At its core, leasing is a type of rental. Therefore, activities in this area are regulated by general rules of civil law, both in relation to leasing, and there are also special provisions relating specifically to leasing. In addition, leasing activities are regulated by Federal Law No. 164-FZ of October 29, 1998 “On financial lease (leasing)”.
Although the laws stipulate general rules for conducting activities in the field of financial leasing, the parties to such relations can independently establish different conditions of leasing agreements. Depending on these conditions, accounting for leasing transactions may vary significantly.
Perhaps the most important thing, which most affects both tax and accounting, is the condition on the balance sheet of which of the parties - the lessor or the lessee - the property will be taken into account.
Leasing agreement
Under a financial lease agreement, the lessor is obliged to purchase the property specified by the lessee and provide this property for use by the lessee. In this case, the latter independently determines from which specific seller this property should be purchased.
This is interesting
The total amount of the leasing agreement may include the redemption price of the leased asset. This is possible if the contract provides for the transfer of ownership of the property to the lessee.
In other words, the main difference between leasing and rental agreements is that the lessor purposefully buys property known in advance to lease it from a seller agreed upon by the parties. When renting, your own property is transferred, which is not specifically purchased for a specific tenant.
The subject of leasing agreements can be any non-consumable things, for example, buildings, structures, vehicles, equipment and other movable or immovable property. The exception is land plots and other natural objects, as well as property, the free circulation of which is prohibited by law.
It is worth noting that the ownership of the leased asset remains with the lessor throughout the duration of the contract. The lessee has the right only to temporary possession or use.
But at the same time, leased property can be taken into account on the balance sheet of either party. Consequently, depreciation will be calculated by the person who is the balance sheet holder. This condition is agreed upon by the parties when signing the contract.
The participants set the validity period of financial lease agreements independently and record it in the document. It is impossible to conclude such an agreement, unlike a lease, for an indefinite period, since leasing payments are tied to the duration of the agreement. It can only be extended, and the previous conditions may be changed or retained. The leasing agreement also stipulates the terms on the amount, method and frequency of payment of leasing payments.
Leasing payments mean the total amount of payments under the leasing agreement for the entire period of its validity, which includes:
- reimbursement of the lessor's costs for the purchase and transfer of the leased asset to the lessee;
- reimbursement of costs for services provided for in the leasing agreement;
- lessor's income.
Payments under leasing agreements can be established:
- in a fixed amount of payments made periodically or at a time;
- in the share of products, fruits or income received as a result of the use of leased property;
- in the provision by the lessee of certain services;
- in the transfer by the lessee to the lessor of a thing stipulated by the contract for ownership or temporary possession (use);
- in imposing on the lessee the costs of improving the leased asset.
Also, the parties may provide in the leasing agreement a combination of these forms or other forms of leasing payment. In addition, the parties can agree to change the amount of leasing payments. But you can change it no more than once every three months.
Results
The lessee depreciates the leased asset recorded on its balance sheet according to the rules of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, PBU 6/01, Methodology for accounting for fixed assets and Guidelines for accounting for leasing operations. The lessee has the right to an accelerated depreciation rate in both NU and BU, but subject to certain conditions.
You can read more about accounting and taxation of leasing transactions in the articles:
- “Transactions for leasing a car from the lessee”;
- “Redemption value of leased property (transactions)”;
- “[INCOME TAX]: Leasing payments are not always another expense”;
- “Who pays transport tax when leasing a car?”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Transfer of property to the balance of the lessee
As noted above, the lessor will have ownership of the property. But the lessee can take it into account on his balance sheet.
Dangerous moment
The lessor may write off lease payments from the current account without dispute if the lessee fails to pay them more than twice in a row.
The transfer of the leased asset is reflected in accounting on the basis of supporting documents - a transfer and acceptance certificate or another document that reflects the fact of transfer.
There is no document form specifically established for these operations. Although many use unified forms of the act of acceptance and transfer. Form No. OS-1 is used when transferring fixed assets, form No. OS-1a when transferring buildings and structures, and form No. OS-1b when transferring a group of fixed assets (all these forms are approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7) .
At the same time, participants in leasing relations can independently develop the form of the transfer document. The main thing is that it contains all the required details:
- Title of the document;
- date of document preparation;
- name of the organization on behalf of which the document was drawn up;
- content of a business transaction;
- natural and monetary expression of a business transaction;
- persons responsible for the transfer of property, indicating their positions;
- personal signatures of these persons.
The lessee can account for the property using the inventory number assigned by the lessor. To do this, you need a copy or extract from the lessor's inventory card for the fixed asset. In this case, it would be better if the lessee’s accountant opens new inventory cards for these objects based on the copies provided. The form of the inventory card is also unified - form No. OS-6.
Accounting with the lessee
Property on the lessor's balance sheet
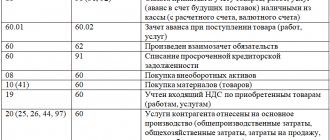
This is perhaps the simplest and most common option. With it, the lessee, as in a regular lease, reflects the property on off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets.”
The leased asset is reflected at the cost specified in the agreement. In this case, the accountant will reflect transactions for receiving property as follows:
DEBIT 001
– property was received on lease;
CREDIT 001
– the leased property is returned at the end of the lease agreement.
Analytical accounting for account 001 is carried out separately both for lessors and for each leasing object.
In this option, depreciation will be charged by the lessor, since the property is reflected on its balance sheet.
In addition, the leased object will also not be reflected in the recipient’s tax accounting. This again relates to the balance holder of the property. Example 1
Orbita LLC leased commercial equipment in March 2010.
In the leasing agreement, the cost of the leased asset is estimated at 1,700,000 rubles. The property is recorded on the lessor's balance sheet. The leasing agreement ended in March 2012. In the accounting records of Orbita LLC it is necessary to reflect: In March 2010: DEBIT 001
– 1,700,000 rubles.
– production equipment was leased. In March 2012: LOAN 001
– RUB 1,700,000. – commercial equipment is returned at the end of the lease agreement.
Property on the balance sheet of the lessee
With this option, the lessee accepts the property as a fixed asset. The initial cost is formed on account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, on the sub-account “Property received on lease” in correspondence with account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” on the sub-account “Lease obligations”.
It is important
The transfer of leased property to the balance of the lessee is not subject to VAT. Since the lessor remains the owner, regardless of whose balance sheet the property is listed on, no sale operation occurs. This means that the value of the property in the lessee’s accounting is reflected without VAT.
The initial cost consists of the cost according to the leasing agreement plus the costs of bringing the property to a condition suitable for use.
The following entries must be reflected in the lessee's accounting:
DEBIT 08, subaccount “Property received on lease” CREDIT 76, subaccount “Rental obligations”
– reflects the cost of the leased property under the contract;
DEBIT 08 CREDIT 60 (76, 70, 69 and others)
– reflects the costs associated with obtaining leased property.
After accounting for the initial cost, the property is included in fixed assets. To do this, you should open a subaccount “Property received on lease” to account 01 “Fixed Assets”. Example 2
Let's use the conditions of example 1 and change them a little.
The property is recorded on the lessee's balance sheet. In addition, transportation of commercial equipment is carried out by Orbita LLC at its own expense. Transport costs amounted to 59,000 rubles, including VAT – 9,000 rubles. Transportation costs were paid in March 2010. The accountant needs to make the following entries (see table 1): Table 1
| Explanation of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The cost of leased equipment is reflected | 08-9 | 76-5 | 1 700 000 |
| Equipment delivery costs reflected | 08-9 | 60 | 50 000 |
| The amount of “input” VAT on the cost of delivery services is taken into account | 19 | 60 | 9000 |
| Leased equipment was put into operation | 01-9 | 08-9 | 1 750 000 |
| Accepted for deduction of VAT on the cost of transport services | 68-1 | 19 | 9000 |
| Transport services paid | 60 | 51 | 59 000 |
Since depreciation on the leased property is calculated by the balance sheet holder, then with this option the lessee will be able to depreciate it in accounting.
Depreciation can be calculated from the month following the month in which the object was accepted for accounting in account 01 “Fixed Assets”. For accounting purposes, the useful life can be taken as the duration of the leasing agreement.
This is interesting
If the validity period of the leasing agreement coincides with the useful life of the object in accounting, this will lead to a discrepancy with tax accounting. Therefore, it is more expedient to use in accounting the useful life that is established for tax accounting.
The lessee must reflect the accrued depreciation in accounting in the general manner, using production cost accounts, depending on the purposes of using the leased property in correspondence with account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets”, under the subaccount “Depreciation of leased property”. In this case, the wiring is done:
DEBIT 20 (23, 25, 26, 44, 91) CREDIT 02-9
– depreciation has been calculated on the leased property.
It is worth noting that the amount of accrued depreciation is directly related to the accrual of lease payments. For accounting purposes, the lease payment is an expense, and it is recommended to reflect it by posting:
DEBIT 76, subaccount “Lease obligations” CREDIT 76, subaccount “Arrears on leasing payments”
– lease payment accrued for the reporting period.
However, in this case there will be no reflection of the expense for accounting purposes. In this regard, it is better to reflect the lease payment as an expense in the general manner, depending on the purpose of using the property:
DEBIT 20 (23, 25, 26, 44, 91) CREDIT 76 (6 0)
– lease payment accrued for the reporting period.
Moreover, if the lessee includes both the lease payment and depreciation in expenses, this will lead to double counting of expenses. So depreciation must be reflected by posting:
DEBIT 76, subaccount “Rental obligations” CREDIT 02, subaccount “Depreciation of leased property”
– depreciation was accrued for the reporting period.
Example 3
Let's use the conditions of example 2. Let's expand them.
Let the useful life of commercial equipment be five years. Since the equipment was registered as a fixed asset in March 2010, depreciation must be calculated from April. The annual depreciation rate will be: 1: 5 years X 100% = 20%. The annual depreciation amount will be: RUB 1,750,000. X 20% = 350,000 rub. Therefore, the amount of depreciation for April will be 29,167 rubles. (RUB 350,000: 12 months). The following entries must be made in accounting (see Table 2): Table 2
| Explanation of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The cost of leased equipment is reflected | 08-9 | 76-5 | 1 700 000 |
| Equipment delivery costs reflected | 08-9 | 60 | 50 000 |
| The amount of “input” VAT on the cost of delivery services is taken into account | 19 | 60 | 9000 |
| Leased equipment was put into operation | 01-9 | 08-9 | 1 750 000 |
| Accepted for deduction of VAT on the cost of transport services | 68-1 | 19 | 9000 |
| Transport services paid | 60 | 51 | 59 000 |
| Depreciation accrued for April on leased property | 76-5 | 02-9 | 29 167 |
Advantages
The possibility of accruing accelerated depreciation when leasing motor vehicles allows you to:
- reduce the amount of tax levied on the property of organizations. The tax base for property tax is determined by the amount of the residual value of each object registered by the company, and the use of accelerated depreciation makes it possible to reduce the value of residual assets, thereby reducing the total amount of tax;
- reduce the amount of corporate income tax by increasing depreciation charges. However, this opportunity is available only during the validity period of the leasing agreement;
- significantly reduce the purchase price of the vehicle. As a rule, leasing agreements are concluded for no more than the useful life of a vehicle (special purpose equipment), which on average is 7–10 years.
The process of calculating accelerated depreciation allows you to actually completely “write off” vehicles from the company’s balance sheet, which will lead to a minimum redemption value.
In addition to these advantages, it can be additionally noted that depreciation allows minimizing the risks of both manufacturers and consumers of automotive and special equipment:
- Manufacturers, by receiving additional amounts, have the opportunity to quickly develop new modifications of vehicles for various purposes, taking into account modern requirements;
- consumers have the opportunity to constantly update their vehicle fleet and work with modern and new equipment, which significantly increases labor productivity and helps increase company profits.
Thus, the possibility of accruing accelerated depreciation allows you to obtain additional profit by reducing the cost of paying income and property taxes of the company.
However, it should be taken into account that the possibility of accruing accelerated depreciation is available only to the company whose balance sheet reflects the property transferred under the leasing agreement.
What the UNIDROIT Convention on International Financial Leasing says is described in the article:
international leasing
.
For car leasing conditions for legal entities in St. Petersburg, see the page.
Find out about leasing trucks for individuals without a down payment from this information.
Accounting with the lessor
Under a leasing agreement, the lessor purchases property specifically for the lessee. To do this, he enters into a purchase and sale agreement with the equipment supplier. A purchase and sale agreement is required to complete a property leasing transaction.
The acquisition of property must be reflected in accounting.
In accounting, the initial cost is formed on account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. Then the object is accepted for accounting in account 03 “Profitable investments in material assets”.
In this case, the lessor has the right to deduct VAT amounts from the cost of the acquired property.
After reflecting transactions for the acquisition of property and its acceptance for registration, transfer to the lessee is carried out.
Property on the lessor's balance sheet
The property should be reflected in account 03 “Income-generating investments in material assets” in the sub-account “Property leased”. At the same time, a second sub-account “Property intended for leasing” is also opened to this account.
The lease transfer is reflected by the following posting:
DEBIT 03, subaccount “Property leased” CREDIT 03, subaccount “Property intended for lease”
– the lessee’s property is leased.
Depreciation in this case is calculated according to the general rules.
The lessor will be able to calculate depreciation in accounting from the month following the one in which the object was accepted for accounting in account 03 “Profitable investments in tangible assets.”
The amounts of accrued depreciation on property leased will be reflected in accounting in the general manner, as for own property - on account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets”. However, depreciation on leased property must be taken into account separately. To do this, you can open an additional subaccount “Depreciation on property leased.”
The depreciation entry will look like this:
DEBIT 20 CREDIT 02, subaccount “Depreciation on property leased”
– depreciation has been calculated on the property leased.
Example 4,000
Lada entered into a leasing agreement with Orbita LLC in March, according to which it purchased retail equipment.
The cost of the equipment was 1,770,000 rubles. (including VAT - 270,000 rubles). The property is accounted for on the lessor's balance sheet. Lada LLC paid the seller for commercial equipment in March. In the same month, the property was transferred to the lessee. The useful life is five years. The annual depreciation rate will be: 1: 5 years XX 100% = 20%. The annual depreciation amount will be: RUB 300,000. (RUB 1,500,000 X 20%). The depreciation amount for April will be: RUB 25,000. (300,000 rubles: 12 months). The accountant of Lada LLC will make the following entries (see table 3): Table 3
| Explanation of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The costs of purchasing equipment are reflected | 08 | 60 | 1 500 000 |
| VAT on purchased equipment has been taken into account | 19 | 60 | 270 000 |
| Payment for equipment has been made | 60 | 51 | 1 770 000 |
| Equipment for leasing accepted for accounting | 03-1 | 08 | 1 500 000 |
| Accepted for deduction of VAT on the cost of equipment | 68-1 | 19 | 270 000 |
| Equipment leased | 03-2 | 03-1 | 1 500 000 |
| Depreciation accrued for April on leased property | 20 | 02-1 | 25 000 |
Property on the balance sheet of the lessee
The question of how the lessor should account for property if it is on the lessee’s balance sheet is not resolved by law.
It is worth noting that it would be incorrect to use financial performance accounts (accounts 90 and 91) for accounting, since there is no transfer of ownership of the property. So you can’t simply write off the cost of the property as an expense.
The operation of transferring property under lease can be reflected on the lessee’s balance sheet in account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” (increase accounts receivable). That is, when transferring, you need to make the following wiring:
DEBIT 76 CREDIT 03
– the leased property is transferred to the balance of the lessee. The leased asset in this case is reflected at its original cost (the cost at which the object is listed on the lessor's balance sheet).
At the same time, the lessor reflects the transferred property on off-balance sheet account 011 “Fixed assets leased out.” The value of the property in this case is indicated according to the leasing agreement.
Posting for this operation:
DEBIT 011
– the value of the leased property transferred to the balance sheet of the lessee is reflected on the off-balance sheet account. Due to leasing payments, the value of the property will be written off as follows:
DEBIT 20 CREDIT 76
– expenses are reflected in relation to the cost of the property included in the lease payment for the current period.
Depreciation on leased property that is transferred does not need to be calculated. In tax accounting, depreciation will also not be charged.
The costs of acquiring leased property will be included in other costs associated with production and sales.
At the same time, such expenses must be taken into account in those reporting periods in which leasing payments are provided. In this case, these expenses are taken into account in an amount proportional to the amount of leasing payments (similar to accounting). Example 5
LLC Lada entered into a leasing agreement with LLC Orbita in March for three years (36 months), according to which it purchased commercial equipment.
The cost of the equipment was 1,180,000 rubles. (including VAT - 180,000 rubles). The property is recorded on the lessee's balance sheet. Payment for the equipment was made in March. In the same month, the property was transferred to the balance of the lessee. The total amount of lease payments for the entire leasing period is 1,699,200 rubles. (including VAT - 259,200 rubles). The cost of the property is equal to the total amount of lease payments and amounts to RUB 1,699,200. The lessee pays monthly lease payments of 47,200 rubles. (including VAT - 7,200 rubles). Lada LLC calculates income tax on a monthly basis. To determine the amount of costs associated with the purchase of equipment, which can be included in income tax expenses for March, you need to calculate the proportion: 40,000 rubles . : (RUB 1,699,200 – RUB 259,200) X 100% = = 2.7778%. Therefore, for March you can include in other expenses an amount of 27,778 rubles. (RUB 1,000,000 X 2.7778%). Lada LLC will reflect the following entries in its accounting (see Table 4). Table 4
| Explanation of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The costs of purchasing equipment are reflected | 08 | 60 | 1 000 000 |
| VAT on purchased equipment has been taken into account | 19 | 60 | 180 000 |
| Payment for equipment has been made | 60 | 51 | 1 180 000 |
| Equipment for leasing accepted for accounting | 03-1 | 08 | 1 000 000 |
| Accepted for deduction of VAT on the cost of equipment | 68-1 | 19 | 180 000 |
| The equipment was transferred to the balance of the lessee | 76 | 03 | 1 000 000 |
| The off-balance sheet account reflects the cost of leased equipment | 011 | 1 699 200 | |
| Lease payment accrued for March | 62 | 90-1 | 47 200 |
| VAT charged on lease payment | 90-3 | 68-1 | 7200 |
| Received leasing payment from the lessee for March | 51 | 62 | 47 200 |
| Expenses are reflected in terms of the cost of equipment included in the lease payment for March (RUB 1,000,000: 36 months) | 20 | 76 | 27 778 |
Who charges and how, example of calculation
So, accelerated depreciation is applied by the party (lessor or lessee) of the leasing transaction on whose balance sheet the leased asset is reflected.
AMu=AM*K,
| AMu | this is the amount of accelerated depreciation |
| AM | depreciation amount |
| TO | applied multiplying factor |
AM = C initial * N,
| From initial | initial cost of the vehicle at the end of the reporting period |
| N | depreciation rate |
N = 1/n*100%,
n is the useful life of the vehicle, established by the manufacturer or the parties to the leasing agreement independently.
AM = B*N|100,
| IN | the total cost of property included in a certain depreciation group |
| N | depreciation rate established by law (reflected in Article 259.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
The increasing coefficient (K), which increases standard depreciation, is determined by the parties to the leasing agreement independently, but taking into account all the requirements of current legislation (that is, in this situation it cannot be more than 3).
For a more accessible understanding of these formulas, we will give an example of calculating the amount of accelerated depreciation.
Let us assume that depreciation accrued according to the accelerated type must be determined for a car worth 1,200,000 rubles.
N = 1/36*100 = 2.78
Under these conditions, the depreciation rate will be 2.78%
AM = 1200000*2.78/100 = 33,333.33,
that is, every month the amount of depreciation conditions using the standard calculation method will be 33,333 rubles.
Accelerated depreciation (AMu) in this example will be 33,333*3=99,999 (rubles).
This means that the company will write off depreciation charges in the amount of 99,999 rubles every month.
AM = 1,200,000*3.8 (indicator obtained from Article 259.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)/100 = 45,600 (rubles).
AMu = 45600*3 = 136,800 (rubles).
As can be seen from the example, calculating depreciation in a non-linear way, all other things being equal, allows you to increase the amount of depreciation charges, but it is worth considering that the parameter calculated in this way will decrease monthly in accordance with the decrease in the residual value of the vehicle.
Property tax
The party to the leasing agreement that has the property on its balance sheet will be charged and paid corporate property tax.
So, if the property is accounted for on the lessor’s balance sheet, then he reflects it in account 03 “Income-generating investments in tangible assets.” The lessee records the leased asset on the balance sheet in account 001 “Leased fixed assets”. In this case, property tax on leased items is paid by the lessor.
If the leased property is taken into account on the balance sheet of the lessee, then it is reflected in account 01 “Fixed Assets”. The lessor records the transferred property on the balance sheet in account 011 “Fixed assets leased out.” Therefore, the lessee pays the property tax.
At the end of the lease agreement, the tax must be paid by the person who becomes the owner of the leased asset. For example, if the purchase of property is provided, then the lessee will pay property tax.
Transport tax
The payer of transport tax is the person in whose name the vehicle is registered.
If the car is registered to the lessor, then he will be the payer during the term of the agreement. And if the repurchase of the property is not provided, then at the end of the contract.
If you decide to register the vehicle in the name of the lessee, then the following options are possible:
1)
temporary registration of the car to the lessee. In this case, upon purchase, the vehicle is first registered in the name of the lessor, and then registered in the name of the lessee for the duration of the contract. The lessor will still be the tax payer (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 16, 2011 No. 03-05-05-04/12);
2)
registration of the vehicle initially in the name of the lessee. In this case, the payer will be the lessee. Moreover, if the purchase of the car is not provided, then the obligation to pay tax at the end of the contract will pass to the lessor only after re-registration of the vehicle.
D. Nacharkin, expert editor