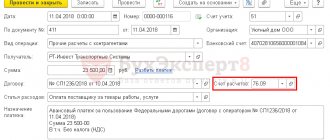
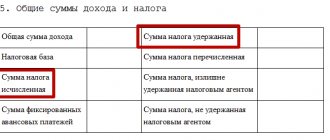
An integral responsibility of an accountant is the correct and timely calculation, registration and transfer of all tax payments.
Taxes and fees are mandatory payments levied on legal entities and individuals intended to finance state municipal expenditures. Tax payments are free of charge. Fees are payment for the performance of legal actions by the relevant authorities: issuing licenses, granting any rights.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes federal, regional and local taxes and fees. Code also provides for the following taxation systems :
- general;
- simplified;
- patent;
- single agricultural tax;
- a single tax on imputed income established for certain types of activities.
Frequency of tax payment and reporting
Compliance with the deadlines for submitting reports and remitting taxes will allow you to avoid penalties and additional inspections of the activities of enterprises by tax authorities. As a rule, even in the absence of a taxable base and accruals, reporting is mandatory.
| Name of tax (payment) | Rates | Payment deadlines | Timing and type of reporting |
| VAT | 0% - for export; 10% - for food, children's goods, book products, medical products, etc.; 18% - for other goods and services. | Quarterly, no later than the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter | The declaration is submitted electronically quarterly, no later than the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter. |
| Income tax | 9% - income from interest on a number of government securities; 10% - income of non-resident carriers; 20% - basic rate; 30% - profit of foreign companies, profit from hydrocarbon production at sea, etc. | Quarterly, no later than the 28th day of the month following the reporting quarter | The declaration is submitted quarterly, no later than the 28th day of the month following the reporting quarter. |
| Personal income tax | 9% - on dividends until 2015, interest on mortgage-backed bonds issued before 2007; 13% is the base rate for individuals, including dividend income from 2015; 15% — dividends of non-resident individuals; 30% - other income of non-resident individuals; 35% - from winnings, prizes, etc. | At the time of payment of income | Register f. 2-personal income tax is provided by enterprises annually until April 1 of the reporting year |
| Excise taxes | Solid, ad valorem and combined, differentiated by type of goods | Monthly until the 25th day of the month following the reporting month, for straight-run gasoline and ethyl denatured alcohol - until the 25th day of the 3rd month following the reporting month | The declaration is submitted every month by the 25th day of the month following the reporting month, for straight-run gasoline and ethyl alcohol - by the 25th day of the 3rd month following the reporting month |
| Contributions to compulsory social insurance | 2.0-2.9% depending on the category of payers | Monthly, until the 15th day of the month following payment | Reporting according to f. 4-FSS quarterly until the 20th day of the month following the reporting quarter |
| Contributions to compulsory pension insurance | 22% | Monthly, before the 15th day of the month following the month of payment | Quarterly report on f. RSV-1 until the 15th day of the 2nd month following the reporting quarter |
| Property tax | Calculated based on cadastral value | Quarterly until the 30th day of the month following the reporting quarter, annually - until March 30 of the reporting year | The declaration is submitted quarterly by the 30th day of the month following the reporting quarter, for a year - by March 30 of the reporting year |
| simplified tax system | 6% of income or 15% of income minus expenses | Quarterly - advance payments until the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter | Declaration annually by March 31 of the year following the reporting year - for LLCs, for individual entrepreneurs - by April 30 |
| Unified agricultural tax | 6% of income minus expenses incurred | For the 1st half of the year - until the 25th day of the month following the end of the half-year, for the year - until March 31 of the following year | Declaration annually before March 31 of the year following the reporting year |
| UTII | 15% of the amount of imputed income | Quarterly – advance payments due by the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter | Declaration quarterly by the 20th day of the month following the reporting quarter |
| Patent system | 6% of potential income | When the patent is valid for up to 6 months. – in full amount until the expiration of the patent, more than 6 months. – 1/3 of the tax amount in the first 90 days, the remaining 2/3 until the expiration of the patent | Providing a declaration is not provided |
Salary
The minimum wage has been increased. The minimum wage in 2021 has been increased to 12,130 rubles. An employee's full-time salary cannot be less than the minimum wage. The accounting department needs to check the staffing table and increase the wages of those workers who receive less to the minimum wage. From January 1, 2021, Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 08/09/2019 No. 561n New payment codes for wages have been established. In payment orders for the payment of wages, field 20 must be indicated new codes. For wages, benefits and compensation for harm, different codes are established, which must be approved by the Central Bank of Russia. New coding is needed for bailiffs so that they can clearly establish which payments can be withheld under writs of execution. From June 1, 2021, Subparagraph “d” of paragraph 3 of Article 1 of the Federal Law of February 21, 2019 No. 12-FZTax accounts
The following accounts are used to reflect transactions related to the calculation, accounting and payment of taxes:
- Account 19 reflects the amount of VAT on material assets acquired by the organization: fixed assets, intangible assets, inventories.
- Account 68 takes into account all payments for personal income tax, taxes on real estate, vehicles, income from transactions with securities, mining, environmental fees, fees for the use of natural resources, etc.
- Account 69 is used to record contributions to social insurance and security, health insurance, and contributions to the Pension Fund.
- Account 90 is intended for accounting for tax payments subject to return (reimbursement) after the sale of products, primarily VAT and excise taxes.
- Account 91 is used to reflect VAT and excise taxes related to sold tangible and intangible assets that were on the balance sheet of the enterprise.
- Account 99 is used to account for the company’s losses, which include paid income tax, penalties, fines for violations of the procedure and deadlines for accrual and payment.
Read more - Article on the payment of various taxes to the budget.
Insurance premiums
Limit value of the base for calculating insurance premiums Since 2021, the maximum value of the base for calculating insurance premiums has been increased:- the maximum base for pension contributions will be 1,292,000 rubles,
- The maximum base for contributions in case of illness and maternity will be 912,000 rubles.
Basic accounting entries for taxes
- Overpayment of taxes is reflected in accounting and returned from the budget.
- Tax penalties - payment of a fine for late taxes.
- Property tax is a regional tax that is imposed on certain types of fixed assets.
- Transport tax is a tax imposed on a company’s transport property.
- Land tax - paid by all land owners, including legal entities.
- Postings on UTII - how to take this type of tax into account in accounting
- Insurance premiums - how to pay taxes to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund and Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
- Personal income tax - how organizations should pay income tax for employees. Reflection of personal income tax in transactions.
- Unified social tax - 34% for employees of the organization.
Income tax
- Income tax - classifier and main entries for accrual and payment.
- Reflection of tax losses - if an enterprise has incurred losses, they can be taken into account to reduce the income tax base for future periods.
- IT and SHE - what they are and how to reflect their accrual and write-off in transactions.
VAT
- Basic transactions for VAT - a list of the main typical operations for calculating and paying tax.
- Postings for writing off VAT are transactions to pay off tax debt or include tax amounts (paid or payable) as costs or losses.
- Posting VAT on sales - accounting for tax on the sale of goods and services.
- Reflection of VAT for deduction in transactions - we reduce the VAT base.
- VAT refund - how to receive VAT compensation from the budget.
- VAT recovery - how to recover previously written off VAT.
- VAT calculation is the method of calculation and tax rate.
- Payment of VAT - how to pay and reflect it in accounting.
- VAT on advances - how to take into account advance amounts.
- Export VAT - features of working with exports.
simplified tax system
- Taxes of the simplified tax system - what taxes are paid under the simplified taxation system.
- Minimum tax is a method of paying taxes for the simplified tax system if the enterprise has a minimum turnover.
Exchange of information with the Federal Tax Service
The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate will provide the reporting of the company’s partners upon its request. The company can request the financial statements of its counterparties from the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate and receive it for a fee. The electronic database, starting with reporting for 2021, will be maintained by the Federal Tax Service, and not by Rosstat, as it was before. Access to this information resource will be paid and amount to 200,000 rubles. for the annual maintenance of one workplace. From January 1, 2021, Federal Law No. 444-FZ of November 28, 2018; Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 25, 2019 No. 811 Notification of separate divisions with a current account. It is necessary to report the granting or deprivation of a separate division of the authority to pay salaries only in if he has a bank account. From January 1, 2021, Federal Law No. 325-FZIFNS of September 29, 2019 will send SMS Tax inspectorates will send SMS messages to debtors on taxes, fines and penalties. To receive SMS, you must give your consent. From April 1, 2021, Federal Law No. 325-FZ of September 29, 2019, information on decisions on interim measures will be made public. Decisions on the adoption or cancellation of interim measures in the form of a ban on the alienation of property will be published on the website of the tax service. .From April 1, 2021, Federal Law of September 29, 2019 No. 325-FZCategories for articles on taxes
- Postings for accrual and payment to extra-budgetary funds
- We accept tax reduction according to the simplified tax system
- Accounting entries for state duties
- UST: postings, who pays and how much
- Basic VAT transactions
- Accounting entries for VAT calculation
- Tariffs and postings for insurance premiums
- Personal income tax: how and who pays, postings
- Paying taxes - how to reflect them in accounting entries
- Postings for land tax in accounting
- SHE and IT: what is it about?
- Transport tax and its components
- Features of income tax: who pays for what, postings
- Enterprise property tax: calculation and postings
- VAT postings when working with exports
- Tax penalties - postings, examples
- Tax loss postings
- Reflection of the minimum tax in transactions
- VAT deductible: transactions, conditions
- Accounting entries for overpayment of tax and its refund
- Postings for VAT on sales
- Postings for writing off VAT
- What is UTII: calculation, postings, legislation, examples
- VAT on advances: postings, examples, law
- Accounting entries for VAT payment
- Taxes according to the simplified tax system: features, postings, regulations, reporting
- Postings for VAT refund from the budget
- Accounting entries for VAT restoration
Child benefits, sick leave
Monthly benefit for up to one and a half years The maximum benefit amount in 2021 will be 27,984.66 rubles. The government has not yet established the minimum benefit amounts for 2021. Maximum and minimum amounts of child benefits in 2021 From January 1, 2021, the indexation resolution will be approved later. Monthly payments for the first and second child under three years of age. Payment for the first and second child is assigned to those families whose average per capita income does not exceed the limit established by law. The payment will be made by social security authorities. From 2020, the income limit for granting benefits will increase to 2 subsistence minimums, and it will be possible to receive it until children reach their third birthday. To calculate the amount of payment, you need to take into account the regional children's minimum for the 2nd quarter of 2021. From January 1, 2021, Federal Law dated August 2, 2019 No. 305-FZ Minimum and maximum amounts of sick leave payments If the calculation of average earnings turns out to be less than the minimum wage calculation, the employee must be paid sick leave based on from the minimum wage. From January 1, 2021, the minimum wage is 12,130 rubles. In 2021, the value of the average daily earnings for calculating the maximum sick leave payment will be no more than: (865,000 + 815,000) / 730 = 2,301.37 rubles. Maximum and minimum sick leave in 2021 From January 1, 2021How to properly formalize labor relations with remote employees
Remote work is not new for Russian companies, but previously it was rarely documented in a special employment contract. However, labor legislation provides options for registering two types of remote work, and also describes the grounds for the transition and other conditions.
Temporary remote work
Temporary remote work is a transition to work outside a stationary workplace, under the control of the employer, for a limited period. Registration of this type of work can occur by agreement of the parties, and in emergency situations - in a simplified form.
Reasons for switching to temporary remote work:
- agreement between employee and employer;
- by necessity;
- industrial accident;
- industrial accident;
- natural or man-made disasters (fire, flood, earthquake);
- epidemic, epizootic and any exceptional cases that threaten the life or normal living conditions of the entire population or part of it.
Mode entry procedure
- Agree on the employee’s schedule: the number and frequency of providing him with working days and working hours in temporary remote work mode. The schedule may differ from what was specified in the main employment contract.
- Establish ways to exchange information about tasks and their implementation between workers. This point is fixed in the contract or additional agreement.
- Regulate the ability to use the organization’s resources at the place where work is performed. For example, decide whether employees can take laptops from the office or ask you to pay for their Internet.
How to pay an employee
- Payments are made in full.
- If an employee, on your initiative, performs tasks outside of working hours, this must be paid as overtime.
Combined remote work
In a contract for combined remote work, you can separately specify the conditions for working in the office and remotely. Such work is also paid in full, and additional payment is due for work outside of school hours.
Combined remote work has two features:
- the mode of combined remote work is established either in an employment contract or an additional agreement to it, or in a simplified manner on the basis of a local regulatory act (Article 312.6 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as amended) in the event of an emergency;
- with combined remote work, the features of the remote work mode do not apply to periods of work in the office.
We'll take care of personnel issues so that you don't have to deal with legal requirements.
Calculate the cost of service in Finguru
Excise taxes
Excise tax deduction has become more accessible. Organizations that generate electricity and heat from middle distillates will be able to obtain certificates for transactions with middle distillates and claim a deduction when receiving middle distillates as fuel. The composition of technological processes for processing middle distillates has been expanded; now such processes include:- delayed coking;
- hydroconversion of heavy residues;
- obtaining carbon black by thermal or thermo-oxidative decomposition of middle distillates;
- production of bitumen by oxidation of tar.
Organizations that perform these operations when processing middle distillates will be able to apply an excise tax deduction.
From April 1, 2021 Art. 1, clause 5, art. 2 of the Federal Law of July 30, 2019 No. 255-FZ Excise tax deduction with a coefficient Organizations that generate electricity and heat from middle distillates will be able to take advantage of a deduction with a coefficient. The deduction can be applied when receiving middle distillates as fuel for combustion and energy generation. List of documents that accounting must prepare to confirm the deduction:- register of invoices (transfer and acceptance certificates) for the supply of middle distillates as fuel;
- registers for accounting for used fuel and energy supply;
- documents confirming fuel production by type of installation.
When selling middle distillates for bunkering sea vessels, the amount of deduction will need to be determined taking into account the new Vdfo coefficient. The procedure for calculating this coefficient has been established
From April 1, 2021 Sub. “b”, “c” clause 11, sub. “a” clause 12 art. 1, clause 5, art. 2 of the Federal Law of July 30, 2019 No. 255-FZA, you will no longer have to pay excise tax on dark marine fuel. Dark marine fuel has been excluded from the list of excisable goods. Any transactions with it will not be subject to excise tax. From April 1, 2021 Sub. "b" clause 4 of Art. 1, clause 5, art. 2 of the Federal Law of July 30, 2019 No. 255-FZStatistical reporting
New forms for statistical reporting have been introducedMore than 100 statistical forms have changedFrom reporting for 2021Orders of Rosstatelectronic edition of 100 ACCOUNTING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS BY EXPERTS
A useful publication with questions from your colleagues and detailed answers from our experts. Don't make other people's mistakes in your work! 7 issues of the publication are available to berator subscribers for free.
Get the edition