What is subject to personal income tax?
An individual’s income is not only a salary. These include prizes in competitions, dividends received, bonuses and incentives at work and not necessarily in the form of money. Gifts in kind are also subject to personal income tax.
Income tax is calculated as follows:
Personal income tax = (Taxable income - Deductions) * 13% (or 9%,15%,30% and 35%)
Taxable income is all types of earnings not listed in Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Here is a list of income on which income tax is not taken:
- state benefits for unemployment, childbirth;
- pensions;
- payments for children;
- compensation for damage to health, etc.
This might also be useful:
- What taxes does the individual entrepreneur pay?
- simplified tax system for individual entrepreneurs in 2021
- Tax system: what to choose?
- Individual entrepreneur insurance premiums for employees in 2021
- Individual entrepreneur reporting on the simplified tax system without employees
- How much taxes does an individual entrepreneur pay in 2021?
Is the information useful? Tell your friends and colleagues
Dear readers! The materials on the TBis.ru website are devoted to typical ways to resolve tax and legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific issue, please contact the online consultant form. It's fast and free!
Income tax rate
First of all, the rate is affected by residency status . Resident - a person who has been in Russia for more than 183 days and does not leave it during this period. Otherwise, the payer will be recognized as a non-resident.
13% of income is deducted from residents' salaries . However, there are also more specific rates. For example, 35% - for winnings over 4,000 rubles, for interest on deposits and coupons on bonds, and so on. Personal income tax of 30% is taxed on income from certain securities. The lowest rate of 9% is available for mortgage-backed bonds that were issued before 01/01/2007, and for the income of the founders of the mortgage-backed trust.
For non-residents, 30% is deducted from their income, but there are exceptions . For example, a rate of 15% is relevant for non-residents who receive dividends from domestic companies. Foreigners can claim 13% personal income tax under the following conditions:
- they are highly qualified specialists;
- they are crew members of sea vessels flying the flag of the Russian Federation;
- they are refugees;
- they are participants in the state program for the resettlement of compatriots;
- they work for hire under a patent.
Tax rates in the Russian Federation
The standard rate of 13% of the income received will be necessarily “removed” from the entire amount of the salary that is issued to the citizen. Let's say, if an employee signed an agreement where his salary is 20,000 rubles, then in fact he will receive less, that is, 17,400 rubles (minus 2,600 rubles as personal income tax). However, most often the salary for candidates is announced taking into account tax deductions. This will also include “sick leave” and “vacation” payments.
At the same time, for non-residents of the country, 30% has already been established, which will be deducted from the earned labor income. The personal income tax rate will be 13% only for the following categories of non-residents:
- visa-free migrants;
- residents of countries that are members of the Eurasian Economic Union;
- foreign specialists with a high level of qualifications;
- refugees.
Another type of income is dividends (profits received from shares by joint-stock companies), since 2015, taxed at 13% of the amount received (previously - nine percent). For non-residents of Russia, this rate automatically increases to 15%. If a citizen decides to try his luck and wins a cash prize of more than 4 thousand rubles, 35% of this amount will be withdrawn from him, the same applies to funds received from deposits in credit institutions, as well as income from savings on interest upon receipt loans
Tax deductions for personal income tax
It is not necessary to pay the full tax. The legislator allows the use of the right to receive deductions to reduce the tax base. You can reduce the tax payable in different life situations: buying a home, paying for treatment or education, and so on. Here are the most common options:
- standard deductions, for example, deductions for children - 1,400 rubles for 1 and 2 children, 3,000 rubles for subsequent ones, or a deduction for Heroes of the USSR and the Russian Federation, participants of the Second World War, blockade survivors, disabled people, and so on - 500 rubles;
- You can get a property deduction for purchasing a home or paying mortgage interest;
- You can claim a social deduction for training yourself, brothers, sisters, children or treatment;
- professional deductions are relevant for individual entrepreneurs, notaries, lawyers, etc.
For example, an employee receives 60,000 rubles per month. Without additional conditions, personal income tax on salary will be 7,800 rubles. And if an employee has 4 children, then the income tax for the month will be:
(60,000 - 1,400*2 - 3000*2) * 13% = 6,656 rubles.
It is impossible to “go into the red” within a year. Only the amount of personal income tax that was paid is accepted for deduction. In addition, many deductions are limited in amount. For example, in 2021, Ivan Sidorov paid for university tuition for 150,000 rubles. He will accept only 120,000 rubles for deduction. This is the maximum for training costs.
The deduction can be used in two ways. The first is to reduce the current personal income tax payable. The second is to apply to the Federal Tax Service and withdraw the income tax paid for the previous year. Then the tax office, after conducting a desk audit, will return the amount due to the account in a lump sum.
An example of calculating personal income tax based on the amount of income of an entrepreneur
The classic sample of personal income tax withholding in 2021 contains the total income of a businessman exceeding 300,000 rubles. It is when such income is achieved that businessmen will have to charge 1% on the amount that is greater than the established limit. The example adds the calculation of mandatory tax to the Federal Tax Service “for oneself”:
- If BASIC mode is not selected. All income received during the reporting period - tax year (2,000,000 rubles) is taken into account. During the reporting period, the entrepreneur spent 450,000 rubles on business support. These are raw materials, materials, employee wages and insurance premiums. The businessman also took advantage of deductions for a child - 1,400 rubles until March inclusive. The tax amount will be: (2000000-450000-1400*3) *0.13=1545800*0.13=200954 rubles;
- Since the general regime is extremely unprofitable, entrepreneurs often have a simplified tax regime. The calculation will be somewhat more complicated. For example, without employees I received 450,000 rubles in the first quarter. In the specified period, the tax will be 450,000 * 6% = 27,000 rubles. From this amount it will be necessary to deduct contributions for pension insurance and medical care in the amount of 6636.25+1460=8096.25 rubles. In total, for the first quarter, taking into account the deduction, it will be necessary to transfer 27,000-8,096.25 = 18,903.75 rubles to budget income
Income tax withholding
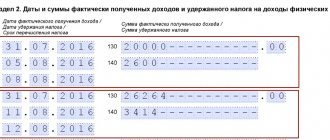
Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation obliges the employer to deduct income tax from employee salaries. Calculation occurs monthly on an accrual basis. In practice, personal income tax calculation is done on the day the salary is paid - on the last day of the month. First of all, tax is deducted, and then other payments: alimony, loan repayment, etc.
Within a month, the deduction amount may exceed the personal income tax base. Then the income tax is equal to or less than zero. Excess tax is carried over to the next month, but only within the year. At the end of the year, excessively withheld personal income tax is not carried over to the next year. The exception is property deductions.
Taxes are different, what will the tax base be?
Each type of tax has its own tax (financial) base. For example, with regard to transport tax, the power of the car’s engine plays a role; with regard to property tax, the cadastral value plays a role. To determine the tax base, you need to have an idea of such data as the total amount of both expenses and income (profits and losses), amounts received from any sales, non-operating money, the difference by which income will decrease due to expenses. This is how the final figure is obtained, which is considered the tax (financial) base. In other words, the base for personal income tax is the total amount of “net” income for the year, from which contributions will be transferred to the state treasury.
Deadlines for transferring personal income tax
The terms vary depending on the method of salary payment:
- in cash - the day the tax is transferred is equal to the day the money is received from the bank;
- non-cash payment - the next business day after the salary is transferred to the employee;
- other sources, including the issuance of income in kind - the next working day
It is important to distinguish between the concepts: transfer and withhold personal income tax. The transfer is usually made the next day after the salary is paid, and is withheld on the same day.
Personal income tax is transferred to the Federal Tax Service, where the company is registered. Branches transfer the tax to the tax office where they are registered.
How to calculate personal income tax if you have other income
If you were given something valuable, you will have to pay personal income tax on the cost. Financial assistance in the amount of over 4,000 rubles is also subject to taxation.
We list the most common sources of additional income, which are often not taken into account by taxpayers when filling out a declaration:
- Renting out real estate.
- Providing professional services without registering a legal entity (freelancing, part-time work).
- Winning.
- Receiving gifts of valuables, shares, money.
- Interest income.
- Profit from trading.
For Russia, tax evasion has become typical behavior, which until now the state has turned a blind eye to. However, the Federal Tax Service has become more active due to the widespread underestimation of income by both payers themselves and their employers.
Personal income tax example
Personal income tax from advance
The Labor Code in Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the payment of wages at least once every half month. The first part is known as an advance - salary for half the month worked. The second part is the rest of the salary for the second half. The interval between issues cannot be more than 15 days .
Employee income is subject to personal income tax. At first glance, it seems that income taxes need to be withheld twice a month. The first is from an advance payment, the second is from the remaining salary. But that's not true. There are two reasons.
Firstly, Letter of the Federal Tax Service No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] dated 05/26/14. It directly states: income tax is withheld from the full salary upon final payment once a month. That is, personal income tax is not paid on the advance .
Secondly, Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-06/33737 dated July 10, 2014. The ministry shares the position of the tax authorities. Personal income tax can only be deducted from the full salary. Advance payments are not subject to income tax .
For example, an employee’s salary is 50,000 rubles. Advance - half the salary. As a result, he will be given 25,000 rubles in advance. From the second part, 6,500 rubles of tax will be withheld and 18,500 rubles will be handed over.
But there are exceptions to this rule:
- the advance was issued on the last day of the month - income tax is withheld and transferred the next day;
- the employee has a personal income tax debt - the amount must be withheld from the advance payment in favor of repaying the debt, while personal income tax is not charged on the advance itself;
- the employee was given income in kind or he received a benefit - this income is subject to personal income tax, which must be withheld from the next cash payment, even if it is an advance, and personal income tax is not charged on the advance itself.
Briefly about personal income tax
It is important to understand that personal income tax is paid at the expense of the employee, not the employer. as a tax agent for personal income tax in relation to the hired persons . This means that he must calculate, withhold this tax from the employee’s income and transfer it to the budget.
Income of individuals is taxed at several rates. The standard rate applicable to employers is 13% for employees who are residents of Russia, and 30% for non-residents.
Chapter 23 of the Tax Code is devoted to personal . When calculating the tax base, there are quite a few features that depend on the type of income. However, employers calculate tax only on those payments that they themselves make in favor of the taxpayer. The most common types of payments to employees are wages, vacation pay, bonuses, disability benefits, and financial assistance. Below we will look at examples of how they are subject to personal income tax.
Income amount
Income can be received both in monetary terms and in kind (Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If income is expressed in foreign currency, recalculate it into rubles at the Bank of Russia exchange rate established on the date of actual receipt of income (clause 5 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If income is received in kind (in the form of property) from an organization or entrepreneur, then when calculating the amount of personal income tax in income, reflect the market value of the property received (Clause 1, Article 211, Article 105.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Do the same when receiving a gift of residential premises from a citizen who is not a relative (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 27, 2015 No. 03-04-05/24025, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 24, 2015 No. BS-19-11/180 ).
Advice: having received housing as a gift from a citizen, income in kind can be determined by the inventory value. But only if there is no cadastral valuation
This position was expressed in paragraph 6 of the Review, approved by the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation on October 21, 2015. And the judges justify it this way.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain special rules on the basis of what data to determine income when receiving housing as a gift from a citizen. And all ambiguities of the law are interpreted in favor of the taxpayer (clauses 6 and 7 of Article 3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, in such a situation, we apply the general rules set out in paragraph 3 of Article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. And they do not exclude the possibility of using information about the inventory value when there is no data about the cadastral value.
The controllers do not yet officially agree with this, so this position will have to be defended in court.
Situation: how to determine the amount of income for personal income tax purposes when receiving a share in the authorized capital as a gift? The share was given by another person who is not a relative.
Determine the amount of income based on the market value of the share. In this case, the market value of the share can be considered:
– the value of the share according to the appraiser’s report;
– part of the value of the organization’s net assets, proportional to the size of the share.
The explanation is this.
If a person receives income in kind from another person (who is not an entrepreneur) in the form of a gift, he must independently calculate the amount of personal income tax and transfer it to the budget. This is stated in subparagraph 7 of paragraph 1 and paragraph 2 of Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain methods for determining the value of a gift in a situation where the donor and recipient are citizens. The norms of paragraph 1 of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not applicable to such a situation.
In addition, the gift agreement also does not provide for the mandatory indication of the value of the gift, since by its nature it is gratuitous (Article 572 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The legislation does not contain methods for determining the market price of a share in the authorized capital for personal income tax purposes. The Ministry of Finance of Russia, in letter dated December 2, 2014 No. 03-04-07/61655, explained that the market value of a share can be determined in one of the following ways:
- by independent assessment;
- as part of the value of the organization’s net assets, proportional to the size of the share (clause 2 of article 14 of the Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ). In this case, calculate net assets using the Procedure approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 28, 2014 No. 84n. Take the data for calculating the net asset value from the balance sheet for the last year.
An example of determining the market value of a share in the authorized capital received as a gift. Market value is determined based on the value of net assets
Citizen A.S. In November 2021, Kondratiev received, under a gift agreement, a share in the authorized capital of Torgovaya LLC in the amount of 1/10.
To determine the amount of income, Kondratiev needs to calculate the market value of the share received as a gift. To do this, Kondratiev first calculated net assets using the formula:
| Net asset value | = | Balance sheet assets | – | Balance sheet liabilities (liabilities) | – | Debt of participants for contributions to the authorized capital |
Kondratyev made the calculation based on the Hermes Balance Sheet for nine months (as of September 30, 2016):
- balance sheet asset indicators - from sections I and II of the Balance Sheet;
- balance sheet liability indicators - from sections IV and V of the Balance Sheet.
At the end of the reporting period (nine months), the balance sheet asset reflected:
- on line 1130 “Fixed assets” – 100,000 rubles;
- on line 1160 “Deferred tax assets” – 5,000 rubles;
- on line 1210 “Inventories” - 400,000 rubles;
- on line 1230 “Accounts receivable” – 150,000 rubles. (there are no debts of participants on contributions to the authorized capital);
- on line 1250 “Cash” – 200,000 rubles.
At the end of the reporting period (nine months), the liabilities side of the balance sheet reflected:
- on line 1520 “Accounts payable” – 605,000 rubles.
There is no debt of participants in contributions to the authorized capital.
The net assets of Hermes as of September 30, 2021 were: (RUB 100,000 + RUB 5,000 + RUB 400,000 + RUB 150,000 + RUB 200,000) – RUB 605,000. = 250,000 rub.
Kondratyev calculated the market value of his share as follows: 250,000 rubles. × 1/10 = 25,000 rub.
Situation: how to determine the amount of income for personal income tax purposes when receiving a plot of land as a gift? The land was donated by another person who is not a relative.
Determine the amount of income:
- based on the value according to the appraiser, if such an assessment was carried out;
- based on the cadastral valuation of the land plot, if the appraiser has not assessed the land.
If a person receives income in kind from another person (who is not an entrepreneur) in the form of a gift, he must independently calculate the amount of personal income tax and transfer it to the budget. This is stated in subparagraph 7 of paragraph 1 and paragraph 2 of Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain methods for determining the value of a gift in a situation where the donor and recipient are citizens. The norms of paragraph 1 of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not applicable to such a situation.
In addition, the gift agreement also does not provide for the mandatory indication of the value of the gift, since by its nature it is gratuitous (Article 572 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The tax base (amount of income) when donating real estate must be determined on the basis of market prices for it (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 28, 2015 No. 03-04-05/3074 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 24, 2015 No. BS-19-11 /180).
The procedure for determining the market value of land plots is contained in land legislation.
According to land legislation, the market value of land can be determined by:
- cadastral valuation;
- assessments from a specialist appraiser.
This conclusion follows from paragraphs 1 and 2 of Article 66 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, Law dated July 29, 1998 No. 135-FZ and paragraph 3 of the Federal Standard approved by Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated October 22, 2010 No. 508.
At the same time, the cadastral value is an officially registered assessment of real estate (Article 24.18 of the Law of July 29, 1998 No. 135-FZ).
The law does not require that a land donation agreement be certified by a notary. At the same time, if the donation agreement was certified by a notary, and an appraiser was involved to calculate the state duty, who determined the market value of the land plot, then determine the income for calculating personal income tax based on this assessment. When notarized, information about the donation agreement and the valuation of the gift item will be received by the tax office (Article 7 of Law No. 135-FZ of July 29, 1998, Clause 6 of Article 85 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 17, 2007 No. MM-3-09/536).
Thus, when receiving a land plot as a gift, determine the amount of income based on the following factors:
- its value according to the appraiser, if such an assessment was carried out;
- cadastral value of the land plot, if an independent assessment has not been carried out.
Accounting for the tax (financial) base
Tax accounting is a system within which all data is summarized to determine the tax base. All companies are required to maintain tax records in order to create a reliable and transparent database of information on the taxation of all transactions. Accounting is necessary to provide internal and external users with the ability to control tax payments, minimize tax risks, and optimize tax payments. Each payer organization creates an accounting system independently.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for two methods by which the tax base is taken into account: cumulative and basic. The cash method takes into account the real income received by payers. As an example, you can take funds that are already in the cash register or an apartment purchased and transferred into ownership. The accumulative method does not take into account actual income, but rights and obligations. In this method, income is taken to be those amounts to which the payer has still only received the right. When accounting using this method, it does not matter whether funds have already been received.
What is the difference between residents and non-residents of the Russian Federation
To understand the differences, you need to refer to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which provides a clear definition of each status.
So, Russian citizens, foreigners, and stateless persons who stay in the country for at least 183 days during a calendar year are recognized as tax residents of the Russian Federation. If this condition is met, the person is recognized as a resident and can count on a tax rate of 13% when calculating personal income tax. If the established requirement is violated, the citizen is considered a non-resident, therefore, a tax rate of 30% is applied to his income. It should be clarified that the status of a citizen is determined with each salary payment, and therefore can change throughout the year.