Any business is built on commodity-money relations, be it a physically tangible product or some kind of service. Accounting is an integral part of the life of any organization. If a company is engaged in the sale of any product, then at the moment when its transfer occurs, ownership also passes to the buyer. At this moment, it is necessary to make a posting to the debit of account 62 “Settlements with customers”. How to do this and for what purpose - let's look at it in more detail.
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” reflects information on settlements with buyers and customers.
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is debited in correspondence with accounts: 90 “Sales”, 91 “Other income and expenses” for the amounts for which settlement documents were presented.
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is credited in correspondence with the accounts for recording cash, settlements for the amount of payments received, including the amount of advances received, etc. Amounts of receivables for which the statute of limitations has expired are written off for each obligation based on inventory data, written justification and an order (instruction) from the head of the organization on the financial results of the organization on the credit of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” and the debit of subaccount 91-02 "Other expenses". Amounts of debts that are unrealistic for collection are credited to the reserve for doubtful debts in account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” and in the debit of account 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts”. If during the period preceding the reporting period, the amounts of these debts were not reserved in the prescribed manner, they are included in the financial results of the organization as a credit to account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” and a debit to subaccount 91-02 “Other expenses”.
The following subaccounts can be opened to account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”:
62-01 “Settlements with buyers and customers”;
62-02 “Calculations for advances received”; 62-
03 “Settlements on bills received”; 62-
04 “Settlements with subsidiaries”; 62-
05 “Settlements with dependent companies”.
Subaccount 62-01 “Settlements with buyers and customers” reflects revenue from the performance of work, provision of services by type of activity in correspondence with the credit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount 01 “Revenue”. The debit of subaccount 62-01 “Settlements with buyers and customers” also reflects revenue from the sale of fixed assets, materials and other assets in correspondence with the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount 01 “Other income”.
The debit of subaccount 62-01 “Settlements with buyers and customers” reflects revenue from: -
performance of work, provision of services to the population and third-party organizations in the field of housing and communal services in correspondence with the credit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount 01 “Revenue”; —
sales of products, performance of work, provision of services by service industries and farms in correspondence with the credit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount 01 “Revenue”; —
sales of goods (materials purchased for resale) by logistics departments in correspondence with the credit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount 01 “Revenue”.
The accrual of fines, penalties, penalties for violation by buyers of the terms of contracts is reflected in the debit of subaccount 62-01 “Settlements with buyers and customers” in correspondence with the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses” subaccount 01 “Other income”.
Receipts of funds from buyers and customers to pay off their debts are reflected in the credit of subaccount 62-01 “Settlements with buyers and customers” in correspondence with cash accounts. In addition, the credit of subaccount 62-01 “Settlements with buyers and customers” reflects the offset of the advance payment for goods, works, and services sold.
Subaccount 62-02 “Settlements on advances received” takes into account calculations on advances received for the supply of material assets or for the performance of work (services). The same sub-account records payments for materials, structures and parts received from customers or paid for by customers.
The amounts of advances received are reflected in the credit of subaccount 62-02 “Calculations for advances received” in correspondence with cash accounts.
At the same time, the debit of account 62-02 “Calculations for advances received” and the credit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” (subaccount 04 “Calculations for value added tax”) reflects the amount of VAT calculated at the established rate on the basis of documents on advances received .
When shipping products, performing work (services) for the amount of previously taken into account tax, a reverse entry is made to the debit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” (subaccount 04 “Calculations for value added tax”) and the credit of subaccount 62-02 “Calculations for advances” received”, and the amount of the advance received is taken from the credit of subaccount 62-02 “Calculations for advances received” to the debit of the accounts (subaccounts):
62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”;
73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations”;
76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” (subaccount 08 “Settlements with individuals”);
76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” (subaccount 80 “Settlements with other debtors and creditors”); depending on which account (sub-account) accounts for settlements with counterparties from whom advances were received.
Subaccount 62-03 “Settlements on bills received” takes into account the debt for settlements with buyers and customers, secured by bills received. The debt is reflected in the amount specified in the bill. Receipt from the client of his own bill of exchange in payment for goods (work, services) is reflected in the debit of subaccount 62-03 “Settlements on bills received” in correspondence with the credit of other subaccounts of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” or account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors." The difference between the face value of the bill and the amount of debt for goods, works and services according to the terms of the agreement is reflected in the debit of subaccount 62-03 “Settlements on bills received” in correspondence with account 90 “Sales”, subaccount 01 “Revenue”.
Receipt of funds in payment of a bill of exchange is reflected in the credit of subaccount 62-03 “Settlements on bills received” and the debit of cash accounting accounts. If interest is provided on a bill received, then as this debt is repaid, an entry is made in the debit of cash accounting accounts and the credit of subaccount 62-03 “Settlements with buyers and customers on bills received” for the amount of debt repayment and the debit of subaccount 91-01 “Other income » by the amount of the percentage.
In case of non-payment of the bill by the drawer on time, the debt listed in sub-account 62-03 “Settlements with buyers and customers on bills received” is written off from the credit of this sub-account to the debit of sub-account 76-09 “Settlements on claims”.
To control and streamline the processing of data on business transactions, consolidated accounting documents are compiled on the basis of primary accounting documents. To record the movement of bills of exchange, the organization draws up a Book (Journal) for accounting for bills received and issued, the construction of which should ensure the receipt of the necessary data on the amounts of bills received and issued and separately interest on them for: -
bills issued, the payment term of which has not yet arrived; —
bills received, the payment term of which has not yet arrived; —
bills issued with overdue payment terms; —
bills received that are overdue for payment.
Subaccount 62-04 “Settlements with subsidiaries” and subaccount 62-05 “Settlements with dependent companies” the organization reflects information on settlements with buyers and customers who are subsidiaries or dependent companies in relation to the organization.
Analytical accounting for account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is maintained for each invoice presented to buyers (customers). At the same time, the construction of analytical accounting should provide the ability to obtain the necessary data on: buyers and customers on payment documents for which the payment period has not yet arrived; buyers and customers for documents not paid on time; advances received; bills for which the due date for receipt of funds has not yet arrived; bills discounted (discounted) in banks; bills for which funds were not received on time.
Shipment of goods posting
The process of selling products manufactured by the enterprise completes the turnover of the enterprise's funds, and makes it possible to reimburse costs incurred, fulfill obligations to the budget for taxes, to the bank for loans provided, to suppliers and contractors, and to employees regarding wages.
In the process of implementation, the final financial result of the production and economic activity of the enterprise is formed - profit or loss.
Profit (loss) from the sale of products (works, services) and goods is defined as the difference between the proceeds from sales in current prices without VAT, excise taxes and the costs of its production and sale. Revenue in accounting is determined by the accrual method, and in tax accounting - by the accrual method or the receipts / cash method / depending on the adopted accounting policy.
In accordance with international accounting standards, products are considered sold if they are shipped to the buyer and he is presented with payment documents - invoices for payment.
This approach is called the accrual method or the method of determining shipment revenue.
.
This method means that revenue and the obligation to pay VAT to the budget arises for the enterprise from the moment of shipment and presentation of settlement documents to the buyer, regardless of the fact of payment.
Cash method
means that this obligation arises from the moment the money is actually credited to the current account or cash register.
With the introduction of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, from 01.01.02, only small enterprises whose sales revenue for the last 4 quarters (excluding VAT) do not exceed an average of 1 million can use the cash method. rubles for each quarter.
Analytical accounting
sales are maintained for each invoice number, product type and buyer name in the product sales accounting sheet.
Synthetic accounting
income and expenses associated with the sale of products in the normal activities of the organization, as well as the determination of the financial result from sales is carried out on active-passive account 90 “Sales”.
Postings:
D-t 62 K-t 90/1 an invoice was issued to the buyer for sold (shipped) products;
D-t 90/2 K-t 43 the actual presented cost of products sold is written off;
D-t 90/2 K-t 20.23 the actual production cost of sold works, services of the main or auxiliary production is written off;
Dt 90/3 Kt 68 VAT is charged, included in revenue and payable to the budget;
D-t 90/4 K-t 68 excise tax is charged, included in the price of products and payable to the budget;
Dt 90/5 Kt 68 accrued export duties payable to the budget;
D-t 90/6 K-t 26 the amount of general business expenses is written off (if, in accordance with the accounting policy, it is written off to the “Sales” account);
D-t 90/7 K-t 44 sales expenses are written off (commercial expenses);
D-t 50.51 K-t 90/1 revenue received from the sale of products (works, services);
D-t 90/9 K-t 99 profit from ordinary activities is written off;
Dt 99 Dt 90/9 loss on ordinary activities is written off.
The accounting register is order journal No. 11 and order journal No. 15.
Task
In accordance with the supply agreement, on September 28, 2005, the buyer transferred an advance in the amount of 708,000 rubles, including VAT 108,000.
On October 2, 2005, the products were shipped; its standard cost is 500,000, deviations (+) 62,000.
An invoice was issued for 1,180,000, including VAT - 180,000.
Accounting for sales of finished products
Selling expenses amounted to 50,000. The rest of the debt was paid off on November 2.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FLkYKZ6Ubsg
Determine the financial result from the sale of products for October and make entries if the input VAT on purchased values, offset in October, is 56,000. In accordance with the accounting policy of the enterprise, the moment for determining revenue is “by shipment”
Solution:
September 28
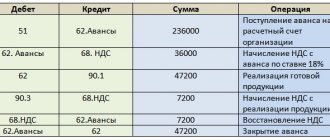
D-t 51 K-t 62/1- 708000 advance payment from buyers was credited to the current account;
D-t 62/1 K-t 68- 108000 VAT is reflected in the amount of the advance received;
D-t 68 K-t 51- 108000 VAT was paid on the advance received;
2 October
D-t 62 K-t 90/1 – 1180000 an invoice for the shipped products was presented;
D-t 90/3 K-t 68- 180000 VAT is charged on the presented invoice;
D-t 68 K-t 62/1 - 108000 the VAT paid on the advance was offset;
D-t 68 K-t 19- 56000 input VAT was credited;
D-t 90/2 K-t 43- 500000 sold products were written off from the balance sheet at standard cost;
D-t 62/1 K-t 62- 708000 the advance payment was offset.
October 31
D-t 90/2 K-t 44-50000 commercial expenses for sales were written off;
D-t 90/2 K-t 43- 62000 positive deviations for sold (shipped) products were written off;
Dt 90/9 Kt 99- 388000 accrued profit from sales of products;
November 2
D-t 51 K-t 62 472000 the remaining amount for the shipped products was credited to the current account;
D-t 68 K-t 51- 16000 the rest of the VAT has been paid.
Date of publication: 2014-11-28; Read: 1746 | Page copyright infringement
Payment to the supplier
Example
The organization Trading House LLC purchases goods from the supplier TF-Mega CJSC for a total amount of 124,490.00 rubles. (including VAT 18% - RUB 18,990.00). Payment is made on an advance payment basis.
The following business operations are performed:
· Payment to the supplier (drawing up a payment order, registering a bank statement);
· Accounting for receipt of goods (registration of delivery note and supplier invoice).
Payment to the supplier
To perform operations 1.1 “Drafting a payment order to pay a supplier” and 1.2 “Registering a payment to a supplier” (see example table), you must first create a document “Payment order”, then, based on this document, enter the document “Write-off from a current account”. As a result of posting the document “Write-off from the current account”, the corresponding transactions will be generated.
If payment orders are created in the “Client-Bank” program, then it is not necessary to create them in “1C: Accounting 8”. In this case, only the document “Write-off from the current account” is entered, which generates the necessary transactions. The document “Write-off from a current account” can be created manually or based on downloading from other external programs (for example, “Client-Bank”).
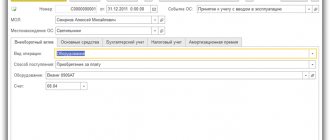
Creating a “Payment Order” document:
1. Call from the menu: Bank - Payment order.
2. “Add” button.
Filling out the document “Payment order” (Fig. 1):
In the Bank account field, you can select the account from which money is transferred.
In the Recipient field, select a supplier from the “Accounts” directory. The Contract field is filled in by default.
In the Recipient's account field, select the supplier's bank account to which the money is transferred.
In the field Item movement money. funds, you must select the appropriate item.
In the Payment amount field, enter the payment amount.
In the VAT field, select the rate of 18%.
In the Payment purpose field, enter the payment purpose text.
Select the Paid checkbox and click the link Enter document debited from current account. In this case, the document “Write-off from the current account” appears, in which all fields are filled in by default from the base document (Fig. 2).
Uncheck the Verified by bank statement checkbox, because The funds have not yet been debited from the current account. When saving the “Write-off from the current account” document, no transactions are generated.
This checkbox is checked at the time of registration of the bank statement (see below).
To call a printed payment order form, use the Payment order button.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ng4Ifp0Mgog
Click “OK” to save and close the document.
Rice. 1
After receiving a bank statement, which records the debiting of funds from the current account, it is necessary to confirm the previously created document “Writing off from the current account” to generate transactions.
Confirmation of the document “Write-off from the current account” (Fig. 2):
Call from the menu: Bank - Bank statements.
Open the document Write-off from current account (not posted).
Select the Verified by bank statement checkbox.
Click the “OK” button to save and post the document.
There are several ways to generate a bank statement. Read more about this in the article “Generating a bank statement.”
Rice. 2
The result of the document “Write-off from the current account” (Fig. 3):
To post a document, click the Post button; to view the postings, click the Result of document posting button.
Rice. 3
The entry is made to the debit of account 60.02, because According to the terms of the example, an advance payment is made to the supplier.
In this case, we do not take into account the input VAT on the prepayment made to the supplier, because an invoice for the transferred advance was not received.
Source: https://buh-experts.ru/otgruzka-tovara-provodki/
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
ACCOUNT 62 “PAYMENTS WITH BUYERS AND CUSTOMERS”
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is intended to summarize information on settlements with buyers and customers, as well as related organizations - for sold: finished products, animals, goods; work performed and services provided; received advances and prepayments.
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is debited in correspondence with accounts 90 “Sales”, 91 “Other income and expenses” for the amount of the presented settlement documents.
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is credited in correspondence with the accounts for accounting for cash, settlements for the amounts of payments received (including the amounts of advances received), etc. In this case, the amounts of advances received and prepayments are taken into account separately.
Sub-accounts can be opened to account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”:
62-1 “Settlements under government contracts”;
62-2 “Settlements with procurement and processing organizations of the agro-industrial complex”;
62-3 “Settlements on bills received”;
62-4 “Calculations for advances received”;
62-5 “Intra-group settlements of interrelated organizations”;
62-6 “Settlements with other buyers and customers.”
Subaccount 62-1 “Settlements under government contracts” is intended to summarize information on settlements with government agencies for sold products and livestock.
As sales are recognized for the fulfillment of government orders, the debt of authorized bodies is reflected in the debit of this subaccount in correspondence with account 90 “Sales”. If the shipment of agricultural products was made to repay a previously received commodity loan, then at the same time an entry is made in the debit of accounts 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”, 67 “Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings” and the credit of subaccount 62-1 “Settlements for government contracts "
Subaccount 62-2 is intended to summarize information on payments for sold agricultural products, animals and services provided for their delivery, in the order of fulfillment of contracts. As sales to procurement organizations are recognized, the debt is reflected in the debit of this subaccount in correspondence with account 90 “Sales”, subaccount 1 “Revenue”. If an agricultural organization and a procurement organization are part of an interrelated group, then such settlements should be taken into account in subaccount 62-6 “Intra-group settlements of interrelated organizations.”
Subaccount 62-3 “Settlements on bills received” reflects information about the debt of buyers and customers secured by bills received.
If interest is provided on the received bill of exchange securing the debt of the buyer (customer), then as this debt is repaid, an entry is made to the debit of account 51 “Currency accounts” or 52 “Currency accounts” and the credit of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” (on amount of debt repayment) and 91 “Other income and expenses” (by the amount of interest).
Subaccount 62-4 “Settlements on advances received” is used to reflect information on settlements on advances received in accordance with contracts for the supply of inventories or for the performance of work performed for customers on partial completion.
The amounts of advances received and prepayments are reflected in the credit of account 62-4 “Calculations for advances received” in correspondence with cash accounts.
Funds received in advances and prepayments, offset when the buyer or customer presents settlement documents for delivered products, are reflected in the debit of subaccount 62-4 “Settlements for advances received” and the credit of subaccounts: 62-2 “Settlements with procurement and processing organizations of the agro-industrial complex”, 62 -6 “Settlements with other buyers and customers.”
Subaccount 62-5 “Intra-group settlements of related organizations” reflects information on settlements of related organizations (holdings, financial and industrial groups, etc.) for products sold, animals, work performed and services rendered. The information from this sub-account is used to determine the adjustments necessary for the preparation of summary (consolidated) statements.
Subaccount 62-6 “Settlements with other buyers and customers” reflects information with other buyers and customers (legal entities and individuals) on transactions for the sale of finished products, goods, animals, as well as the performance of work and provision of services not provided for in other subaccounts of the account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers.” In particular, the following calculations may be reflected in the specified subaccount:
- with individual entrepreneurs without forming a legal entity for products sold to them and work performed;
— with agricultural organizations for services rendered (processing of customer-supplied raw materials, work performed by auxiliary production, etc.).
When shipping products, animals, materials; For the execution of work and provision of services, the corresponding primary documents are drawn up: invoices, acceptance certificates for completed work, etc. The main documents for the emergence of settlement relationships between agricultural and procurement organizations are acceptance receipts. The form of receipts depends on the type of products sold: grain, milk, livestock, etc. In accordance with tax legislation, the information reflected in the listed documents is subject to registration in invoices of the established form. When receiving funds in the form of advances or other payments for upcoming deliveries of animal products (performance of work, provision of services), the organization also draws up an invoice.
Analytical accounting for account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is maintained for each report presented to buyers (customers), and for settlements using scheduled payments - for each buyer and customer. At the same time, the construction of analytical accounting should provide the ability to obtain the necessary data on: buyers and customers on payment documents for which the payment period has not yet arrived; buyers and customers on payment documents not paid on time; advances received; bills for which the due date for receipt of funds has not yet arrived; bills discounted (discounted) in banks; bills for which funds were not received on time.
Accounting for settlements with buyers and customers within a group of interrelated organizations, the activities of which are compiled consolidated financial statements, is kept on account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” separately.
The buyer's debt for the wiring is reflected
The contract stipulates that the buyer pays for goods and materials after shipment. Postings: Dt Ct Description Amount Document 62.1 90.1 Reflected revenue from the sale of inventory items RUB 50,000. Consignment note 90.2 41 The cost of inventory and materials is written off 23,000 rubles. Costing 90.
3 68 VAT VAT charged 18% RUB 7,627 Consignment note 51 62 The buyer received payment for the shipped goods of 50,000 rubles. Bank statement 90.9 99 Profit from the supply of inventory items is reflected (50,000 – 23,000 – 7,627) RUB 19,373. Consignment note, cost calculation Example 2.
Accounting for advances received on account 62 Kalina LLC entered into an agreement with the buyer in the amount of 60,000 rubles, VAT 9,153 rubles. The contract provides for prepayment. Postings: Dt Ct Description Amount Document 51 62.2 An advance payment under the supply agreement of 60,000 rubles was received from the buyer LLC.
Bank statement 76 Advances received 68 VAT VAT accrued on the advance 18% RUB 9,153.
/ accounting entries
Postings to account 62 for a regular sale: Debit Credit Name of transaction 62 90/1 Reflected revenue from the sale of goods (work, services) 90/3 68 Accrued VAT on sold goods (work, services) 62 91/1 Reflected revenue from the sale of fixed assets , intangible assets, materials 91/2 68 VAT accrued on sold assets 51 62 Payment received from the buyer Accounting for advances received in settlements with buyers If the buyer pays for the goods in advance and transfers the advance, then to account for settlements with buyers in this case a sub-account is opened on account 62 2 “advance received”, while subaccount 1 will reflect settlements with customers in the general case.
VAT is considered and payable on advances received. Then, when goods, works or services are transferred to the buyer, VAT is charged again, this time on the proceeds.
Accounting info
Debit Credit of business transactions Primary documents 62 91-1 The buyer's debt for the sold fixed asset item is reflected in the amount specified in the contract. Sales and purchase agreement 01 subaccount “Disposal” 01 The initial cost of fixed assets has been written off.
Accounting certificate-calculation, No. OS-4 “Act on write-off of fixed assets (except for vehicles)”, No. OS-4a, No. OS-4b. 02 01 subaccount “Disposal” Accrued depreciation is written off.
Accounting statement-calculation 91-2 01 subaccount “Disposal” The residual value of the fixed asset item has been written off. Accounting statement-calculation 83 84 The amount of the additional valuation of the sold fixed asset was written off.
Accounting certificate-calculation 91-2 Miscellaneous accounts Expenses for the sale of fixed assets are written off. Agreements for the provision of services, Certificate of acceptance and delivery of work performed, Accounting certificate and calculation.
Account 62 “settlements with buyers and customers” postings and examples
Postings: Debit Account Credit Account Posting amount, rub. Description of the posting Document-base 55.04 62.02 95,000.00 Advance payment received from the buyer in electronic money Register of payments. 76.AB 68.
02 14,491.53 We charge VAT on the advance Invoice issued 51 55.04 91,675.00 (95,000 – 3,325) Funds transferred to the current account Bank statement. 76.09 55.
04 3,325.00 Bank commission withheld Bank statement.
Accounting for fixed assets: main entries
Settlements with buyers and customers." Analytical accounting on account 62 and sub-accounts: - Account 62.01 - payment received in the general manner; — Account 62.02 – advances from buyers. . .
Postings to the accounting account 62 Postings to account 62 for regular sales: Debit Credit Name of transaction 62 90.1 Reflected revenue from the sale of goods (work, services) 90.3 68 VAT accrued on goods sold (work, services) 62 91.
1 Reflected revenue from the sale of fixed assets, intangible assets, materials (not the main activity) 91.2 68 VAT accrued on sold assets (not the main activity) 51 62 Payment received from the buyer to the current account Entries for accounting for advances received (account 62.
2) If the buyer pays for the goods in advance and transfers an advance, then to account for settlements with customers in this case, subaccount 2 “advance received” is opened on account 62.
Debts of buyers and suppliers in accounting
Get 200 video lessons on accounting and 1C for free:
The contract with the buyer may provide for discounts if certain conditions are met. The discount can be expressed:
- In price reduction
- In kind (receiving free goods or additional goods)
If a discount is provided at the time of shipment or before the transfer of goods, then the company must reflect the sale according to the documents, taking into account the price reduction.
If the discount is provided after shipment, then it is necessary to prepare an adjustment invoice.
Reflection of shipped goods in accounting
In accounting, the cost of shipped products belongs to the inventory section, where finished products of other types are also reflected. Reflection (according to account 45) is carried out at actual or planned cost, taking into account sales costs.
The moment of receipt of revenue (payment) is recorded by the seller upon shipment of the product with the transfer of ownership of the subject of the transaction. For companies using a simplified taxation system, revenue is recorded after actual payment for the product.
At the time of recognition of revenue, expenses associated with the manufacture and sale of the product are subject to accounting (PBU 10/99; Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 119n, December 28, 2001).
When transferring ownership of a product after final settlement and determining the VAT base after shipment of the subject of the transaction, accounting transactions look like this:
- Debit account 45 / Credit account 41 (shipment of the product based on its actual cost).
- Debit account 45 / Credit account 44 (writing off other expenses incurred on shipment).
- Debit account 90 / Credit account 45 (recognition of the fact of sale after payment).
- Debit account 45 / Credit account 68 (VAT accrual on shipped products).
When ownership changes and its transfer to the acquirer, a sale takes place, and accordingly, receipts and expenses are subject to accounting on the account. 90 based on primary documents (Federal Law No. 402, December 6, 2011).
When selling products for cash, the following posting is made in accounting: Debit account. 50 / Credit account 90.1 , for non-cash payments: Debit account. 62 / Credit account 90.1.
For your information! The actual cost of sales must be written off in a manner that takes into account the method of registration of finished goods by the enterprise (at actual or standard cost).
The cost of products to be written off as expenses is determined in one of the following ways:
- at cost (inventory units);
- using the FIFO method;
- at average cost.
The choice of valuation method must be enshrined in the accounting policy of the enterprise (order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 119, December 28, 2001; letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 07-05-14/298, November 16, 2004; PBU 5/01).
Non-monetary payment of obligations
The contract may stipulate that the buyer will repay his debt with non-monetary means.
When repaying a debt with a bill of exchange, you need to open a separate sub-account for it in account 62. And when repaying the debt, the following entries are made:
- Debit 62 Credit 62 – a bill of exchange was received to repay the debt
The organization shipped goods worth RUB 223,742 to the buyer. (VAT 34130) their cost is 112,120 rubles. The buyer issued a promissory note to repay the debt. He paid it off after 2 months.
Penalties for late repayment of debt
When the buyer does not fulfill his obligations on time, measures established by the terms of the contract may be applied to him. In other words, penalties and fines. Penalties can be calculated based on current legislation in relation to tax debts. Or the contract may reflect a different procedure for calculating penalties.
Fines can be set at a fixed amount or as a percentage of the debt amount.
The receipt of such amounts is recognized as unrealized income and is reflected in 91 accounts. Posting: Debit 91.1 Credit 76.2.
There are two conditions under which fines and penalties can be collected. One of them must be fulfilled:
- They must be recognized by the debtor himself
- The court must make a decision on recovery
This type of income is not subject to VAT.
The company shipped goods worth RUB 175,500 to the buyer. (VAT 26771). Cost of goods 81,700 rubles. The buyer did not transfer payment for them on time. According to the terms of the agreement, the amount of sanctions is calculated based on 0.2% of the debt for each day of delay. The debt was repaid 22 days after the expected due date.
Return of goods sold in bulk
When returning the goods to the supplier due to improper fulfillment of the terms of the contract, the parties return to their original state; The purchase and sale agreement is considered invalid, and the transfer of ownership of the goods is considered unfulfilled.
To correctly reflect in the accounting of operations of returning goods from the buyer to the supplier, the accountant must have documents confirming the reason for the return. Such documents can be: the buyer’s claim, drawn up by him in any form, and the invoice issued by the buyer.
The documents presented by the buyer provide the basis for adjusting the turnover of goods sold by the supplier organization, which is reflected in the accounting entries:
debit of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” credit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount 1 “Revenue” - reversal for the amount of the cost of the returned goods;
debit of account 90, subaccount 3 “Value added tax” credit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” - reversal for the amount of previously accrued value added tax;
debit account 90, subaccount 2 “Cost of sales” credit account 41 “Goods” - reversal for the amount of the accounting value of the returned goods.
This is the first time I’ve heard such a concept as an adjustment invoice. Usually, the final price, already taking into account discounts, is displayed in the invoice, in the invoice, and accordingly is posted according to the reports, and if the discount is provided later, an adjustment invoice is issued, and the postings have already been made according to the main document, what to do in this case ?
Account 62 is one of the most frequently used in accounting, postings to it are made regularly, due to the fact that debts of both buyers and suppliers are a standard part of any business process, it is almost impossible to avoid them...
Posting received from buyer for products
Settlements with buyers and customers." Analytical accounting on account 62 and sub-accounts: - Account 62.01 - payment received in the general manner; — Account 62.02 – advances from buyers. . .
Postings to the accounting account 62 Postings to account 62 for regular sales: Debit Credit Name of transaction 62 90.1 Reflected revenue from the sale of goods (work, services) 90.3 68 VAT accrued on goods sold (work, services) 62 91.
1 Reflected revenue from the sale of fixed assets, intangible assets, materials (not the main activity) 91.2 68 VAT accrued on sold assets (not the main activity) 51 62 Payment received from the buyer to the current account Entries for accounting for advances received (account 62.
2) If the buyer pays for the goods in advance and transfers an advance, then to account for settlements with customers in this case, subaccount 2 “advance received” is opened on account 62.
Postings for the sale of goods and services in accounting
Read more about the sale of fixed assets in this article. The credit of account 62 shows a decrease in the buyer's receivables, the credit reflects the receipt of payment from the buyer, and posting D51 (50) K62 is performed.
If the seller is a VAT payer, then the sales price includes a tax that is applied to the cost of goods, products, assets sold and is payable to the budget. If goods or products are sold, then VAT is charged by posting D90/3 K68.VAT.
If assets are sold, and this is not the usual type of activity of the enterprise, then posting D91/3 K68.VAT is performed.
Accounting entries Accounting for advance amounts from the client It is possible that the seller organization first receives an advance payment (advance payment) from the buyer, and then, on account of this advance payment, ships goods and products.
Postings for accounting for sales of finished products
The accrued amount of VAT on the advance received is restored, and then an entry is made to offset the advance. You can read more about accounting for VAT on advance payments in the article: “Accounting for VAT on advance payments and gratuitous transfers.”
Postings for accounting for advances received (account 62) Debit Credit Name of transaction 51 62. Advance received An advance was received from the buyer to current account 76.
VAT on advances received 68 VAT accrued on advance received 62/1 90/1 Revenue from sales of goods is reflected 90/3 68 VAT accrued on goods sold 62. Advance received 62/1 Offset of advance against debt repayment 68 76.
VAT on advances received Accepted for deduction of VAT in connection with the sale of goods paid in advance Accounting for bills received from the buyer: If the buyer issued a promissory note to the seller, it must be accounted for in subaccount 3 “Bill received” of account 62.
Payment from the buyer of the transaction
Any business is built on commodity-money relations, be it a physically tangible product or some kind of service. Accounting is an integral part of the life of any organization. If a company is engaged in the sale of any product, then at the moment when its transfer occurs, ownership also passes to the buyer.
At this moment, it is necessary to make a posting to the debit of account 62 “Settlements with customers”. How to do this and for what purpose - let's look at it in more detail.
- Reflection of debt
- Debt repayment Accounting for advances
- Accounting for bills received
Reflection of debt First, you need to understand that there are two types of debt: receivables and payables.
Account 62 in accounting: postings, subaccounts, examples
Accounting account 62 is a special analytical account that is used to reflect the supplier’s transactions with the buyer and customer. This article will give you an idea of the main transactions on account 62, which is reflected in the debit and credit of account 62, as well as the documents that are the basis for their implementation.
Account 62 - can reflect both our debt to the buyer (credit) and the buyer's debt (debit). Therefore, this account is considered active-passive - it can be included in the balance sheet as a Liability or an Asset.
Analytical accounting on account 62 and its subaccounts
Under loan 62, funds from the sale of shipped products are credited to the account. as well as the amount of advance payment for goods and services. In this case, payments for services rendered and advances are taken into account in different subaccounts:
In addition, there is a sub-account for separate accounting of bills received (62.03). If the supplier receives a bill of exchange from the buyer providing for the payment of interest, the amount of interest is reflected in accounting account 91 “Other income and expenses.” Repayment of the principal amount of the debt is reflected by posting Dt account 51 (for foreign currency accounts DT 52) and Kt 62.
For the convenience of the accountant, analytics for account 62 are carried out in the context of each invoice sent to the buyer, as well as separately for each counterparty and agreement with him. In addition, operations can be classified according to the following criteria:
- payment method (availability of advance payment or payment upon shipment, provision of services);
- payment deadline (payment is overdue or not due);
- presence of a bill of exchange (the bill of exchange has been accounted for in the bank, its maturity has not yet come, or payment on the bill of exchange is overdue).
The accountant has the right to independently choose the criteria on which the analytical accounting of account 62 at the enterprise will be based.
Purchasing accounts receivable: features
The creditor transferring the rights of claim is called the assignor in legislation and the assignment agreement, and the buyer of the debt is called the assignee. From an accounting point of view (PBU 19/02), debtors’ debts acquired by assignment of the right to foreclose are considered an investment if, according to the assignment agreement, certain conditions are met:
- There are documents certifying the right to receive assets or money;
- With the acquisition of debt, the risks associated with it are transferred to the buyer, for example, the risk of non-payment, price fluctuations and decreased liquidity of the asset. It is no coincidence that a large volume of such purchases by an unprepared buyer, as a rule, does not provide tangible profits;
- The likelihood that the buyer will receive future economic benefits, such as an increase in the value of an asset. Many assignees conduct similar transactions to secure start-up capital. It is important that the purchase of accounts receivable is handled by an experienced specialist who is familiar with such operations first-hand.
If the acquired debt meets these criteria, it will be reflected in the account. 58 “Financial investments” (Draft of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 94n dated October 21, 2000).