The authorized capital is the totality of contributions from the founders of the organization. Based on it, the minimum amount of company property is calculated. In a situation of financial crisis, outstanding debts of the management company are used for settlements with creditors. It guarantees that the interests of the persons providing loans are respected. There is a minimum size of the charter capital. You cannot reduce it yourself. All changes must undergo state registration. The corresponding data is also entered into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
In what account is additional capital accounted for and how is it reflected in the statements?
Since additional capital is the company’s own funds, and according to general accounting rules they belong to the organization’s liabilities, therefore, accounting for additional capital should be carried out in the context of a passive account.
This account is account 83. Credit transactions on account 83 mean that additional capital is growing. If the entry is made as a debit, then, on the contrary, this means that the operation reduces additional capital.
When preparing the company's financial statements for any specific date, the value of additional capital is also subject to reflection in the company's own funds. For this purpose, there is line 1350 in the balance sheet “Additional capital without revaluation.” It should indicate the amount of additional capital, excluding from it the amount of the identified positive revaluation (revaluation) of fixed assets.
How to do this in practice? It is necessary to subtract from the total balance on the credit of account 83 the amount attributable to the previously identified total revaluation of the company’s non-current assets.
Please pay attention! In accordance with clause 68 of Regulation No. 34n, each amount forming additional capital must be reflected in accounting separately. Consequently, when accounting for additional capital, companies conduct analytics of individual amounts that form additional capital in separate subaccounts in the context of account 83. Therefore, the company is able to identify the total amount of revaluation of fixed assets by looking at the credit balance in the corresponding subaccount of account 83.
The amount of revaluation of fixed assets, in turn, is recorded in another line of the balance sheet, namely in line 1340.
For information about what aspects are important for an accountant to know when keeping records of other parts of a company’s equity capital, see the article “Procedure for accounting for an organization’s equity capital (nuances).”
In practice, as stated above, there are several possible situations in which a company's additional capital can be formed or used. Moreover, some situations are “mirror”, i.e. under some circumstances they increase additional capital, and under others they decrease it.
Let's consider such situations.
Results
Accounting for transactions involving contributions to the capital company and its increase is generally simple. It may be quite labor-intensive to formalize the process of transferring property to the founder's contribution if the volume of this property is significant.
Thus, correct accounting of additional capital allows the company to smooth out such potentially negative situations as identifying a markdown of non-current assets, lack of funds to pay dividends to participants, etc. In addition, there are other areas for the possible use of the company’s additional capital.
According to accounting rules, the formation and increase in additional capital is reflected in the credit of account 83, and its decrease is reflected in the debit. It is important for the company’s accounting service to remember that correct accounting is only possible if detailed analytics are maintained for each component of additional capital (which includes amounts that are identical in their economic nature) in the corresponding subaccount of account 83.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Termination of criminal proceedings and criminal prosecution
Reduction methods and corresponding postings
When there is an obligation to reduce, situations are divided into two groups:
- Part of the Criminal Code is not actually paid and must be cancelled. These are shares (shares) at the disposal of the business entity. They are taken into account in account 81. When conditions arise for reducing the capital, a posting is made for them Dt 80 Kt 81.
- The activities of the legal entity are unprofitable or ineffective, as shown by the ratio of the net asset value to the capital asset. By reducing the capital in this case, the loss is covered or the retained earnings are increased by the amount missing to pay off the share in the LLC: Dt 80 Kt 84. In relation to each participant (shareholder), there will be a commensurate decrease in his share or the nominal value of the shares.
When reducing at the initiative of the owners, the following options are possible:
- The participant leaves HT, fully withdrawing his share of participation: Dt 80 Kt 75.
- The economic society buys out part of the management company. These may be full shares of retiring participants or a specific number of shares. The redemption is recorded by posting Dt 81 Kt 75 (50, 51, 52). Then this part of the Criminal Code is canceled: Dt 80 Kt 81.
- Existing shares or par value of shares are reduced in the required proportion. With this method, the difference in the amount of the contribution to the management company can remain at the disposal of the legal entity and become its income: Dt 80 Kt 91. Or it can be paid to participants (shareholders), and then this will be their income: Dt 80 Kt 75. If the participant refuses to receive such amounts, then they will also become the income of the legal entity: Dt 75 Kt 91.
Find out how a decrease in capital assets affects the taxation of an LLC in the Guide from ConsultantPlus. Trial access to the system can be obtained for free.
It will be impossible to pay income to participants if:
- The Criminal Code has not been paid or has not been paid in full.
- The legal entity has signs of bankruptcy.
- Dividends already declared for payment have not been paid or have not been paid in full.
- Shares or shares for which there is a redemption requirement have not been repurchased.
Legal basis
The legal basis for reflecting business facts is Law 402-FZ “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011. The normative act establishes the general principles of reporting. All participants in business transactions are required to follow its provisions. The nuances of registration related to the organizational structure are regulated by the provisions of Federal Law-14 “On LLC” dated 02/08/98.
Orders of the Ministry of Finance, letters from the tax service, instructions from Rosstat, the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation are of great importance. The same departments approve unified forms of documents. Basic accounting principles are listed in the fifth paragraph of PBU 1/2008:
- Property separation. The assets of the enterprise are not the property of the founders. The owners are liable for the obligations of the company to the extent of their contributions. Exceptions are cases of deliberately bringing a company to a state of financial insolvency (Article 3 of Law 14-FZ).
- Continuity of recording economic facts. Accounting is maintained from the moment of establishment of the company until its exclusion from the state register (official liquidation).
- Clear sequence. Transactions and business events are reflected by accrual (clause 5 of PBU 1/2008). What is key is the date the obligation arose, not the actual settlement. The cash method is used in tax accounting, but not in accounting.
We should not forget about precedents. The positions of the Supreme and Constitutional Courts of Russia are regularly published in open sources. The clarifications provide guidance in bridging legal gaps.
Tax consequences of reducing the authorized capital
Many questions arise for accountants when a company, either compulsorily or voluntarily, in accordance with the decision of the founders, reduces its authorized capital. Elena Gorneva examined the issues of reflecting these transactions in accounting and tax accounting for both the company and the founding organizations.
The company has the right, and in some cases is obliged, to reduce its authorized capital (Clause 1, Article 20 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies”). In our article we will talk about paying participants the value of part of the deposit in cash, not in property. Let's start with the company's accounting when reducing its authorized capital.
Income tax
A) The company is obliged to make a decision to reduce the capital
The company is obliged to make a decision to reduce the authorized capital of the company to an amount not exceeding the value of its net assets if the value of the company’s net assets remains less than its authorized capital at the end of the financial year following the second financial year or each subsequent financial year (clause 1, paragraph. 4 Article 30 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ).
Since the reduction will occur in accordance with the requirements of the law, the amounts by which the authorized capital will be reduced are not recognized as income of the company (clause 17, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia 09/17/2015 No. 03-03-06/1 /53369).
B) Reducing the capital on a voluntary basis
If the authorized capital is reduced voluntarily (by decision of the founders) and the decrease in the authorized capital is not accompanied by a corresponding payment (return) of the cost of part of the contribution to the company’s participants, then, in the opinion of the Ministry of Finance (with reference to the Determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2009 No. VAS- 11664/09), the amount of reduction in the authorized capital of the company will be considered non-operating income of the company and taken into account for profit tax purposes (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 23, 2014 No. 03-03-RZ/24777). But if payments (returns) of the cost of part of the contribution are made to participants, then the company does not generate income.
In this case, the amount of money paid to participants cannot be recognized as an expense, since the payment in question does not meet the requirements of paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, since it is not aimed at generating income.
C) Reducing the capital by paying off shares owned by the company
The share passes to the company, for example, when a participant leaves the company. Clause 2 of Article 24 of Law No. 14-FZ determines that within a year from the date of transfer of a share or part of a share in the authorized capital of a company to the company, they must, by decision of the general meeting of participants of the company:
- distributed among all participants of the company in proportion to their shares in the authorized capital of the company;
- offered for purchase to all or some members of the company and (or), unless prohibited by the company's charter, to third parties.
A share or part of a share in the authorized capital of the company that is not distributed or not sold within the period established by this article must be redeemed, and the size of the authorized capital of the company must be reduced by the amount of the nominal value of this share or part of the share (clause 5 of Article 24 of Law No. 14- Federal Law).
In this case, the amount by which the company will reduce its authorized capital is not subject to income tax (clause 17, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
VAT
Reducing the size of the authorized capital of the company in the situations under consideration does not entail the emergence of an object of VAT taxation (clause 1, clause 2, article 146, subclause 1, clause 3, article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting for a company when reducing its authorized capital
In accordance with the chart of accounts, account 80 “Authorized capital” is intended to summarize information about the state and movement of the organization’s authorized capital. Entries to account 80 are made in cases of increase and decrease of capital only after making appropriate changes to the constituent documents of the organization.
A) Reduction of authorized capital in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation
When reducing the capital in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on bringing the amount of the authorized capital to the value of net assets, as well as when the difference between the net assets of the company and its authorized capital is insufficient to pay the actual value of the share (part thereof) to the participant, the following entry is made in the accounting records:
- D80 “Authorized capital” ‒ K84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” - reflects the reduction of the authorized capital in order to bring its value to the net asset value.
B) Reducing the authorized capital by reducing the nominal value of shares on a voluntary basis
The law does not contain rules prohibiting the payment of funds to participants or the transfer of other property to them when the nominal value of the share is reduced. Consequently, the specified payment can be made by decision of the general meeting of participants (clause 1, article 32, subclause 2, clause 2, article 33 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ).
If the capital is reduced voluntarily by decision of the company with the return of the corresponding part of the contribution to the company's participants:
- D80 “Authorized capital” ‒ K75 subaccount “Calculations for contributions to the authorized capital” - reflects the decrease in the authorized capital with the return of the corresponding part of the contribution to the company’s participants.
Then, as the debt is repaid to the founders, an entry is made:
D75 subaccount “Calculations for contributions to the authorized capital” - K50 (51) - funds were issued to pay for the shares of participants.
For reference. Since the timing of payments to participants (shareholders) of the company in the event of a decrease in the authorized capital is not regulated by law, payments can begin before changes are made to the charter.
When reducing the capital, by decision of the company, with the simultaneous adoption of a decision to refuse to return to participants the cost of the corresponding part of the contribution:
- D80 “Authorized capital” ‒ K75 subaccount “Calculations for contributions to the authorized capital” - reflects the decrease in the authorized capital at the expense of the participants;
- D75 subaccount “Calculations for contributions to the authorized capital” - K91 - other income is recognized in the amount not returned to the participants.
C) Reducing the authorized capital by redeeming shares acquired from participants
To account for the value of shares acquired by the company itself, account 81 “Own shares” is intended.
When a company acquires shares, the following entries are made in the accounting records:
- D81 “Own shares” ‒ K75 subaccount “Calculations for contributions to the authorized capital” - reflects the debt to pay the participant the cost of shares acquired from him;
- D75 subaccount “Settlements for contributions to the authorized capital” - K50 (51) - funds were paid for shares purchased from participants.
When reducing the authorized capital by redeeming shares owned by the company, by decision of the general meeting, the following entries are made in accounting:
- K80 “Authorized capital” – D81 “Own shares” - the par value of the shares belonging to the company has been repaid;
- D91 “Other expenses” ‒ K81 “Own shares” - reflects the difference between the actual costs of repurchasing shares and the nominal value.
The accounting of the founder is regulated differently .
Income tax
Income in the form of property, property rights, which are received within the limits of the contribution (contribution) by a company participant when reducing the authorized capital, are not taken into account when determining the tax base for income tax (clause 4, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It should be noted that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not establish what is meant by the contribution (contribution) of a participant for the purpose of applying the norm of subparagraph 4 of paragraph 1 of Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The Ministry of Finance of Russia in its clarifications indicated that the contribution (contribution) of a participant should be understood as contributions to the authorized capital of the company (both during its establishment and when increasing its authorized capital) or in the case of acquiring a share from other participants (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 17.03. 2006 No. 03-03-04/2/81).
Although these clarifications relate to other situations, namely the withdrawal of a participant from the company and the liquidation of the company, the conclusion made therein, in our opinion, is also applicable in the case of assessing the size of the contribution when receiving property in connection with a decrease in the authorized capital. This is due to the fact that all of the listed cases are provided for by subparagraph 4 of paragraph 1 of Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Consequently, income received by a company participant when reducing the authorized capital is not recognized for profit tax purposes within the limits of the contribution he previously made (both initial and additional).
Accounting for a participant when reducing the authorized capital
In the synthetic accounting of a participant, only a decrease in the authorized capital is reflected by reducing the nominal value of the share and only if it is accompanied by the receipt of corresponding payments by the participant.
If previously the authorized capital was not increased at the expense of the company’s property, then on the date of state registration of changes made to the charter, it is necessary to make an entry (clause 18 PBU 19/02, clause 6 PBU 1/2008 “Accounting Policy of the Organization”):
- D76 “Calculations for due dividends and other income” ‒ K58-1 “Shares and shares” - the contribution to the authorized capital has been reduced.
If previously the authorized capital was increased at the expense of the company’s property, then the participant recognizes the payment due as income from participation in another organization (clause 7 of PBU 9/99, clause 6 of PBU 1/2008). On the date of state registration of changes made to the charter, the following entry must be made:
- D76 “Calculations for due dividends and other income” ‒ K91-1 “Other income” - reflects the arrears of payment in connection with the reduction of the authorized capital in the amount by which the nominal value of the share was previously increased at the expense of the company’s property.
A decrease in the authorized capital by reducing the nominal value of shares without making payments to participants or by redeeming shares owned by the company is not reflected in the participant’s accounting records, because as a result of such a decrease in the authorized capital, only changes occur in the structure of the LLC’s equity capital.
If the founder is a non-resident
As we noted above, when calculating income tax, income in the form of property and property rights received by a participant within the limits of his contribution when reducing the authorized capital in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (clause 4, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) is not taken into account.
However, if it is voluntarily reduced, participants who are legal entities will experience taxable income. Such income can be obtained when the subsidiary pays them the difference between the original and new value of the share. If such payments are not made, taxable income does not arise for participants or shareholders in the event of a voluntary reduction of the authorized capital (Article 41 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In accordance with Article 7 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if an international treaty of the Russian Federation containing provisions relating to taxation and fees establishes rules and regulations other than those provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the normative legal acts on taxes and fees adopted in accordance with it, the rules and regulations are applied international treaties of the Russian Federation.
Let's look at an example.
A company from the Netherlands received income in the form of a payment made as a result of reducing the authorized capital of a Russian organization. What are the tax consequences?
An Agreement on the avoidance of double taxation of income and property (hereinafter referred to as the Agreement) was concluded between the Government of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
When applying international treaties of the Russian Federation on taxation issues, one should take into account the comments to the Model Convention of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development on Taxes on Income and Capital, on the basis of which agreements on the avoidance of double taxation are concluded with foreign countries.
According to paragraph to Article 10 “Dividends” of the Model Convention, payments considered as dividends may include not only the distribution of profits based on a decision made at the annual meetings of shareholders of the company, but also other payments in cash or having a cash equivalent, such as bonus shares, bonuses, liquidation payments and hidden profit distribution.
Thus, income in the form of payments made to participants as a result of a reduction in the authorized capital of a Russian company, not exceeding the company’s contribution to the authorized capital , qualifies as “Other income” in accordance with the norms of agreements on the avoidance of double taxation (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 17, 2016 No. 03-08-05/67758).
According to paragraph 1 of Article 21 “Other income” of the Agreement, types of income of a resident of one contracting state, regardless of the source of their origin, which are not mentioned in the previous articles of this Agreement, are subject to taxation only in that state.
That is, the income of a resident of the Netherlands in the form of payments made to a participant as a result of a reduction in the authorized capital is not subject to income tax in the Russian Federation.
And in order for a Russian organization not to withhold income tax as a tax agent on income received by a resident of the Netherlands (if the amount is paid within the initial deposit), the latter must provide the necessary documents to confirm his residence (clause 1 of Article 312 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Income in the form of payments made to a foreign legal entity as a result of a reduction in the authorized capital of a Russian organization to the extent that it exceeds the amount of the foreign participant's contribution to the authorized capital must be qualified as dividends for tax purposes and subject to withholding tax at the rate established by the Agreement.
If the recipient has the actual right to dividends, then the tax levied by the Russian organization should not exceed (clause 2 of Article 10 of the Agreement):
a) 5% of the total amount of dividends, if the beneficial owner of the dividends is a company (other than a partnership) whose direct participation in the capital of the company paying the dividends is at least 25% and which has invested in it at least ECU 75,000 or its equivalent in the national currency of the contracting states;
b) 15% of the total amount of dividends in all other cases.
We hope that the article will help you take into account all the nuances of accounting, as well as the norms of international acts, if the founder decides to reduce the authorized capital.
Rules for accounting entries
The establishment of accounting begins with the registration of founding contributions. Information is reflected in debit and credit. The main accounting account becomes “Authorized capital” (No. 80). The balance on it is considered a liability and is reflected in the third section of the balance sheet. The final value of this account must correspond to the constituent documents of the company.
Before the actual payment of contributions by the owners, the debt is formed in account No. 75. Subsequently, operations on the fulfillment of their obligations by the participants are reflected here. If necessary, the accountant opens additional accounts. Thus, transactions involving the formation, increase or decrease of capital are classified as subgroup 75.1. The payment of dividends is recorded in subaccount 75.2.
The rules for registering founding contributions depend on the form of receipts.
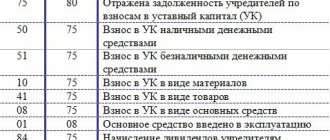
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| Registration of a company with an authorized capital (debt of founders for contributions) | 75 | 80 |
| Making a monetary contribution by a participant to a current account | 51 | 75.1 and 75 |
| Payment of a contribution to the company's cash desk | 50 | 75.1 and 75 |
| Transfer of property (fixed assets, materials, other valuables) as a contribution | 08, 10, 11, 41, 21, 67, 58, 66, 97 | 75.1 and 75 |
Dt 01 Kt 83.
Dt 83 Kt 02.
Dt 83 Kt 01.
Dt 02 Kt 83.
Dt 91-2 Kt 01.
Dt 01 Kt 91-1.
Examples
When is the Criminal Code reduced?
Authorized capital (AC) is a concept inherent in commercial organizations: business entities (PJSC, JSC, LLC), business partnerships (HT), state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises (UP). The smallest amount of the Criminal Code is fixed by law (except for HT, which does not have such restrictions):
- for PJSC – 100,000 rubles;
- for JSC and LLC – 10,000 rubles;
- for state unitary enterprises – 5,000 minimum wages;
- for municipal unitary enterprises – 1,000 minimum wages.
In this case, the minimum wage is equal to the value established on the date of registration of the UE.
The owners of the listed legal entities have the right to reduce the capital on their own initiative, and in some situations this procedure is required by law. However, in any case, the charter capital cannot fall below its minimum value (as of the date of registration of changes in the constituent documents of the charter capital in the case of a voluntary reduction and on the date of registration of a legal entity in the case of a reduction due to obligation). If this happens, the legal entity will be liquidated. State unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises that find themselves in a situation of mandatory reduction (when the capital capital is greater than the value of net assets (NA), but if reduced to NA, the capital capital will become less than required by law), they have 3 months from the end of the year to correct the situation, based on the results which this situation was created.
According to the decision made by the owners, a reduction is possible when:
- The organizational and legal form of a legal entity is changing, and the new form allows for a lower value of the Criminal Code.
- The owners made this decision. Since with a voluntary reduction it is possible to pay them income, this procedure can be regarded as an analogue of the calculation of dividends.
The obligation to reduce the capital capital arises in the following situations:
- A PJSC, JSC or LLC has unpaid or undistributed shares (or unsold shares of the primary issue) or shares (shares) purchased by the business entity that could not be sold during the year.
- In a PJSC, JSC or LLC for 2 years, and in a unitary enterprise - at the end of the year, the value of the authorized capital turns out to be greater than the calculated value of the NA.
- A participant leaves the LLC, and he needs to pay his share at its real value, and the difference between the private equity and the charter capital is not enough for this.
Regardless of the reason for reducing the capital, you need to do the following before doing so:
- Notify the Federal Tax Service.
- Twice a month publish a message about these intentions, intended for creditors who have the right to demand payment of their debts.
- Register the conversion of shares or redemption of their quantity in the SBRFR (for PJSC and JSC).
- Make sure that as a result of the reduction procedure at the initiative of the owners of the management capital there is no more than the NAV.
Brief conclusion
Company accounting begins with reflecting the facts of formation of the authorized capital. Separate entries record the deposit of funds, securities, and property. The content of the records depends on the method of transmission of the contribution, its type and other aspects. Contributions for each participant are made individually.
Reducing the capital of an LLC is possible by reducing the value of shares without changing their size, or by redeeming shares with a change in their size, but without adjusting the value.
In this case, the reason for this procedure may be both the society’s own desire and the requirements of the law.
The procedure is necessarily carried out through the tax authority, where changes are made to the Charter and the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
For changes made, a fee of 800 rubles is paid.
| The article describes typical situations. To solve your problem, write to our consultant or call for free: 7 (499) 938-43-28 — Moscow — CALL 7 St. Petersburg - CALL 7 Other regions - CALL It's fast and free! |
basic information
There are two procedures for reducing capital:
Regardless of the order in which changes are made, they must not contradict the law. In particular, the minimum size of the authorized capital is at least 10 thousand rubles. The amount of capital should not be below this level.
Reducing the amount of capital on a voluntary basis is carried out by reducing the nominal value of the founders' shares. However, the ratio of shares does not change, since redistribution occurs.
IMPORTANT! Reducing the capital on a voluntary basis cannot be a method of avoiding the company's liability to creditors. In particular, an organization cannot avoid paying its debts in this way. Creditors to whom there are early obligations must be notified of the changes being considered. The presence of the notification must be confirmed.
The amount of capital can be reduced both through money and property. For example, the organization’s capital is 10 thousand rubles. The new founder contributed to the company's assets in the form of a production building. However, the entrepreneurial project began to bring only losses. In this regard, the founder decided to withdraw his contribution. The accountant must deal with the registration of disposal of fixed assets. Then the cost of the building is written off from accounting. In this case, you need to draw up an act of acceptance and transfer of the OS object.
ATTENTION! Personal income tax is deducted from the amount of disposal of objects that are transferred to the founders. The founder, in turn, receives taxable income. This rule is specified in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated August 26, 2016. However, the founder has the opportunity to provide a tax deduction for the amount of expenses associated with the acquisition of rights to property. The rule in question is stipulated by Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Is it possible to reduce the capital of an LLC?
Yes, a limited liability company can reduce the amount of its authorized capital.
Article 20 of Law No. 14-FZ as amended. dated 04/23/2018 allows organizations to reduce the level of their capital, while establishing the reasons for carrying out this procedure.
According to this article, an LLC can itself initiate a reduction in the fund, or it can act in connection with the need to comply with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
A decrease in the size of the fund entails updating the constituent documents, so the procedure must go through the tax authority.
Examples
Let's consider an example of reducing the size of a charter capital by reducing the nominal value. The society includes two participants. The authorized capital is 500 thousand rubles. Share ratio:
- Ivanov I. I. owns a share of 80% of the capital. It amounts to 400 thousand rubles.
- Petrov V.V. owns a share of 20%. It is 100 thousand rubles.
It was decided to reduce the size of the management company by half. As a result, it should amount to 250 thousand rubles. However, when making changes, it is important to maintain the original percentage. After the changes, the size of the shares will be:
- Ivanov I.I. will continue to own 80% of the management company, but the size of his share will be 200 thousand rubles.
- Petrov V.V. will own 20% of the capital, the size of the share will be 50 thousand rubles.
Maintaining the ratio of shares is regulated by Article 20 of the Law “On LLC”.
Let's consider another situation. The participant left the society. His share was transferred to the LLC. The authorized capital is equal to 1 million. Distributed in the following ratio:
- The share of the LLC is 20% of the capital (200 thousand rubles).
- A. A. Sidorov’s share is 40% of the capital (400 thousand rubles).
- Meshcherikov V.V.’s share is 40% (400 thousand rubles).
The size of the management company is reduced by the value of the LLC share. That is, after the changes it will be 800 thousand rubles. The ratio of participants' shares is being increased. Now they will be not 40%, but 50%.