Direct material costs are the costs associated with the production of goods, performance of work and provision of services. Each organization has the right to establish its own list of such MH.
An accountant is a universal profession; specialization in it is only temporary, when the accounting department and the company are large and each specialist is engaged in a separate area. To ensure that employees do not lose versatility and useful skills, experienced chief accountants try to regularly change their positions. And then the specialist who dealt with wages has to remember how to correctly calculate material costs and what they are. Let's refresh our memory of basic knowledge together and start with the concept itself.
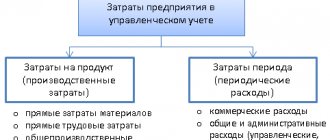
Product cost
Of this value, the influence of prices on materials is + 0.33 kopecks. Consequently, the impact of product prices accounts for + 0.39 - (+ 0.33) = + 0.06 kopecks. This means that a decrease in wholesale prices for the products of this enterprise increased the costs of 1 ruble of marketable products by + 0.06 kopecks. The total influence of all factors (balance of factors) is:
- material costs;
- labor costs;
- insurance contributions;
- depreciation of fixed assets (funds);
- other costs (depreciation of intangible assets, rent, mandatory insurance payments, interest on bank loans, taxes included in the cost of production, deductions to extra-budgetary funds, travel expenses, etc.).
Material cost ratio
The material cost coefficient is calculated using the formula:
Kmz = MZf / MZp.
Where:
- MZf – actual expenses of a material nature;
- Minimum wages are planned indicators of material costs, which are calculated for the actual volume of production.
Similar articles
- Material costs
- Dependence of fixed costs on production volume
- Production cost formula
- Production costs
- Fixed and variable production costs
Production costs of sold products
production costs are one of the main indicators calculated in accordance with international and many national accounting standards and indicated in the income statement. Russian accounting retains the use of the indicator “cost of sales of goods, products, works, services”, which (unlike the generally accepted cost calculation in the world) includes the standard “accrued depreciation of assets for production (shop) purposes”, which is not shown in full (in a separate article ) in the income statement, as is customary in the global community. This makes it difficult to perform the recalculations necessary to estimate the value of the property.
total sales costs - The total costs of production and sales of products, and this amount includes depreciation charges, as well as management and administrative (general business) and commercial expenses. In international practice (IFRS, MCO) the value... ...
WIP in the reporting of small businesses
It is possible to sum up the quantity of materials only if they are identical in quality indicators and are reduced to the same unit of measurement.
In the “Production Costs” section of the Explanations to the Balance Sheet and the Income Statement, you need to decipher the lines of the Income Statement “Cost of Sales”, “Administrative Expenses” and “Selling Expenses”.
P. Rudanovsky, M.P. Ter-Davydov, as well as in the works of the German economist N.F. von Dietmar. Before this they wrote “own cost”, “total cost”, “own cost”, “production cost”, “factory cost”, “productive cost”, “real cost”, “true price”, etc. The above list of synonyms shows how long and with what difficulty accountants searched for the right word.
If you are filling out such Explanations for the statistics department or tax office, then after the column “Name of the indicator”, additionally enter the column “Code” into the tables.
Costs of production in the balance sheet
When filling out line 5650, data on debit turnover for the reporting year according to cost accounting accounts is used (20 “Main production”, 23 “Auxiliary production”, 25 “General production expenses”, 26 “General expenses”, 28 “Defects in production”, 29 “ Servicing production and facilities”, 44 “Sales expenses”) in correspondence with accounts 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, 96 “Reserves for future expenses”, etc. minus internal turnover.
Changes in the balance of account 41 when determining the indicators of lines 5670 and 5680 are taken into account by organizations engaged in trading activities, provided that they have entered an additional line “Actual cost of goods purchased for resale.” If an organization accounts for goods on account 41 at sales prices with a reflection of the trade margin on account 42 “Trade margin”, then when calculating the indicators of lines 5670 and 5680, the debit balance on account 41 at the beginning and end of the reporting year is reduced by the credit balance on account 42 for these dates.
Production costs on balance sheet
Thus, in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, direct material costs are expenses of an economic entity aimed at providing the production cycle with the necessary materials, raw materials, semi-finished products, components, as well as for the purchase of services and work necessary in production. In other words, direct costs include expenses that are directly related to the implementation of the main activity.
If the resulting value is less than one, this indicates that the enterprise is unprofitable. If the indicator is equal to one, then the profit received is equal to the expenses, and the organization did not earn anything in the reporting period. If the indicator is greater than one, this means that the enterprise is profitable, that is, its activities bring profit.
Interesting to read: Temporary Registration for a Child for a Kindergarten in the Moscow Region
What it is
The concept of material costs (MC) is found in both accounting and tax accounting. According to the provisions of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, material costs include the following items:
- expenses for the purchase of raw materials, materials and components;
- expenses for the purchase of fuel, water, energy of all types spent for technological purposes;
- expenses for the purchase of works and services of a production nature;
- losses from shortages and damage to inventories within the limits of natural loss;
- other expenses.
The list of what is included in material costs in tax accounting is closed. In accounting, the concept of MH is defined in paragraph 8 of PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization,” but without a list. For this reason, each organization has the right to independently determine the definition of the concept in accounting and be sure to prescribe the list in its accounting policies. In fact, these will be the same expenses that are prescribed in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taking into account the specifics of the company’s activities.
Reflection of main production in the balance sheet
The debit balance formed on account 20 at the end of the month precisely represents the cost of work in progress (refinery). This balance accumulated over the year must be added to other indicators at the stage of entering data into the balance sheet line “Inventories”.
The volume of products that has not gone through all stages of the production process is considered work in progress (clause 63 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n). This category also includes products that have not passed testing or technical acceptance. The above definition also applies to works and services.
Material costs: formula
The balance of accounts 20 “Main production”, 23 “Auxiliary production”, 29 “Service production and facilities” as of the reporting date indicates the balance of work in progress (WIP). The balance of work in progress, own semi-finished products (account 21 “Semi-finished products of own production”) and unwritten off losses from defects (account 28 “Defects in production”) are reflected in the balance sheet asset on line 1210 “Inventories” (clause 20 PBU 4/99, Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 07/02/2021 No. 66n).
At the same time, it is difficult to say what the balance sheet calculation formula is for material costs. Indeed, in the data in the “Inventory” line, along with material costs, labor costs in WIP and other expenses can be reflected, depending on the method of assessing WIP. In addition, the line “Inventories” reflects the materials themselves in the form of their warehouse balance, which has not yet been used up, accordingly, they are not yet material costs, as well as finished products, the material costs for which have already taken the form of a finished product of labor and not are WIP, etc.
How are inventories reflected?
Inventories on the balance sheet consist of several categories:
- materials, raw materials;
- finished products;
- Future expenses;
- unfinished production;
- goods for sale.
What to do with materials
Raw materials and materials that were not given for the manufacture of products, in line 1210 of the balance sheet, information is collected on the balances of debit and credit accounts:
The specifics of raw materials can be very diverse depending on what the enterprise does. For example, when making wine, the raw material can be grapes and all the accompanying ingredients needed in the preparation process.
Materials, in addition to raw materials, are divided into narrower subtypes:
- Purchased semi-finished products and components.
- Tara.
- Fuel.
- Spare parts.
- Materials outsourced for processing.
- Construction materials.
- Inventory and tools.
- Workwear.
- Other stocks.
Each category in the Chart of Accounts has its own subaccount. In accounting materials during the year:
- are bought;
- are written off;
- participate in the manufacture of the product of the technological process.
However, they are displayed at actual cost excluding VAT. This means that the cost of the material includes, in addition to the price in the invoice, associated costs for:
- transportation;
- workpiece;
- insurance;
- acquisition consultations;
- customs duties;
- bonuses to intermediaries.
But inventories can be written off in three different ways at the organization’s discretion. The most common method and easiest to use is writing off at actual cost.
Note from the author! If the organization does not have warehouse accounting, then at the end of the year materials should be written off as much as possible. The presence of inventories in accounting causes confusion among inspectors, since there is nowhere for the balances to be stored. Only overalls can be left.
Materials must reflect fixed assets worth less than 40,000 rubles.
Costs of production in the balance sheet
The costs of production and sales of products significantly affect the amount of profit and, accordingly, the amount of tax payments to the state budget. To ensure the unity of approaches of all economic entities to the formation of profit and the rules for its taxation, the state establishes the principles and procedure by which taxpayers are required to keep records of the costs of production and sales of products, and regulates the sources of coverage for different groups. The document regulating the formation of the cost of products (works, services) in the Republic of Belarus is the Basic Provisions on the composition of costs included in the cost of products (works, services).
The group of other costs covers elements of various economic content: travel expenses, entertainment expenses, advertising expenses, audit and consulting services, rent; leasing payments; payment for bank services, communication services and contributions to the repair fund and other costs. This also includes a block of taxes and deductions included in the cost price: land tax, deductions from state enterprises to the innovation sector fund. Other costs also include insurance premiums for types of compulsory insurance, including compulsory insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases.
Main production in the balance sheet (nuances)
Defects subject to correction are also written off for the main production (Dt 20 Kt 28). Every month, from the credit of account 23 to account 20, part of the costs of auxiliary production is received, from the credit of account 25 - indirect costs (or part thereof) to ensure production, from the credit of account 26 - part of general business expenses (if the organization does not use the direct costing method and does not write off these expenses are debited to account 90).
Interesting read: How to find out your housing office by address
The balance on the accounts “Main production”, “Auxiliary production”, “Service production and farms” at the end of the reporting period indicates that there is unfinished production. The cost characterizing work in progress at the end of the reporting period is taken into account in the data that forms the indicator of line 1210 of the “Inventories” balance sheet.
* * *
So, the balances accumulated on account 20 by the end of the reporting period should be entered into balance sheet line 1210 called “Inventories.” When a certain balance is formed in the “Main Production” account at the end of the reporting period, this indicates a balance of work in progress at the enterprise.
Direct production costs should be recorded on account 20. In addition, at the end of each month, a certain share of expenses from accounts 23, 25, 26 should be attributed to this account.
The accounting policy should be formulated so that this document provides a criterion for distinguishing direct costs from indirect ones, principles for assessing oil refineries, and methods for closing the account of indirect costs.
Care must be taken to ensure that work in progress is recorded correctly, since such data is entered into the balance sheet and, if incorrectly calculated, can significantly distort the financial performance of the organization.
Similar articles
- Direct and indirect production costs
- Direct material costs
- Accounting for costs of auxiliary production
- Finished products are reflected in the balance sheet...
- Production costs
Analysis of costs for production and sales of products (works, services)
One of the most intensive areas of accounting is accounting for production costs and calculating the cost of products produced, work performed or services provided. The success of a company depends on the formation of production costs for the following reasons: 1) the cost of producing a product is the most important element in determining the selling price, 2) information about the cost of production often underlies the forecasting and management of production and costs, 3) knowledge of the cost is necessary to determine the balance of material accounts at the end of the reporting period.
There are a number of articles in the financial statements that directly indicate the unfavorable financial position of a commercial organization. These are the so-called “sick” items: “Losses”, “Loans and loans not repaid on time”, “Overdue receivables and payables”, “Overdue bills issued (received)”. When reading the balance sheet, you need to pay attention to these items first.
We analyze the costs of - production of products - calculation of the profitability of the enterprise
Based on this formula, you can determine the level of profitability of any of the above indicators. For this purpose, the company's balance sheet is usually used (Form No. 1). It contains data on the amount of fixed assets, equity and borrowed capital, the amount of current and non-current assets, as well as the liabilities of the organization.
Calculations and subsequent analysis of profitability is a rather labor-intensive process, but it gives a clear idea of how profitable a business is in a specific period of time, and in which direction it should move to increase the return on investment.
Conclusions about what a change in indicator means
If the indicator is higher than normal
If the indicator is below normal
If the indicator increases
Negative factor of financial stability
If the indicator decreases
Positive factor of financial stability
Notes
The indicator in the article is considered from the point of view not of accounting, but of financial management. Therefore, sometimes it can be defined differently. It depends on the author's approach.
In most cases, universities accept any definition option, since deviations according to different approaches and formulas are usually within a maximum of a few percent.
The indicator is considered in the main free online financial analysis service and some other services
If you need conclusions after calculating the indicators, please look at this article: conclusions from financial analysis
If you see any inaccuracy or typo, please also indicate this in the comment. I try to write as simply as possible, but if something is still not clear, questions and clarifications can be written in the comments to any article on the site.
Costs in work in progress
Definition: in clause 63 of the Regulations on maintaining accounting and financial statements in the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n, according to which work in progress refers to products (works) that have not passed all stages (phases, redistributions) provided for by the technological process, as well as incomplete products that have not passed testing and technical acceptance.
The article “Costs in work in progress” (line 213) reflects the presence of costs for work in progress and unfinished work (services), which are accounted for in the appropriate accounting accounts. In this case, work in progress is reflected in the assessment adopted by the organization when forming its accounting policy in accordance with regulatory documents on accounting. In trading organizations, the balance of work in progress is reflected in account 44 “Sales expenses”, and in other organizations - in account 20 “Main production”.
Increase or decrease row 1210
Every year, each company must submit financial statements, including a balance sheet, which is called Form No. 1. The balance is drawn up in accordance with clearly defined instructions, which can be found in PBU 4/99. This document requires the reliability of the information in the report, therefore the “Reserves” item should be collected strictly according to the formula:
Debit 10, 11 – Credit 14 + Debit 15, 16 + Debit 20, 21, 23, 28, 29 + Debit 43 + Debit 41 – Credit 42 + Debit 44, 45 + Debit 97.
Inventories on the balance sheet are a current asset that indicates the company’s financial security. The absence or sharp decrease in indicators in line 1210 of the current assets section, which collects all data on inventories, may indicate a scarcity of resources in the enterprise’s warehouses. On the other hand, there is an option that the process of turning an asset into money occurs so quickly that the company can barely keep up with its marketing service.
Since financial receipts to the company’s accounts depend on the rate of inventory turnover, it is necessary to maintain the proper level of resources by pursuing an effective marketing policy.
Production costs are
The main goal of any industrial commercial enterprise is to obtain maximum profit, this is the difference between the funds received for shipped products and the costs of their production and sale. Thus, the costs of the enterprise directly affect the formation of profit. The lower the cost of manufactured products, the more competitive the enterprise, the more accessible the products are to consumers, and the greater the economic effect from its sale.
Expenses are the movement of funds in the process of economic activity, leading to a decrease in the enterprise’s funds or an increase in its debt obligations. Usually associated with resource support for production, purchase of materials, equipment, payment of workers, equipment repair, payment of interest on loans, rent, and payment of taxes. Costs or expenses, expenses - the amount of resources used in the process of economic activity of an enterprise.