03.26.201659.76 Kb13Microsoft Office Word document.docx
- # 01.06.2015432.64 Kb1law on the protection of consumer rights.doc
- # 06/01/2015637.32 Kb507 Application for issuance of a passport (Form 1P).PDF
- # 03.26.2016628.63 Kb17igp.docx
- # 01.06.2015443.39 Kb171KL_Org calculation with b-volume and external f_Strygina_2014.doc
- # 01.06.2015161 Kb17KL_Tekhnol comp. accounting report_Strygina_2014.docx
- # 03.26.2016290.84 Kb18constitutional.docx
- # 06/01/201555.19 Kb5Culturology 2.docx
- # 03.26.2016611.84 Kb19 course of lectures intro. in prof..doc
- # 03/26/2016605.18 Kb21 course of lectures introduction to the profession..doc
- # 01.06.20153.25 Mb13 Course of lectures.doc
Loan when calculating income tax
In the column “Reserve capital” - the difference between the credit turnover of account 82 in correspondence with account 84 and the debit turnover of account 82 in correspondence with accounts 84 and 81 (or 75).
But here it is necessary to take into account that the balance of account 67 “Long-term loans and borrowings” can be transferred in whole or in part to line 1410. This is possible if, as of the reporting date, account 67 contains liabilities whose maturity as of that date does not exceed 12 months.
The balance sheet of an enterprise is very important for banks, which will be able to assess, based on the indicators of this form, how creditworthy the future client is, and what is the maximum loan amount that can be provided to him.
Long-term loans can be accounted for in account 67 until maturity, or can be transferred to account 66 after 365 days remain until maturity.
In which account is interest receivable and payable?
leon
- 08.08.2018 /
- 0 Comments
Debit 91-2 Credit 66 (67) - 48,105 rubles. (RUB 2,360,000 x 24%: 365 days x 31 days) - interest accrued on the loan for May; Debit 91-2 Credit 66 (67) - 46,553 rubles. (RUB 2,360,000 x 24%: 365 days x 30 days) - interest accrued on the loan for June. At the end of the reporting period, interest on the loan is entered in line 2330 “Interest payable” of the new unified report form in the amount of: 46,553 + 48,105 + 46,553 = 141,211 rubles. Additional loan costs excluding VAT (RUB 10,000) are indicated in line 2350 “Other expenses” of the report. ...on bonds issued by the company Since the issue of bonds is carried out to attract borrowed capital, operations related to their movement are reflected in accounting in accordance with PBU 15/2008.
Long-term liabilities on the balance sheet
Changes in financial statements relating to both the current and last year (after their approval) are made in the statements prepared for the reporting period in which distortions in its data were discovered.
We looked at accounting for loans and borrowings in ours. And on which line of the balance sheet is debt on short-term loans and borrowings reflected?
The simplest method is the so-called “open account”, when, in accordance with the concluded contract, the consumer is issued an invoice, which is recognized by him. In the balance sheet, such receivables are combined into the item “accounts receivable”. A more reliable way is to obtain a written commitment to pay money, i.e. bills. The repayment of the loan by the debtor company is reflected by entry 66 or 67 of the passive account in the debit. For example, the return of borrowed funds on a loan from the company’s account - Dt 66/1, Kt 51. Interest on the use of loan funds is credited to part of the other expenses of the reporting period in which the accountant accrued them.
To account for short-term loans, the chart of accounts provides account 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”; for accounting for long-term loans, account 67 “Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings”.
Short-term are those whose maturity is no more than 12 months after the reporting date. All other assets and liabilities are long-term.
Balance on account 67 “Settlements on long-term loans and borrowings” (the amount of the principal debt and accrued interest*. The exception is interest, the payment period of which as of the reporting date is less than 12 months.
Interest receivable
Settlements with various debtors and creditors” - if, in accordance with the company’s activities, such income is classified as other;
- on the credit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount “Revenue” in correspondence with account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” - if, in accordance with the areas of the company’s activities, such income is recognized as income from ordinary activities.
Reflection of interest receivable in the financial statements Interest receivable is reflected:
- on line 2320 “Interest receivable” of the Statement of Financial Results - if, in accordance with the areas of the company’s activities, such income is classified as other;
- on line 2110 “Revenue” of the Statement of Financial Results - if, in accordance with the areas of the company’s activities, such income is recognized as income from ordinary activities.
Error No. 3 The balance sheet reflects only the paid authorized capital
An enterprise accountant spends a whole year working towards reliable annual reporting: organizing accounting, conducting an inventory of property, and reconciling settlements with counterparties. But the matter does not end with mutual confirmation of the amount of debt. It is important to correctly reflect debt on the balance sheet. Especially during periods of non-payment.
Important Below is a fragment of the balance sheet for 2011: Name of indicator As of 12/31/2011 As of 12/31/2010 As of 12/31/2009 IV. COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF THE CULTURAL EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT AND ACCOUNTING OF NATIONAL STEREOTYPES OF BEHAVIOR IN INTERNATIONAL MANAGEMENT…
Percentage to be paid
Positive exchange rate differences on interest are entered in line 2340 “Other income” of the new unified reporting form. Their sum will be: 59 + 361 = 420 rubles. ...for bank deposits the Company can place available funds in bank deposit accounts in order to receive income from them. Interest on the deposit is accrued on the terms stipulated in the agreement with the bank.
In accounting, they are reflected on the day when the company has the right to receive them in accordance with its terms (for example, after a certain number of days, at the end of each month, quarter, half-year). Interest is taken into account on account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” in correspondence with account 91 “Other income and expenses” (subaccount 1 “Other income”). They do not affect the deposit amount. Example In January, a company deposited money into a long-term bank deposit in the amount of RUB 1,000,000.
How to get a tax deduction for mortgage interest paid
Preparing documents yourself is not particularly difficult. For this you need:
- Register on the Federal Tax Service website and create a personal taxpayer account.
- Fill out the 3-NDFL tax return on the Federal Tax Service website. Download and print it.
- From the accounting department at your place of work, obtain a certificate in Form 2-NDFL about the taxes withheld from you.
- Prepare copies of documents confirming the mortgage: loan agreement, loan or mortgage agreement concluded with the bank and payment schedule.
- Prepare copies of payment documents that confirm payment of interest on the loan (mortgage) agreement. These can be cashier's checks, statements of personal accounts, bank statements.
- The completed package of documents must be submitted to the tax office at your place of residence. You can also send it by mail, but you may then be asked to present the original documents.
All! You can expect a payment to the bank details you provided.
Interest receivable which accounts are included
When issuing a loan in foreign currency, it becomes necessary to take into account exchange rate differences. With the cash method, this situation is impossible. Typical accounting entries When constructing real estate, interest on the loan is included in their initial cost:
- Debit 08 Credit 66 (67).
After construction is completed, a note is made:
- Debit 91.2 Credit 66 (67).
If the interest rate exceeds the standard for controlled debt, then a deferred tax liability arises, which must be reflected at:
- debit account 68.4.2 and credit 77 account.
Example of entries for a loan from a legal entity Example: A company was provided with a cash loan for a period of 11 months at a rate of 12% per annum in the amount of RUB 350,000.
Maximum amount to be refunded
Let's take a closer look at recent adjustments to tax legislation. The right to a refund of taxes previously paid to the budget has been reserved for citizens paying a mortgage for a long time.
At the same time, in 2013 there were a number of clarifications in tax legislation.
In particular, the changes affected the maximum amount of interest deduction:
| Property purchase date | The maximum amount of interest paid to the bank from which compensation can be received, rub. | Maximum amount to be refunded, rub. |
| Until December 31, 2013 (inclusive) | is not limited | is not limited |
| After 01/01/2014 | 3 000 000 | 3 000 000 × 13% = 390 000 |
Thus, provided that a home is purchased before December 31, 2013 inclusive, a citizen has the right to return funds without restrictions on the amount of interest paid to the bank.
If the property was purchased in 2014 or later, the amount of interest on which
compensation may be received, cannot exceed 3 million rubles.
You can use the right to deduct mortgage interest once in your lifetime within the framework of one property. In this case, the date of purchase of real estate with a mortgage does not matter.
Calculation of interest on loans received
Their amount is used to increase sales revenue recorded on line 2110 “Revenue” of the report. Example: A company purchased a financial bill worth RUB 500,000. The bill can be presented for payment in 3 months. from the moment of its issue. Interest is charged on it at the rate of 18% per annum.
After 3 months The company presented the bill for payment. The number of days of circulation of the bill was 90. Interest accrued on the bill will be reflected by the entry: Debit 76 Credit 91-1 - 22,192 rubles. (RUB 500,000 x 18%: 365 days. What applies to interest receivable? If errors were discovered in previous reporting periods that do not affect the current income tax of the reporting period, then the adjustment amounts should be reflected in a separate item in the income statement and losses after the current income tax item No changes are made to the accounting data of previous periods.
Operations for the issuance and repayment of a loan, as well as interest on it, will be reflected in the entries: Debit 76 Credit 91-1 - 17,286 rubles. (592 USD x 29.2 rubles/USD) - interest accrued for April; Debit 76 Credit 91-1 - 17,932 rubles. (612 USD x 29.3 rubles/USD) - interest accrued for May; Debit 76 Credit 91-1 - 59 rub. (592 USD x (29.3 rubles/USD - 29.2 rubles/USD)) - reflects the positive exchange rate difference on interest accrued for April; Debit 76 Credit 91-1 - 17,523 rubles. (592 USD x 29.6 rubles/USD) - interest accrued for June; Debit 76 Credit 91-1 - 361 rub. ((612 USD + 592 USD) x (29.6 rubles/USD - 29.3 rubles/USD)) - reflects the positive exchange rate difference in interest accrued for April and May. Line 2320 “Interest receivable” of the new unified report form will indicate the amount of interest receivable in the amount of: 17,286 + 17,932 + 17,523 = 52,741 rubles.
Form 2 of the balance sheet: one report - two titles
Form 2 of the balance sheet - by this name we traditionally mean a reporting form that contains information about the income, expenses and financial results of the organization. Its current form is contained in the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n, in which it is called a report on financial results.
In the Law “On Accounting” dated November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ, which was in force until 2013, this form was called the Profit and Loss Statement, and in the law that replaced it dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, it was called the Financial Results Report. At the same time, the form itself began to bear this name quite recently: the “Profit and Loss Statement” was officially renamed to the Financial Results Statement only on May 17, 2015, when Order No. 57n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 6, 2015, which introduced changes to the reporting forms, came into force .
By the way, now Form 2 is not the official, but the generally accepted name of the report. It has ceased to be official since 2011, when the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 22, 2003 No. 67n, which approved the previous forms of accounting, which were called: Form 1 “Balance Sheet”, Form 2 “Profit and Loss Statement”, Form 3 “Statement of changes in capital.”
In 2021, changes were made to Form 2 (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated April 19, 2019 No. 61n). So, when filling out the report for 2021, consider:
- you cannot fill out reports in millions; the unit of measurement has become thousands of rubles;
- OKVED was replaced by OKVED2;
- line 2410 changed the name “Income Tax” (instead of “Current Income Tax”);
- lines 2421, 2430, 2450, dedicated to tax liabilities (assets), disappeared;
- lines 2411 “Current income tax”, 2412 “Deferred income tax”, 2530 “Income tax from transactions, the result of which is not included in the net profit (loss) of the period” appeared.
And the total financial result is determined as the sum of the lines:
- "Net income (loss)";
- “The result of the revaluation of non-current assets, not included in the net profit (loss) of the period”;
- “Result from other operations not included in the net profit (loss) of the reporting period”;
- “Tax on profits from transactions, the results of which are not included in the net profit (loss) of the period.”
You can download a sample of Form 2 in the new edition with comments on completion from K+ experts in the ConsultantPlus legal reference system. To do this, get a free trial demo access to K+:
For more information about the forms that supplement the balance sheet and financial results report, read the article “Filling out forms 3, 4 and 6 of the balance sheet.”
Interest receivable. line 2320
Attention Postings: Account Dr Account Kt Posting description Posting amount Document-basis 51 66 Cash loan received 350,000 Loan agreement Bank statement 91.2 66 Interest accrued under the loan agreement 38,500 Accounting statement 66 51 Interest transferred 38,500 Payment order 66 51 Loan repaid 35 0 000 Payment order If the lender is an individual, personal income tax must be withheld from the amount of interest paid to him: 13% for residents and 35% for non-residents. This operation is documented by posting: Debit 73 (76) Credit 68 Personal Income Tax. Transfer of interest to an individual is carried out by recording Debit 66 (67) Credit 51 (50). Loan from an individual The organization received a loan from the director in the amount of 80,000 rubles. at 5% per annum for 3 months. Important Share in Art. 3 837 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Terms and procedure for interest payments. Interest on the deposit is accrued from the day following the day the bank receives funds for placement in the deposit until the day they are returned to the depositor (clause 1 of Article 839 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the interest accrued on the deposit can be paid to the depositor periodically (monthly, quarterly, etc.) or in a lump sum upon expiration of the deposit term.
If the procedure for paying interest is not established in the agreement, they are paid to the depositor at the end of each quarter upon his request, and unclaimed interest is added to the deposit amount on which interest is accrued (clause 2 of Article 839 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Procedure for calculating interest.
How to record interest on a deposit
At the same time, according to Art. 250-1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, interest on a deposit is the organization’s non-operating income, which should be recorded in the accounting data every month, regardless of the terms of payment and the accrual of interest under the agreement. In addition, interest should be reflected on the date of termination of the contract (Art.
271 – 6 para. 1, 3 Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In total, interest is calculated as specified in the agreement.
It is also important to know the method of calculating interest. With simple interest, the amount invested is taken as the basis, on which interest is calculated. The base amount does not increase. Payment is made according to periods.
With compound interest, interest is added to the deposit amount and interest is charged on the newly formed amount. Paid on the day the deposit is returned in one amount. When calculating income tax (OSNO), a difference is created. It needs to be corrected.
If the contractual relationship with the bank began and ended in the same year, then the data for the reporting periods are adjusted by submitting updated declarations or by entering data to reduce them in the declaration of the period when the contract was terminated (Article 81-1, Article 54-1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
- D 55. 3(58) K51(52) - deposit transferred for storage.
- D 55. 3(58) K91. 1 - interest has been accrued on the deposit for the month (each month the base increases by the amount of interest calculated in the previous period).
- D 51(52) K 55. 3(58) - return of money from the deposit and interest.
Accounting for loans and borrowings in accounting
In both situations, the amount of interest payable on the bonds is reflected on line 2330 “Interest payable” of the new unified report form. If a company buys back its bonds without waiting for their maturity, then this is reflected in accounting in the same way as their redemption. In this case, the amounts of accumulated coupon income must be accrued for the actual period that the bonds were held by the holder.
That is, the coupon income must be reflected on the date of redemption of bonds. Additional costs associated with the circulation of bonds (for example, exchange fees, costs of paying for the services of intermediaries or brokers, etc.) are taken into account as part of other expenses, subaccount 2 “Other expenses”). In this case, such costs are entered in line 2350 “Other expenses” of the report.
Info Interest receivable and payable (lines 2320 and 2330) In line 2320 “Interest receivable” of the new unified report form, enter the amount of interest that is due to the company, accrued on loans issued to other persons; on deposits placed in banks for the purpose of generating income; on bonds and other securities (for example financial bills); accrued by the bank based on the balance of funds in the current account. Such income is included in other income and reflected in account 91 “Other income and expenses” (subaccount 1 “Other income”). A number of similar incomes are not indicated in this line. Other report lines are intended to account for them. For example, income from commercial loans provided to customers. The company’s revenue, reflected in line 2110 “Revenue” of the report, is increased by their amount. Interest accrued on a loan or credit payable to the lender (creditor) is reflected as part of the company's other expenses. An exception is provided only for those received for the purchase of investment assets (property that requires significant costs and time to acquire). Interest on such funds is included in the cost of the investment asset until the termination of its acquisition, construction and (or) production. Attention! Small businesses have the right to count interest on any loans as other expenses. Interest receivable. line 2320 Attention Tax accounting of interest on deposit
- General taxation system
Interest on a deposit for the purposes of calculating income tax is recognized as non-operating income (clause 6 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is necessary to take into account interest in tax accounting as part of income on the last day of each month (para.
- Amount of interest accrued in accounting for August-December 2015: RUB 33,315.07 (1,000,000 x 8% / 365 x (30 + 30 + 31 + 30 + 31))
- Amount of interest calculated at a reduced rate for August-December 2015: RUB 41.64. (1,000,000 x 0.01% / 365 x (30 + 30 + 31 + 30 + 31)
- The amount of interest accrued excessively in accounting, subject to adjustment: RUB 33,273.43.
Interest receivable. line 2320 Note that interest receivable by the organization is shown on line 2320 “Interest receivable” only if it qualifies it as other income and is reflected in accounting under the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount 91-1 “Other income” (clause 4 of PBU 9/99).
Reflection of Interest on Deposit in Form 2 Line Interest Received
- on line 070 “Other income” or on free lines 180 and 190 as cash flows from current activities;
- and (or) on line 240 “Interest received” or on free lines 330–340 as cash flows from investment activities.
If the insurer does not carry out compulsory health insurance operations, then line 460 of column 3 “Cash balance at the end of the reporting period of form No. 4-insurer should be equal to line 260 of column 4 of form No. 1-insurer. Otherwise, the insurer must provide an explanation of the reasons for the discrepancy in the explanatory note. According to Order No. 67n, the amount on line 335 of form No. 5-insurer must be greater than or equal to the amount on line 142 of form No. 1-insurer. In our opinion, this means that line 260 of form No. 1-insurer can reflect part of the deposits, which, for the purposes of forming form No. 5-insurer, are included in line 335. Thus, in form No. 1-insurer, data on deposits is distributed according to their types, and in form No. 5-insurer they are reflected on one line, regardless of the type.
Funds invested in deposits fully meet the requirements of this provision: 1) the deposit is formalized by a bank account agreement; 2) at the time of opening a deposit, funds are temporarily removed from circulation, since the organization cannot actually manage them. An exception may be called demand deposits; 3) during the period when the organization’s funds are in deposits, it bears risks associated with the activities of a particular bank and the functioning of the market as a whole; 4) the main purpose of opening a deposit is to generate income. The bank is obliged to pay interest on deposits in accordance with the terms of the bank deposit agreement.
More found about accounts receivable
- Financial recovery of the enterprise The crediting of the received loan to the current account is recorded as an accounting entry in the debit of account 51 Current accounts and the credit of account
- “Imaginary” liabilities taken into account when calculating the organization’s net assets Increase in own funds obtained by accounting for hidden assets in management accounting 390 Decrease in own funds received for
- Analysis of sources of capital formation for LLC thousand rubles and a minimum of materials for approximately 3 million rubles, which can then be periodically replenished from the proceeds received. Contributions of founders to the authorized capital amount to 10 million rubles The remaining 6 million
- Analysis of the creditworthiness of small enterprises by a bank credit expert Including - cash 1,476 1,299 - inventories 3,115 6,674 - accounts receivable 2,027 2,266 - advances issued to suppliers 912 1,150 -
- Efficiency of use of borrowed capital Due to the fact that interest payments for the loan are made at the expense of the profit received from the use of capital, after paying interest on the loan, less funds will remain on
- Analysis of the amount of economic benefit of a corporation when implementing various approaches to calculating depreciation bonuses In this regard, it is especially important in the conditions of reindustrialization of the national economy to attempt to increase the share of its own sources of financing by obtaining material benefits from the rationalization of tax revenues and maximizing depreciation amounts Own sources of financing
- How to increase the efficiency of financial flow management Both in the central office and in branches, the application for making a payment was an invoice received from the counterparty with the signature of an authorized executive Since the bulk of payments are in advance
- Analysis, accounting and evaluation of the company's intangible assets in the conditions of an innovative economy Some current assets such as accounts receivable and certain expenses paid in advance do not have a physical substance, but they do not
- Assessment of the borrower's creditworthiness according to the financial statements N5 3 7 Using the formula for calculating the indicator F, we obtain the following value F 0.075 1 7 0.3 1 7 0.5 ... According to Table 4, the obtained value of the complex indicator F means that with 80% confidence 10 0 .65 0.63
- Analysis of financial statements. Practical analysis based on accounting (financial) statements After the organization’s fixed expenses are paid off from the received marginal income, it begins to receive operating profit Before this
- Rent The main advantages of leasing are increasing the market value of the enterprise by obtaining additional profit without acquiring fixed assets into ownership; increasing the volume and diversification of the economic
- Valuation of shares The par value determines the amount paid to the shareholder in the event of liquidation of the company; the issue price is the cost of the initial public offering of shares, which may differ from the par value either up or down; book value is a method of measuring the share capital of a company; it is an accounting indicator that is widely used in studying the financial activities of a company and when valuing shares, book value is determined by subtracting the amount of the company's liabilities and capital contributed by the owners of preferred shares from the total assets of the company; liquidation value is the amount of the company's assets that would remain in the event of a sale or auction sale of assets and repayment from the proceeds of liabilities and payments on preferred shares, it is obvious that as long as
- Analysis of accounts payable and measures aimed at reducing it in the enterprise. The Armed Security Center does not have the opportunity to pay off accounts payable by obtaining a loan from a commercial bank, then the organization can pay off part of the accounts payable in the amount
- Key issues of financial management of an enterprise in a self-financing mode The key principles of building such a system are the following: • it is unacceptable to use the existing working capital of an enterprise without taking into account its increase due to the received marginal income to cover current and investment expenses • to cover current and
- Profit sharing Profit sharing is a system of incentives for the personnel of an enterprise carried out at the expense of the profits they receive. The forms of this incentive can be in the form of direct cash payments, provision of additional
- Analysis of the sustainability of economic growth according to the financial statements of an insurance company. For example, an increase in the share of reinvested profit was noted due to the receipt of a larger absolute amount of net profit and a decrease in the share of that part that was
- Internal audit of the organization's fixed assets - part 3 of the Chart of Accounts, paragraph 11 of PBU 10 99 The resulting difference between the residual value of the car is 741,000 rubles
- Features of the financial policy of companies in a crisis The general focus of these measures is the capitalization of the business, including through retained earnings received from core activities and the sale of part of the assets, as well as reducing the debt burden 9 reducing or stopping dividend payments, repaying the most urgent obligations, prolongation of short-term loans, transfer of short-term loans loans loans for long-term obtaining deferments from suppliers in order to reduce the need for capital exchange of claims for shares in the authorized capital in which the organization's creditors become its participants obtaining deferred settlements for certain forms of internal accounts payable debt between group members, etc.
- Budgetary accounting of the Chart of Accounts of categories to obtain additional information necessary for internal users In addition, in the absence of correspondence
- Current problems of accounting for future income Settlements with various debtors and creditors sub-account Advances received reflect the receipt of rent, etc. as part of advances received 2 Difference
The Financial Analysis program - FinEkAnalysis for analyzing the financial condition of an enterprise, allowing you to calculate a large number of financial and economic ratios. A program for conducting financial analysis based on financial statements Conduct Financial Analysis Online Online service for conducting financial analysis based on financial statements Try FinEkAnalysis Library
- Articles
- Books
- Dictionary
- Normal documentation
Products & Services
- FinEcAnalysis
- Financial analysis Online
- Financial analysis to order
Company
- About company
- Contacts
- Search
Contacts
Receipt of loan principal
Receipt of the loan amount to the account is reflected in the document Receipt to the current account transaction type Repayment of loan by counterparty in the Bank and cash desk - Bank statements - Receipt button.
Please indicate:
- Payer - borrower under the agreement;
- Settlement account - 58.03 “Loans provided”;
- Income item - a predetermined item from the directory Cash Flow Items Receipts from the repayment of loans : Type of movement - Proceeds from the repayment of loans, from the sale of debt securities ;
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt Kt 58.03 - return to the account of the loan amount.
Interest receivable and interest payable decreased decreased
Free hotline: St. Petersburg Moscow Federal number Back
According to the terms of the agreement, the company pays interest on it at the rate of 24% per annum. The loan was received on March 31. It was not repaid before the end of the reporting period (half year). In March, the company paid additional costs for the loan (legal analysis of the agreement), the amount of which amounted to 11,800 rubles. (including VAT - 1800 rubles). According to the accounting policy, loan interest is included in other expenses. When calculating interest on the loan and paying additional expenses, the accountant will make the following entries: Debit 19 Credit 60 - 1800 rubles. — VAT on additional costs associated with obtaining a loan is taken into account; Debit 91-2 Credit 60 - 10,000 rub. (11,800 - 1800) - additional expenses for obtaining a loan are taken into account; Debit 68 Credit 19 - 1800 rub. — accepted for deduction of VAT on additional expenses for obtaining a loan; Debit 91-2 Credit 66 (67) - 46,553 rubles. (RUB 2,360,000 x 24%: 365 days.
Legal interest
In cases where the law or agreement stipulates that interest is subject to accrual on the amount of a monetary obligation for the period of use of funds, their amount is calculated at the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in force during the relevant periods (legal interest), unless a different interest rate is established by law or agreement (clause 1 of article 317.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The condition of the obligation providing for the accrual of interest on interest is void (with the exception of the terms of obligations arising from bank deposit agreements or from agreements related to the implementation of business activities by the parties).
According to the Russian Ministry of Finance, the interest provided for in Art. 317.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, are not penalties, but are recognized as payment for the use of funds and are taken into account in the manner prescribed by clause 6 of Art. 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Letter dated April 22, 2016 N 03-03-06/1/23412).
Financial Dictionary
X's attention turned out to be insignificant, which increased the cost of materials by only 39,300 thousand rubles. For material Y, there was a decrease in the cost of materials by 90,550 thousand rubles, due to a decrease in the amount of material consumption from 1610 to 1240 tons. Task 12 Let us determine the degree of influence of individual factors on the level of labor costs and the reserve for reducing these costs. To do this, we will draw up an analytical table 12 and use the method of absolute differences to determine the influence of these factors on the wage fund of workers. Sources of information for filling out this table are:
- Appendix to the balance sheet (form No. 5) from Appendix No. 3
- certificate No. 1 from Appendix No. 4
Table 12 - Initial data for calculating the influence of individual factors on changes in labor costs No. Indicators last year reporting year Deviation (+;-) 1 2 3 4 5 1 Number of employees, people.
The largest role - 99% in the formation of income of Agat LLC in the past and reporting years was played by revenue from product sales, the value of which increased by 1,005,420 thousand rubles. or by 0.12%. The share of other income in their total amount is insignificant (about 0.04%), their value in the reporting year increased by 137 thousand rubles, which can also be assessed positively. A decrease in interest receivable by RUB 2,786 thousand had a negative impact. or by 0.08%, this indicates that the company is not expanding its financial activities, is not actively investing its finances in shares and bonds of other enterprises. Expenses for the reporting period increased by 987,403 thousand rubles. Accordingly, the most significant contribution of 67.61% to the total amount of expenses of the enterprise is made by expenses for ordinary activities - production costs. Although the cost of production in the reporting year increased by 607,575 thousand compared to the previous year.
What does Form 2 of the balance sheet look like?
Form 2 of the balance sheet is a table above which are given:
- reporting period and date;
- information about the organization (including codes OKPO, INN, OKVED, OKOPF, OKFS);
- unit of measurement (from 2021 - only thousand rubles).
The table with reporting indicators consists of 5 columns:
- number of the explanation to the report;
- name of the indicator;
- line code (it is taken from Appendix 4 to Order No. 66n);
- the value of the indicator for the reporting period and the same period of the previous year, which is transferred from the report for the previous year.
The indicators of the previous and reporting year must be comparable. This means that if the accounting rules change, last year’s ones should be transformed to the rules in force in the reporting year.
Read about how such a transformation is done in the material “Balance sheet of an enterprise for 3 years (nuances).”
Comprehensive economic analysis of economic activity (7)
In both situations, the amount of interest payable on the bonds is reflected on line 2330 “Interest payable” of the new unified report form. If a company buys back its bonds without waiting for their maturity, then this is reflected in accounting in the same way as their redemption. In this case, the amounts of accumulated coupon income must be accrued for the actual period that the bonds were held by the holder.
That is, the coupon income must be reflected on the date of redemption of bonds. Additional costs associated with the circulation of bonds (for example, exchange fees, costs of paying for the services of intermediaries or brokers, etc.) are taken into account as part of other expenses, subaccount 2 “Other expenses”). In this case, such costs are entered in line 2350 “Other expenses” of the report.
What is the purpose of calculating the interest coverage ratio?
There are at least 5 situations in which calculating the interest coverage ratio is very useful. The ICR indicator allows you to:
- see a picture of the financial stability of the enterprise in terms of repaying interest on loans (if we consider the trend in the interest coverage ratio);
- find out the financial condition of the organization in the near future;
- determine the degree of sustainability of the enterprise, incl. to external influences (low ICR indicates that there is a likelihood of non-payment of debt in the future);
- assess the risks of creditors in case of issuing a loan;
- determine the company’s ability to fulfill loan obligations and pay interest on borrowed funds.
Section 1. comprehensive diagnostics of the financial condition of the enterprise
- We determine the impact of changes in the average annual salary of 1 employee on changes in labor costs:
∆yb = a1 * (b1 – b0) = 29230 * 7.0279 = 205427 thousand rubles, i.e. an increase in average annual wages by 7.0279 thousand rubles per 1 employee led to an increase in labor costs by 205426 thousand rubles; The cumulative influence of factors, i.e. the balance of deviations was: ∆yY = ∆yа + ∆yb =32436+ 205427 = 237863 thousand rubles. Thus, both factors led to an increase in the wage fund. The growth in the number of employees depends on the number of new jobs and expansion of production. Increase in the number of workers by 710 people. in the reporting year speaks of the expansion of production for the manufacture of new products, which in turn leads to greater output and, as a consequence, increased profits.
Analysis of business activity and profitability
Info Debit 76 Credit 91-1 - 25,000 rub. ((RUB 2,000,000 - RUB 1,400,000): 24 months) - income accrued for the 2nd month of circulation of the bill; Debit 76 Credit 91-1 - 25,000 rubles. ((RUB 2,000,000 - RUB 1,400,000): 24 months) - income accrued for the 3rd month of circulation of the bill, etc. Often the specific date for repayment of the bill is unknown. For example, if it contains a repayment clause “upon presentation, but not earlier...”. To calculate discount income on such securities, you need to use the expected period of their circulation. This is 365 (366) days plus the period from the date of the bill of exchange to the minimum date of its presentation for payment. Formation of interest payable (line 2330) ... The procedure for recognizing such expenses is regulated by the Accounting Regulations “Organization Expenses” (PBU 10/99) * (318).
Example No. 2 of calculating the interest coverage ratio
Let's introduce the MyasKo company, a large domestic manufacturer of semi-finished meat products. The management of the enterprise has planned to expand its activities, however, the company does not have enough finance to purchase equipment for the new workshop. It was decided to apply for a loan at one of the city’s banking institutions, and applications for loans were submitted. MyasKo LLC provided credit organizations with its financial statements containing the following information:
- accounting profit (revenue before interest and taxes) amounted to RUB 4,960,000,000;
- interest expenses – 930,000,000 rubles;
- tax payments – 620,000,000 rubles.
The bank's internal financial analyst calculates the interest coverage ratio and obtains the following value:
4,960,000,000 : 930,000,000 = 5,04
An expert on credit products concludes that the company MyasKo LLC is able to repay the interest on the loan 5.04 times from operating profits. And since the company will be able to fulfill its debt obligations without any problems, the bank has no reason to refuse to issue a loan.
Interest payable 2330
Including those received for the purchase of investment assets. In addition, paragraph 6 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for inventories” (PBU 5/01) * (319) provides that interest on loans received for the purchase of inventories (materials or goods) is included in their initial cost if they are accrued before the date of their receipt. A similar norm is contained in paragraph 6.2 of PBU 10/99. At the same time, the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for Loan and Credit Expenses” (PBU 15/2008) * (320) establishes that interest on any loans is reflected as part of the company’s other expenses.
As we said above, exceptions to this rule only affect loans received for the purchase of investment assets. But materials or goods are not considered such assets.
Balance Sheet Analysis
In the latter case, it is defined as the difference (discount) between the purchase price of the bill and the amount received upon its redemption (face value). Interest income on a bill of exchange is reflected in accounting in the same manner as on loans provided to other persons.
The general purpose of balance sheet analysis is to identify and disclose information about the financial condition of an economic entity and the prospects for its development, necessary for decision-making by interested users of the statements.
Loans provided to other organizations are classified as financial investments and are reflected in account 58 “Financial investments”. This is stated in paragraph 3 of PBU 19/02 “Accounting for Financial Investments” and Instructions for the Application of the Chart of Accounts.
Let us emphasize once again that the above description of the balance sheet and income statement items serves the purpose of characterizing the state of the enterprise and its dynamics over some time. This description should not be considered as guidance to an accountant in preparing financial statements.
Course work: comprehensive economic analysis of economic activity
Important Debit 91-2 Credit 66 (67) - 48,105 rubles. (RUB 2,360,000 x 24%: 365 days x 31 days) - interest accrued on the loan for May; Debit 91-2 Credit 66 (67) - 46,553 rubles. (RUB 2,360,000 x 24%: 365 days x 30 days) - interest accrued on the loan for June. At the end of the reporting period, interest on the loan is entered in line 2330 “Interest payable” of the new unified report form in the amount of: 46,553 + 48,105 + 46,553 = 141,211 rubles. Additional loan costs excluding VAT (RUB 10,000) are indicated in line 2350 “Other expenses” of the report. ...on bonds issued by the company Since the issue of bonds is carried out to attract borrowed capital, operations related to their movement are reflected in accounting in accordance with PBU 15/2008. Situation 1 According to the company's accounting policy, interest is accrued at the end of the period for which the company must pay interest. In this situation, the accrual of interest is reflected by the entry (on the last day of the first quarter of bond circulation): Debit 91-2 Credit 66 (67) - 39,890 rubles. (RUB 2,000,000 x 8%: 365 days x 91 days) - interest accrued on bonds for the first quarter of bond circulation. Situation 2 According to the company's accounting policy, interest is accrued evenly over the circulation period of the bonds. The accrual of interest is reflected in the entries (on the last day of each month of circulation of bonds): Debit 91-2 Credit 66 (67) - 13,151 rubles. (RUB 2,000,000 x 8%: 365 days x 30 days) - interest accrued on bonds for April; Debit 91-2 Credit 66 (67) - 13,589 rubles. (RUB 2,000,000 x 8%: 365 days x 31 days) - interest accrued on bonds for May; Debit 91-2 Credit 66 (67) - 13,151 rub. Task 13 According to PBU 9/99 “Income of the Organization” and PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the Organization”, income is recognized as an increase, and expenses as a decrease in economic benefits as a result of the receipt or disposal of assets, as well as the repayment or occurrence of liabilities, leading to corresponding changes in the capital of the organization . Income and expenses are divided into income (expenses) from ordinary activities and other income (expenses). The excess of income over expenses means profit, the excess of expenses over income means a loss from the corresponding type of activity. We will analyze the income and expenses of Agat LLC in Table 13.1. based on data from Form No. 2 “Profit and Loss Statement” from Appendix No. 2. Table 13 - Composition, structure and dynamics of income and expenses No. Indicator Last year Reporting year Change (+,-) Amount, thousand rubles. % of the total Amount, thousand rubles. % of the total Amount, thousand rubles.
Which line of Form 2 shows interest on a bank guarantee?
- as counter security when applying to the court for interim measures.
- as security for the payment of customs duties in certain cases;
- when purchasing federal special “alcohol brands”;
- when concluding a state or municipal contract; ;
- when exempt from payment of advance payment of excise duty on alcoholic and alcohol-containing products;
On March 31, 2014, the register of bank guarantees came into force and is posted on the all-Russian official website. ——————————— www. zakupki. gov. ru. A bank guarantee is, on the one hand, a convenient tool for bank clients, and on the other, a source of income for the bank itself, of course, with a proper assessment of the risks of possible losses on it. You can get acquainted with the list of banks that meet the established requirements for accepting bank guarantees for tax purposes: section “Tax relations” section “Tax and customs tariff policy” In addition, you may need a guarantee, for example: Moreover, in the future the debt may not arise. Before moving on to accounting for such an operation, let’s define the terminology.
There are three parties involved in the transaction: - the bank, called the “guarantor”; -; - the potential Lender. How does the transaction itself take place?
- as part of non-operating expenses as costs of carrying out activities not directly related to production and (or) sales (clause 15, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- as part of other expenses associated with production and sales (clause 25, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
In accordance with Art. 368 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, under a bank guarantee agreement, the bank acting as a guarantor issues, at the request of the client (principal), a written obligation to pay the client’s creditor (beneficiary) a sum of money* upon submission by the beneficiary of a written demand for its payment. *In accordance with the terms of the obligation given by the guarantor. Providing a bank guarantee in some cases is mandatory, for example: Reflection of Interest on Deposit in Form 2 Line Interest Received
Read on the Russia-Ukraine website:
- Reflection of Inventory Results in Accounting
- Reflection of Financial Investments in Accounting and Reporting
- Reporting to the Tax Service for the First Half of 2021 for HOAs
- Registration by the Shareholder of an Apartment in Ownership in Shares
- Registration of Ownership of an Apartment in a New Building through a housing cooperative
Attention!
Due to recent changes in legislation, the legal information in this article may be out of date! Our lawyer can advise you free of charge - write your question in the form below.