Until recently, in the field of tax optimization, individual entrepreneurs on UTII were most often encountered, but in 2021, UTII began to be abolished, not in words as before, and some OKVED codes can no longer be used. UTII will no longer be used; in 2021, UTII will completely disappear. Insurance premiums for entrepreneurs of this special. regime must be paid in any case, regardless of their level of income and expenses, as long as they are registered with the Federal Tax Service. Individual entrepreneurs on UTII when transferring insurance premiums can reduce the tax base. How insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs on UTII can be reduced - we will consider further.
In what ways can you reduce
It does not matter whether the dues for the current period have been paid. For example, the company paid in October for September. Mandatory contributions for June are transferred in the same month. Then the tax for the fourth quarter is reduced, quite legally.
The basis is only calculated mandatory contributions. It doesn’t matter what the overpayments were, or whether they exist at all.
You can reduce the amount for employees with a maximum of 50%. Here other indicators also do not play a role.
Restrictions
346.32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes some features associated with this process. In some situations, the reduction of UTII for insurance premiums occurs by no more than half.
Let's look at an example.
- The company is registered with the tax authority at its current location.
- Payment of the appropriate insurance premiums is mandatory.
- In the neighboring urban district, activities are carried out that are subject to UTII. With the corresponding role, the company is registered with the regulatory authorities there.
- When insurance premiums are calculated, the company has the right to take into account the amounts paid where the company is actually located at the moment.
Attention! If you have no employees, your UTII will be reduced by the entire amount of your insurance premiums. The rule applies to those quarters in which contributions were paid. In this case, the 50% limit does not apply.
Reducing UTII for individual entrepreneurs without employees
An entrepreneur without employees can completely reduce the tax by the amount of contributions paid; the procedure is completely legal, even if in the end the UTII is reduced to zero.
The UTII of an entrepreneur without hired employees can be reduced by contributions for himself, which he is obliged to pay for pension and health insurance.
In order to evenly reduce their expenses, a self-employed individual entrepreneur needs to pay insurance premiums in fractions, quarterly. That is, divide them into four approximately equal parts and pay them quarterly.
As a result, a businessman without hired employees must pay 7,338.50 rubles for pension insurance and 1,721 rubles for medical insurance once a quarter.
Dividing insurance premiums into quarters is necessary when the tax amount can be brought closer to zero.
Example. With annual insurance premiums of 36,238 rubles. a self-employed individual entrepreneur must pay 10,000 rubles. tax once a quarter. If he forgets to divide the insurance premiums and pays them at once, for example, in the 4th quarter, then, in this case, in three quarters he will spend 10,000 rubles on taxes, and in the fourth, after making contributions for 36 238 rubles, he will have the right to deduct them from the UTII tax for this quarter, reducing the tax to zero. Thus, an entrepreneur will pay for 2021: (10,000 * 3) + 36,238 = 66,238 rubles. But if he decided to pay insurance premiums in equal installments, 9,059.50 rubles each. per quarter and each time reduce the UTII on them to 940.50 rubles, then in a year he would spend (940.50 * 4) + (9,059.50 * 4) = 40,000 rubles.
For clarity, let's present this example in the form of a table:
| Time interval | Option 1 | Option 2 | ||
| Period | UTII (RUB) | Insurance premiums (RUB) | UTII (RUB) | Insurance premiums (RUB) |
| 1st quarter | 10 000 | 0 | 940,50 | 9 059,50 |
| 2nd quarter | 10 000 | 0 | 940,50 | 9 059,50 |
| 3rd quarter | 10 000 | 0 | 940,50 | 9 059,50 |
| 4th quarter | 0 | 36 238 | 940,50 | 9 059,50 |
| Total for 2021: | 66 238 rub. | 40,000 rub. | ||
What is included in insurance premiums?
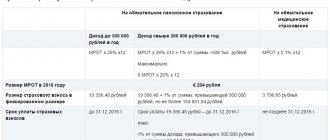
For 2021, there are two categories, one of which may include insurance premiums. There is a fixed amount that remains the same for all entrepreneurs. Even the field of activity does not affect the indicator.
- Medical insurance amounting to almost 7,000 rubles.
- Mandatory pension insurance, 29,500 rubles.
36,200 rubles – the total amount of contributions for enterprises whose revenue does not exceed 300 thousand rubles. 1% of the difference is added to the contribution amount if the company’s profit increases. But such calculation methods apply only to pension insurance. An entrepreneur with individual entrepreneur status pays for himself. Contributions for employees are also separately controlled by law.
Typically, the estimated income of an individual entrepreneur is lower than the actual profit. Under the PSN system, approximately the same rules apply. By ignoring business expenses, down payments are often the largest.
Reference! The general indicator from all taxation systems is applied when the entrepreneur himself chooses a combined approach to his business.
Where and how are fixed payments paid in 2019
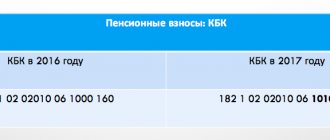
An important change in fixed payments for individual entrepreneurs in 2021 was the fact that they are now paid not directly to the Pension Fund and Compulsory Medical Insurance, but to your tax office.
At the same time, the KBK was changed, so it is no longer possible to pay using the old details. The control function over contributions was thus transferred to the Federal Tax Service. If earlier it was clear that payments were paid to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund, then where should they be paid now if the individual entrepreneur does not operate at the place of registration and what to do if there are employees?
If the activity is carried out at the place of registration, then no questions will arise, but if the individual entrepreneur is registered in one tax office, but reports, for example, on UTII to another tax office at the place of business, where do you need to pay contributions?
So, where to pay fixed payments:
- The individual entrepreneur operates in the place where he was registered as an entrepreneur - he pays fixed payments for himself to his tax office.
- If an individual entrepreneur is registered in one tax office, but does not operate in his own area and submits reports to another tax office, in this case, the individual entrepreneur pays fixed payments for himself to the tax office where he was registered as an individual entrepreneur.
- If an individual entrepreneur has employees and also operates outside of his area, then payments for himself are paid at the place of registration. In this case, payments for employees are paid to the tax office at the place of registration of the entrepreneur, regardless of the applied tax regime. This clarification is indicated in the letter of the Federal Tax Service No. BS-4-11/3748 dated 03/01/17.
Attention! In more detail, how fixed payments for individual entrepreneurs are calculated, their size, as well as new BCCs are described in a separate article.
Rates
Article 425 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation specifies the basic tariffs that apply to all individual entrepreneurs. This also applies to those who apply UTII. They are:
- 22% - in relation to payments that do not exceed the amount for calculating contributions to compulsory pension insurance.
- 10% - from payments that exceed the specified amount.
The occupational risk class for a particular activity determines what payments will be made for contributions for protection against accidents at work. For individual entrepreneurs, there is an additional payment that is sent to the Pension Fund. 8-fold fixed payment for the year - this amount should not exceed all contributions paid by a particular entrepreneur.
1% on income exceeding 300,000 rubles
As before, in 2021, individual entrepreneurs whose annual income exceeds 300,000 rubles will have to pay (in addition to fixed payments) to the Federal Tax Service 1% of the amount of income exceeding these 300,000 rubles.
This payment is calculated using the following formula:
(Income of individual entrepreneurs for a calendar year excluding expenses – 300,000 rubles) x 1%
Payers of OSN, simplified tax system, UTII and PSN (patent) must take as income:
- UTII – imputed income for all quarters of the calendar year;
- PSN is the potential income from which the cost of the patent was calculated.
- OSN – income reduced by expenses.
- STS – income.
If different taxation systems are combined, income from each of them must be summed up.
note
, 1% from income over 300 thousand rubles.
in 2021 there cannot be more than 8 times the amount of the contribution established by clause 1 of Art. 243 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (32,448 x 8 = 259,584 rubles
).
The deadline for paying the 1% contribution on income is July 1 of the next year (for 2021 - until July 1, 2021, for 2021 - until July 1, 2021), but you can start paying it this year if income has already exceeded 300 000 rub.
Favorable fee
If the individual entrepreneur does not have employees, then you can apply the simplest tips:
- Insurance premiums “for yourself” are transferred at the end of each quarter.
- Sometimes, by the end of the reporting period, the figures exceed 300 thousand rubles.
Then you need to first make a calculation of exactly how much UTII remains for payment. Then the money is transferred to the Pension Fund so that the UTII becomes zero. If at the end of the year the payment for the Pension Fund remains the same, then you can choose other periods of time to reduce it.
For an individual entrepreneur, you can use a similar procedure.
No one will return the UTII paid, which is why it is so important to minimize other tax payments. There is no need to transfer excess funds to the Pension Fund in advance; there is simply no point in doing so. It is better to use free finance to generate additional profit or solve other production problems.
Important! Online accounting typically uses the same principles to solve problems.
What other features might there be?
A single tax on imputed income is paid by those companies and entrepreneurs engaged in certain types of activities. This applies to specific services with goods and to serving the population equally. Each region independently determines which areas of work fall under UTII in a given case. An important factor is the economic characteristics of the area.
The main feature is that payment is not made from actual income, but only from estimated profit. At the same time, the payment itself remains fixed; it can only be affected by the current location.
The amount of revenue does not matter - when switching to UTII, everyone is required to pay funds. Payment of the fee remains a mandatory requirement even for periods when there were no contracts or transactions at all. Exceptions are made only if the activity was suspended for valid reasons, which requires additional evidence. The presence of documentary evidence becomes an important condition.
To resolve the issue, it is recommended to consider the following factors:
- The presence or absence of employees at the individual entrepreneur. If modes are combined, it is important to assess which subordinates are engaged in which type of activity. This is important for taking into account the fees that apply to individual entrepreneurs.
- The mode used, whether several options are combined at once.
- The date on which fixed contributions are paid.
- Actual amounts transferred for fixed contributions.
Additional Information
Only what was actually transferred is paid into the calculation. If the fee is not paid, it is forgotten until this situation is corrected.
It will not be possible to take into account anything that will be more than the established annual amount. This even applies to situations where the individual entrepreneur himself decides to transfer more. Calculated and paid contributions are concepts that are similar to each other, but it is important not to get confused between them. The calculated amounts are otherwise called accounting amounts. The second concept concerns the amounts that were actually transferred.
The procedure for calculating contributions for individual entrepreneurs is established in No. 212-FZ of 2009. Quarterly or monthly payments are not provided in this case. You only have to pay for the year as a whole. However, you cannot simply pay out more money than originally stated.
Next, the dates of transfer must be controlled. There are only general dates for fixed transfers, which serve as a limitation.
Under the simplified tax system, entrepreneurs can transfer arbitrary amounts throughout the year. Or choose a specific moment when the entire amount is transferred. Individual entrepreneurs themselves choose the order that would be most convenient for them. The reduction is also made for the period when the money is definitely paid. If any part remains unaccounted for, it cannot be transferred to the next year.
The procedure for accounting for fixed contributions does not depend on whether the entrepreneur has employees or not. All you need is the date of actual transfer of the full amount.
Reductions are allowed not only for the contributions themselves, but also for other indicators:
- Paid sick leave.
- Voluntary personal insurance contracts.
The main thing is that the reduction does not exceed 50%.
If employees are hired during the year, the entrepreneur is deprived of the right to completely reduce the tax. This requirement always applies.
Contributions of individual entrepreneurs for themselves when combining UTII and simplified tax system
Taxes can be reduced by the amount of payments transferred to the Pension Fund and compulsory medical insurance, both for employees and for the individual entrepreneur himself. When combining tax regimes, it is necessary to correctly calculate how to distribute the shares of contributions. In accordance with Art. 346.18 clause 8 of the Tax Code, taxpayers must keep separate records if they combine several tax regimes.
Things to consider:
- Whether there are employees or not. If there are none, then taxes can be reduced by the amount of the listed fixed payments for the entrepreneur in full, but if there are employees, then only by 50%.
- It is necessary to determine the shares by which taxes will be reduced - fixed contributions of individual entrepreneurs, payments are divided in accordance with the income received for each type of activity.