Establishing and maintaining off-balance sheet accounting is clearly not a priority for companies today. The reason is simple: although with the help of accounting management can control the company's assets and liabilities, as well as obtain operational information on them, the costs of accounting should not exceed the potential benefits from it. And all accountants should not ignore off-balance sheet accounting. Let's tell you why.
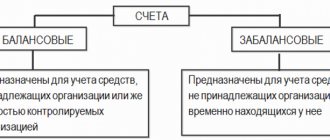
Off-balance sheet accounts are subsidiary accounts of accounting, the balances of which should not be reflected in the balance sheet. They are used when the accountant needs information that is not on the balance sheet accounts. The need to maintain off-balance sheet accounting is caused by several circumstances.
First. Chief accountants who have been audited know that without proper off-balance sheet accounting, the auditors' report will not be ideal. Of course, there is no direct responsibility for the lack of off-balance sheet accounting. But there is administrative liability for distortion of any indicator of accounting (financial) statements expressed in monetary terms by no less than 10% (Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Second. Recently, there has been a tendency that tax authorities are particularly keen on checking off-balance sheet accounting. For example, they may have a question: where in the balance sheet is the rented premises in which the company's employees work reflected? If it is not reflected in the accounting, it turns out that the organization’s employees sit on the street or work remotely from home. And if the premises are not accounted for, how can rental costs be included in income tax expenses? That is, if there is no property on the balance sheet, there are no expenses.
Third. Maintaining off-balance sheet accounting allows you to bring together accounting and management accounting. For example, management may have a question: a laptop costing less than 40,000 rubles. not reflected in accounting, since it was written off as materials and then as expenses? So the laptop no longer belongs to the company and any employee can take it home? Or an office software package was purchased several years ago, and after it “left” the deferred expenses account, this license was no longer recorded. It is logical that management wants to see the number and terms of such licenses on the balance sheet.
What are off-balance sheet accounts?
Off-balance sheet accounts (AB) are intended to store information about the objects used by the company. Their key feature is that the company does not have ownership rights to these objects. They are temporarily part of the company. Provided on the basis of various agreements. These objects may include:
- rented premises, warehouses;
- valuables transferred for safekeeping;
- raw materials accepted for processing;
- equipment adopted for the purpose of installation work.
How can a tenant account for leased objects (premises, equipment, other property) on off-balance sheet account 001?
The principle of property separation and off-balance sheet accounts
The organization of off-balance sheet accounts is based on the principle of property separation. It states that the accounting of an organization's assets should not coincide with the accounting of the assets of its owners, as well as the assets of other organizations under the care of this organization. The same principle applies not only to assets, but also to liabilities.
Objects temporarily included in the assets, provided under certain agreements, do not belong to the enterprise. However, during a certain period of time, it is the enterprise that is responsible for them, which means it must take them into account in a certain way. But such values cannot be mixed together with those owned by right of ownership within the same accounting accounts.
When and how to take into account inventories on off-balance sheet accounts ?
Off-balance sheet accounts are auxiliary accounts within the framework of accounting. They become relevant if you need to obtain information not contained in balance sheet accounts. This feature explains their name. Balances from off-balance sheet accounts will not be included in the balance sheet. They are displayed behind the total of this indicator. That is, they are recorded on the balance sheet.
IMPORTANT! Information from the accounts in question does not affect financial performance. For this reason, they will not appear in the company's financial statements.
What are off-balance sheet accounts for?
Off-balance sheet accounts perform the following functions:
- Accounting for the availability of property and tracking transactions with it. Accounting may also concern objects that belong to the enterprise, but their value is written off as expenses.
- Collection of data necessary for the formation of explanations for the main balance sheet and financial statements.
- Control over the operation of property to which the enterprise does not have ownership rights.
- Control over the safety of the objects in question.
- Supporting role to monitor the execution of property papers without delays. In particular, documents are drawn up on the receipt of objects and their disposal.
- Full organization of accounting in this area.
Properly executed off-balance sheet accounts allow you to obtain all the data on objects that are located on the territory of the enterprise, but do not belong to it. Information is necessary to analyze the company's creditworthiness and determine its financial stability.
Off-balance sheet accounts, their purpose and application procedure
Let's look at the most common assets and liabilities that need to be reflected on the balance sheet.
- Off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets ”
records leased fixed assets at the cost specified in the agreement. The object arrives on the basis of the acceptance certificate, which is an annex to the contract. If the lessor refuses to announce the value of the property, the lessee can establish a conditional valuation of the property by specifying these rules in the accounting policy. The tenant should issue an inventory card for the received object. - Off-balance sheet account 002 “Inventory and materials accepted for safekeeping.” Cases when valuables may be stored in another enterprise are listed in paragraph 155 of the Methodology for Inventory Accounting. Goods can be transferred for storage under agreements with an approved procedure for the transfer of ownership, for example, if the agreement stipulates that the recipient becomes the owner of the goods after paying its cost in full. When receiving goods and materials before the payment has been made, the buyer records the cost of the delivered goods and materials in account 002. After payment, account 002 is credited on the basis of an act of form MX-3, and the goods are credited to balance sheet account 10 (41).
- Off-balance sheet account 003 takes into account the so-called customer-supplied raw materials accepted by the contracting company from the customer for processing, production of products from them, or other processing. The contractor does not pay for the materials and after the work is completed returns them to the customer in full. The cost of raw materials is reflected in the debit of account 003 at the prices specified in the contract (invoices). If there is no cost of materials in the accompanying documents, the contractor has the right to reflect them off balance in the quantitative assessment. They are written off from account 003 after complete use by the contractor and transfer to the customer.
- Off-balance sheet account 006 “BSO” informs the user about the presence and movement of BSO. These include documents equivalent to cash receipts, receipts, lottery tickets, forms of work books, diplomas, certificates, and securities. For each type of BSO, an accounting journal is kept, which reflects the receipt, issuance of them for reporting, and return. Based on the journal data, postings are made. The valuation of these assets is not important, since the number of forms is more important here.
- Off-balance sheet account 010 “Depreciation of fixed assets” is intended to account for the depreciation of fixed assets, the cost of which is not depreciated. For example, the property of non-profit organizations, mothballed and inactive objects, housing stock and objects with a constant value.
- Off-balance sheet account 011 “Assets leased out” is used when concluding a rental (leasing) agreement. The transferred property can be taken into account on the balance sheet of the lessee, and then he credits the property to balance sheet account 01, and behind the balance sheet, the value of the object at the prices stipulated by the agreement is taken into account by the lessor.
The chart of accounts for commercial enterprises provides for 11 off-balance sheet accounts, but if necessary, it is not forbidden to open new ones for a more complete disclosure of information. For example, with the introduction of IFRS, additional accounts are often used to provide management accounting:
- off-balance sheet account 012 “Intangible assets received for use”;
- account 013 “Securities received as collateral”;
- account 014 “Contingent assets”;
- off-balance sheet account 015 “Contingent liabilities”, which takes into account existing or possible liabilities arising from past events and not meeting the criteria for recognizing a liability. Contingent liabilities are not recorded in the Statement of Financial Position (other than in business combinations) because their amount cannot be determined.
Accounting programs also contain additional accounts used to detail business transactions. For example, off-balance sheet account MC 04 “MC in operation” is used for quantitative accounting of inventory and tools transferred into operation. Receipts are recorded by program users as a debit to the account, and disposals are recorded as a credit.
We have provided a non-exhaustive list of off-balance sheet accounts designed to record assets and liabilities. This list can be significantly expanded and adapted to the needs of the company.
are applied in accordance with the rules approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n. Read the material for what off-balance sheet accounts are intended for and how to display them correctly in accounting.
Types of off-balance sheet accounts and their accounting
The required type of off-balance sheet account is determined depending on what kind of object is subject to accounting. There are the following types of ES:
- 001 “Fixed assets leased.” Their cost must be confirmed by an agreement concluded with the lessor.
- 002 “Valuables taken under safekeeping.” Typically, an agreement is concluded in relation to these objects, after the fulfillment of the terms of which the values become the property of the enterprise. Until this moment, the company's objects will not belong to the company. The condition is certain deductions. The postings must indicate their size.
- 003 “Raw materials taken for processing.” Materials for processing can be indicated on off-balance sheet accounts only if they were transferred by the customer and the manufacturer does not pay their cost.
- 004 “Materials for commission.” The products that were taken by the commission agent for sale are indicated.
- 005 “Equipment intended for the performance of installation services.” The equipment used to perform installation services is indicated.
Off-balance sheet accounts reflect assets owned by the enterprise that have been written off as expenses:
- 006 “Reporting forms”. May include various receipts and subscriptions.
- 007 “Bad debts written off at a loss.” Displayed on accounts for five years. It is assumed that during this time the financial position of the debtor may change.
Off-balance sheet accounts are relevant for collecting information necessary as additional information to the explanations of the statements:
- 008 “Collateral received.” Needed to store data on transferred guarantees to ensure compliance with conditions;
- 009 “Issued collateral.” Relevant for collecting information on issued guarantees to ensure payments.
- 011 “Funds received for rent.” This account is placed in the reporting of both the lessor and the tenant.
All account data is indicated in a special accounting plan. An enterprise can open other accounts that are not in the plan if this is required to support its activities.
An organization has the right to open a sub-account to an existing off-balance sheet account or introduce a new account if it is not provided for in the plan. The main thing is that this change is properly spelled out in the accounting policies.
IMPORTANT! Organizing off-balance sheet accounts is extremely important. If, as part of a tax audit, objects are discovered that do not appear in the reporting, they will be written off as non-operating income. That is, they will be subject to income tax.
Features of accounting on the AP
Off-balance sheet accounts are presented in the form of a table with two columns. One of them displays debit, the other – credit. Accounting for APs is carried out using a simplified system. No double entry required. That is, you don’t have to write the same amount in debit and credit. The following transactions must be indicated in the debit column:
- getting objects;
- acquisition or issuance of security.
The loan column displays:
- disposal of the object;
- termination of security.
The debit will show the income, and the credit will show the expense.
What are off-balance sheet accounts intended for and how are they used?
The chart of accounts (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), in addition to the main balance sheet accounts, provides additional ones that carry information about the company’s temporarily owned assets, as well as about contingent rights and obligations. Such accounts do not appear on the balance sheet and are therefore called off-balance sheet accounts.
For an algorithm for compiling a balance, see the material.
These accounts differ from the standard ones by a three-digit code designation and registration of records using a simple system. That is, when compiling transactions, the double entry method is not used here, and business information is displayed either only by debit of the account or by credit.
Transactions with off-balance sheet accounts
On off-balance sheet accounts, just like on regular ones, procedures for registering and writing off values are carried out. You can also make sales from off-balance sheet accounts. There are some nuances to take into account.
How to put an asset into an off-balance sheet account
The legislation does not regulate the accounting of individual off-balance sheet values, leaving the accounting department to independently choose a strategy, specifying it in the accounting policy. An organization can open an additional account for, for example, low-value property, assigning it a number next to the planned ones and reflecting this in the policy. It is convenient to account for low-value assets in off-balance sheet accounts because:
- such assets will not get lost among the “voluminous” balance sheet assets;
- property is assigned to a specific employee responsible for it.
Sales from an off-balance sheet account
If management decides to sell an asset held in an off-balance sheet account that they previously used and continue to do so, they must write off the asset as a credit to the corresponding off-balance sheet account. The funds received from the sale must be reflected as income from sales and VAT must be added. At the same time, in tax accounting, this operation will entail the reflection of income included in the income tax base.
ATTENTION! Since the initial cost of the asset was already taken into account at the time of commissioning, it is not reflected in accounting or tax accounting, otherwise distortions in financial results are possible.
Write off an asset from an off-balance sheet account
Objects can not only be accounted for in off-balance sheet accounts, but, if necessary, can be written off from them. This happens if the asset has become completely unusable, or it is about to be sold, for these reasons it is no longer used in the activities of the enterprise. Information about the transaction is entered into a special journal of material assets, which is maintained specifically for objects of off-balance sheet accounts. The following information is required:
- name of the asset;
- date of its commissioning;
- price;
- inventory number;
- person responsible for it (full name, position);
- write-off date (added after this operation).
After the date of write-off is entered in the journal, the enterprise can no longer use the specified asset, which is confirmed by a special act.
Results
Off-balance sheet accounts
must be used along with “standard” accounts. Failure to use off-balance sheet accounts will lead to the impossibility of generating reliable financial statements and, therefore, is a violation of the law.
Off-balance sheet accounting of property: nuances and transactions
The company's own fixed assets, materials, goods and other material assets are recorded in the appropriate accounts. Sometimes an organization takes or leases fixed assets, uses customer materials for production, accepts goods on commission - these and other similar transactions should be reflected in off-balance sheet accounts. In addition, very often accountants have to keep records of low-value fixed assets behind the balance sheet. We will tell you in the article how to organize off-balance sheet accounting, in what cases it is necessary and what transactions to reflect off-balance sheet transactions.
The chart of accounts provides for 11 off-balance sheet accounts—they account for property and liabilities. Accounting for off-balance sheet accounts is carried out without using double entry. Off-balance sheet accounts are not closed at the end of the year. Let's consider accounting for various types of property in off-balance sheet accounts.
Postings to off-balance sheet accounts using an example
Two enterprises entered into an agreement with each other for the supply of goods. One of the parties provides security for payment in the form of equipment pledged. The cost of the equipment is 200,000 rubles. Payment under the contract was not made, and therefore another enterprise receives the equipment at its disposal and then sells it. These transactions will be reflected using the following entries:
- DT 008 “Payment Security” 200,000 rubles;
- KT 008 “Write-off of collateral” 200,000 rubles;
- DT 002 “Accounting for valuables received under a pledge agreement.” Document – pledge agreement;
- KT 002 “Sale of valuables.” Document – act of acceptance and transfer;
- DT 51 CT 91 “Income from sales.” The document is a bank statement.
From this diagram you can extract information about the movement of values and the transaction amount. All operations are confirmed by primary documentation.
Off-balance sheet accounting of fixed assets
Fixed assets need to be taken into account off the balance sheet in several cases.
Fixed assets worth up to 40,000 rubles
Perhaps the most common situation for accounting for fixed assets off the balance sheet is accounting for assets worth up to 40,000 rubles.
Let us remind you that fixed assets no more than 40,000 rubles can be written off at a time as expenses in accounting (clause 5 of PBU 6/01). First, such assets are credited to the inventory account (account 10), and then written off to cost accounts (accounts 20, 25, 26, etc.). When writing off low-value fixed assets from the balance sheet, the question arises of control over the safety of property. This is where off-balance sheet accounts come in handy.
The chart of accounts does not provide an off-balance sheet account for recording assets written off the balance sheet. The company has the right to independently introduce a new off-balance sheet account by assigning a code to it (for example, account 015 “Property worth up to 40,000 rubles”). Information about created off-balance sheet accounts should be reflected in the accounting policies of the enterprise.
Example.
The company purchased a chair for the director at a cost of 24,780 rubles, including VAT of 3,780 rubles. According to the accounting policy, the company writes off such assets to off-balance sheet account 015. The postings will be as follows:
Debit 10 Credit 60 - 21,000 - chair was capitalized as part of inventories
Debit 19 Credit 60 - 3,780 - VAT allocated
Debit 68 Credit 19 - 3,780 - VAT taken for deduction
Debit 44 Credit 10 - 21,000 - the cost of the chair is included in the costs of the trading company
Debit 015 - 21,000 - the chair is included in the balance sheet
When the chair becomes unusable, it should be written off off-balance sheet with the following posting:
Credit 015 – 21,000
When conducting an inventory, off-balance sheet accounting data should also be taken into account.
Fixed assets under a rental or leasing agreement
Off-balance sheet accounts will be needed by tenants and landlords. Keeping records of rented objects is prescribed by paragraph. 7 clause 32 PBU 6/01. In appendices to the financial statements, the accountant is also required to disclose information about leased fixed assets (clause 27 of PBU 4/99). The absence of off-balance sheet accounting for a significant share of such objects can lead to fines (Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tenants rent various objects - from office space to industrial equipment. Based on a rental or leasing agreement, the tenant (lessee) must register the received fixed assets. For this purpose, a special account 001 “Leased fixed assets” is provided. The lessee takes into account the received property on its balance sheet if the agreement stipulates that the property is taken into account on the lessor's balance sheet.
Leased objects are accepted for off-balance sheet accounting at the price specified in the contract. The lack of property value in the lease agreement is not an obstacle to reflecting the property off the balance sheet. Analytical accounting is usually carried out by types of fixed assets and lessors.
When a leased fixed asset is received, the following posting is made:
When disposing of a leased property (returning it to the lessor), you need to make a reverse entry:
Credit 001
Off-balance sheet accounting will confirm the appropriateness of lease payments transferred to the lessor. With reliable off-balance sheet accounting, the lessee will be able to reasonably write off the amount of lease payments as expenses.
Lessors also keep records of fixed assets if, under the terms of the agreement, the property is taken into account on the balance sheet of the tenant (lessee). Account 011 “Fixed assets leased out” is intended for accounting.
Off-balance sheet accounts in budgetary organizations
If the organization is classified as a budget organization, off-balance sheet values are recorded in it according to a simplified scheme - there is no need to keep corresponding records. When property is capitalized, the necessary entry is made in the debit of a certain off-balance sheet account. At the time of write-off, this entry is made against the loan. It is allowed to introduce additional off-balance sheet accounts for greater reliability of management accounting, naturally, indicating them when developing accounting policies.
So. Off-balance sheet accounts allow you to display information about property that is located on the territory of the enterprise, but does not belong to its property. Other data is also stored on the AP. Having off-balance sheet accounts during tax audits will allow you to avoid making unnecessary tax deductions. It is also a source of important information about the company's activities. The information allows you to track operations carried out by the enterprise.
Which accounts are considered off-balance sheet according to accounting rules?
The list of off-balance sheet accounts is given in our table:
| Purpose |
| Rented OS |
| Inventory accepted for storage |
| Materials accepted for recycling |
| Goods accepted for commission |
| Equipment accepted for installation |
| Written off debt of insolvent debtors |
| Security for obligations and payments received |
| Security for obligations and payments issued |
| Leased operating systems |
IMPORTANT! In case of economic necessity, companies can open sub-accounts or additional off-balance sheet accounts, securing them in the working chart of accounts.
A sample working chart of accounts can be found in the article.
Off-balance sheet accounting of materials and equipment
In addition to fixed assets and goods, other material assets can be taken into account on the balance sheet.
Inventory in safekeeping
In some cases, buyers cannot account for material assets on balance sheet accounts. In this case, records should be kept.
Invoice 002 is needed if the buyer accepted inventory items for storage when:
- receiving goods and materials from suppliers for which the organization legally refused to accept invoices of payment requests and pay them;
- receiving from suppliers unpaid inventory items that cannot be used under the terms of the contract until they are paid;
- receipt of goods and materials, the ownership of which has not been transferred to the organization, etc.
Note!
VAT deduction cannot be claimed while inventory items are taken into account on the balance sheet (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 22, 2016 No. 03-07-11/48963).
Suppliers can also take into account inventory items on account 002 if the goods are paid for, but not removed by the buyer for reasons beyond the control of the organizations.
Provided raw materials
If a company works with customer-supplied raw materials, then account 003 “Materials accepted for processing” is used for accounting. Most often, they work with customer-supplied raw materials during the construction of facilities. In this case, the customer’s building materials are used to complete the work. Also, customer-supplied raw materials are used in the production of products for the customer. While the manufacturing process is underway, customer-supplied materials are accounted for in account 003.
Reception of customer-supplied raw materials is reflected in the debit of account 003, disposal (return of remaining raw materials or manufactured products) is reflected in the credit of account 003. Analytical accounting in account 003 is carried out by customers, types, grades of raw materials and materials and their locations.
Installation equipment
When installing equipment owned by the customer, contractors keep records of the equipment in account 005 “Equipment accepted for installation.”
Acceptance of equipment for installation is reflected in the debit of account 005; write-off of equipment from accounting after installation and delivery of it to the customer is reflected in the credit of account 005. Analytical accounting is carried out for customers, objects, and components of the equipment being installed.
Recording property in off-balance sheet accounts will help control its safety. Also, such accounting will increase the vigilance of financially responsible persons and help the company avoid fines.
Service Expert Standard
Rogacheva E.A.