According to Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the following employee expenses for a business trip are subject to mandatory reimbursement:
- daily allowance;
- travel by public and private transport;
- payment for accommodation;
- other payments related to the trip and agreed with the employer.
The procedure for sending employees on business trips is developed and approved by the company in a local regulatory act, taking into account the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Government Decree No. 749 of October 13, 2008.
Accounting for travel expenses in 2021 is carried out on account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
What does the law guarantee when sending an employee on a business trip?
A business trip is a trip by an employee by order of the employer for a certain period of time to carry out an official assignment outside the place of permanent work. Moreover, if the permanent work of employees is carried out on the road or has a traveling nature, then their business trips are not recognized as business trips (Article 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
According to Articles 167, 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees sent on a business trip are provided with the following guarantees:
- maintaining a job (position);
- average earnings;
- reimbursement of travel expenses;
- reimbursement of expenses for renting residential premises;
- reimbursement of additional expenses associated with living outside the place of permanent residence (daily allowance);
- reimbursement of other expenses incurred by the employee with the permission or knowledge of the employer.
It is the listed standards that characterize the content of a business transaction for reimbursement of expenses incurred on a business trip that we will be guided by when choosing the CVR and sub-articles of KOSGU. We remember that expenses are included in the sub-items of KOSGU depending on their economic content (clause 3 of Order No. 209n).
Reflection in accounting of return or exchange of air tickets.
When organizing business trips and purchasing air tickets, situations may arise when it is necessary to return or exchange an air ticket.
Example 1.
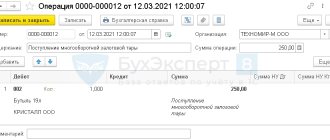
- 02. NPP Technoservice paid for the trip to St. Petersburg for supply manager Bystrokov by bank transfer. 19.02. It became known that Bystrokov could not fly to St. Petersburg due to illness. The return was made on 20.02. 21.02. received for the return of funds to the current account.
Postings
| Date of operation | Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| 18.02. | Paid for the road to St. Petersburg by bank transfer | 60 | 51 |
| 18.02. | Received itinerary receipt in electronic form | 50.3 | 60 |
| 20.02. | Return made | 60 | 50.03 |
| 21.02. | Received cashless payment for return | 51 | 60 |
| 21.02 | The difference between the cost of the returned ticket (excluding VAT) and the amount received when returning the ticket is taken into account as part of other expenses. | 91.2 “Other expenses” | 60 |
Example 2.
To test prototypes at the Naberezhnye Chelny foundry, an air ticket to Kazan airport was purchased. Afterwards, it was decided to fly to the airport in Naberezhnye Chelny. The ticket was returned to the supplier and then a new ticket was received from him and issued to technical director Borovoy.
| Contents of operation | Debit account | Account credit |
| The cost of the flight to Kazan was paid from the bank account of Tekhnoservice LLC | 60 | 51 |
| Received itinerary receipt in electronic form | 50.3 | 60 |
| Documents were returned to the supplier | 60 | 50.3 |
| Received a ticket to Naberezhnye Chelny | 50.3 | 60 |
| A ticket was issued to Borovoy | 71 | 50.03 |
| Business trip report provided | 26 | 71 |
Principles for choosing KVR and KOSGU
First of all, we note that when sending an employee on a business trip, ensuring the guarantees enshrined in Articles 167, 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation can be carried out in two ways:
- The employee is given an advance to purchase travel documents and pay for the hotel, and is paid a daily allowance. Expenses actually incurred for the business trip are also reimbursed upon return.
- The institution independently purchases travel (flight) tickets for the posted employee, pays for the hotel, purchases fuel, lubricants, etc.
The procedure for allocating expenses to CWR and KOSGU in both cases will differ.
Travel expenses - postings
To account for travel expenses, account 71 is used. Debit account 71 takes into account all the money issued to the employee for reporting, and the Credit accounts for all expenses incurred by him.
The employee should not spend his own money on travel arrangements. Therefore, he is given a pre-calculated amount in advance in the form of an advance from the cash register in cash or the money is transferred to his personal plastic card account:
- issued from the cash register for travel expenses - posting D71-K50;
- issued non-cash for travel expenses - posting D71-K51.
If, after returning from a trip and presenting an advance report, the traveler has excess money in his hands, the unused balance is deposited into the cash desk:
- unspent money for travel expenses was received at the cash desk - posting D50-K71.
Sometimes the opposite happens: an employee spends more than the amount planned and received on a business trip. In this case, the overexpenditure is issued in cash or by non-cash transfer:
- money was issued for travel expenses - wiring D71-K50 or D71-K51. This operation is similar to the original posting (“a report was issued for travel expenses”), but the wording of the purpose of payment adds that it is: “overspending on the advance report.”
KOSGU
As noted above, travel expenses are considered in the context of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as reimbursements (compensations) related to the employee’s performance of work duties. In international statistical practice, such payments are not considered as payments in the interests of employees, but belong to the category of expenses made by the employee for the purpose of performing work duties. In this regard, reimbursement of expenses related to business trips (travel, accommodation, other expenses related to the performance of official assignments on a business trip), starting in 2021, were transferred to subarticle 226 “Other work, Other payments” * (3) KOSGU ( clause 7, clause 10.2.6 clause 10 of Procedure No. 209n, clause 2.1.4 of the Methodological recommendations for the procedure for applying KOSGU, communicated by letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 29, 2018 No. 02-05-10/45153).
More on the topic: OKOF from 2021
If we are not talking about reimbursement of expenses, but about providing the employee with everything necessary before a business trip (when the institution independently purchases tickets, pays for a hotel, etc.), then the institution’s expenses will include, in particular:
- to subarticle 222 “Transport Other work, Payment for work, services” of KOSGU, articles and subarticles of group 300 “Receipt of non-financial assets” of KOSGU, based on the economic sense.
Note! Expenses regarding daily allowances are still included in subarticle 212 “Other non-social payments to staff in cash” of KOSGU (clause 10.1.2 clause 10 of Procedure No. 209n).
New analytical accounts.
When an institution pays (reimburses) funds to seconded persons, they are recognized as accountable persons. To reflect settlements with them in accounting, account 0 208 00 000 “Settlements with accountable persons” is intended (clause 212 of Instruction No. 157n).
Since the use of analytical accounts for account 0 208 00 000 is closely related to the use of the corresponding KOSGU codes, when reflecting travel payments:
- personnel (except for daily allowances) from 2021 need to use the analytical account 0 208 26 000 (instead of the account 0 208 12 000);
- students, athletes - analytical account 0 208 26 000 (instead of account 0 208 96 000).
An increase (decrease) in receivables of business travelers (accountable persons) on account 0 208 26 000 is reflected by budgetary (state) institutions indicating in the 24th - 26th digits the number of the corresponding KOSGU code (clause 21 of Instruction No. 157n). Until 2021, the following KOSGU codes were used for this:
- 560 “Increase in other receivables”;
- 660 “Decrease in other receivables.”
Since 2021, these codes have been detailed (561 – 569, 661 – 669) depending on the type of counterparties with whom settlements are made (clauses 13.6, 14.6 of Procedure No. 209n).
According to the author, when reflecting settlements with business travelers (as well as with other accountable persons), budgetary (government) institutions in 2021 should use codes 567, 667 KOSGU, indicating settlements with individuals.
KVR
One of the essential requirements of the approved structure of types of expenses, enshrined in clause 46.5 of Procedure No. 85n, is the reflection of travel expenses * (4), as follows:
- issuance of cash to seconded workers (employees) (or transfer to a bank card) on account of the guaranteed expenses listed above - according to CVR 112 “Other payments to personnel of institutions, with the exception of the wage fund”, 122 “Other payments to personnel of state (municipal) authorities, with the exception of the wage fund", 134 "Other payments to military personnel and employees with special ranks" and 142 "Other payments to personnel, with the exception of the wage fund" (see also clause 48.1.1.2, clause 48.1.2.2, clause 48.1.4.2 clause 48 of Order No. 85n);
- payment for the purchase of tickets for travel to and from the place of business trip and (or) rental of residential premises for seconded workers under agreements (contracts) - according to KVR 244 “Other procurement of goods, works and services”.
Thus, Procedure No. 85n clearly establishes the use of various CVRs when reimbursing an employee’s expenses and when an institution purchases services for him under a contract.
More on the topic: Information on accounts receivable and payable (f. 0503169, 0503769): how to check control ratios with other forms (Video materials for the 2019 annual reporting - topic 10)
Note! According to clause 46.5 of Procedure No. 85n, the list of other expenses incurred by a posted employee with the permission or knowledge of the employer, attributable to CVR 112, 122, 134 or 142, is determined by the employer in a collective agreement or local regulation (due to the specifics of the activities of individual main managers of budget funds - in a normative legal act). That is, if the relevant act does not indicate certain expenses incurred by an employee on a business trip with the knowledge of the employer, they cannot be attributed to CVR 112, 122, 134 or 142. In this case, the expenses will be attributed to CVR 244 * (5) .
As we can see, the attribution of travel expenses can be carried out according to various CVR and KOSGU, depending on whether funds are issued (compensated) to the employee or whether the institution purchases services for him. And the procedure for attributing other expenses incurred by an employee on a business trip depends on the availability of a list of such expenses, enshrined in the relevant act, and the presence of specific expenses in such an act.
Along with the above, it is interesting that if the purpose of the business trip is the purchase of material supplies, for example, fuels and lubricants, then the purchase costs should be reflected according to KVR 244 and subarticle 343 of KOSGU (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 15, 2019 No. 02-05-10/17872 ).
Let us remind you that the CWR and KOSGU expenditure subitems are used in mutual coordination. In this regard, we advise you to always check the CVR for coordination with the articles (sub-articles) of the KOSGU according to what is posted by the Ministry of Finance of Russia on its official website (www.minfin.ru). Please note: the table of correspondence between the CWR and the articles (subarticles) of the KOSGU related to expenses often undergoes changes. At the time of preparation of the material, the correspondence table posted on the website of the Ministry of Finance of Russia on 04/09/2020 is valid (Budget - Budget classification of the Russian Federation - Methodological office).
Login for clients
Persons involved in work under a civil contract cannot be seconded.
Guarantees and compensations provided for by labor legislation, including those related to business trips, do not apply to them (Article. Thus, it is prohibited to send on business trips:
- workers under the age of 18, with the exception of athletes and creative workers (Article 268, Part 3, Article 348.8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- pregnant women (Part 1 of Article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- employees during the period of validity of the apprenticeship contract, provided that the business trip is not related to apprenticeship (Article 203 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Sending women with children under 3 years of age on business trips is permitted only with their written consent and provided that this is not prohibited to them in accordance with a medical certificate.
11 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, when making a decision on business trips, it is necessary to take into account the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which prohibit or limit sending certain categories of employees on business trips.
3 tbsp. 259 Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- for workers who care for a sick family member in accordance with a medical report.
- for single parents and guardians raising children under 5 years of age;
- for employees with disabled children;
Standards for reimbursement of travel expenses.
Women must be informed in writing of their right to refuse to be sent on a business trip (Part 2 of Article 259 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Similar rules apply (Part.
Dimensions