For certain reasons, it happens that a company is unable to receive funds for shipped products for a certain period of time. It is precisely in these cases that it is necessary to reflect such operations in the 45th position. Today’s topic is devoted to the questions of what finished products are, what should be understood by shipped goods and how they are sold, what is the purpose of account 45 in accounting, what accounting records are kept, and we will also look at one of the practical examples.
Definition of finished products and goods
Upon completion of the production process, the company obtains a finished product from the raw materials used. This product is fully stocked, transferred to the warehouse and is ready for sale.
Finished products should be perceived as part of the inventory that will subsequently be sold and meet the required technical parameters and quality standards.
Goods that were received or purchased from business entities or citizens for subsequent sale can also be perceived as part of production inventories.
If we consider the flow diagram of the finished product, it consists of the following stages:
- receipt of a batch of product at the warehouse;
- shipment of the finished batch to consumers.
When maintaining accounting records, a unit of a finished product is determined by the company in such a way that the company's management can obtain adequate information about the status of these inventories, as well as ensure adequate control over their movement and balances. Finished products enter the warehouse from the production workshop under the responsibility of the material person.
Options for the sales volume analysis methodology
There are two main options for researching sales volume. They depend on how the organization recognizes revenue.
- The first option involves recognizing revenue from shipment, that is, the number of goods shipped is considered equal to the number of products sold.
- In the second option, revenue is recognized upon payment, that is, not immediately upon shipment, but only after receipt of money from the buyer into the account (by the way, this can happen before the goods are sent to him; in this case, the fact of shipment itself is not taken into account).
Goods shipped are...
This definition should be understood as those inventories, the proceeds from the sale of which cannot be recorded in the appropriate accounting records.
If we talk about Form No. 1 of financial statements, then the price of finished products shipped to customers is recorded on line 080 of the balance sheet. In this line, the accountant enters the debit balance of account 45 at the end of each reporting period.
In general, property rights to certain inventories are transferred to the customer after their delivery last. However, there are some exceptions to this general rule:
- in the case of transfer of goods in accordance with an exchange agreement (in this case, the buyer acquires property rights only after the counter shipment has been made;
- if the goods are transferred under a purchase and sale agreement, which provides for a special procedure for transferring ownership. According to such documents, the person purchasing the goods receives ownership of it only after certain conditions are met, for example, payment of its cost or delivery to the designated point;
- in case of transfer to an intermediary for further sale. In this case, we are talking about a commission, commission or agency agreement.
In what cases is count 45 used (brief description of the count)
Account 45 - Goods shipped - is used if goods are sold with a delay in the transfer of ownership, for example, when exporting products, barter exchange, transferring goods to a commission agent (intermediary, agent) for sale for a commission and under similar agreements.
Until the special conditions of the contract are met, the goods continue to belong to the seller. Hereinafter, the word “goods” should be understood as any transferred property: goods, products, semi-finished products, materials, farmed animals, works, services.
Revenue from such transfer of goods cannot be recognized until a number of conditions specified in the contract are met, for example: when selling for export - until supporting documents are received from the buyer; when transferring for sale on a commission - until the commission agent's report and payment are received goods sold by him.
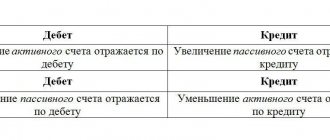
Account 45 is the active account. In the seller's accounting, the debit of account 45 - Goods shipped - reflects the actual (production) cost and commercial expenses for the shipment/delivery of transferred goods. The loan is written off at cost when conditions are met to reflect actual sales.
The debit balance on account 45 represents the balance of goods shipped but not sold at the end of the period and is included in line 1210 “Inventories” of the seller’s balance sheet.
In the buyer's accounting, these goods (products) are reflected in off-balance sheet accounts until the contract is executed.
Analytical accounting of the account is carried out for individual types of goods shipped and by their location (counterparties).
Sale of shipped goods
The reflection of transactions for the sale of the shipped lot will depend on the conditions reflected in the contract, including such points as:
- how the goods are transferred to the buyer, i.e. is there an intermediary or is the work carried out directly;
- at what stage the ownership of the goods passes to the buyer, for example, at the time of shipment or after the transfer of funds as payment for the products received.
Let us assume that the contract concluded with the buyer includes special conditions for the transfer of ownership and disposal of purchased products. The terms of such an agreement should also provide for the risk of accidental damage to the goods received after receiving payment for them.
An example of reflecting sales on account 45
Conditions of the problem
Company A sold goods for the amount of 35,400 rubles, including VAT 18%, with the condition that the rights to the goods would be transferred to the buyer after full payment. The cost of the goods was 20,000 rubles.
The accounting policy of company A establishes the accrual method and determination of the taxable base for VAT after shipment of goods and materials.
Solution
Postings in the accounting of company A in account 45 for this operation:
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | Contents of operation |
| After the goods have been shipped: | |||
| 45 | 41 | 20 000 | The cost of shipped goods is written off |
| 45 (VAT) | 68 | 5 400 | VAT charged on shipment (35,400 / 118 × 18) |
| After payment for the goods: | |||
| 51 | 62 | 35 400 | Buyer's payment taken into account |
| 62 (76) | 90.1 | 35 400 | Revenue is recognized from actual sales |
| 90.3 | 45(VAT) | 5 400 | VAT charged to the buyer is reflected |
| 90.2 | 45 | 20 000 | The cost of this sale has been written off |
| 90.9 | 99 | 10 000 | The financial result based on the sales results was calculated (35,400 – 5,400 – 20,000) |
Necessity and significance of position 45
45 account is necessary in order to summarize data on available shipped products and their movement, the proceeds from the sale of which cannot be recognized at this stage. For this item, companies also keep records of finished products transferred to the commission for subsequent sale.
The specified account is active. Accounting reflects the cost of the shipped consignment based on its actual cost and the cost of shipping the goods.
Account 45 is debited in correspondence with positions 41 and 43.
Results
Finished products remaining in the warehouse on the reporting date will appear in the balance sheet line reflecting the amount of inventory and will become its component.
The cost of finished products is formed by 2 rules: acceptance for accounting at the actual costs of its creation and disposal in the assessment chosen by the taxpayer (at the cost of a unit, average or first acquisitions). Accounting for the movement of products during the month of production, when the actual cost has not yet been formed, is carried out at the accounting cost, which is then adjusted for the amount of deviations. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to calculate the volume of products sold according to the balance sheet
Reporting is the main source of information for analyzing all the economic characteristics of any enterprise. After all, it presents the final indicators for the time period under study.
To calculate the volume of goods produced and sold using reporting forms, we will need the following lines:
- 2110 “Revenue” from the income statement;
- 2120 “Cost of sales” from the income statement;
- 12105 “Inventories” from the balance sheet.
The volume of products sold is equal to the number on line 2110 of the second form.
Production volume is calculated as follows:
the amount on line 12105 at the end – the amount on line 12105 at the beginning + the amount on line 2120.
Products shipped to the buyer. Accounting, accounting
Shipped products, which are part of the finished product and goods intended for resale, are accounted for as part of the organization's current assets.
Data is generated in a separate account in accounting due to the fact that transaction operations may be accompanied by commission payments, special conditions relating to the transfer of ownership of the object of the agreement (before or after payment), and barter relations.
Some features of the sale of the shipped product
The shipment of commercial products is accompanied by a change and transfer of ownership of it. A change of owner takes place in a situation where goods are sold when (Article 223 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- the product is delivered to the buyer by the seller;
- delivery of valuables to the buyer is carried out by a third-party carrier;
- The transfer of products by the manufacturer is made to the seller directly.
The fact of sale is accompanied by documents (contracts, invoices, acceptance certificates).
It is not prohibited by law to use in a contract the moment of changing ownership of the commodity mass upon its receipt or during a certain period, including after making partial payment, immediately at the time of transfer of the product to the buyer’s warehouse. But any condition must necessarily be reflected in the agreement of the parties to the transaction.
Payment for the commodity mass is made by the buyer at the time of receipt or within a certain period agreed upon by the parties. After making the payment, the recipient of the product becomes its full owner.
If money for the delivered product is not transferred within the time period previously agreed upon by the parties, the goods must be returned to the seller. If the payment deadline is missed, the seller has the right to demand the return of the product or payment for it.
For your information! Such conditions are indicated in the agreement of the parties, as well as the criteria for changing the copyright holder of the subject of the contract or the right of disposal by the acquirer before the end of the settlement procedure.
Reflection of shipped goods in accounting
In accounting, the cost of shipped products belongs to the inventory section, where finished products of other types are also reflected. Reflection (according to account 45) is carried out at actual or planned cost, taking into account sales costs.
The moment of receipt of revenue (payment) is recorded by the seller upon shipment of the product with the transfer of ownership of the subject of the transaction. For companies using a simplified taxation system, revenue is recorded after actual payment for the product.
At the time of recognition of revenue, expenses associated with the manufacture and sale of the product are subject to accounting (PBU 10/99; Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 119n, December 28, 2001).
When transferring ownership of a product after final settlement and determining the VAT base after shipment of the subject of the transaction, accounting transactions look like this:
- Debit account 45 / Credit account 41 (shipment of the product based on its actual cost).
- Debit account 45 / Credit account 44 (writing off other expenses incurred on shipment).
- Debit account 90 / Credit account 45 (recognition of the fact of sale after payment).
- Debit account 45 / Credit account 68 (VAT accrual on shipped products).
When ownership changes and its transfer to the acquirer, a sale takes place, and accordingly, receipts and expenses are subject to accounting on the account. 90 based on primary documents (Federal Law No. 402, December 6, 2011).
When selling products for cash, the following posting is made in accounting: Debit account. 50 / Credit account 90.1 , for non-cash payments: Debit account. 62 / Credit account 90.1.
For your information! The actual cost of sales must be written off in a manner that takes into account the method of registration of finished goods by the enterprise (at actual or standard cost).
The cost of products to be written off as expenses is determined in one of the following ways:
- at cost (inventory units);
- using the FIFO method;
- at average cost.
The choice of valuation method must be enshrined in the accounting policy of the enterprise (order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 119, December 28, 2001; letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 07-05-14/298, November 16, 2004; PBU 5/01).
Accounting in the presence of special contract conditions
The right of ownership may remain with the seller even after the actual transfer of the product to the buyer until the occurrence of certain circumstances provided for by the relevant agreement of the parties to the transaction (Article 491 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In such situations, there is a discrepancy between the periods of product shipment and recognition of receipt of funds.
Therefore, if there is a special moment in the transaction (change in ownership), VAT will be charged at the time of shipment without taking into account the fact of receipt of payment.
Revenue will be recognized only after receipt of additional payment from the buyer (Article 39, 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Deferment of VAT obligations from the time of shipment of the product until the receipt of payment for it is not permitted.
Due to the time difference between the date of shipment and the date of payment, the reflection of VAT on the sales invoice (Dt) to the tax settlement accounts (Kt) is incorrect. As an option, you can use an account for settlements with debtors and creditors:
- Debit account 76 / Credit account 68 – upon shipment.
- After the change of owner and recognition of payment (revenue) – Credit account. 76 / Debit account. 90 (sales).
But in this option, there is the formation (Dt account 76) of fictitious receivables. It would be more correct to use account 97 for VAT accounting for expenses expected in future periods.
If there is a special point in the agreement between the parties to the transaction regarding the change of the holder of ownership of the product, the shipped goods (from accounts 41 (goods) or 43 (finished products)) cannot immediately be taken into account in the debit of the sales account (90). Until the owner changes, the product is listed on account 45, intended for accounting for shipped products. Accounting is carried out not at the sales price, but at the cost used for accounting on the account. 41(43).
Return of shipped products
The purchaser, who discovers upon acceptance of receipt a discrepancy between the shipped products and the terms of the agreement, draws up a report on the identified discrepancies, issues a written claim to the seller, and an invoice with a return note. The second copy of the document is recorded by the consumer in the sales book, the seller enters the received invoice into the purchase book as the right to a tax deduction is formed (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-15/29, 03/07/2007).
If the return of the defect occurred in the same tax period, the seller makes adjustments to sales (account.
90), if the return occurred in the next calendar year, then the cost of the returned object is included in the accounts of non-operating costs as a loss of the past period, which was determined in the reporting year (account 91):
- Debit account 91 / Credit account 62 (loss of the past period discovered in the reporting period);
- Debit account 43 / Credit account 91 (restoration of the cost of returned goods, previously written off);
- Debit account 68 / Credit account. 91 (profit of previous years calculated in the reporting year in the amount of VAT paid).
Defects identified before the end of production are accounted for in the main production: Debit account. 28 (manufacturing defect) / Credit account. 20, and defects detected upon completion of production - in finished products: Debit account. 28 / Credit account 43.
For your information! When returning goods, the seller has the right to deduct the VAT amount (Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). A deduction is allowed no later than 12 months from the date of return and in full after reflecting adjustment entries for the return (rejection) of the product.
The amount of VAT sent by the seller to the budget upon sale is deducted for the period in which there are adjustment entries due to returns. In this case, when sending a replacement to the buyer, the seller issues an invoice to him.
If the defect returned in the next tax period, then the profit tax base is subject to recalculation for the period when the goods were sold, or the costs of the cost of the returned product can be attributed to expenses in the form of damage from the defect (Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; letter from the Ministry of Finance RF No. 03-03-05/47, 04/29/2008).
If a defective product can be used in production, perform the following operations:
- Debit account 28 (marriage) / Credit account. 43 (reflection of the cost of marriage);
- Debit account 10 (materials) / Credit account. 28 (posting of the product at the price of possible use);
- Debit account 20 (production) / Credit account. 28.
Therefore, damage from defects will be reduced by the price of a spoiled product suitable for use.
Source: https://assistentus.ru/buhuchet/otgruzhennoj-produkcii/
Analysis of product sales, overall profitability of sales
In general, the volume of products sold can be calculated using the formula:
ORPr = KPr(x) * TsPr(x) , where
KPr(x) – quantity of products of type x;
TsPr(x) – price of product type x.
Example. During the quarter, the plant produced 200 parts A at a price of 200 rubles and 400 parts B at a price of 100 rubles. This means that the volume of products sold in monetary units was:
200 * 200 + 400 * 100 = 80,000 rubles.
This so-called absolute indicator is compared with planned values and levels of previous periods, and growth and growth rates are also calculated from it.
But, as you know, analysis is not limited to the study of absolute indicators. For a more reliable assessment of the enterprise's performance, relative indicators are needed to demonstrate the effectiveness of certain actions. When studying sales volumes, this coefficient is the total return on sales, which is calculated as follows:
RentPr = PPr/Vyr , where
PPr – profit from sales;
Vyr – revenue.
Depending on the purposes of the study, the indicators in the numerator may change. For example, if it is necessary to determine net profitability, then net profit is used instead of operating profit.
Profitability is also studied in dynamics and in comparison with planned values. The factors influencing it are studied. Thus, under other constant circumstances, an increase in the selling price of a unit of a product always leads to an increase in profitability.
Assessment of the dynamics of the volume of products sold
The volume of products sold is generally calculated using the following formula:
ORPr = Vpr + OGPrn – OGPrk , where
ORPR – sales volume;
Vpr – gross product;
OGPRn, OGPRk - the balances of the finished product, respectively, at the beginning and end of the period (usually a year).
The formula contains the concept of gross product. This definition is worth understanding in more detail.
Gross product is the cost of all manufactured products (work performed) for a specific period, including production that has not yet been completed.
Along with this concept, there is also a commodity product - this is the volume of products that are ready for sale, that is, processed accordingly.
In some cases, the volumes of gross and commercial output are equal.
Example. The annual output of products at the plant amounted to 400,000 rubles. At the same time, the balance of finished products at the beginning of the year amounted to 45,000 rubles, and at the end - 70,000 rubles. Accordingly, the annual sales volume is calculated as follows:
400,000 + 45,000 – 70,000 = 375,000 rubles.
Sales volume indicators are studied in dynamics over a certain period. Let's look at how this happens using a specific example. Sales data for the drilling equipment plant over the five-year period are presented in the table.
| Quantities | 1st year (base) | 2nd year | 3rd year | 4th year | 5th year |
| Comparison with base period (%) | 100 | 109,7 | 122,2 | 133,2 | 151 |
| Comparison with the previous period (%) | – | 109,4 | 111,6 | 110,1 | 110,4 |
The average annual growth rate is calculated using the weighted average as follows:
Т = N√Т1*Т2*Т3*…ТN
Substituting the numbers from the table into the formula, we get:
4√1,094*1,116*1,101*1,104 = 1,104 = 110,4%
We conclude that over the five-year period, sales volume increased by 51% with an average annual growth rate of 10.4%.
Volume of product sales in the balance sheet (line)
The balance sheet does not provide a separate line to reflect revenue (or the volume of goods sold). After all, this form of reporting shows the company’s assets, but the sold products, in essence, are no longer assets.
But the revenue is reflected in form number 2 - the Profit and Loss Statement. Here it is shown on line 2110 of the same name.
The balance sheet may reflect products that have already been shipped to the buyer (a sales contract has been concluded with him), but the money for it has not yet been credited to the account. In this case, the organization has accounts receivable, which are shown on the balance sheet line of the same name 1230. It is important to understand that in the balance sheet, revenue on this line is entered with VAT, while in the profit and loss statement a net indicator is used: revenue cleared of tax.
Profit from the sale of the product is reflected in balance sheet line 1370 “Retained earnings/uncovered loss.” Here, the operating profit is supplemented by the profit received from other operations in all types of activities of the company (both main and other).