How to cancel an erroneous advance invoice? We will tell you using the example of the 1C: Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0.
Having discovered in the current period an error from the previous period, as a result of which VAT was paid in excess (for example, due to the erroneous recognition in advance of postpayment received from the buyer), the taxpayer can correct it: cancel the extra registration entry for the erroneous invoice in the sales book, recalculate the tax VAT base during the period when the error was identified and submit an updated VAT return. The mechanism for correcting these errors is not provided for by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137, but in accordance with the explanations of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, erroneous registration entries can be canceled using additional sheets of the sales book.
Issuing an invoice for advance payment by the supplier
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code, an advance invoice must be issued no later than 5 days from the date the supplier receives the advance payment. The document must be drawn up in two copies, one of which should be sent to the buyer, and the second one should be registered in your sales book.
It would seem that everything is extremely simple. However, accountants often make annoying mistakes when creating an advance invoice .
The first of them is failure to issue a document every time an advance is received from a buyer within the period. Accountants sometimes believe that an invoice can be issued once a month or quarterly for the total amount of the advance payment received from the buyer. However, this is not true - for each amount received there must be an invoice issued no later than 5 days from the date of receipt.
Another common mistake is failure to issue an advance invoice if the shipment occurs in the same quarter. Articles 168 and 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation require that an “advance” invoice be issued within a 5-day period after receiving an advance payment, and a “shipment” invoice must be issued within the same period after shipment.
By the way, there are clarifications from the Ministry of Finance ( letters dated October 12, 2011 No. 03-07-14/99, dated March 6, 2009 No. 03-07-15/39 ) regarding the situation when the shipment occurred within 5 days after receiving the advance payment . Officials believe that in this case there is no need to issue an advance invoice - it is enough to issue a document upon shipment. At the same time, the Federal Tax Service in its letters ( dated 03/10/2011 No. KE-4-3/3790, dated 02/15/2011 No. KE-3-3/ [email protected] ) expressed the opposite position . Therefore, just in case, many accountants prefer to issue an advance invoice even when no more than 5 days pass between receiving the advance payment and shipment.
When an advance invoice is not issued
An advance invoice is not issued in the following cases:
- if the transaction is not subject to VAT in accordance with Article 149 Code of the Russian Federation;
- if the supplier applies tax exemption in accordance with Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- if the transaction is subject to VAT at the “ zero ” rate;
- if the advance was transferred towards the future supply of goods with a long production cycle ( more than 6 months ) in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for making corrections to an invoice after the end of the tax period
According to paragraph 1 of Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a taxpayer who has discovered in the declaration submitted to the tax authority that information is not reflected or is incompletely reflected, as well as errors:
- is obliged to make the necessary changes to the tax return and submit an updated tax return to the tax authority if errors (distortions) led to an understatement of the amount of tax payable;
- has the right to make the necessary changes to the tax return and submit an updated tax return to the tax authority if errors (distortions) do not lead to an understatement of the amount of tax payable.
If in the current tax (reporting) period errors (distortions) are discovered in the calculation of the tax base that relate to previous tax (reporting) periods, then the tax base and tax amount are recalculated for the period in which these errors (distortions) were made (para. 2 clause 1 article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, the taxpayer has the right to recalculate the tax base and the tax amount in the tax (reporting) period in which errors (distortions) were identified if (paragraph 3, clause 1, article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- it is impossible to determine the period of commission of these errors (distortions);
- such errors (distortions) led to excessive payment of tax.
When applying these provisions to the calculation of VAT and the presentation of tax reporting, the following features must be taken into account:
- the norm of paragraph 1 of Article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not apply to those errors that were made due to incorrect reflection of tax deductions. This is due to the fact that by using tax deductions the taxpayer reduces the amount of tax already calculated from the tax base (clause 1 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 25, 2010 No. 03-07-11/363);
- recalculation of the tax base for VAT in the period of discovery of an error made in previous tax periods is not provided for by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137 (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 1137).
As defined by the Rules for Maintaining the Sales Book, approved. Resolution No. 1137, when corrections are made to an issued invoice after the end of the tax period, registration of the corrected invoice and cancellation of the entry on the original invoice are made in an additional sheet of the sales book for the tax period in which the invoice was registered before entering into it corrections (clause 3, clause 11 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, approved by Resolution No. 1137).
Despite the fact that these norms of Resolution No. 1137 correlate the procedure for correcting the sales book only with making corrections to invoices, the use of additional sheets of the sales book is prescribed in relation to any changes to the sales book for expired tax periods (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 6, 2006 No. MM- 6-03/ [email protected] , dated 04/30/2015 No. BS-18-6/ [email protected] ).
The data from such additional sheets is used to make changes to the VAT tax return (clause 5 of the Rules for filling out an additional sheet of the sales book). At the same time, the updated tax return, in addition to those sections that were previously submitted to the tax authority, includes Appendix 1 to Section 9 (clause 2 of the Procedure for filling out a VAT tax return, approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7- 3/ [email protected] ).
Errors in details
The invoice is the basis for the buyer to deduct VAT. If the supplier made errors in the document, then the counterparty may be denied this right. At the same time, the Ministry of Finance has repeatedly explained that the only grounds for refusing a deduction can be errors that prevent the identification of the buyer, seller, object of the transaction, its price, as well as the VAT rate and amount. But so that the buyer does not have to defend his case before the tax authority, it is better to avoid such mistakes and fill out the invoice details correctly.
First of all, indicate the invoice number and the date of its preparation. Note that advance documents must be numbered in general chronological order with shipping invoices. The lines before the tabular part indicate the full or abbreviated name of the buyer and seller, their tax identification number and checkpoint. In lines 3 and 4 of the advance invoice (Consignor and Consignee) there is a dash.
It is important to correctly indicate in line 5 the number and date of the payment for which the advance was received. Line 7 indicates the name of the currency “Russian ruble” and its code 643.
In the tabular part of the invoice for advance payment, columns 1, 7, 8 and 9 are filled in. In the rest, dashes should be added. If the advance is transferred towards the future delivery of goods with the simultaneous completion of certain work (for example, the sale of equipment and its installation), then column 1 indicates both the goods and a description of the work. Often, an advance payment is made not for any specific product, but in general for the supplier’s products. In this case, column 1 indicates the general group of goods, for example, confectionery, stationery.
Which form to use for an advance invoice
An invoice for the advance payment is issued using a regular account form. It was approved by Resolution No. 1137.
A sample advance invoice can be downloaded for free from the link below:
The main difference between a regular account and an advance account is the order in which data is entered into the document.
The header of the form is filled out in the same way as for a regular account:
- enter information about the payer, buyer, details of the payment order for which the advance was received. The lines “shipper” and “consignee” are crossed out;
- The order of filling out the table is different;
- The accountant for the advance is signed by the manager and chief accountant or persons authorized to do so.
You can download a sample of filling out an advance invoice from the link:
Filling out sales and purchase books by the supplier
The supplier registers the advance invoice in the sales book with transaction type code 02 . This must be done in the same period in which the prepayment was received. Column 11 indicates the payment number, and columns 4-6, 14-16 and 19 remain blank.
Within 5 days after shipment, a shipping invoice is recorded in the sales book. In this case, in column 11, the payment for the advance payment is indicated as a document confirming payment.
At the same time, the previously issued advance invoice must be reflected in the purchase book with transaction code 22. In column 7, information from the same payment document for which the advance was received should be indicated.
How should a buyer fill out a purchase book?
For a buyer, an invoice is an extremely important document. Only if it is available, filled out correctly and registered can you receive a deduction of input VAT.
After transferring the advance payment and receiving the corresponding invoice from the supplier, the document should be registered in the purchase ledger. This must be done in the quarter in which the advance is listed. Columns 4, 6, 8 and 9, as well as 10 to 12, are not filled in, and column 7 reflects information about the advance payment .
Once the advance invoice has been received, the VAT on the advance payment can be claimed as a deduction. But you can not do this, but wait until the shipment is made, and claim VAT for deduction from the shipping invoice. However, if the first path is chosen, the VAT previously deducted on the advance invoice will have to be restored. This must be done in the period when the goods, work or services for which the advance payment was transferred are received and capitalized. If VAT on the advance payment was not claimed for deduction, then there is nothing to recover.
When a shipping invoice is received, it should also be recorded in the purchase ledger. This can be done after the goods, works or services received under it are accepted for accounting. However, it is not necessary to register the document immediately - this can be done at any time within three years from the date of receipt of goods. This opportunity is used when they want to deduct input VAT on these goods in one of the following quarters.
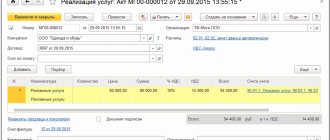
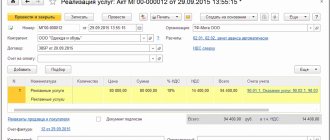
Cancellation of an invoice by the buyer
In the considered example, for Vasilek LLC and Kolosok LLC, the cancellation of an erroneous invoice did not create additional problems, since no entries were made in the purchase book based on this invoice. However, situations are different: suppose an erroneous invoice addressed to Vasilek LLC, along with a lot of other invoices, ended up in the accounting department of Kolosok LLC, after which the absent-minded accountant of Kolosok LLC, reflecting the received invoices in the purchase book, mistakenly entered amounts from all invoices into the purchase ledger. As a result, the tax deduction for the 3rd quarter turned out to be overstated, which was discovered after filing the return.
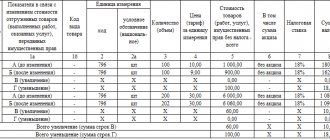
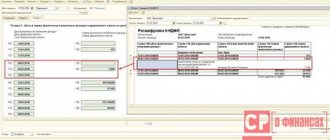
In this case, the buyer, Kolosok LLC, will have to cancel the invoice and correct the purchase book. To do this, the accountant needs to draw up an additional sheet to the purchase book for the 3rd quarter, in which in gr. Enter items 15 and 16 of the erroneous invoice with a minus sign (clause 5 of the rules for filling out the additional sheet of the purchase book). Then you need to submit an update, having previously paid additional tax and penalties in order to avoid a fine (Clause 1, Article 81 of the Tax Code, Clause 6 of the rules for filling out the additional list of the purchase book).
You can also find a sample of filling out an additional sheet of the purchase book when canceling an invoice in K+, having received a trial full access to the system for free.
Accounting for taxable and non-taxable VAT transactions by the buyer
VAT on goods, works and services that are used to carry out activities both subject to and non-taxable to VAT must be accounted for separately . Paragraph 4 of Article 170 , which establishes this rule, is silent about the need to apply this approach in relation to prepayment, which is transferred towards the supply of such goods. Thus, the prepayment in this case is recorded in the purchase ledger as a total amount. Also, all of it can be claimed as a deduction.
When the goods for which the advance payment was transferred are received, the VAT accepted for deduction should be restored. It must then be accounted for separately. The part that corresponds to transactions subject to VAT is accepted for deduction. The remaining tax amount is written off to increase the cost of the goods.
In conclusion, let us mention one more circumstance. Accountants often make errors in deductions on advance invoices when selectively approaching their application. If you always declare (or do not declare) the deduction of VAT on prepayments, then the process has been worked out to the point of automaticity. If you use a selective approach, then each time you receive a shipping invoice you should check whether VAT has been deducted from the corresponding advance. Otherwise, it’s easy to miss the errors, and your VAT return will not pass the automatic check of the Federal Tax Service.