How to work in the program - instructions for filling out
As a rule, working in the program does not raise any questions, and if any arise, you can use the instructions that come with the software. Immediately after launch, a window with software settings will appear. Here you can specify information about the administrator, general data about program management, and also select the Federal Tax Service with which the legal entity works:
Next, you need to go to the tab with available declarations and add a new one:
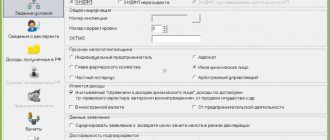
After the declaration has been added, you can start filling it out:
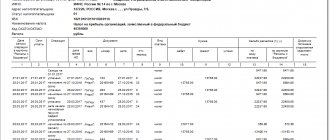
After the VAT refund declaration is completed, it must be saved and a document generated that will be submitted to the tax service. This is quite simple to do - you just need to transfer the necessary documents to the right column and select the “Generate” menu button:
It is possible to use the “VAT Refund: Taxpayer” program together with the standard 1C configuration. In order to use this opportunity, it is necessary to download the data in *NDS format and then load it into the program in question, and then use it to refund VAT.
Unloading occurs in several steps - the period and organization are filled in, the unloading catalog is completed, after which the data is corrected or approved. The last step is to upload the file and re-upload it into “VAT Refund: Taxpayer”.
Where to find and how to install the program
The current version of the software is located on the official website of the tax service in the “Software” section. Using this link you can go to a page with download files, which include instructions and documentation for working with the program.
Installation is not difficult - just download and run the archive file on your PC:
After the installation is complete, you can see two shortcuts on the desktop - to enter directly into the program, you must use the shortcut with the image of the key. The second shortcut is used for configuration settings:
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
VAT refund, how it happens - conditions
Taxpayer VAT refund: latest version 2021 is available to all users and citizens of the Russian Federation. When exporting from the budget, the taxpayer returns the amount declared in the declaration. If the user has some tax debts, the territorial authority can collect an amount equal to the amount. Objections in this case will not be accepted.
In practice, returning the amount is a complex science that requires time and effort. Of course, very often people may encounter incorrect amounts, an incorrectly structured process and the actions of certain authorities. If for any reason you do not agree with the tax decision, you have the opportunity to appeal it to the arbitration court, according to the order. A range of taxation services is provided to all who contact the service.
The named supplier may charge fees for services provided. Exceeding calculus is something anyone can do.
Application for VAT refund to the current account,
In practice, reimbursement occurs to any bank account. In order to carry out this procedure, you must fill out a sample application, which must indicate the card account number. When concluding an exchange agreement, the export conditions are somewhat different from the usual ones. The customs procedure for leasing has a number of organizations that monitor the reimbursement of VAT amounts. What's happened? What to do when buying an apartment? Is there a bank guarantee?
VAT refund from the budget
A bank guarantee for the return of certain amounts of VAT has a period. Most often this is three years. Transferring to the next month when importing is possible with early agreement. The acceptance procedure will not take much time. An explanatory note about the reasons for non-return is required. How does a refusal occur? The reasons for the delay in refunding the amount must be stated in writing.
VAT refund on export
In case of compensation upon export, a declaration with the designation export is submitted. In this case, the fee may be slightly higher than the established one. Payment is made to the bank account within the established time frame. It is highly undesirable to exceed the specified days, as an additional percentage of the amount may be charged. Once a year, a desk audit of the enterprise's activities is carried out. Payment can be made through third parties, but with the indication of the head of the enterprise. If disputes arise, it is highly advisable to resolve them in court. You can also go to court if unresolved issues arise regarding one or another payment of VAT upon export.
VAT refund when importing goods
The most difficult procedure is a tax refund from the import of a particular product. Most often, the specifics of the service itself are somewhat complex and require effort and time. In addition to submitting the appropriate application, a special package of documents for the organization is submitted. The money transfer takes place through a current account. This year, sometimes there are problems with application refusal. In this case, judicial practice comes to the rescue, which can provide answers to all unfinished questions.
Desk audit of VAT for refund
A desk audit of an enterprise means a thorough study of materials and packages of documents provided by a particular organization. In practice, the entire process takes about 3 business days. Afterwards, reporting is provided indicating all obvious errors. These corrections must be corrected within the time limit established by the territorial tax authority. Electronic submission is not possible.
The Tax Service conducts audits of all declarations filed by an organization for a certain tax period. If no inconsistencies or violations were found, the tax office to which the declarations were submitted makes a decision on VAT refund within 7 working days. If any violations are discovered, the tax office will draw up a report, which is reviewed by the head of the tax service. Based on the results of the review, a decision is made whether any sanctions will be taken due to the violations committed.
In addition, the tax office may consider the amount of the taxpayer’s recoverable amount. In some cases, a decision may be made to partially refund VAT. So, if there are previously unpaid fees, state duties and other obligatory payments, their amount will be deducted from the amount of the restored VAT.
To reflect information on export transactions of taxpayers and tax audits carried out in relation to them, a software and information complex PIK VAT has been developed. This module reflects information about what contracts the company has concluded with foreign counterparties, whether control measures were carried out in relation to it, and whether it was previously reimbursed for taxes from the budget. Entering information into a common database is the right of a legal entity, not its obligation.
Russian companies have the right to download the VAT PIK for free on the website of the Federal Tax Service or the State Scientific Research Center of the Federal Tax Service. If you use the module autonomously, the accountant will be forced to enter information about export-import transactions twice: the first time this must be done in the enterprise’s accounting program. To avoid unnecessary work, you can integrate the module with 1C or other systems.
It is not difficult to understand which version of the program is currently the latest. This information is posted on the Federal Tax Service portal. There is also information about which systems the module is compatible with, what modifications were made to it compared to previous versions.
When was the latest version of the program released?
All information about which version of the “VAT Refund: Taxpayer” program is relevant right now can be found on the sites mentioned above.
When searching for information, pay attention to the following subtlety. The text editor contains a file called Readme. It contains information about what services are included in the software package. This is where information is located about the version number of the program available for download, and about what adjustments have been made to the previous version of the complex.
Is working with the program required?
Not a single legal act in force in Russia provides a direct indication of the obligation of taxpayers to enter data into the VAT program. It is easy to download, it is freely available, it is easy to learn and integrate with the enterprise accounting system, but no one forces companies to use this module. This is a right of legal entities that they may not take advantage of.
Explanations from tax authorities state that taxpayers do not have an obligation to enter data into the program. The Federal Tax Service may ask for this, expressing a wish as a recommendation. Fiscal departments note that completing the module is in the interests of the organizations themselves. This helps them speed up the VAT refund process (in practice, not always), and avoid unreasonable refusals given by tax authorities due to technical failures and malfunctions.
Fiscal services indicate that entering information into the program allows the taxpayer to control its completeness and correctness, which will simplify the refund procedure. Accountants believe that using the module means double control, which is not objectively necessary. Be that as it may, non-use of the system cannot become a basis for refusing a VAT refund.
The VAT program is an easy-to-use application that can be easily integrated with the company's accounting system. This can be done independently or with the help of service companies. Its use is not mandatory, but it is desirable, because it can speed up tax refunds and reduce the risk of unjustified refusals.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Current format (from 01/01/09) Version 3.06 Value added tax refund
VAT refund: Taxpayer 3.0.8.6 dated 12/07/2017
During a desk audit, tax officials consider the validity of the amount of VAT desired by the payer to be refunded.
Refund procedure
Refusals of funds subject to offset
The refusal can be appealed on the basis of well-founded arguments. Quite often the appeal is beneficial for the taxpayer.
If the tax service does not return VAT amounts on time, then these structures can also be held legally accountable.
General information about the declaration
Entering information to generate information from documents confirming the validity of applying a zero VAT rate begins with adding a declaration that reflects exports. By clicking on the name of the declaration, you need to fill out general information about it.
In the “Reporting period” field, select the quarter and year in accordance with the period for which the declaration was prepared.
In the “Declaration type” field select:
- “primary” – if no changes were made to the declaration;
- “updated” – if additions or adjustments were made to the primary declaration.
The “Adjustment number” field reflects which account-specific updated declaration is being submitted to the tax authority (for example, “1”, “2”, etc.).
In the “Taxpayer (exporter) attribute” field, within the framework of the organization’s (or individual entrepreneur’s) activities, one of the proposed options is selected. So, if the exporter (organization or individual entrepreneur) himself produces goods sold for export, then the attribute “manufacturer of export goods” is selected; if he sells previously purchased goods for export, then he is a “reseller”, etc.
In the subsection “Type of activity of the taxpayer (exporter)”, those types for which VAT is declared for deduction in this declaration are selected, and the tax base and the amount declared for deduction are indicated separately for each type.
Activity code “01” is indicated by taxpayers who sell goods in export mode.
Attention! Tax base according to code “01”, lines 020 of section 4 of the VAT tax return for transaction codes 1011410, 1011412, 1010410, 1010456, 1010457, 1010458, 1010459 and 1010460 (in terms of sales of goods for export).
Attention! “01” must correspond to the VAT value for transaction codes 1011410, 1011412, 1010410, 1010456, 1010457, 1010458, 1010459 and 1010460 (in terms of sales of goods for export), calculated using the formula:
Amount of VAT to be deducted = section 4 – page 080 section 5 VAT
The activity code “04” is indicated by taxpayers who sell goods under the free customs zone regime.
Attention! The tax base for code “04” must correspond to the sum of the tax bases reflected in lines 020 of section 4 of the VAT tax return under transaction codes 1011411, 1011413, 1010410, 1010456, 1010457, 1010458, 1010459 and 1010460 (in terms of sales of goods in the free customs zones).
Attention! The amount declared for deduction under code “04” must correspond to the VAT value for transaction codes 1011411, 1011413, 1010410, 1010456, 1010457, 1010458, 1010459 and 1010460 (in terms of sales of goods in the free customs zone regime), calculated using the formula:
Amount of VAT to be deducted = (line 030 + line 040 – line 050) section 4 – line 080 section 5 VAT tax
Activity code “05” is indicated by taxpayers who perform work and provide services directly related to the export of goods and the sale of goods in the free customs zone regime.
Attention! The tax base for code “05” must correspond to the amount of tax bases reflected in lines 020 of section 4 of the VAT tax return, attributable to the implementation of work (services) directly related to the export of goods.
Attention! The amount declared for deduction under code “05” must correspond to the value of VAT on transactions for the sale of work (services) directly related to the export of goods, calculated using the formula:
Amount of VAT to be deducted = (line 030 + line 040 – line 050) section 4 – line 080 section 5 VAT tax
Activity code “06” is indicated by taxpayers selling goods to EAEU member countries (Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan).
Attention! The tax base for code “06” must correspond to the sum of the tax bases reflected in lines 020 of section 4 of the VAT tax return under transaction codes 1010421, 1010422, 1010461, 1010462, 1010463, 1010464, 1010465 and 1010466.
Attention! The amount declared for deduction under code “06” must correspond to the VAT value for transaction codes 1010421, 1010422, 1010461, 1010462, 1010463, 1010464, 1010465 and 1010466, calculated using the formula:
Amount of VAT to be deducted = (line 030 + line 040 – line 050) section 4 – line 080 section 5 VAT tax
VAT on exports: accounting, declaration, refund
rub.
+ 18 thousand rub. = 38 thousand rubles. instead of 18 thousand rubles. Organizations are required to transfer VAT on goods exported abroad to the relevant authorities. But this is not always necessary. When selling products abroad, businessmen have the right to apply preferential zero interest rates. However, if the transaction is not confirmed within the prescribed period, the entrepreneur pays the fee in full.
0% VAT applies to the export of the following works and services:
- work in river and sea ports for the transportation and storage of goods exported across the Russian border.
- for oil supply via pipeline;
- water transport for the transportation of products exported under the customs export procedure;
- for the provision of trains and containers;
- on international transportation of goods;
- for processing of goods in the customs territory;
- for gas supply;
- provided by the national grid;
The article states that 0% VAT on exports may be levied on products exported under customs regime.
Contract details
The section is filled out by exporters for all international contracts within the framework of which goods were sold for export during the reporting period and reflected in the VAT return.
To fill out contract information, you must add a contract. Then, by clicking on it, the following data is indicated:
- date and number of the international export contract concluded by the exporter with the foreign buyer;
- code of the type of activity of the exporter to which the contract relates;
- details of the foreign buyer (recipient) according to information from the contract: name, tax identification number (if available), address;
- transaction passport number (if available), which is issued in the bank where the exporter’s account is opened, to which the buyer should receive proceeds for goods under the contract;
- contract amount - the total amount of the transaction in the contract currency. If the value of exported goods is determined in several currencies, then it is converted into the prevailing currency;
- delivery amount - the cost of a specific delivery in the contract currency, subject to its stage-by-stage execution and stage-by-stage reimbursement of VAT amounts to the exporter. If the value of exported goods is determined in several currencies, it is recalculated into the prevailing currency;
- delivery terms according to INCOTERMS standards;
- form of settlements with the taxpayer: cash, non-cash, etc. When specifying the cash form of settlements, the total amount of revenue for all receipts is also reflected;
- details of the bank from whose account the export proceeds were received (subject to non-cash payment): name, BIC and bank account number;
- details of the exporter's bank (commission agent), into whose account the proceeds from the foreign buyer were received: BIC and bank account number;
- information about cash receipt orders (subject to cash payment) - the number and date of each PCO;
- details of the application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes: number and date of registration of the application with the tax authority.
Attention! Details of the application for the import of goods are filled in only when selecting the activity code “06”.
The “Additional” section contains information about the receipt of revenue, as well as about agreements with other persons.
The subsection is intended to reflect information about the receipt of revenue from export supplies of goods based on bank statements.
Attention! cash or non-cash form selected.
In the subsection “Information on bank statements on receipt of proceeds” the following is indicated:
- the date of actual crediting (in accordance with the bank statement) of export proceeds to the taxpayer’s account from a foreign buyer;
- the amount of export proceeds received by a Russian bank in rubles and foreign currency.
The subsection is intended to reflect data on the termination of the right of mutual claims between the exporter and the foreign buyer on the basis of other receipt documents (except for bank statements and PKO).
Attention! This subsection is required to be filled out if a form other than cash or non-cash is selected in the “Form of settlements with taxpayer” field.
In the subsection “Information about other documents (IPD)” the following is indicated:
- the name of the document submitted by the exporter to the tax authority (including an order agreement for payment for goods concluded between a foreign person and the organization (person) that made the payment);
- number and date of the document submitted to the tax authority.
The subsection “Agreements with other persons” is filled in if the exporter (commission agent) concludes an agreement with another person, incl. and with the carrier.
This subsection specifies:
- number and date of conclusion of an agreement by the exporter (commission agent) with another person;
- the subject of the contract, which is selected from the proposed list;
- name (full name) of the other person, his tax identification number and checkpoint (if available);
- the cost of goods (work, services) including VAT under an agreement with another person and separately VAT.
Attention! When choosing the activity code “04”, the subsection “Certificate of registration of a person as a SEZ resident” is additionally filled in, which indicates the number and date of the certificate, as well as the name of the federal executive body authorized to carry out the functions of managing the SEZ, which issued the registration certificate.
The section “Information about the commission agent” is filled out subject to the conclusion of a commission agreement (order, agency agreement) for the commission agent (attorney, agent) to carry out a foreign trade transaction in the interests of the exporter.
Attention! The section “Information about the commission agent” is not filled in when selecting the activity code “05”.
This section reflects the following data:
- name (full name) of the commission agent (attorney, agent), his tax identification number and checkpoint (if any);
- date of conclusion and number of the agreement between the exporter and the commission agent (attorney, agent), type of agreement;
- BIC of the Russian bank of the exporter, to whose account the commission agent (attorney, agent) transferred export proceeds when implementing an international contract through the commission agent.
The section “Information about suppliers” contains information about Russian (including Eurasian) suppliers of goods used for the production or resale of export goods.
Attention! The section “Information about suppliers” is not filled out if the supplier is a resident of another state (except for member countries of the EAEU). In this case, information about imported customs declarations is filled in.
This section contains the following information:
- number and date of conclusion by the exporter (commission agent) of the agreement with the supplier of inventory items (inventory);
- sign of a supplier selling goods and materials to an exporter (manufacturer, reseller, etc.);
- name (full name) of the supplier, his tax identification number and checkpoint (if available), address;
- bank details (BIC and account number) that received payment from the exporter (commission agent) for goods and materials purchased from the supplier (in the case of non-cash payments);
- information about goods in the contract with the supplier: name of goods and materials, form of payment between the exporter (commission agent) and the supplier, quantity and value of goods and materials recorded on invoices, cost of goods and materials according to invoices issued by the supplier and the amount of VAT.
The “Information about goods” section is intended to reflect information about the goods specified in the international export contract. This section also contains information about export and import customs declarations, as well as shipping documents (TCD).
In the “Information about goods” section, the name and volume of supply of the exported goods are indicated in accordance with the contract and the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity.
Information about export customs declarations includes: customs declaration number; total invoice value of goods and currency code; data on the marks of the customs authority through which the goods were exported outside the customs territory of the Russian Federation.
Attention! Information about export customs declarations is not filled in when selecting the activity type code “06”.
Information on import customs declarations reflects: the customs declaration number and the amount of VAT claimed by the taxpayer for deduction under the import declaration.
The information on shipping documents (TSD) contains the following data:
- type, number and date of registration of transport, shipping and (or) other document;
- data on the marks of the customs authority through which the goods were exported outside the customs territory of the Russian Federation;
- carrier details: name (full name), tax identification number and checkpoint (if available).
Attention! After entering information on the contract, all necessary sections will be generated automatically.
Documents required to confirm the zero rate
A comprehensive list of documents that will be required to confirm the 0% rate for export is given in Art. 165 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In general this is:
- contract with a foreign supplier;
- customs declaration with the necessary customs marks;
- accompanying, transport documentation for the goods with customs marks;
- intermediary agreement (if export is not carried out directly).
As for transport documents, for sea transport this could be: a sea waybill, a bill of lading or another similar document. For air transportation, cargo waybills are provided with the obligatory name of the loading airport. For road transport, you will need to present the appropriate transport or shipping document.
The list we have given is very general. There are many practical situations (different types of goods, services, methods of export, etc.) - and the requirements of tax legislation for them are also different. Let us remind you that you can find the most complete information on the necessary supporting documents for export in Art. 165 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Below we will consider several practical situations.
Filling out the VAT PIK
I know what I'm saying 07/05/2018 18:17
Section: Information about suppliers
This section contains information about the first supplier (suppliers) of goods (in the chain of suppliers) used for the production of goods sold for export, or goods purchased and then sold for export (resale), the exporter (commission agent, attorney, agent). When reselling, the first supplier in this section refers to the last supplier of the goods from the manufacturer.
Line 102 “Date of conclusion of the agreement with the supplier” indicates the date of conclusion by the exporter (commission agent, attorney, agent) of the agreement with the supplier of inventory items (inventory).
Line 103 “Number of agreement with supplier” indicates the number of the agreement concluded by the exporter (commission agent, attorney, agent) with the supplier of goods and materials. The contract number may contain letters, numbers, punctuation marks and special characters.
Line 104 “Supplier INN” indicates the INN assigned to the taxpayer-supplier upon registration with the tax authorities. If the supplier is a resident of a foreign country, then zeros are entered in this field.
Line 105 “Supplier checkpoint (LE)” indicates the checkpoint assigned to the taxpayer-supplier upon registration with the tax authorities, provided that the supplier is a legal entity. If the supplier is a Russian individual or a resident of a foreign country, then zeros are entered in this field.
Line 106 “Name of the supplier (LE) / Full name (FL)” indicates the name of the supplier (LE) or the full name of the supplier (FL).
Line 107 “Address of location of the supplier (LE) / address of place of residence (FL)” indicates the officially registered address of the supplier - legal entity / full address of permanent residence of the supplier - individual based on an identification document or other a document confirming the address of permanent (or primary) residence.
Line 108 “Supplier attribute (manufacturer, reseller)” indicates one of the proposed options for the attribute of a supplier selling goods and materials to an exporter (commission agent, attorney, agent).
Line 109 “BIC of the bank in which the supplier’s ruble current account is opened for settlements with the exporter (commission agent, attorney, agent)” indicates the BIC of the supplier’s bank in which the supplier’s account is opened, to which payment was received from the exporter (commission agent, attorney, agent) for goods and materials purchased from the supplier, in the case of using a non-cash form of payment.
If another form of calculation is used, zeros are entered in this line.
Line 110 “Number of the supplier’s account(s) used for settlements with the exporter (commission agent, attorney, agent)” indicates the number(s) of the supplier’s account(s) to which from the exporter (commission agent, attorney, agent) payment has been received for goods and materials purchased from the supplier, in the case of using a non-cash form of payment.
If another form of calculation is used, zeros are entered in this line.
Line 111 “Name of goods and materials (under contract)” indicates the name of goods and materials in accordance with the contract (and specifications for it) for the supply of goods by the supplier to the exporter (commission agent, attorney, agent).
Line 112 “Cost of inventory items capitalized by the exporter (according to invoices)” indicates the cost of inventory items capitalized by the exporter in accordance with the data contained in the invoices.
Line 113 “Cost of inventory items according to issued invoices” indicates the cost of inventory items in accordance with the data contained in the invoices issued by the supplier to the exporter (commissioner, attorney, agent).
Line 114 “Including VAT” indicates the amount of VAT on inventory items in accordance with the data contained in the invoices issued by the supplier to the exporter (commissioner, attorney, agent).
Export of non-commodity goods to the EAEU: how to reflect VAT deduction in 1C
Accounting, taxation, reporting, IFRS, analysis of accounting information, 1C: Accounting
09/08/2016 From July 1, 2021, in relation to non-commodity goods for export accepted for accounting, a VAT deduction can be claimed in the generally established manner, without waiting for confirmation of the validity of applying the 0% rate.
In the article, 1C experts consider an example of reflecting the new procedure for claiming VAT deductions in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0, when exporting non-commodity goods to the countries of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU).
The procedure for claiming VAT deductions when selling goods in the customs export procedure has a number of features and since July 1, 2016, after amendments to the Tax Code by Federal Law No. 150-FZ dated May 30, 2016, depend on what goods are shipped for export - raw materials or non-raw materials. Changes are supported in 1C:Enterprise 8.
VAT refund when exporting goods (instructions)
Taxes
- Taxes 08/23/2013 Today, the topic of VAT refund when exporting goods to Kazakhstan is very relevant.
The Kazakhstan market is characterized by stable demand not only for Russian-made goods, but also Chinese ones. Many managers mistakenly believe that the procedure for refunding VAT from the budget for export operations to Kazakhstan takes a lot of time and does not guarantee a positive result.I am the head of a consulting company that has been successfully providing this service for two years now. As a result, my Clients receive VAT refunds from the budget strictly
Comments and clarifications
Are taxpayers required to submit information from documents to confirm export VAT electronically to the tax authority?
Currently, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not impose such an obligation on taxpayers. However, the tax authorities ask to provide the specified information in order to carry out more prompt and effective control in relation to the amounts of VAT declared for reimbursement from the budget (letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 20, 2006 No. 03-2-03 / [email protected] , 08.09.2006 No. ShT -6-03/ [email protected] ). In this regard, VLSI users can generate the specified information in the VLSI program in the form “VAT Refund”, which is similar to the Federal Tax Service PC “VAT Refund: Taxpayer” (https://www.nalog.ru/rn76/program//5961282/).
PIK VAT is the name of the program that allows you to summarize and generate information on desk audits carried out on VAT claimed for refund. Using this information complex, the processed data is subsequently transported from the local tax level to higher ones - regional and federal.
When was the latest version of the program released?
Purpose of PIK VAT
Should a taxpayer use the VAT PIK?
Confirmation of a zero tax rate using PIK VAT
Deadlines for confirming the zero rate
You must confirm the zero export rate no later than 180 calendar days from the date of affixing the customs stamp on the documents. If you do not meet this deadline, you will not only have to pay VAT at general rates, but also submit an updated declaration, as well as pay a penalty for late payment of tax. The same applies to the situation when, for some reason, there are no customs stamps on the convoys.
But even if you meet the deadlines and the package of documents meets the requirements of the law, this does not guarantee that the zero rate will be confirmed and the tax authority will make a decision on VAT refund. So far we are talking only about the fact of confirmation of export. The final goal is still far away: tax officials need to check the authenticity of the documents, their correct completion and compliance with the requirements of the law; make sure that the exporter has no debt to the budget.
Should a taxpayer use the VAT PIK?
Not a single legislative norm contains any indication that the taxpayer is obliged to form the PIK VAT base himself. However, the Federal Tax Service, represented by its local authorities, constantly asks you to fill out the columns of this program. What should a taxpayer do: ignore the requests of tax officials or not spoil his authority and provide the requested data?
It seems to us that it is right to meet the inspection halfway and create the required data block. The tax authorities' arguments in favor of this decision are as follows:
- PIK VAT can be downloaded without any problems.
- This program is easy to use.
- The data entered into it will allow tax authorities to reduce the time required for desk audits and to better examine the information provided. As a result, it is possible to avoid refusals of VAT refunds due to technical inaccuracies and lack of data.
However, a greater role here is played by the issue of diplomacy and reluctance to receive a “black mark” from the Federal Tax Service. Accountants believe that the use of PIK VAT in an organization leads to double control by the tax service.
Results
Taxpayers themselves have the right to decide whether or not to enter data into the “VAT Refund: Taxpayer” program. If this does not cause any difficulties for the accountant, then it is still worth entering. And even if this does not reduce the time for conducting a desk audit, there is every reason to believe that such a concession can protect the company from unjustified refusals to refund VAT.
If an accountant has problems entering information into this program, then turning to service companies to purchase special applications will simplify these difficulties.
Thus, using special applications and settings, data from your accounting database can be integrated into the program offered by the fiscal department. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
VAT information program: obligation or right?
Due to the fact that no legislative act states that taxpayers are required to enter data into the VAT PIK on their own, and based on the information given above, it becomes clear that taxpayers may not comply with the tax office’s request to fill out data in this program. Although, of course, as mentioned above, it is absolutely easy to download the VAT PIK, and it is quite simple to master.
The fiscal department itself has also repeatedly stated that taxpayers are not required to enter data into this program, but the request to do so does not violate their rights. Taxpayers themselves should be interested in implementing these recommendations. The interest of taxpayers, according to tax officials, is to reduce the time required for an audit (although in fact this does not always happen) and to help the tax authorities conduct a more thorough and high-quality audit in order to prevent refusals of reimbursement due to technical errors. This is exactly the explanation that can be found in the recommendations of the Federal Tax Service, for example, in the letter dated 08/09/2006 No. ШТ [email protected]
Fiscal officials also suggest that this program will allow the taxpayer, when entering information, to independently verify its correctness and completeness. That is, instead of an obligation, the taxpayer allegedly gains a benefit that will allow him to overcome all obstacles on the way to receiving the requested compensation. According to many accountants, in fact we are talking about double control.
Read more about the procedure for refunding VAT from the budget.
* * *
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs are given the right to determine for themselves whether they need the PIK VAT
and whether information should be included in it. Nevertheless, for tactical reasons it should still be used. Using this program, you can reduce the time for a tax audit, but most importantly, the taxpayer will improve his position in the ranking of tax authorities.
Similar articles
- How and in what cases is VAT refunded - refund procedure?
- Electronic submission of reports to the tax office
- How to correctly fill out an invoice without VAT?
- Filling out a VAT return form - example
- How to find out the size of the safe share of VAT deductions?