01.07.2019
0
277
4 min.
Paying taxes is an obligation that applies to every employed member of society. The existing system of collecting fees is a product of gratuitous contributions by individuals and organizations to ensure the functionality of the state, municipalities and the maintenance of disabled categories of citizens. Employees who decide to quit often ask their employer the question: is compensation for vacation subject to an insurance premium or not?
For officially employed people, the employer automatically makes monthly contributions to the inspectorate. Taxable income includes salary, bonuses and vacation payments, work on holidays and overtime, sick leave, compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal.
What payments are due upon dismissal?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes three ways to terminate employment contracts: at the request of the employee, at the initiative of the employer and by agreement of the parties. For each of them, the manager is obliged to transfer the following payments to the resigning person no later than the last working day:
- compensation for unused vacation;
- salary for the period worked.
If the dismissal is due to staff reduction, severance pay is transferred. It may also be provided for by agreement of the parties.
If the dismissed person was in the position of a manager, his deputy or chief accountant, he is also entitled to compensation payments.
In what cases is an employee entitled to compensation?
Sooner or later, every company becomes obliged to provide compensation to an employee who has invested his existing professional knowledge in improving the well-being of the company and its development.
When an employee is entitled to receive funds for vacation without taking a vacation
This obligation arises in two cases:
- if the accumulated period of vacation not taken by the employee exceeds 28 days in quantity and the employee does not intend to use it;
- if the employee decided to quit or was fired.
In the first case, only those employees who have been granted extended leave of a basic nature or have been given an additional period can exchange their days off for money.
From what payments is personal income tax withheld upon dismissal?
Personal income tax stands for personal income tax. They are subject to most of the payments, including compensation upon dismissal. For residents of the Russian Federation, its value is 13%, for non-residents – 30%.
Compensation for unused vacation is transferred regardless of the reason for the employment contract. Taxation of personal income tax is a priority: only after the tax has been calculated, alimony and other payments are withheld from the amount received.
Personal income tax is also transferred from the following income:
- salary, bonuses, allowances;
- temporary disability benefits.
The employing organization is a tax agent, therefore the obligation to transfer personal income tax rests with it. Violation of this rule is subject to administrative liability in the form of a fine, so it is very important to comply with the deadlines and procedure for calculating the tax.
Features of collection and transfer of taxes to the budget
The accounting department deals with taxation issues and transfer of payments. The employee only receives his monthly salary - the remainder after all deductions.
Taxes have an amount and payment deadlines. An individual, not an entrepreneur, as a rule, pays only one tax on his own - on property. Any property owned by a citizen is subject to taxation: a garage, apartment or house.
- Transport tax is paid by car owners; these are annual deductions depending on the cost and year of manufacture of the car. You need to fill out declarations yourself and visit the Tax Committee. However, now you can pay all your bills via the Internet; all you need is a bank card or an e-wallet.
- Income tax is paid by entrepreneurs and people with passive income.
- VAT is a mandatory tax for entrepreneurs; they need to tax the price of products and services.
Tax rates may change; the Tax Code is updated every year. A certificate of the amount and deadline for payment, as well as the code of the required tax, can be found in the code or asked from a tax specialist.
Important: taxes must be paid on time; unscrupulous taxpayers face penalties.
Income not subject to taxation
The list of income from which personal income tax is not withheld is determined by Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This includes the following:
- monthly payments in connection with the birth of children;
- compensation for harm to health;
- payment of allowances in kind;
- severance pay not exceeding three times the average monthly salary, for residents of the North - six times the amount;
- daily allowance up to 700 rubles. while on a business trip.
Expert commentary
Kamensky Yuri
Lawyer
Thus, if on the date of dismissal an employee is due to receive compensation for vacation time and severance pay, these payments will not be taxed. If an employee terminates an employment contract during illness, temporary disability benefits are paid no later than 10 days from the date of receipt of sick leave, while the tax is withheld on the day the benefits are transferred and paid to the Federal Tax Service no later than the last day of the month.
Typical mistakes when calculating personal income tax
Correctly completed tax reporting saves the company from unnecessary costs of fines and other sanctions. Experienced accountants fill out forms correctly, but there is a list of common mistakes. These include:
- It is in vain to apply for a tax deduction after the employee has reached the maximum amount of income from which the benefit can be received.
- Personal income tax is not withheld from a forgiven debt to an individual employee.
- Transfer of authority to pay personal income tax to employees who are not entrepreneurs, for example, for their property.
- The employee's bonus is not taken into account as a type of income when determining personal income tax.
As for the situation with compensation for vacation, a common mistake is to sum up all payments to a citizen and submit one form. As noted above, these are different types of income, so they must be recorded separately.
How is compensation for unused vacation calculated?
The minimum duration of annual paid leave for citizens working under employment contracts is 28 calendar days. For some categories of persons, additional days of rest are provided.
How compensation is calculated:
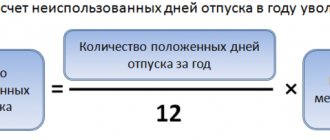
- The number of days of non-vacation is established. To do this, the personnel officer determines the product of the number of days of rest due to the employee for each month worked and subtracts the days already used.
- The resulting number of vacation days is multiplied by the citizen’s average daily earnings.
For example, if a quitter is entitled to 14 days of vacation, and the average daily earnings are 1,500 rubles, the calculation will be carried out as follows: 14 x 1,500 = 21,000 rubles. – the total amount from which personal income tax will be withheld.
21,000 x 13% = 2,730 rub. – personal income tax amount.
21,000 – 2,730 = 18,270 rubles. - the total is in the hands of the employee.
18,270 x 22% = 4,019.4 rubles. – the amount of contribution to the insurance part of the pension paid by the employer.
18,270 x 5.1% = 931.77 rubles. – the amount of payment to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund from the employer’s funds.
Conducting a mandatory audit of financial statements
Possible changes in legislation regarding the criteria for conducting a mandatory audit
Currently, the State Duma is studying a bill that considers increasing the size of the indicators that are the basis for conducting mandatory audits of enterprises.
The original text of the document suggests increasing the limits of financial indicators, which will enable small businesses to leave the category requiring a mandatory audit.
Estimated dynamics of growth in the value of limiting indicators
| Indicator name | Year | ||
| 2021 | 2021 | 2021 | |
| 1. Amount of income, million rubles. | 400,0 | 600,0 | 800,0 |
| 2. Amount of assets, million rubles. | 60,0 | 200,0 | 400,0 |
| 3. Number of employees, people. | more than 100 | ||
According to deputies, the adoption of the bill with amendments regarding increasing the criteria for conducting a mandatory audit will allow small businesses to legally avoid this procedure and direct the freed-up funds to their development.
How to withhold personal income tax from compensation upon dismissal: step-by-step instructions
To understand this issue, you must first study the features of the dismissal procedure:
- The employee submits his resignation. If necessary, the employer has the right to assign mandatory work of 2 weeks.
- The manager issues a dismissal order indicating a specific date. The person leaving gets acquainted with it against signature, then the document is transferred to the personnel department and accounting department. It is the accountant who makes all the deductions, but this can only be done if there is a reason - an order.
- The accountant calculates wages, compensation for unused vacation and other payments minus personal income tax, contributions to the Social Insurance Fund and pension contributions.
- On the last working day, the employee is transferred or given cash. He must also be issued with education documents, a salary certificate, 2-NDFL, and information about the status of his personal account with the Pension Fund.
Important! All charges must be reflected in the documentation. The accountant deals with them, and he also draws up the postings.
Nuances of the procedure
When can I receive my severance pay upon dismissal? Immediately as soon as the corresponding order is issued. The employee takes it to the accountants, who make the calculation.
Is compensation only due to those who quit? No, any employee has the right to ask to replace his vacation with money. To do this, he negotiates personally with the manager, then writes a statement. The accounting department will make the calculations. It is worth remembering that only unused vacation can be compensated.
Can I count on payments if an employee is transferred? Yes, the organization from which he is leaving will make a full payment to him by agreement of the parties.
Is it possible to refuse to pay personal income tax? No. This is a mandatory tax and is paid equally by all employees. Only the amount differs, since the tax is calculated based on the amount of the entire compensation or salary.
Is an employee entitled to compensation if he is fired at the time of layoff? Yes. The employer is obliged to make official payments and registration to the employee. Additionally, he may ask for a reference, to which he also has the right.
According to the current labor legislation of the Russian Federation, it is possible to receive monetary compensation for the annual paid period in several cases.
Thus, Article 126, paragraph 1 of the Labor Code of Russia allows working citizens to replace part of the granted annual vacation period exceeding 28 calendar days with compensation in the form of cash.
This article talks about typical ways to resolve the issue, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, call:
Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the right of an enterprise employee upon dismissal to receive compensation for all unused vacation periods. Relatives of a deceased employee have the same right.
The issue of paying income tax on monetary compensation for the vacation period is regulated by Article 217, Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law No. 117 dated 08/05/2000 (as amended on 12/25/2018, with additions dated 01/01/2019).
Transfer deadline
The deadline for transferring tax to the budget depends on the method of receiving compensation:
| Cash in the bank | No later than the day of issue |
| To the employee's bank account (non-cash transfer) | No later than the day of transfer |
| Cash from the company's cash desk | No later than the day following the date of issue |
Important! If compensation is paid not upon dismissal, but during the citizen’s work, it must be transferred on payday. Payment according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is made every 15 calendar days. If the payment date falls on a weekend, the money must be transferred on the previous weekday.
For example, when an organization pays salaries on the 15th and the date falls on a Sunday, the money must be issued on Friday.
Transfer of funds on the next business day is not allowed, because this will already be considered a delay in wages, and the employer undertakes to pay a penalty for each day of delay.
Types of compensation
There are two types of compensation, depending on the nature and order of their application:
- The compensations provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are so-called mandatory.
- Compensations that are established on a voluntary basis between the employer and the employee are so-called voluntary.
For example , one of the most common types of mandatory compensation may be compensation to an employee for vacation that he did not use.
Calculation and accounting entries
As mentioned earlier, the tax rate on employment contracts for residents of the Russian Federation is 13%. Non-residents are subject to an increased tax of 30%. If citizens have applied for tax deductions or other social benefits, they must be deducted from their salaries, and personal income tax will be withheld from the final amount.
Let's look at practical examples:
A citizen has been working at the company for 3 years. Previously, he received a tax deduction, according to which 1,000 rubles are deducted from the tax amount every month. In May 2021, he decided to quit. The salary for the period worked was 30,000 rubles, compensation for several days of unused vacation was 15,000 rubles. In total, an amount of 45,000 rubles is used to calculate personal income tax and other contributions. How personal income tax is calculated:
45,000 x 13% = 5,850 rub.
After withholding personal income tax, 39,150 rubles remain. Insurance premiums and payments to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund must be paid from this amount. They are transferred by the employer from the enterprise budget.
39,150 x 22% = 8,613 rubles. – the amount of contributions to pension insurance.
39,150 x 5.1% = 1,996.65 rubles. – payment to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
The second example is the payment of state contributions for a non-resident of the Russian Federation:
A foreign citizen works at the enterprise for 2 months, i.e. less than 183 days. This alone does not give him the right to be considered a resident. The decision to resign was made by him in November 2021. He does not yet have the right to leave, so no compensation will be paid. Only wages for the period worked are subject to transfer. In a month, a citizen earned 50,000 rubles. From this money, the employer must withhold 30% of personal income tax - the tax is paid from the employee’s funds. Also, 22% is withheld for the insurance part of the pension, and 5.1% for the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. The last two payments are made from the organization's budget.
50,000 x 30% = 15,000 rub.
50,000 – 15,000 = 35,000 rub. – the foreigner finally received it.
35,000 x 22% = 7,700 rub. – transferred by the company towards pension contributions.
35,000 x 5.1% = 1,785 rubles. – the amount of contributions to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
Accounting entries
In the postings, the accountant reflects all payments as follows:
| DT 44 Kt 70 “F.I.O. employee" | Payroll |
| DT 70 (full name of the employee) Kt 68 Personal Income Tax | Tax withholding |
| DT 70 (full name of employee) Kt 50 (51) | Issuance of wages |
| DT 68 Personal income tax Kt 51 | Transfer of tax to the budget |
Holiday pay accounting
When withholding income tax, the following entries are used:
- DT 68 “Calculations for tax collections.”
- DT 70 “Wages and salaries”.
Accounts numbered 68, 51 can be used for the loan.
Examples
Employee Vasiliev will go on vacation for 28 days from July 2, 2021. His salary was 38,629 rubles. Funds are transferred to the company's reserve account. No deductions are made from vacation pay. Their size will be 5,022 rubles. In this situation, the following wiring is used:
- DT 70 CT 68. Explanation: tax withholding. Amount: 5,022 rubles.
- DT 68 CT 51. Explanation: tax transfer. Amount: 5,022 rubles.
Employee Vasiliev goes on vacation. His salary is 30 thousand rubles. An employee has the right to a tax deduction in the amount of 1,900 rubles. As a result, the amount of vacation pay will be 3,653 rubles. The following wiring is used:
- DT 70 CT 68. Explanation: personal income tax withholding. Amount: 3,653 rubles.
- DT 68 CT 51. Explanation: transfer of the amount to the treasury. Amount: 3,653 rubles.
The information specified in the accounting must be confirmed by primary documentation.
Responsibility for non-payment of personal income tax
The employing organization is a tax agent, and the obligation to remit personal income tax rests entirely with it.
The agent's responsibility for untimely transfer is assigned to Art. 123 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It all depends on the specific situation:
| The tax was withheld from the employee, but was not transferred to the budget | Arrears of 20% of the unpaid amount will be charged. An additional penalty will be charged for each day of delay. |
| The tax is not transferred to the budget and is not withheld | According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, personal income tax is always withheld only from employee salaries. Collection of tax from the employer for personnel is not allowed (clause 9 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the arrears cannot be recovered, no penalty will be charged. |
What changes have occurred during the mandatory audit in 2021
Until 2021 In the Federal Law on auditing activities there was a term of audit secrecy. He implied that the information obtained by auditors during the audit is open only to the parties to the contract for the provision of audit services, i.e. closed to other persons, organizations, etc. Since this year, the essence of this concept has changed somewhat in connection with the new article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation 93.2, which gives tax employees the right to demand from auditors data obtained during the audit.
Tax officials expect to exercise this right if an enterprise refuses to provide them with information they are interested in about the company’s financial assets. In this case, the tax inspectorate has the right to request information from auditors and receive a response within ten days.
When compensation is not taxable
In all cases, compensation for unused vacation is subject to taxation. The exception is when relatives of a deceased employee apply for it: in such a situation, there is no need to withhold personal income tax.
To receive compensation and other salary payments for a deceased relative, you must do the following:
- Guided by Art. 141 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, according to which relatives of the deceased employee are entitled to payments, draw up an application and collect the necessary package of documents for the employer. This must be done within 4 months from the date of death of the citizen.
- Submit a package of documentation to the organization. Money must be transferred no later than 1 week from the date of application.
Along with the application, the employer is provided with a death certificate, passport and a document confirming the relationship of the citizen with the deceased employee.
Important! If wages are paid into staff bank accounts, the employer must not transfer funds upon learning of the employee's death, otherwise it will no longer be considered a legal payment. The money must be given to close relatives. If they do not apply within 4 months, the amount is included in the inheritance mass, and only the heirs can apply for it after six months.
In addition to compensation for unpaid vacation, the employer must give relatives the amount of salary for the period worked, as well as other payments due to the employee during his lifetime. There are no taxes or insurance contributions, since a citizen’s tax obligations cease due to death.
Compensation for unused vacation and other payments upon dismissal are subject to personal income tax without fail, with the exception of the death of the employee: in this case, his relatives receive the amount without withholding tax.
If personal income tax is not paid on time, the tax agent may oblige the Federal Tax Service to pay arrears and penalties, so it is very important to comply with the deadlines for the transfer and know the specifics of accounting entries.
Calculation of the number of days for which compensation is due
In any situation upon dismissal, be it:
- vacation followed by dismissal
- receiving payment for vacation not taken
the employee needs to calculate the number of unused vacation days for the period from the beginning of his work in this organization.
Sometimes it happens that an employee takes vacation for the whole year, but quits before the expiration of the vacation period. Therefore, it is necessary to check the vacation record for the entire period from the date of employment.
Important! The employer has the right to refuse to provide leave with subsequent dismissal due to the fact that it is necessary to hire a new employee for this position. In the meantime, while the resigning employee is on vacation, this position cannot be filled.
Penalties
Mandatory audit is mandatory because failure to comply with this requirement can entail a lot of fines, there are several reasons for this:
- The company did not submit an audit report to Rosstat within the required period. In this case, the official will be fined 300-500 rubles. A legal entity may be fined 3-5 thousand rubles. Additionally, they may be fined for the fact that the financial statements were not presented in full.
- The joint stock company did not publish the audit report on the official website within the established time frame. An official can be fined 30-50 thousand rubles and disqualified for 1-2 years. A legal entity can be fined from 700 thousand to 1 million rubles.
- The company did not enter information about the results of the mandatory audit into the Unified Federal Register on the facts of the activities of legal entities. persons (or contributed, but untimely). For delay or failure to provide this information, a fine of 5-50 thousand rubles is imposed.
- The company violated the deadlines for storing the auditor's report. That is, during an on-site tax audit, the company was unable to show audit reports for the last 5 years. In this case, a fine of 5 to 10 thousand rubles may be imposed.