The specificity of monitors is such that, during long and active work, the screens lose color quality and become less contrasting. These are the reasons for discarding the monitor: due to these problems, working with displays becomes hazardous to health. And in order to replace monitors, you must first write off and dispose of existing displays: Russian legislation prohibits the unauthorized removal of electronic equipment to a landfill. All operations for decommissioning and recycling of equipment must be carried out by companies that have a license and certificate for these types of activities. offers its clients professional services for the write-off and recycling of office equipment, including computer monitors. We explain why it is important to trust professionals in this matter.
Replacing a Monitor in a Computer Wiring Budget 2021
The material was prepared on the basis of individual written consultation provided as part of the Legal Consulting service. For detailed information about the service, contact your service manager.
Having considered the issue, we came to the following conclusion: When replacing part of a fixed asset, accounting simultaneously reflects a decrease in its book value and accrued depreciation by the amount attributable to the component being replaced, and an increase in its book value by the cost of the new spare part.
Typical malfunctions of modern CRT monitors:
- Power supply failure - occurs as a result of voltage surges in the electrical network. Failure of the power supply, as a rule, entails damage to other monitor modules;
- Failure of the frame scanning unit. This mainly occurs due to a violation of the temperature regime of the unit;
- The line scanner is faulty. Most often, due to the heavy contamination of the monitor with dust, as a result of which breakdown of high-voltage circuits and TDKS occurs;
- Violation of color rendition and geometric distortion of the image. Such malfunctions arise due to malfunction of the deflection system due to aging of the elements and magnetization of the kinescope. Mainly occurs due to impacts during transportation and exposure to sources of electromagnetic radiation;
- Failure of the video signal generation and processing board is due to aging of the elements and violation of the operating temperature conditions.
To prevent premature failure of CRT monitors, we recommend:
- Connect the monitor to the mains via a UPS or at least a surge protector;
- Do not install the monitor in direct sunlight, or near radiators or heating devices;
- Do not place newspapers or magazines on the monitor so as not to deprive it of the ability to cool through the ventilation holes;
- Do not allow your beloved cats to bask on the monitors;
- Do not arrange shelves with flowers above the monitor and then water them;
- Clean it from dust periodically;
- Wipe the monitor with antistatic wipes to remove static electricity;
- Install the monitor in such a way that there is unobstructed access to fresh air.
What postings should state employees use to account for fixed assets?
Fixed assets are material assets that are planned to be used to carry out the activities of the institution for at least 12 months. Moreover, in the process of recognizing fixed assets in accounting, its value does not play any role.
- if the cost of fixed assets is up to 10,000 rubles - it is considered to be of low value and is recorded on off-balance sheet accounts;
- when assessed up to 100,000 rubles, but more than 10,000 rubles. — the object is accounted for in the corresponding account 101, while the original cost (posting below) is written off to the corresponding depreciation account 0 104 00 000 in the amount of 100%;
- objects costing more than 100,000 rubles are subject to accounting on balance sheet account 101 with periodic depreciation accrual, according to the chosen method.
BASIS: VAT
Input VAT on components purchased for replacement in a computer should be deducted in the usual manner (paragraph 1, clause 5, article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). That is, after registration of the specified components and in the presence of an invoice (clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Exceptions to this rule, in particular, are cases when:
- the organization enjoys VAT exemption;
- the organization uses the computer only to perform VAT-free transactions.
In these cases, include input VAT in the cost of components used to upgrade or repair the computer. This procedure follows from paragraph 2 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If an organization uses a computer to perform both taxable and non-VAT-taxable operations, distribute the input tax on the cost of components (clause 4 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When calculating property tax, take into account the costs of purchasing components included in the initial cost of the computer from the 1st day of the month following the completion of modernization (clause 4 of Article 376 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Budget accounting entries with examples of basic transactions
The Federal Treasury of the Russian Federation is responsible for accounting for operations on the movement of budgetary funds. This body also draws up and approves the accounting methodology in budgetary institutions, as well as the reporting procedure.
Let’s imagine that a budgetary institution “Hospital” and LLC “Magnit” entered into an agreement for the supply of materials in the amount of 64,000 rubles, VAT 9,762 rubles. The contract provides for an advance payment of 20% of the cost of the goods, which was paid by the Hospital (RUB 12,800). The remaining part (RUB 51,200) was transferred to Slavutich LLC upon delivery of the goods.
Which KVR and KOSGU to use for government procurement
Subsidies (grants in the form of subsidies) for financial support of expenses, the procedure (rules) for the provision of which do not establish requirements for subsequent confirmation of their use in accordance with the conditions and (or) purposes of the provision
Subsidies (grants in the form of subsidies) for financial support of costs in connection with the production (sale of goods), performance of work, provision of services, the procedure (rules) for the provision of which establishes a requirement for subsequent confirmation of their use in accordance with the conditions and (or) purposes of the provision
Budgetary accounting of fixed assets in 2018-2019 (nuances)
To account for fixed assets, a synthetic account 010100000 “Fixed Assets” is provided. The budget accounting account number consists of 26 digits, and only 18–26 digits are used in the accounting of the institution. Depending on the group and type of fixed assets, as well as the essence of their movement, the code in the 22–26 digits changes in the account number.
In accordance with paragraph 21 of Order No. 157n, the concept of “budget accounting of fixed assets” applies only to certain government organizations. For example, government institutions, government agencies, extra-budgetary funds. In addition to the unified chart of accounts, a special chart of accounts must be used in budget accounting (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 6, 2010 No. 162n).
A little about taxes
If the replacement of an obsolete monitor with a new one is carried out by a budgetary institution as part of the implementation of statutory budgetary activities, no economic benefit in the form of the market value of the obsolete monitor for profit tax purposes arises, since according to the norm of paragraphs. 1 item 2 art. 256 of the Tax Code, depreciable property of budgetary institutions acquired through budgetary allocations is not subject to depreciation when determining the tax base.
Consequently, when a budgetary institution replaces an outdated monitor with a new one as part of its statutory budget activities, the market value of the outdated monitor is not taken into account as part of non-operating income.
A.A.Komleva
Expert Editor
magazine "Budget Accounting"
Examples of application of articles 310 KOSGU and 340 KOSGU in 2018-2019
- to the provisions of the Instructions to the Unified Chart of Accounts No. 157n;
- on the purpose, timing and procedure for using material assets;
- on the provisions of the accounting policy - it prescribes an exact list of property that is classified as fixed assets or inventories in the accounting of the institution.
- if you have concluded one agreement with a contractor for the purchase and installation of a meter - article KOSGU 310 “Increase in the cost of fixed assets”;
- if you buy the meter yourself - article KOSGU 340 “Increasing the cost of inventories”, the contractor installs it - subarticle KOSGU 226 “Other work, services”.
Please note => Certificate of acceptance of transfer of premises after repair sample
Purchasing an external hard drive Kosgu 340
To which sub-article of KOSGU should the costs of its acquisition be attributed?
What is the procedure for accounting and calculating depreciation? Answer: The procedure for applying the classification of operations of the general government sector (KOSGU) is regulated by section. V Instructions on the procedure for applying the budget classification of the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 2009 N 150n.
These Guidelines have been developed in accordance with the standards of Chapter.
4 and art. I.V. Artemova, chief accountant, consultant Computer equipment is available in every institution.
Spare parts, accessories, storage media, etc. are purchased for it.
d. Accountants often have questions about how to account for individual parts - as part of one object or as independent units, as fixed assets or as inventories. One object or several? Computers belong to the fixed assets of an institution, since they are tangible objects of property with a useful life of more than 12 months, intended for repeated or permanent use with the right of operational management during the activities of the institution when performing work, providing services, for the exercise of government powers (functions). ) or for the management needs of the institution (clause
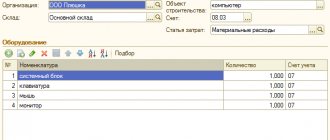
Replacing a computer monitor
Tell me how to replace a broken monitor in a complex of structurally articulated objects “computer assembly”. We buy a new monitor as a spare part - according to account 105, and what documents and postings are necessary to seize, write off and dispose of the old one!
The need for repair work must be documented (Part 1, Article 9 of Law No. 402-FZ, Clause 7 of Instruction No. 157n). The form of the document for this is not legally established - you can use a self-developed form (for example, a report on identified malfunctions (defects) of an OS object or a defective statement). These documents must indicate the defects of the object and proposals for their elimination.
DIY LCD monitor repair
A common malfunction is when the LCD monitor lights up for a second and goes out. What to do in this case and how to use this TOP of faults.
It's simple. To repair your LCD monitor, follow these steps:
- Step 1. Disconnect the monitor from the 220 V network and from the computer and decide whether we will repair it ourselves or take it to a service center for diagnostics at an inexpensive price.
- Step 2. If you decide to figure it out yourself, then take the tools: screwdrivers, a knife or scalpel and a soft base to lay the monitor down with the matrix.
- Step 3. Disassemble the LCD display, observing safety precautions and remembering the latches. How they open is shown in the animation above.
- Step 4. Discharge the high voltage capacitor. It is necessary! Especially if you want to achieve a positive result of the repair.
- Step 5. Inspect the board for swollen capacitors, burnt transistors and microcracks.
- Step 6. If any findings are found in Step 5, replace the burnt ones and solder the cracked ones.
- Step 7. Check the functionality of the monitor, observing safety precautions. If everything is ok, then go to Step 10.
- Step 8. Take a multimeter and test the fuses, diode bridge, transformers and transistors. Replace burnt radio elements.
- Step 9. Check the operation of the LCD monitor. If the monitor continues to blink, check the voltage at the test points on the board. This requires knowledge of circuit design, as well as a service manual with an ideal circuit. Further actions are difficult to describe in general terms. This is where the creative process of the Repairman begins. To discuss, write in the comments or contact.
- Step 10: If you successfully repair the flickering LCD monitor yourself, do a test run for 2-3 hours in a disassembled state. After this, the monitor can be assembled and used.
Replacing an old monitor with a new one
The new monitor is accounted for as a separate fixed asset item. At the same time, according to the accounting policy of the company, OS worth up to 10,000 rubles. taken into account as part of inventories. The accountant will reflect these transactions with the following entries:
By recording such a transaction in accounting, the company has the right to partially liquidate the computer. That is, reduce its initial cost by the cost of the old monitor with its subsequent capitalization and reflection in the composition of materials (as part of the fixed asset).
How to write off a monitor
Obsolescence of a computer as an object of fixed assets occurs several times faster than physical wear and tear.
When distinguishing between modernization and repair of a computer, the decisive factor is not how its operational characteristics have changed, but the fact that the operability of the inventory object remains intact, without changing the performance of its functions as a whole. ...the costs of replacing failed elements of computer equipment are included in the costs of repairing fixed assets, taken into account in the manner established by Art. 260 of the Code." Based on the norms of paragraph.
2 tbsp. 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the conclusions from the above Letter, it is impossible to recognize the replacement of a monitor due to a breakdown by upgrading a computer and increasing its initial cost, since the initial cost of fixed assets changes in cases of completion, additional equipment, reconstruction, modernization, technical re-equipment, partial liquidation of relevant facilities and other similar reasons.
Replacing an old system unit with a new one in a public sector institution in accordance with the FSB
The institution also determines the materiality of the value of a part of the property independently. This can be stated in the accounting policy as a percentage. For example, the cost of a part of a property is considered significant if it amounts to 30 percent or more of the total cost of the fixed assets.
In our example, the cost of a new system unit is significant, its useful life differs from other parts of the computer, and then, instead of completing the computer with a new system unit, this system unit can be taken into account as a separate fixed asset. It is necessary to assign an inventory number to it and create a separate inventory card.
Accounting for monitors and system units as separate inventory objects
Only those items that the computer can operate without and that meet the criteria for a fixed asset can be taken into account as separate fixed asset objects. For example, a printer - OKOF code 330.28.23.23 “Other office machines.” After all, the computer will work without it. As well as those components that the institution plans to operate as part of various sets of computer equipment. For example, if you plan to connect the monitor to different computers.
Institution - State Autonomous City of Moscow Information Technology Center. Is it possible to account for monitors and system units (SU) as separate inventory items of fixed assets. In practice, monitors or SBs are often changed due to production needs. Some workplaces have 1 SB and two monitors. There is no need to write them off; they are used at other workplaces.
Replacing a computer mouse: how to reflect it in accounting
, there is no need to separately record the write-off of the old mouse . After all, the latter as a separate object was never taken into account. An old mouse (removed during repair) should be included in the balance sheet only if it can be used for repairs or in another way. Otherwise, if its use does not provide for the receipt of future economic benefits, it is not recognized as an asset, and therefore is not subject to crediting to the balance sheet ( clause 1, section II of the National Regulation (standard) of accounting in the public sector 123 “Inventories”, approved by order Ministry of Finance dated October 12, 2010 No. 1202
).
Please note => Sample claim under a contract for late payment
Let us briefly recall the main idea that follows from the above letter
Ministry of Finance.
Thus, partial liquidation of a computer complex in the case of replacing its main functional parts, such as the system unit or monitor. And the acquisition of new components in this case should be considered as an improvement of the fixed asset. Since the replacement of these components involves increasing the technical and economic characteristics of such a complex (increasing future economic benefits from its use and/or increasing the useful life of the facility). Consequently, the costs of purchasing a new monitor or system unit of an institution should be attributed to the increase in the initial cost of the computer complex. This is indicated by paragraph 1 of section.
III National Regulation (Standard) of Accounting in the Public Sector 121 “Fixed Assets”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 12, 2010 No. 1202 (hereinafter referred to as
NP(S)BU 121
), and
clause 3 of Section.
VI Methodological recommendations for accounting of fixed assets of public sector entities, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated January 23, 2015 No. 11 (hereinafter referred to as
the Method Recommendations
).
Decommissioning of computer equipment
Account correspondence Debit Credit Received LBOto purchase a monitor
to replace the broken one
9400 KRB 150115340 KRB 150113340 Budget adoptedpayment obligations
purchased monitor
9400 KRB 150113340 KRB 150211340 Accepted for accountingpurchased monitor
(as part of material
stocks)
9400 KRB 110506340 KRB 130222730 Paid for purchasedmonitor
9400 KRB 130222830 KRB 130405340 Purchased written offmonitor used
during repairs
(replacing a broken
monitor)
9400 KRB 140101272 KRB 110506440 Components have been capitalizedfrom a broken monitor
1200 KRB 110506340 KDB 140101180If an institution replaces the monitor of a computer purchased as part of an income-generating activity and used in the provision of paid services, transactions for the purchase and replacement of a monitor using funds from income-generating activities are reflected in the following records:
- purchasing a monitor from a supplier by bank transfer:
Debit KRB 210506340 “Increase in the cost of other inventories”
Credit KRB 230222730 “Increase in accounts payable for the acquisition of inventories”
- the monitor purchased to replace the broken one is reflected;
Debit KRB 230222830 “Reduction of accounts payable for the acquisition of inventories”
Credit CIF 220101610 “Disposal of institution funds from accounts”
- paid for the purchased monitor.
At the same time, an increase in off-balance sheet account 18 “Retirement of funds from the institution’s accounts” according to KOSGU 340 is reflected;
- purchasing a monitor for cash (through an accountable person):
Debit KRB 221003560 “Increase in accounts receivable for cash transactions of recipients of budget funds”
Credit CIF 220101610 “Disposal of institution funds from accounts”
- cash received by check for issue on account.
At the same time, an increase in off-balance sheet account 18 “Retirement of funds from the institution’s accounts” according to KOSGU 340 is reflected;
Debit KIF 220104510 “Receipts to the cash desk”
Credit KRB 221003660 “Reducing accounts receivable for cash transactions of recipients of budget funds”
- posting funds to the cash register;
Debit KRB 220822560 “Increase in accounts receivable of accountable persons for the acquisition of inventories”
Credit KIF 220104610 “Disposals from cash”
- cash was issued to an accountable person to purchase a monitor to replace the broken one;
Debit KRB 210506340 “Increase in the cost of other inventories”
Credit KRB 220822660 “Reduction of accounts receivable of accountable persons for the acquisition of inventories”
- a monitor purchased by an accountable person to replace a broken one was accepted for accounting (based on an approved advance report with documents confirming the purchase attached);
- write-off of a purchased monitor during repairs (replacing a broken monitor with a new one):
Debit KRB 210604340 “Increase in the cost of manufacturing inventories, finished products (works, services)”
Credit KRB 210506440 “Decrease in the value of other inventories”
- a new monitor used for repairs (replacing a broken monitor) was written off;
- receipt of usable components from a broken monitor that can be used or sold (if any arise when replacing monitors):
Debit KRB 210506340 "Increase in the cost of other inventories"
Credit KRB 240101180 “Other income”
- Based on the results of the repairs, components from the broken monitor were capitalized and could be used or sold.
Example 2 . Let's change the conditions of example 1 and assume that:
- replacement of a broken monitor is carried out as part of an income-generating activity;
- The purchase of the monitor is made through an accountable person.
In this case, the accountant will make the following entries:
| Contents of operation | Sum, rub. | Account correspondence | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| The amount of approved estimated assignments on acquisition costs monitor in return broken for the current fiscal year | 9400 | KRB 250411340 | KRB 250412340 |
| Commitments accepted on purchasing a monitor to replace the broken one | 9400 | KRB 250412340 | KRB 250212340 |
| Cash received to the cash register from your personal account for issuance on report | 9400 | KRB 221003560 | KIF 220101610 |
| When posting to the cash register | 9400 | KIF 220104510 | KRB 221003660 |
| Simultaneously reflected increase in off-balance sheet accounts 18 according to KOSGU 340 | 9400 | 18 (KOSGU 340) | |
| Cash issued accountable person for purchasing a monitor | 9400 | KRB 220822560 | KIF 220104610 |
| Accepted for registration acquired by the accountable face monitor | 9400 | KRB 210506340 | KRB 220822660 |
| Purchased written off monitor used during repairs (replacing a broken monitor) | 9400 | KRB 210604340 | KRB 210506440 |
| Components have been registered from a broken monitor | 1200 | KRB 210506340 | KDB 240101180 |
In practice, it is quite possible that the system unit of a computer whose monitor has broken is also already outdated, and the management of the institution may decide to write off the computer completely (both the broken monitor and the not broken, but obsolete system unit).
In this case, transactions on decommissioning a computer must be reflected in the generally established order:
Debit KRB 010404410 “Reducing the cost of machinery and equipment due to depreciation”
Credit KRB 010104410 “Reducing the cost of machinery and equipment”
- the amount of accrued depreciation on the written-off computer is written off;
Debit KDB 040101172 “Income from the sale of assets”
Credit KRB 010104410 “Reducing the cost of machinery and equipment”
- the residual value of the computer has been written off (if at the time of write-off it has not yet been fully depreciated);
Debit KRB 010506340 “Increase in the cost of other inventories”
Credit KDB 040101180 “Other income”
- materials (components) received upon decommissioning of the computer are capitalized (if some components are suitable for further use or can be sold).
M.L.Anikina
Expert Consultant
Publishing House
"Accountant Advisor"
Question: The organization has a computer on its balance sheet
Later, they decided to write off the computer from the balance sheet due to the fact that the components were outdated and out of order, their repair was impractical, but this object included a new monitor, which they wanted to replace the failed monitor of another computer. What entries should be made to account for this situation?
Replacing a monitor that has become unusable and performs its function only as part of the complex, and not independently, is considered as the use of other materials when carrying out repairs. The accounting entries will be as follows:
Procedure for recycling computers in the presence of precious metals
Computer equipment contains various elements, including precious metals and harmful substances. Detailed information on the composition is contained in the attached technical data sheet. If the technical passport is lost, it becomes necessary to conduct an additional examination for the presence of precious metals in the computer.
If the presence of these components in a computer unit is confirmed, then such equipment should be given for disposal to an organization that has the competence to resolve these issues. The recycling organization must have a license for this type of activity and proper registration with the Assay Office.
This disposal procedure is reflected in the documentation for decommissioning of computer equipment. Expenses incurred in connection with the disposal of equipment are classified as non-operating expenses when calculating income tax (
Buying a laptop accounting entries 2021
Fixed assets are material assets that are planned to be used to carry out the activities of the institution for at least 12 months. Moreover, in the process of recognizing fixed assets in accounting, its value does not play any role.
If a limit is set, then property valued within this limit will be reflected in synthetic account 10 “Materials” (preferably in a separate sub-account). Accounting for these objects is carried out according to the rules defined in: According to clause 5 of PBU 5/01, inventories are taken into account at actual cost, which consists of actual costs minus VAT and other refundable taxes, namely (clause 6 of PBU 5 /01): General business expenses do not participate in the formation of the cost of inventories, except in cases where such expenses are directly related to their acquisition.
Please note => The class rank of a state civil servant is assigned through
Enter the site
RSS Print
Category : Accounting Replies : 48
You can add a topic to your favorites list and subscribe to email notifications.
« First ← Prev.1 Next → Last (5) »
| Alesya [email protected] Belarus Wrote 101 messages Write a private message Reputation: | |
| Dear Colleagues! We need your advice... We purchased an LCD monitor to replace the old one. The PC set was capitalized in 2005, which included an old monitor. Based on the conclusion of a third-party organization, the old monitor cannot be repaired and is recommended for write-off. The PC set has not yet been fully depreciated. I believe that we need to write off the old monitor and take into account precious metals... What kind of transactions need to reflect the transactions of capitalizing the new one and writing off the old monitor??? And is it necessary to increase the useful life of the PC kit? Thank you in advance! | |
| I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because: Notification is being sent... |
| Natalie [email hidden] Belarus, Vitebsk Wrote 799 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #2[224029] November 12, 2010, 17:00 |
Scroll: Chart of Accounts
Account 01 “Fixed Assets” Account 01 “Fixed Assets” reflects the presence and movement of the organization’s own fixed assets that are in operation, in reserve, in conservation, received for rent (leasing), trust management. Fixed assets include buildings and structures; transfer devices; cars and equipment; vehicles; tools, equipment and accessories; draft animals and main herd animals; perennial plantings; capital expenditures for land improvement; other fixed assets. (Part two of account 01 was introduced by Decree of the Ministry of Finance dated December 11, 2008 N 187) The limit on the value of property related to fixed assets is over 30 basic units per unit (except for carpets and carpet products, the limit for which is set within 10 basic units per unit) and service life over twelve months. (Part three of account 01 was introduced by Decree of the Ministry of Finance dated December 11, 2008 N 187) Fixed assets are accepted for accounting under account 01 “Fixed assets” at their original cost. An object of fixed assets owned by two or more organizations is reflected by each of them on account 01 “Fixed assets” in the corresponding share of the cost, fixed by contracts, regulations or other documents. Real estate objects subject to mandatory state registration in accordance with the legislation, for which capital investments have been completed, primary accounting documents on acceptance and transfer have been drawn up, are accepted for accounting as fixed assets and are reflected in a separate sub-account “Fixed assets subject to registration” to account 01 "Fixed assets". (part five of account 01 was introduced by resolution of the Ministry of Finance dated December 11, 2008 N 187) After state registration of ownership of real estate objects in the manner prescribed by law, the specified fixed assets are reflected on account 01 “Fixed Assets” as part of their own fixed assets. (Part six of account 01 was introduced by Decree of the Ministry of Finance dated December 11, 2008 N 187) In a similar manner, individual fixed assets that are subject to mandatory registration or certification are reflected in accounting, for which primary accounting documents on acceptance and transfer are drawn up. (Part seven of account 01 was introduced by Decree of the Ministry of Finance dated December 11, 2008 N 187) Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting, as well as changes in their initial cost during completion, retrofitting, reconstruction, modernization, technical re-equipment or carrying out other work registered as capital investments, is reflected according to the debit of account 01 “Fixed assets” in correspondence with the credit of account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. A change in the initial value during a revaluation (revaluation, markdown) carried out in accordance with the law of the corresponding fixed assets is reflected in the debit of account 01 “Fixed assets” in correspondence with the credit of account 83 “Additional fund” or a reversal entry in the same correspondence of accounts. (as amended by the resolution of the Ministry of Finance dated December 11, 2008 N 187) To account for the disposal of fixed assets (sale, write-off, partial liquidation, gratuitous transfer, etc.), a subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” is opened to account 01 “Fixed Assets”. The value of the retired fixed asset item is transferred to the debit of this subaccount, and to the credit - the amount of depreciation accrued for the entire period of operation (from the debit of account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets”). The residual value of the object is written off from the credit of account 01 “Fixed assets” of the subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” to the debit of account 91 “Operating income and expenses”, in case of gratuitous transfer - to the debit of account 92 “Non-operating income and expenses”. Analytical accounting for account 01 “Fixed Assets” is carried out for individual inventory items of fixed assets. Account 01 “Fixed assets” corresponds to: ?????????????????????????????????????????? ?????????????????????????????? ? By debit and credit accounts? By credit with debit accounts? ???????????????????????????????????????????????? ?????????????????????? ? 01 Fixed assets? 01 Fixed assets? ? 02 Depreciation of fixed assets? 02 Depreciation of fixed assets? ? 03 Profitable investments in ? 03 Profitable investments in ? ? material values ? material values ? ? 08 Investments in non-current ? 08 Investments in non-current ? ? assets? assets? ? 58 Financial investments? 11 Animals in cultivation and ? ? 76 Settlements with different debtors? fattening? ? and creditors? 58 Financial investments? ? 79 On-farm calculations? 75 Settlements with founders? ? 80 Authorized fund? 76 Settlements with different debtors and? ? 83 Additional fund? creditors? ? 91 Operating income and expenses? 79 On-farm calculations? ? 92 Non-operating income and ? 80 Authorized fund? ? expenses ? 91 Operating income and expenses ? ? ? 92 Non-operating income and ? ? ? expenses ? ? ? 94 Shortages and losses from spoilage? ? ? values? ???????????????????????????????????????????????? ?????????????????????? Account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” Account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” reflects the movement of depreciation accumulated during the operation of fixed assets. Depreciation is calculated in accordance with the law based on the depreciable cost of fixed assets, the established useful life of objects involved in business activities, or the standard service life of objects not involved in business activities, and the chosen method (method) for calculating depreciation. The accrued amount of depreciation of fixed assets is reflected in the accounting records under the credit of account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” in correspondence with the debit of production cost (sales expenses) accounts 20 “Main production”, 23 “Auxiliary production”, 25 “General production expenses”, 26 “General business expenses”, 29 “Service production and facilities”, 44 “Sales expenses”, 91 “Operating income and expenses” (in cases established by law) and others. Depreciation deductions for a rental (leasing) object are made monthly during the term of the rental (leasing) agreement, regardless of whether the object is on the balance sheet (registered with an individual entrepreneur) by the tenant (lessee) or by the lessor (lessor). Upon disposal (sale, write-off, partial liquidation, gratuitous transfer, etc.) of fixed assets, the amount of depreciation accrued on them is written off and reflected in the debit of account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” and the credit of account 01 “Fixed assets” (sub-account “Disposal of fixed assets” ). A similar entry is made when writing off the amount of accrued depreciation for missing or completely damaged fixed assets. Account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” corresponds to: ?????????????????????????????????????????? ?????????????????????????????? ? By debit and credit accounts? By credit with debit accounts? ???????????????????????????????????????????????? ?????????????????????? ? 01 Fixed assets? 01 Fixed assets? ? 02 Depreciation of fixed assets? 02 Depreciation of fixed assets? ? 03 Profitable investments in ? 08 Investments in non-current ? ? material values ? assets? ? 79 On-farm calculations? 20 Main production? ? ? 23 Auxiliary production? ? ? 25 General production expenses? ? ? 26 General business expenses? ? ? 29 Service industries and ? ? ? farms? ? ? 44 Implementation costs? ? ? 79 On-farm calculations? ? ? 83 Additional fund? ? ? 90 Implementation ? ? ? 91 Operating income and expenses ? ? ? 92 Non-operating income and ? ? ? expenses ? ? ? 97 Deferred expenses? ???????????????????????????????????????????????? ??????????????????????
2. The new monitor would be credited to account 10. IMHO (of course, if it fits in there in terms of cost).
I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:Notification is being sent...
When you rise, your friends will know who you are. When you fall, you find out who your friends are. If you've been told your train has left, remember - there are still planes and yachts.| bAtT [email protected] Wrote 326 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #3[433340] November 16, 2011, 10:33 |
Notification is being sent...
| Tatiana Gaenkova [email protected] Belarus, Minsk Wrote 17697 messages Write a private message Reputation: 1901 Group: Moderators | #4[433369] November 16, 2011, 10:53 |
bAtT wrote:
Tell me, please: the organization purchased a monitor worth 1130 thousand rubles including VAT. does it belong to OS if the accounting policy says to include assets worth more than 30 BV? Thank you.
it is included in the cost of the OS (PC), because Separately, it cannot perform any function. So you will either have an OS upgrade or a repair. P.S. You can’t just write off an old monitor, it contains precious metals.
I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:Notification is being sent...
I’m rarely on the forum, so I can’t advise everyone in private messages. Sorry.| bAtT [email protected] Wrote 326 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #5[433373] November 16, 2011, 11:00 |
Notification is being sent...
| Tatiana Gaenkova tgaen[email protected] Belarus, Minsk Wrote 17697 messages Write a private message Reputation: 1901 Group: Moderators | #6[433375] November 16, 2011, 11:02 |
bAtT wrote:
Andromeda, if I don’t have a PC on my balance sheet (my own), I can’t put the monitor into operation on its own?
you can not. Why did you buy it then? That means you store it in account 10 and do not put it into operation.
I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:Notification is being sent...
I’m rarely on the forum, so I can’t advise everyone in private messages. Sorry.| VALYUSHA [email hidden] Belarus Europe, Minsk Wrote 12250 messages Write a private message Reputation: 1344 | #7[433387] November 16, 2011, 11:15 |
bAtT wrote:
Andromeda, if I don’t have a PC on my balance sheet (my own), I can’t put the monitor into operation on its own?
I think that everything is possible, for example: 1. arrange for the founder to transfer a personal computer for free use (the situation may occur: for example, an enterprise does not have extra money to buy the entire computer due to a lack of funds for these purposes and due to the high cost of the equipment ) 2.Next, purchase a monitor (for fear’s sake, assign depreciation to account 92).
I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:Notification is being sent...
| Elena is one of... [email hidden] Belarus, Minsk Wrote 490 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #8[433390] November 16, 2011, 11:17 |
Notification is being sent...
| Tatiana Gaenkova [email protected] Belarus, Minsk Wrote 17697 messages Write a private message Reputation: 1901 Group: Moderators | #9[433397] November 16, 2011, 11:25 |
Notification is being sent...
I’m rarely on the forum, so I can’t advise everyone in private messages. Sorry.| bAtT [email protected] Wrote 326 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #10[433502] November 16, 2011, 1:29 pm |
 I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:
I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:Notification is being sent...
« First ← Prev.1 Next → Last (5) »
In order to reply to this topic, you must log in or register.
Rebus Company
Be sure to establish in your accounting policy how to account for a computer as an inventory item and what the cost of a part of the computer will be significant for your institution. Accounting for the replacement of a failed or obsolete computer part depends on this.
If a decision on the further use of the system unit removed from the computer has not been made, then it should be reflected in off-balance sheet account 02 “Material assets accepted for storage.” In this account, the system unit is taken into account until a decision is made on its further use (sale, disposal) (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 28, 2018 No. 02-06-10/12969).
Hard drive for kosgu server
It is worth noting that in paragraph
45 of Instruction No. 157n not all unified functioning systems that can be installed in a building are mentioned, therefore it is advisable to define the general procedure for organizing the accounting of such systems in the accounting policy.
In addition, if one object has several parts - fixed assets that have different useful lives, each such part is accounted for as an independent inventory item.
Considering that a video surveillance system, as a rule, consists of structural items that have different useful lives, including ones significantly different from the useful life of the building in which it is installed, individual elements of such a system should be taken into account as independent inventory objects. A similar opinion is expressed in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 20, 2016 N 02-07-10/42570, dated December 30, 2014 N 02-07-10/69030.
Changes in accounting from 2021: table
Changes in accounting in 2021 affected the activities of individual entrepreneurs, commercial enterprises and public sector institutions. Innovations have appeared in the accounting rules; a number of clarifications and new provisions relate to tax accounting. Some reporting documents have been updated - a number of “gaps” in sample documents have been eliminated, new fields and codes have been added.
An increase in the minimum wage will entail changes in accounting in terms of calculations for wages, certificates of incapacity for work and child benefits. From 2018, the temporary order of indexation of child benefits becomes permanent - the amount of these social payments will be adjusted by inflation annually from February of the new reporting period.
Which depreciation group does a computer in the Russian Federation belong to in 2021?
If any structurally articulated object has several components (in particular parts) - OS, with different periods of use, each component is taken into account as a separate inventory object.
According to the Instructions, the definition of useful life period means the period during which it is possible to use, during the work of the organization, an object of non-financial assets for the purposes for which it was purchased, formed or received.
OKOF codes for office electronics
Answer: Light panels with built-in lamps are a type of electric lighting fixture, an electrical household appliance, i.e. belong to the OKOF code group “Other machinery and equipment, including household equipment, and other objects” (code 330). Consequently, by the commission for the receipt and disposal of assets, they can quite reasonably be assigned to the OKOF group code 330.28.29 “Other general purpose machinery and equipment, not included in other groups” (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 27, 2016 N 02-07-08/ 78243).
It is worth noting that for some objects it is possible to use several OKOF codes at once. Decisions on such issues are made by authorized officials of the institution - as a rule, a permanent commission on the receipt and disposal of assets.
ACCOUNTING FOR LIGHTING DEVICES
I.V. Artemova, chief accountant, consultant
Properly selected lighting is an integral factor in occupational health and safety. Rational lighting is created by achieving certain regulated parameters - optimal illumination, minimal glare, correct direction of light. All this influences the choice of types and quantities of lighting fixtures used in an institution.
What about lighting fixtures?
Currently, manufacturers offer a huge number of different devices for indoor lighting. But specifically lighting devices include: · outdoor lighting devices (lanterns, spotlights); ·interior lighting devices (lamps, chandeliers, sconces, floor lamps, table lamps, etc.); ·specialized lighting devices (for example, flash lamps, lamps for projectors, quartz lamps for bactericidal irradiation, stage lighting equipment, etc.); ·decorative lighting fixtures (for example, garlands). Lighting with lighting fixtures is called artificial lighting, as opposed to natural sunlight.
Lighting regulation
The basic requirements for artificial lighting are reflected in the Sanitary Rules and Standards “Hygienic requirements for natural, artificial and combined lighting of residential and public buildings, SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03”, approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation on April 6, 2003 No. 34 ( hereinafter referred to as SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03). According to clause 3.1.3 of SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03, working lighting should be provided for all premises of buildings, as well as areas of open spaces intended for work, the passage of people and traffic.
How to reflect the purchase of a computer in an accounting report
The chart of accounts does not provide for a separate off-balance sheet account for accounting for computers put into operation. Therefore, you need to open it yourself. For example, this could be account 013 “Inventory and household supplies”.
The components of a computer are a monitor, system unit, keyboard, mouse, etc. According to regulatory agencies, it is impossible to take into account a computer in parts. This is explained by the fact that the components of a computer cannot perform their functions separately. Therefore, these items must be taken into account as part of a single fixed asset item. This point of view is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 4, 2007 No. 03-03-06/1/639*.
21 Dec 2021 marketur 218
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Benefits for teachers in rural areas in 2019
- Fixed-term employment contract for a seller with an individual entrepreneur, sample
- Is it possible to sell a debt under a writ of execution?
- Deprivation of benefits for military personnel in Ukraine in 2021
Issues of application of budget classification: 225 KOSGU
; putty, window covering; services for organizing nutrition for animals under operational management, as well as their veterinary care; Refilling cartridges; other similar expenses.
If these are advertising services, when the contractor himself prepares and places the banner without transferring it to the customer, use the subsection. Example 1 The institution reflected the costs of conducting an examination of computer equipment, which was necessary in order to confirm the malfunction of the computer and its write-off, under subarticle 226 of KOSGU. The accountant motivated the choice of subarticle 226 of KOSGU by the fact that this examination is not related to operation. However, Instructions No. 180n, as part of subarticle 225 of KOSGU, states: an inspection of the technical condition of non-financial assets, carried out for the purposes of... determining the possibility of further operation.
You might be interested...
Recycling
The services of companies recycling monitors will cost much less than paying a fine.
In processing companies, the final cost is affected by:
- number of units written off;
- removal costs;
- attraction of special equipment;
- carrying out technical examination.
Parts divided by hazard class and component composition are sent for processing. Mercury waste is stored in an isolated room for no more than 24 hours and transported in sealed containers. Non-hazardous waste is transported in textile bags.
There are 8 factories in Russia that produce highly purified precious metals from computer equipment.
Old models
Bulky cathode ray tube monitors contain more hazardous compounds than modern ones. Analysis into constituent elements according to chemical composition is carried out automatically and partially manually. The sorted components are sent for recycling or disposal.
New models
Every year the share of plasma and LCD displays among electronic waste increases. For recyclable materials, dismantling is performed, in which the extracted elements are sorted according to their component composition.
In European countries and the United States, lead glass screens are suitable as raw materials for producing lead. In Russia there are no metallurgical melting furnaces for glass screens.