Region codes of the Russian Federation are digital designations (two or three digits) that allow you to identify a region of the Russian Federation. These codes are used when registering vehicles with the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate, as well as when assigning a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) to the Federal Tax Service. The Federal Tax Service code always corresponds to the traffic police code. If a region runs out of two-digit numbers, then the next series is allocated with a nine at the beginning, if it is not occupied, then another series (three-digit) is allocated, in which the code consists of the serial digit of a hundred plus the region code itself (for example, Moscow codes 77, 97 , 177). Below is a list of area codes:
01 Republic of Adygea 02 Republic of Bashkortostan (also 102) 03 Republic of Buryatia 04 Republic of Altai 05 Republic of Dagestan 06 Republic of Ingushetia 07 Kabardino-Balkarian Republic 08 Republic of Kalmykia 09 Karachay-Cherkess Republic 10 Republic of Karelia 11 Republic of Komi 12 Republic of Mari El 13 Republic of Mordovia 14 Republic Sakha (Yakutia) 15 Republic of North Ossetia 16 Republic of Tatarstan (also 116) 17 Republic of Tyva (Tuva) 18 Udmurt Republic (also 118) 19 Republic of Khakassia 20 Chechen Republic (old numbers) 21 Chuvash Republic (also 121) 22 Altai Territory 23 Krasnodar region (also 93) 24 Krasnoyarsk region 25 Primorsky region (also 125) 26 Stavropol region 27 Khabarovsk region 28 Amur region 29 Arkhangelsk region 30 Astrakhan region 31 Belgorod region 32 Bryansk region 33 Vladimir region 34 Volgograd region 35 Vologda region 36 Voronezh region 37 Ivanov Skye region 38 Irkutsk region (also 138) 39 Kaliningrad region 40 Kaluga region 41 Kamchatka region 42 Kemerovo region 43 Kirov region 44 Kostroma region 45 Kurgan region 46 Kursk region 47 Leningrad region 48 Lipetsk region 49 Magadan region 50 Moscow region (also 90, 150) 51 Murmansk region 52 Nizhny Novgorod region (also 152) 53 Novgorod region 54 Novosibirsk region (also 154) 55 Omsk region 56 Orenburg region 57 Oryol region 58 Penza region 59 Perm region (also 159) 60 Pskov region 61 Rostov region (also 161) 62 Ryazan region 63 Samara region (also 163) 64 Saratov region (also 164) 65 Sakhalin region 66 Sverdlovsk region (also 96) 67 Smolensk region 68 Tambov region 69 Tver region 70 Tomsk region 71 Tula region 72 Tyumen region 73 Ulyanovsk region (also 173 ) 74 Chelyabinsk region (also 174) 75 Chita region 76 Yaroslavl region 77 Moscow (also 97, 99, 177, 197, 199) 78 St. Petersburg (also 98) 79 Jewish Autonomous Region 80 Aginsky Buryat Autonomous Okrug 81 Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug 82 Republic of Crimea 83 Nenets Autonomous Okrug 84 Taimyr Autonomous Okrug 85 Ust-Ordynsky Buryat Autonomous Okrug 86 Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug 87 Chukotka Autonomous Okrug 88 Evenki Autonomous Okrug 89 Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug 90 Moscow Region (also 50, 150) 92 Sevastopol 93 Krasnodar Territory (also 23) 94 Territories that are located outside the Russian Federation and are served by the Department of Security Facilities of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (for example. Baikonur) 95 Chechen Republic (new numbers) 96 Sverdlovsk region (also 66) 97
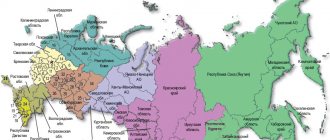
Automobile codes of regions of Russia. Region numbers.
St. Petersburg (also 98) 79 Jewish Autonomous Region 80 Aginsky Buryat Autonomous Okrug 81 Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug 82 Republic of Crimea 83 Nenets Autonomous Okrug 84 Taimyr Autonomous Okrug 85 Ust-Ordynsky Buryat Autonomous Okrug 86 Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug 87 Chukotka Autonomous Okrug 88 Evenki Autonomous Okrug 89 Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug 90 Moscow Region (also 50, 150) 92 Sevastopol 93 Krasnodar Territory (also 23) 94 Territories that are located outside the Russian Federation and are served by the Department of Security Facilities of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (for example, Baikonur) 95 Chechen Republic (new numbers) 96 Sverdlovsk region (also 66) 97 Moscow (also 77, 99, 177, 197, 199) 98 St. Petersburg (also 78) 99 Moscow (also 77, 97, 177, 197 , 199) 102 Republic of Bashkortostan (also 02) 116 Republic of Tatarstan (also 16) 118 Udmurt Republic (also 18) 121 Chuvash Republic (also 21) 125 Primorsky Territory (also 25) 138 Irkutsk Region (also 38) 150 Moscow Region (also 50, 90) 152 Nizhny Novgorod region (also 52) 154 Novosibirsk region (also 54) 159 Perm region (also 59) 161 Rostov region (also 61) 163 Samara region (also 63) 164 Saratov region (also 64) 173 Ulyanovsk region ( also 73) 174 Chelyabinsk region (also 74) 177 Moscow (also 77, 97, 99, 197, 199) 197 Moscow (also 77, 97, 99, 177, 199) 199 Moscow (also 77, 97, 99, 177, 197)
Tax registration of foreign companies and assignment of TIN/KPP is carried out in the following cases:
- if they have branches, representative offices, and other separate divisions on the territory of Russia;
- if they have real estate and/or vehicles on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Tax registration of foreign companies and assignment of a KIO (foreign organization code) is carried out in the case of opening bank accounts in Russia.
1.
TIN and religion [edit | edit code ]
In some religious communities, obtaining a TIN is considered sinful and ungodly. Archimandrite Zacchaeus (Wood) recalled: “To accept or not to accept an individual number - at one time it seemed that there was no more important problem in the Orthodox community” [6]. At the same time, the Greek Orthodox Church in 1998 and the Russian Orthodox Church in 2001 announced the possibility of using TIN for Orthodox citizens. However, there are other theological judgments. A striking example is the so-called Address of Bishop Diomede, which condemns the blessing by the spiritual authorities of the personal identification of citizens.
In 2003, the Church of the Kazan Icon of the Mother of God published a book by Hierodeacon Abel (Semyonov) and Alexander Drozdov, “The Sign is Impenetrable,” which is addressed to a wide range of readers. The book goes into great detail to explain the “spiritual essence” of identification numbers and why they are being introduced in all countries of the world. In 2003-2005, this book was withdrawn from sale in some dioceses (for example, Vladimir and Suzdal) and many churches of the Moscow diocese.
On February 4, 2013, the Council of Bishops of the Russian Orthodox Church adopted a statement “The position of the Church in connection with the development of technologies for recording and processing personal data,” which says: [7]
“The use of an identifier, coupled with modern technical means, will allow total control over a person without his consent - to track his movements, purchases, payments, medical procedures, receipt of social assistance, other legally and socially significant actions, and even his personal life.
Many believers express fundamental disagreement with the mandatory assignment of an identification code and its transformation into an irreplaceable, lifelong and posthumous attribute
».
TIN starts with 97 - based on what?
Documents required for registering a branch or representative office and assigning a TIN/KPP:
- Certificate of registration of a foreign legal entity or an extract from the trade (banking) register, or 4 certificates: for the company, for participants (shareholders), for the address, for the directors - (legalized or with an apostille, translated into Russian) - notarized copies;
- Constituent documents (legalized or with an apostille, translated into Russian) - notarized copies;
- A certificate from a tax authority of a foreign state in any form on the registration of a foreign organization as a taxpayer in the country of incorporation indicating the taxpayer code (or its equivalent), issued within the last 3 months (legalized or with an apostille, translated into Russian) - notarized copy;
- The decision of a foreign legal entity to open a Representative Office in Moscow and appoint the Head of the Representative Office (legalized or with an apostille, translated into Russian) - notarized copy;
- Regulations on the Representative Office - notarized copy;
- Power of attorney for the Head of the Representative Office (legalized or with an apostille, translated into Russian) - notarized copy;
- Permission (accreditation) to open a Representative Office - notarized copy;
- Certificate of inclusion in the Consolidated State Register - notarized copy.
2. Documents required for registering companies with real estate or vehicles and assigning TIN/KPP:
- Certificate of registration of a foreign legal entity or an extract from the trade (banking) register, or 4 certificates: for the company, for participants (shareholders), for the address, for the directors - (legalized or with an apostille, translated into Russian) - notarized copies;
- Constituent documents (legalized or with an apostille, translated into Russian) - notarized copies;
- A certificate from a tax authority of a foreign state in any form on the registration of a foreign organization as a taxpayer in the country of incorporation indicating the taxpayer code (or its equivalent), issued within the last 3 months (legalized or with an apostille, translated into Russian) - notarized copy;
- Notarized copies of documents confirming ownership of property or rights of possession and (or) use and (or) disposal.
3. Documents required for registering companies opening bank accounts in Russia and assigning a KIO (foreign organization code):
- Certificate of registration of a foreign legal entity or an extract from the trade register.
- Certificate:
— For participants (shareholders). If the founder of the company is a legal entity, then an extract from the trade register (registration certificate);
- To the address;
- For directors.
- Constituent documents: charter, constituent agreement.
- A certificate from a tax authority of a foreign state in any form regarding the registration of a foreign organization as a taxpayer in the country of incorporation, indicating the taxpayer code (or its equivalent), issued within the last 3 months.
All documents must be translated into Russian and notarized, as well as legalized and have an apostille.
Moscow, Putilkovskoe highway, 12 Phone: +7 (495) 740-6788 +7 (495) 740-6388 Fax: +7 (495) 617-1107
|
Find out the checkpoint code using the organization's tax identification number
It is quite easy to find out the checkpoint by TIN. Special services for checking counterparties and official resources will help you do this quickly and almost always for free. Let's talk about ways to search for basic details on the Internet.
KPP - reason code for registration. Organizations receive this combination of numbers, which complements the TIN, upon registration.
It is impossible to find out an individual entrepreneur by the INN, since this code is not assigned to individual entrepreneurs.
The combination consists of 9 characters and is deciphered as follows:
- The first 2 digits are the code of the region where the company is registered. For the largest taxpayers who are registered with interregional inspectorates, the checkpoint begins with the numbers “99”. This is an additionally assigned detail that is indicated when paying federal taxes; The regional code of such companies is also retained. Therefore, the largest taxpayers have two assigned codes, which are used in different cases.
- The 3rd and 4th digits are the number of the tax office that registered the company. Together, the first 4 digits make up the code of the Federal Tax Service to which the company is attached.
- The 5th and 6th characters are the encrypted reason for registration;
- The last 3 digits are the serial number when registering.
Separate divisions - branches and representative offices - are not registered as separate legal entities. There is one legal entity, and the divisions are considered part of it, having the same TIN as the main enterprise. Despite the same identification number, the registration code of a branch or representative office may differ from the code of the main legal entity.
The code of a separate division is tied to the Federal Tax Service where the branch itself is registered.
It is difficult to check the checkpoint of a separate division online - official extracts from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities do not contain such detailed information about branches and representative offices of companies. If you need to know exactly the department code, it is better to contact the branch itself for details or use commercial versions of the programs.
Automobile codes of regions of Russia. Region numbers.
Car codes of regions of Russia Numbers of regions of Russia (rus)
| 01 Region code Republic of Adygea | 52 Region code Nizhny Novgorod region |
| 02 Region code Republic of Bashkortostan | 53 Region code Novgorod region |
| 03 Region code Republic of Buryatia | 54 Region code Novosibirsk region |
| 04 Region code Altai Republic | 55 Region code Omsk region |
| 05 Region code Republic of Dagestan | 56 Region code Orenburg region |
| 06 Region code Republic of Ingushetia | 57 Region code Oryol region |
| 07 Region code Kabardino-Balkarian Republic | 58 Region code Penza region |
| 08 Region code Republic of Kalmykia | 59 Region code Perm region |
| 09 Region code Karachay-Cherkess Republic | 60 Region code Pskov region |
| 10 Region code Republic of Karelia | 61 Region code Rostov region |
| 11 Region code Komi Republic | 62 Region code Ryazan region |
| 12 Region code Republic of Mari El | 63 Region code Samara region (also 163) |
| 13 Region code Republic of Mordovia | 64 Region code Saratov region |
| 14 Region code Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | 65 Region code Sakhalin region |
| 15 Region code Republic of North Ossetia | 66 Region code Sverdlovsk region (also 96) |
| 16 Region code Republic of Tatarstan | 67 Region code Smolensk region |
| 17 Region code Republic of Tyva (Tuva) | 68 Region code Tambov region |
| 18 Region code Udmurt Republic | 69 Region code Tver region |
| 19 Region code Republic of Khakassia | 70 Region code Tomsk region |
| 20 Region code Chechen Republic (old numbers) | 71 Region code Tula region |
| 21 Region code Chuvash Republic | 72 Region code Tyumen region |
| 22 Region code Altai Territory | 73 Region code Ulyanovsk region |
| 23 Region code Krasnodar region (also 93) | 74Region code Chelyabinsk region |
| 24 Region code Krasnoyarsk Territory | 75 Region code Chita region |
| 25 Region code Primorsky Krai | 76 Region code Yaroslavl region |
| 26 Region code Stavropol Territory | 77 Moscow region code (also 97, 99, 177, 197) |
| 27 Region code Khabarovsk Territory | 78Region code of St. Petersburg (also 98) |
| 28 Region code Amur region | 79 Region code Jewish Autonomous Region |
| 29 Region code Arkhangelsk region | 80 Region code Aginsky Buryat Autonomous Okrug |
| 30 Region code Astrakhan region | 81 Region code Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug |
| 31 Region code Belgorod region | 82 Region code Koryak Autonomous Okrug |
| 32 Region code Bryansk region | 83 Region code Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
| 33 Region code Vladimir region | 84 Region code Taimyr Autonomous Okrug |
| 34 Region code Volgograd region | 85 Region code Ust-Ordynsky Buryat Autonomous Okrug |
| 35 Region code Vologda region | 86 Region code Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug |
| 36 Region code Voronezh region | 87 Region code Chukotka Autonomous Okrug |
| 37 Region code Ivanovo region | 88 Region code Evenki Autonomous Okrug |
| 38 Region code Irkutsk region | 89 Region code Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
| 39 Region code Kaliningrad region | 90 Region code Moscow region (also 50, 150) |
| 40 Region code Kaluga region | 93 Region code Krasnodar region (also 23) |
| 41 Region code Kamchatka region | 94 Region code of territories located outside the Russian Federation and served by the Department of Security Facilities of the Ministry of Internal Affairs |
| 42 Region code Kemerovo region | 95 Region code Chechen Republic (new numbers) |
| 43 Region code Kirov region | 96 Region code Sverdlovsk region (also 66) |
| 44 Region code Kostroma region | 97 Moscow region code (also 77, 99, 177) |
| 45 Region code Kurgan region | 98 City region code |
The procedure for issuing license plates in Russia
Let's consider the most common type of numbers in the Russian Federation:
These are the numbers that are installed on most cars.
At first glance, the number consists of a random sequence of letters and numbers. In fact, not everything is so simple here.
All numbers from 0 to 9 are used on license plates. However, unlike numbers, not all letters of the Russian alphabet can appear on license plates. This privilege is given only to those letters that have similar spellings in the Latin alphabet. Those. Only the letters A, B, E, K, M, N, O, R, S, T, U, X can be used on license plates.
You might have learned about this fact before, but the next thought will probably seem interesting to you. We will talk about the order in which the numbers are issued .
Numbers are issued in order (except for special series). However, the order in which the characters change in the number is far from normal perception. The symbols change not from right to left, but in a slightly different way - in a rather confusing sequence.
1. Most often, the third digit in the license plate changes (in the figure it is number 6). After the number T356OK the number T357OK will be issued.
2. The second most frequently changing character is the 2nd digit (in Figure 5). After the number T359OK the number T360OK will be issued.
3. The third most common symbol is the 1st digit (in Figure 3). After the number T399OK the number T400OK will be issued.
The numbers seem to be okay, but the same cannot be said about the letters.
4. The fourth most common symbol is the 1st letter (T in the picture). After the number T999OK the number U001OK will be issued.
5. The fifth most common symbol is the 3rd letter (K in the picture). After the number X999OK the number A001OM will be issued.
6. The sixth most common symbol is the 2nd letter (O in the picture). After the number X999OX the number A001PA will be issued.
The procedure is quite complicated, so if you didn’t understand it the first time, re-read points 1-6 again.
The symbols on the left side of the registration plate, which were discussed above, are responsible for vehicle numbers within a specific region. By the way, I inform statistics lovers that no more than 1 million 726 thousand 272 car registration plates can be issued with one region code.
After this limit is exhausted, the number of the Russian region written on the right side of the number changes. From this moment on, numbers begin to be issued again within the new region. Each subject of the Russian Federation has its own code, and some subjects of the federation, which have a very large number of cars, are assigned several region codes at the same time.
AUDIT 97, Moscow
St. Petersburg (also 78)
- 1 – this figure acts as an indication that the record number is assigned to the OGRN.
- 08 – entry made in 2008.
- 78 is the number of the subject, that is, St. Petersburg.
- 47 – number of the registration authority. This is interdistrict Federal Tax Service No. 15 for St. Petersburg.
- 03649 – record number.
- 6 – control number.
The last number is determined using a formula. Divide the OGRN without the check digit by 11, that is, 108784703649/11=9889518513.5455. We discard the remainder after the decimal point, and multiply the result by 11, that is, 9889518513*11=108784703643. Then from this number you need to subtract 12 OGRN characters: 108784703649-108784703643=6. This is the control number.
Decoding the TIN of a legal entity
Firms are also assigned a TIN, the decoding of ten digits means:
- characters 1-4 – number of the Federal Tax Service that registered the company (the first digits also indicate the region where the registration was made);
- characters 5-9 - serial number when an enterprise or company is included in the state register;
- 10 is a control number according to a special algorithm, introduced to check the correctness of the remaining digits in the TIN.
Enterprises must enter the TIN in any documents sent to the Federal Tax Service, as well as when paying taxes and other budget obligations.
Legal entity in the Russian Federation: how to determine its status - resident or non-resident
Trust the bank? Sorry, but the level of responsibility of the bank is obvious from the fact that it “notified” the person by printing pieces of paper addressed to him and storing them under his printer for 2 years. And as a result, in the accumulated notifications there is NO payment for 2000 rubles received from AAA (USA) LLC, represented by its branch in Moscow. Organization address: Russia, 109028, Moscow, BBB st., no.5. Bank details: CB "Garanti Bank-Moscow" No. 40807810********On clerk.ru they clearly said that this is a NON-resident.
Calculation of check digits [edit | edit code ]
For a 10-digit TIN assigned to a legal entity, the control [9] [10] is the last, tenth digit:
n 10 = ( ( 2 n 1 + 4 n 2 + 10 n 3 + 3 n 4 + 5 n 5 + 9 n 6 + 4 n 7 + 6 n 8 + 8 n 9 ) mod 11 ) mod 10 <1>+ 4n_<2>+10n_<3>+3n_<4>+5n_<5>+9n_<6>+4n_<7>+6n_<8>+8n_<9>)10>
< >>10>> It is interesting that the check digit, calculated by such an impressive method at first glance, allows you to make mistakes even in one TIN digit. For example, 1181111110 and 1191111110. For the first number 121 mod 11 = 0, for the second 131 mod 11 = 10, 0 mod 10 = 0.
For a 12-digit TIN assigned to an individual, the last two digits are the control ones:
n 11 = ( ( 7 n 1 + 2 n 2 + 4 n 3 + 10 n 4 + 3 n 5 + 5 n 6 + 9 n 7 + 4 n 8 + 6 n 9 + 8 n 10 ) mod 11 ) mod 10 <11>=((7n_<1>+2n_<2>+4n_<3>+10n_<4>+3n_<5>+5n_<6>+9n_<7>+4n_<8>+6n_<9> +8n_<10>)
< >>10> n 12 = ( ( 3 n 1 + 7 n 2 + 2 n 3 + 4 n 4 + 10 n 5 + 3 n 6 + 5 n 7 + 9 n 8 + 4 n 9 + 6 n 10 + 8 n 11 ) mod 11 ) mod 10 <12>=((3n_<1>+7n_<2>+2n_<3>+4n_<4>+10n_<5>+3n_<6>+5n_<7>+ 9n_<8>+4n_<9>+6n_<10>+8n_<11>)
< >>10>
Explanation
. Expression a mod b
< >>b> means the remainder when a is divided by b .
Tax authorities constantly require us to be careful when choosing suppliers, and it is accountants who are forced to carefully check all documents and pay attention to all kinds of details. We have long been accustomed to these abbreviations - INN and KPP. And it seems that no questions can arise here. Meanwhile, if many people have an idea about the TIN and know where to check it, then, apart from how the checkpoint is deciphered, as a rule, no one else knows anything about it. These are the questions we are asked.
The checkpoint will help you determine who you are dealing with: an organization or its branch
For all our counterparties, the checkpoint ends with 01001. But recently, while filling out a payment form, I discovered some strange checkpoint from a new supplier - the last numbers are 43001. How do you understand what this means?
: Such a checkpoint means that you are transferring money to a branch of your counterparty and Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 06/02/2008 No. CHD-6-6/ [email protected] .
For example, KPP 770601001 means that the organization is located in Moscow and the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. 6 for Moscow registered it as a taxpayer at its location (code 01).
If the checkpoint numbers (ZZ) are not 01 (for example, like your counterparty’s - 43), then this means that the organization was registered on other grounds.
A complete list of reason codes for registration is given in the departmental directory (SPPUNO) approved. 10/11/99. But this guide is an internal document. And if previously it was posted for public viewing on the official website of the Federal Tax Service, now it is problematic to find it in the public domain. But we will tell you what some codes mean.
Here and here you can try to get a transcript of the checkpoint - find out the region and inspection that registered your counterparty, the reason for registration. But this information is unofficial.
| Code | Reason for registration |
| 02*, 03*, 43 | Registration of a branch of a Russian organization |
| 04*, 05*, 44 | Registration of a representative office of a Russian organization |
| 31*, 32*, 45 | Announcement about the opening of a separate division of a Russian organization |
* These codes are not currently assigned Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 06/02/2008 No. CHD-6-6/ [email protected] . But checkpoints with these codes assigned earlier remain valid.
Gearbox may change
Our counterparty's checkpoint has changed. OGRN and TIN remain the same. What does this mean? Moving? Or could there be other options?
: The organization may have a new checkpoint, in particular clause 2.1.4 of the Procedure:
- when changing the location of the organization (moving), when you have to register with another tax office;
Moving a company to a new location is the most common reason for changing checkpoints
- when registering at the location of separate divisions;
- when registering at the location of real estate and (or) vehicles;
- on other grounds provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, when registering at the location of a subsoil plot (assigned to organizations recognized as taxpayers of mineral extraction tax), Art. 335 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Most often, the checkpoint changes if an organization moves and has to register with another tax office and clause 2.1.4 of the Procedure; subp. “c” clause 1, clause 5 art. 5 of the Federal Law of 08.08.2001 “On state registration of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs”. For example, if the checkpoint used to be 77 07 01001, and then became 77 19 01001, this means that your counterparty was registered with the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate No. 7 for Moscow, and now with the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate No. 19 for Moscow.
Inn
TIN of a legal entity TIN of a legal entity is a sequence of 10 Arabic digits, of which the first two represent the code of the subject of the Russian Federation in accordance with Article 65 of the Constitution (or “99” for the interregional inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service), the next two are the number of the local tax inspectorate, the next five are the number tax record of the taxpayer in the territorial section of the Unified State Register and the last one is the control digit. The TIN together with the checkpoint make it possible to identify each separate division of a legal entity, therefore both of these codes are often displayed and used together, for example, when indicating the payment details of organizations. TIN of a foreign legal entity Since January 1, 2005, it always begins with the numbers “9909”, the next 5 digits correspond to the Code of the foreign organization, the last one is a check digit.
Decoding TIN, checkpoint and other codes
A code decoding service is now available - Deciphering TIN, KPP and OGRN codes on the Raccoon Poiskun website
—
TIN
Taxpayer identification number (abbr. TIN) is a digital code that streamlines the accounting of taxpayers in the Russian Federation. Assigned to both legal entities and individuals. It has been assigned to organizations since 1993, to individual entrepreneurs - since 1997, to other individuals - since 1999 (since the beginning of the first part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). (see TIN on Wikipedia)
There are two types of TIN in Russia: TIN of an organization - 10-digit and TIN of an individual or individual entrepreneur - 12-digit.
The general structure of the TIN is similar.
So the 10-digit TIN of organizations consists of the following parts:
- 4 digits - department code of the Federal Tax Service of Russia (SOUN directory)
- 5 digits - unique taxpayer number within this division of the Federal Tax Service
- 1 digit - verification code according to the verification code
The TIN of an individual consists of 12 digits, differs slightly and consists of:
- 4 digits - department code of the Federal Tax Service of Russia (SOUN directory)
- 6 digits - taxpayer number, unique within this division of the Federal Tax Service
- 2 digits - verification code according to the verification code
You can read more about how to check TIN codes at https://www.polytech.ural.ru/checkvalues.htm
I will dwell in more detail on what information the TIN carries.
1. Using the TIN, you can always and unambiguously determine the region of the organization/individual. persons since the Federal Tax Service division code consists of a region code + a Federal Tax Service division code within a given region. The region code corresponds to the serial number of the region in the Constitution of the Russian Federation - by analogy with car license plates and so on.
2. Using the code of the Federal Tax Service division, it is possible, with some error, to determine the location of the division and the area it covers, respectively, the location of the person/legal entity. For legal entities individuals, this is of little relevance since information on their location is already available online with great detail, according to physical information. There is no such information online for individuals, and there shouldn’t be.
3. Taxpayer number is an incremental number. If you take a closer look and look at at least a few TINs, you will notice that the later the organization is registered, the larger this number is. Accordingly, knowing the dates of registration of several organizations at intervals of values, one can with some probability assume the time of issuance of the TIN for another organization. However, retrieving this information for TIN of organizations is not relevant since information about the date of issue of OGRN/TIN is already provided by the Federal Tax Service online.
4. It is possible to check the TIN both by the control code and by the Unified State Register of Legal Entities provided by the Federal Tax Service in the public part at https://egrul.nalog.ru/fns/
checkpoint
The reason for registration code (RRC) is a nine-digit digital code that, together with the organization’s TIN, allows you to uniquely identify its separate divisions (see RRCC on Wikipedia).
Checkpoint structure:
- 4 digits - department code of the Federal Tax Service of Russia (SOUN directory);
- 2 digits - reason code for registration;
- 3 digits - serial number of registration;
In most cases, the checkpoint looks like: Federal Tax Service division code + 01001 since not many organizations have separate divisions.
The disadvantages of the checkpoint include the impossibility of checking the checkpoint using a checksum. At most, you can check the “reasonableness” of filling out each of its elements. In general, the checkpoint does not carry more information than the TIN, and is almost never used separately in the organization’s TIN.
OGRN
OGRN (main state registration number) - the state registration number of a record of the creation of a legal entity or a record of the first submission in accordance with the Federal Law “On State Registration of Legal Entities” of information about a legal entity registered before the entry into force of this Law (clause 8 of the Rules of Administration Unified State Register of Legal Entities) (see OGRN on Wikipedia).
OGRN structure:
- 1 digit - code, OGRN sign (always equal to 1);
- 2 digits - the last two digits of the year the entry was made in the state register;
- 2 digits - region code according to the list of regions in Article 65 of the Constitution
- 7 digits - the serial number of the record from the beginning of the year;
- 1 digit - OGRN verification code;
What you can find out by knowing the OGRN:
1. Year of registration of the organization according to the last two digits.
2. With some accuracy, the month (or maybe even a week) of registration of the organization according to the serial number of the record.
3. Region code of the organization according to Article 65 of the Constitution.
4. Using the OGRN code, other public information about the organization can be obtained - TIN, KPP, name, address from the public register of the Federal Tax Service.
Please note that INN and OGRN differ in the principles of maintaining serial numbers of organizations. If in the TIN they are linked to the tax office, then in the OGRN they are linked to the year of registration. Accordingly, based on the ability to determine the date of its assignment by the serial number of the TIN, we can say that the TIN carries a little more information (inspection number) than the OGRN.
Passport ID
The passport number consists of 10 digits where the first 4 are the series number, and the last digits are the number in this series.
But there are also certain features. Of the 4 digits in the series, the first two are digits of the region, but not according to Article 65 of the Constitution, but according to OKATO.
The big open question is what the next two numbers are. They are definitely not the last digits of the year the document was issued, even according to passport data disclosed in the public domain, for example, in court decisions you can see that passports with the numbers 07 can be issued in 2003 and 2004.
My assumption is that the last two digits of the series are, in fact, part of the number since the dependence of the number of the last two digits of the series + number on the date of issue of the document is noticeable.
Yes, to the question of why the name of the Department of Internal Affairs and the date of its receipt are always written along with the passport number. If the INN code provided for the SOUN directory, then the passports, in fact, inherited their numbers from the Soviet ones and there is still no register of responsible police departments anywhere, at least in the public domain, and the number itself will not allow identifying the police department by its code.
And, of course, the key is not extracting information from a specific number or identifier, but obtaining by linking sets of external directories.
How to determine the region by TIN?
- By TIN (or rather by its number) you can actually determine in which region it was issued. The TIN of individuals contains 12 digits, legal ones - ten.
In any case, the region is recognized by the first four digits - the first two are responsible for the region, the next two are the number of the department where the TIN was received. See the code decoding table on this website.
- By the TIN number (code), you can determine not only the region in which the document was issued, but also the name of the authority that issued it.
The code can be divided into segments consisting of a certain number of digits. Regardless of whether the TIN is a legal entity or an individual, the first four digits indicate the code of the department that issued the TIN. This code can be entered into the form on the website nalog.ru and you will be given all the information about the region.
- Using the individual taxpayer number (or, in short, TIN), you can determine the region in which a person or organization is registered.
The TIN code consists of ten digits for organizations and twelve digits for individuals and legal entities. The first four digits indicate the Federal Tax Service department code.
In turn, this Federal Tax Service code consists of a region code and a Federal Tax Service division code within this region. And the region code (like car license plates) coincides with the serial N of the region in the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
Maybe it will be useful to someone - there is now a service for deciphering codes (inn, ogrn, checkpoint), you can find it here.
- Indeed, by using the TIN (taxpayer identification number), you can determine the region where the TIN was issued.
If the case concerns any organization, then the TIN consists of 10 digits, but if it is an individual, then of 12. In both cases, the first four digits in the TIN indicate the region (this is the code of the Federal Tax Service region where the TIN was issued).
All that remains is to see which region the code of one or another division of the Federal Tax Service corresponds to.
- You can only find out in which region the TIN was issued. This can be determined by the first two digits - the code of the subject of the Russian Federation. But if a person moves to another region, the TIN is not changed. That is, a person can live, for example, in Moscow, but have a TIN starting with 55 - the code of the Omsk region, because he lived there before and that’s where he was given the TIN. Region codes can be found here.
- Indeed, by using the TIN you can easily find out in which region it was issued, which means where the person lives or is registered with the tax office. You just need to know what they mean.
There are two types of TIN and they have different numbers of digits. For individuals - 12 numbers, and legal entities are assigned 10 numbers.
In a 10-digit TIN, you can find out the region where the TIN was issued by the first four digits. And an ordinary person (12 digits) also uses the first 4 digits. Here two numbers are responsible for the region, and the remaining numbers are the number of the specific branch where the TIN was obtained. For example, in Crimea the first numbers are 82 and 92 (Sevastopol). TIN code table is here.
- According to Federal Law-154 dated December 23, 2003 and the order of the Ministry of the Federal Tax Service dated March 3, 2004 under BG-3-09/178, a unified standard for registration and numbering of certificates for registration of individual entrepreneurs and legal entities "LLC" was established.
First, registration and issuance of TIN to Russian citizens occurs once at the place of their permanent registration (registration).
The TIN number is a set of 10 digits (for legal entities and LLCs) and 12 digits (for entrepreneurs and individuals).
Second, on the merits of the issue, the first two digits in the TIN number mean the number of the region that issued and assigned the TIN to the citizen. Many people sometimes confuse the first digits of the TIN number when an entrepreneur conducts his business in another region of the Russian Federation, considering this region to be the region of registration of the TIN.
The second two digits in the TIN number just mean the number of the tax office that issued the certificate (TIN).
- Using your TIN number, determining the region is quite possible and completely easy. This can be done for both legal entities and individuals. So, it is precisely the first four digits in your TIN code that will imply the region you are looking for; all that remains is to decipher the specific region by numbers in the directory here and that’s it.
- The first two digits in your TIN are the number of your region, and the next two digits are the number of your tax office, where you submit reports and declarations.
- The TIN of individuals and legal entities contains in the first four digits the code of the department of the Federal Migration Service of Russia that issued the identification code. You need to find a directory of four-digit codes for FMS departments to find the region by TIN.
- You can determine the region by TIN as follows; the first two digits indicate the region where the Entrepreneur or legal entity is registered; regardless of its status, either LLC, or CJSC, or OJSC.
The second two digits mean; number of the tax authority where you registered as a taxpayer.
Entrepreneurs, if they are engaged in business activities in another region, then the TIN remains the same, but they are temporarily registered with the tax authority of another region and pay taxes there, but insurance contributions to the Pension Fund are paid at the place of issue of the Certificate of Registration and assignment of the TIN
- In the TIN of both an individual and a legal entity, each number has its own functional purpose and carries certain information.
Thus, the region can be compared with the table below and the first two digits of the TIN.
Inn for non-resident legal entities
Info
Home page / Individuals / I am interested in / Taxpayer identification number - a sequence of 12 Arabic digits, of which the first two represent the code of the subject of the Russian Federation according to Art. 65 of the Constitution, the next two are the number of the local tax office, the next six are the number of the taxpayer’s tax record and the last two are the so-called “check digits” to check the correctness of the entry. TIN of an individual entrepreneur Assigned upon registration of an individual as an individual entrepreneur, if this person did not previously have one.
Otherwise, the existing TIN is used.
How to determine the region by TIN?
How to determine the region by TIN?
- By TIN (or rather by its number) you can actually determine in which region it was issued. The TIN of individuals contains 12 digits, legal ones - ten.
In any case, the region is recognized by the first four digits - the first two are responsible for the region, the next two are the number of the department where the TIN was received. See the code decoding table on this website.
- By the TIN number (code), you can determine not only the region in which the document was issued, but also the name of the authority that issued it.
The code can be divided into segments consisting of a certain number of digits. Regardless of whether the TIN is a legal entity or an individual, the first four digits indicate the code of the department that issued the TIN. This code can be entered into the form on the website nalog.ru and you will be given all the information about the region.
- Using the individual taxpayer number (or, in short, TIN), you can determine the region in which a person or organization is registered.
The TIN code consists of ten digits for organizations and twelve digits for individuals and legal entities. The first four digits indicate the Federal Tax Service department code.
In turn, this Federal Tax Service code consists of a region code and a Federal Tax Service division code within this region. And the region code (like car license plates) coincides with the serial N of the region in the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
Maybe it will be useful to someone - there is now a service for deciphering codes (inn, ogrn, checkpoint), you can find it here.
- Indeed, by using the TIN (taxpayer identification number), you can determine the region where the TIN was issued.
If the case concerns any organization, then the TIN consists of 10 digits, but if it is an individual, then of 12. In both cases, the first four digits in the TIN indicate the region (this is the code of the Federal Tax Service region where the TIN was issued).
All that remains is to see which region the code of one or another division of the Federal Tax Service corresponds to.
- You can only find out in which region the TIN was issued. This can be determined by the first two digits - the code of the subject of the Russian Federation. But if a person moves to another region, the TIN is not changed. That is, a person can live, for example, in Moscow, but have a TIN starting with 55 - the code of the Omsk region, because he lived there before and that’s where he was given the TIN. Region codes can be found here.
- Indeed, by using the TIN you can easily find out in which region it was issued, which means where the person lives or is registered with the tax office. You just need to know what they mean.
There are two types of TIN and they have different numbers of digits. For individuals - 12 numbers, and legal entities are assigned 10 numbers.
In a 10-digit TIN, you can find out the region where the TIN was issued by the first four digits. And an ordinary person (12 digits) also uses the first 4 digits. Here two numbers are responsible for the region, and the remaining numbers are the number of the specific branch where the TIN was obtained. For example, in Crimea the first numbers are 82 and 92 (Sevastopol). TIN code table is here.
- According to Federal Law-154 dated December 23, 2003 and the order of the Ministry of the Federal Tax Service dated March 3, 2004 under BG-3-09/178, a unified standard for registration and numbering of certificates for registration of individual entrepreneurs and legal entities "LLC" was established.
First, registration and issuance of TIN to Russian citizens occurs once at the place of their permanent registration (registration).
The TIN number is a set of 10 digits (for legal entities and LLCs) and 12 digits (for entrepreneurs and individuals).
Second, on the merits of the issue, the first two digits in the TIN number mean the number of the region that issued and assigned the TIN to the citizen. Many people sometimes confuse the first digits of the TIN number when an entrepreneur conducts his business in another region of the Russian Federation, considering this region to be the region of registration of the TIN.
The second two digits in the TIN number just mean the number of the tax office that issued the certificate (TIN).
- Using your TIN number, determining the region is quite possible and completely easy. This can be done for both legal entities and individuals. So, it is precisely the first four digits in your TIN code that will imply the region you are looking for; all that remains is to decipher the specific region by numbers in the directory here and that’s it.
- The first two digits in your TIN are the number of your region, and the next two digits are the number of your tax office, where you submit reports and declarations.
- The TIN of individuals and legal entities contains in the first four digits the code of the department of the Federal Migration Service of Russia that issued the identification code. You need to find a directory of four-digit codes for FMS departments to find the region by TIN.
- You can determine the region by TIN as follows; the first two digits indicate the region where the Entrepreneur or legal entity is registered; regardless of its status, either LLC, or CJSC, or OJSC.
The second two digits mean; number of the tax authority where you registered as a taxpayer.
Entrepreneurs, if they are engaged in business activities in another region, then the TIN remains the same, but they are temporarily registered with the tax authority of another region and pay taxes there, but insurance contributions to the Pension Fund are paid at the place of issue of the Certificate of Registration and assignment of the TIN
- In the TIN of both an individual and a legal entity, each number has its own functional purpose and carries certain information.
Thus, the region can be compared with the table below and the first two digits of the TIN.
How to get a tax identification number for a foreign citizen
Attention
A foreign organization wishing to be a member of the Russian Society does not need to register in the Russian Federation) Almaz55 Activist Messages: 1,086 1 2 3 « Previous topic | Next topic » Reg Smileys On Code On HTML Code Off Forum rules Quick transitionMy accountPrivate messagesSubscriptionsWho's on the forumSearch the forumForum main pageInformation and analytical department News and articles Press releasesRegistration of legal entities and related industries Registration, changes, reorganization of legal entities General questions MIFTS No. 46 for Moscow Registration during the creation of MIFTS No. 15 for St. Petersburg Changes and Re-registration Mos.
region Reorganization and liquidation Regions Correction of errors of individual entrepreneurs Failures OKVED Forms and sample documents Archive Interaction with the state.
Application [ edit | edit code ]
Currently, a TIN may be required from an individual when applying for a job [4], but its receipt remains voluntary. It is only necessary for government officials and individual entrepreneurs, however, the number can be assigned without the knowledge of the person if it is necessary to maintain tax records in relation to this person [5].
A foreign citizen who entered the Russian Federation in a manner that does not require a visa and has received a temporary residence permit is required to submit a copy of the certificate or notification of tax registration within 12 months from the date of entry into the Russian Federation.
It is used in tax accounting instead of using personal data in almost all documents.
Accounting and tax reporting of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs must contain an INN.
What is ogrn and its decoding
Each subject of the Russian Federation has a specific number.
- Next come four numbers that show which specific Federal Tax Service Inspectorate this company belongs to in a particular region.
- The next five digits are the resolution number under which the company was incorporated. It is interesting that, despite the fact that data is added to the tax register throughout the year, this number is also unique.
- The thirteenth digit is a verification digit; it is the one used to check the OGRN.
It is known that twelve digits are a single number that is divisible by eleven. The remainder obtained by division will be in the place of this thirteenth digit.
It is easy to see that repeating two identical numbers is impossible.
Important
The numbers that indicate the year will be repeated in a hundred years using the same accounting procedure. Also, there cannot be repetitions in the numbers of the region and the Federal Tax Service.
One of these important numbers is OGRN. This number helps to identify legal entities; moreover, each organization individually receives its own OGRN. Using this code, it is easy to see complete information about the company you are interested in, while using the TIN, little information is available about the company, and only about the tax service that assigned this number.
- Purpose ↓
- LLC ↓
- IP ↓
- For non-residents ↓
- Examples ↓
- Differences between OGRN and GRN ↓
- Who issues OGRN ↓
- Cost ↓
- Search and verification of enterprises ↓
- OGRN of the branch ↓
But what is OGRN? OGRN is the main state registration number, which usually consists of thirteen digits, each of which has a specific meaning.
Decoding TIN, checkpoint and other codes #legislation #EDS #ECMJ
Ivan Begtin's blog
The meaning of numbers in passport numbers, TIN and other official documents. The following blogs will reveal the magic of numbers of bank identification codes, current and correspondent accounts, bank cards, as well as codes of the All-Russian Classifier of Economic Activities and some others...
TIN
Taxpayer identification number (TIN) is a digital code that streamlines the accounting of taxpayers in the Russian Federation. Assigned to both legal entities and individuals. It has been assigned to organizations since 1993, to individual entrepreneurs - since 1997, to other individuals - since 1999 (from the beginning of the first part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) (see TIN on Wikipedia).
By the way, information about the TIN also contains a qualified electronic signature certificate of a legal entity.
There are two types of TIN in Russia: TIN of an organization - 10-digit and TIN of an individual or individual entrepreneur - 12-digit.
The general structure of the TIN is similar.
So the 10-digit TIN of organizations consists of the following parts:
● 4 digits - department code of the Federal Tax Service of Russia (SOUN directory);
● 5 digits - unique taxpayer number within this division of the Federal Tax Service;
● 1 digit – verification code according to the verification code.
The TIN of an individual consists of 12 digits, differs slightly and consists of:
● 4 digits - department code of the Federal Tax Service of Russia (SOUN directory);
● 6 digits - taxpayer number, unique within this division of the Federal Tax Service;
● 2 digits - verification code according to the verification code.
You can read more about how to check TIN codes at https://www.polytech.ural.ru/checkvalues.htm
I will dwell in more detail on what information the TIN carries.
1. Using the TIN, you can always and unambiguously determine the region of an organization/individual, since the Federal Tax Service division code consists of the region code + the code of the Federal Tax Service division within a given region. The region code corresponds to the serial number of the region in the Constitution of the Russian Federation - by analogy with car license plates and so on.
2. Using the code of the Federal Tax Service division, it is possible, with some error, to determine the location of the division and the area it covers, respectively, the location of the person/legal entity. For legal entities, this is of little relevance, since information on their location is already available online with great detail, according to physical information. There is no such information online for individuals, and there shouldn’t be.
3. Taxpayer number is an incremental number. If you take a closer look and look at at least a few TINs, you will notice that the later an organization is registered, the larger this number is. Accordingly, knowing the dates of registration of several organizations at intervals of values, one can with some probability assume the time of issuance of the TIN for another organization. However, retrieving this information for TIN of organizations is not relevant, since information about the date of issue of OGRN/TIN is already provided by the Federal Tax Service online.
4. It is possible to check the TIN, both by the control code and by the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, provided by the Federal Tax Service in the public part at https://egrul.nalog.ru/fns/
checkpoint
The registration reason code (RPC) is a nine-digit digital code, which, together with the organization’s TIN, allows you to uniquely identify its separate divisions (see KPP on Wikipedia).
Checkpoint structure:
4 digits - department code of the Federal Tax Service of Russia (SOUN directory);
2 digits - reason code for registration;
3 digits - serial number of registration.
In most cases, the checkpoint looks like this: Federal Tax Service division code + 01001 since not many organizations have separate divisions.
The disadvantages of the checkpoint include the impossibility of checking the checkpoint using a checksum. At most, you can check the “reasonableness” of filling out each of its elements. In general, the checkpoint does not carry more information than the TIN, and is almost never used separately in the organization’s TIN.
OGRN
Main state registration number (OGRN) - the state registration number of the record on the creation of a legal entity or the record on the first submission in accordance with the Federal Law “On State Registration of Legal Entities” of information about a legal entity registered before the entry into force of this Law (clause 8 of the Rules of Administration Unified State Register of Legal Entities) (see OGRN on Wikipedia).
OGRN structure:
● 1 digit – code, OGRN sign (always equal to 1);
● 2 digits - the last two digits of the year the entry was made in the state register;
● 2 digits - region code according to the list of regions in Article 65 of the Constitution
● 7 digits — serial number of the record from the beginning of the year;
● 1 digit – OGRN verification code.
What you can find out by knowing the OGRN:
1. Year of registration of the organization according to the last two digits.
2. With some accuracy, the month (or maybe even a week) of registration of the organization according to the serial number of the record.
3. Region code of the organization according to Article 65 of the Constitution.
4. Using the OGRN code, other public information about the organization can be obtained - TIN, KPP, name, address from the public register of the Federal Tax Service.
Please note that INN and OGRN differ in the principles of maintaining serial numbers of organizations. If in the TIN they are linked to the tax office, then in the OGRN they are linked to the year of registration. Accordingly, based on the ability to determine the date of its assignment by the serial number of the TIN, we can say that the TIN carries a little more information (inspection number) than the OGRN.
Passport ID
The passport number consists of 10 digits, where the first 4 are the series number, and the last digits are the number in this series.
But there are also certain features. Of the 4 digits in the series, the first two are digits of the region, but not according to Article 65 of the Constitution, but according to OKATO.
The big open question is what the next two numbers actually are. They are definitely not the last digits of the year the document was issued, even according to passport data disclosed in the public domain, for example, in court decisions you can see that passports with the numbers 07 could be issued in 2003 and 2004.
My guess is that the last two digits of the series are, in fact, part of the number, since the dependence of the number of the last two digits of the series + number on the date of issue of the document is noticeable.
Yes, to the question of why the name of the Department of Internal Affairs and the date of its receipt are always written along with the passport number. If the INN code provided for the SOUN directory, then the passports, in fact, inherited their numbers from the Soviet ones and nowhere, at least in the public domain, is there still no register of responsible police departments, and the number itself will not allow identifying the police department by its code.
And, of course, the key is not extracting information from a specific number or identifier, but obtaining by linking sets of external directories.
What is the tax identification number for non-resident legal entities?
Didn’t ask - no (In your case, but I don’t know the details) Financial monitoring doesn’t fine anyone, but besides it, the currency control authorities are up to their ass. If you violated the rules for conducting currency transactions, you may be fined. Or you may not be fined. The fines are large .You need to live in the UK or somewhere else where there are normal banks and laws. There is nothing more to discuss. Úlfhéðinn 07/15/2010, 21:09 # Great, thanks Myallo 07/12/2010, 19:13 # Re: How to determine non-resident based on details The easiest way to determine residency is by the account number of the sender of the payment (payer). The first five digits of the account in the payment slip are always different for residents and non-residents.
Despite the fact that at least 2 banks out of the top 10 clearly said “we don’t need absolutely anything for transactions under $5,000.” It turns out that in one bank you would not be in danger, but in another - 5,000 rubles for each account, many of which are much smaller? Well, not from the bank, but based on the information leaked by it? Funny.
Or does the bank still not provide the authorities with any information on transactions that, as it itself sees, are less than $5,000? And all the papers for smaller amounts - just to see for yourself? Let's close the topic. For an amount less than 5,000, you do not have to issue a transaction passport. However, the transaction is considered a currency transaction. The bank may request information on it. It may not. If it does, you must provide it. Bank accounts differ in their ownership (Bank of Russia Regulation No. 579-P dated February 27, 2017) and contain the attribute of a resident or non-resident company.
Using the bank account number (consists of 20 digits), it is possible to determine the residence of a legal entity.
Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)
A taxpayer identification number (TIN) is a digital code that is assigned to individuals and legal entities in order to streamline tax accounting. The TIN is uniform throughout the Russian Federation for all types of taxes and fees.
The taxpayer (individual or legal entity) indicates the identification number in documents submitted to the tax authorities: applications, reports, declarations, etc., as well as in other cases provided for in Art. 84 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In turn, the tax authority indicates the taxpayer identification number in all notifications sent to it.
The Tax Code reserves the right for an individual who is not an individual entrepreneur not to indicate the TIN in tax returns, applications and other documents. In this case, the citizen must provide his personal data: last name, first name and patronymic, date and place of birth, gender, place of residence, passport and other document details, citizenship data (see ibid.).
When applying for a job, the employer does not have the right to require a TIN certificate, since this is not provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. If a personnel employee refuses to register a new employee without a TIN, his actions are illegal. The identification number is required to be presented only when applying for a civil service when concluding a contract (Article 26 of Federal Law No. 79-FZ, Article 28 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
However, some categories of workers are recommended to have a TIN. In tax returns, it is easier to indicate the identification numbers of the chief accountant and manager than to fill out complete data on a specially designated page. Bank employees and tax inspectors also do not have the right to insist that an individual provide TIN information. For example, in the declaration in form 3-NDFL, the taxpayer must indicate the last name, first name and patronymic, as well as, optionally, passport data or TIN.
The identification number of an individual remains unchanged throughout life. If a person moves to a new place of residence, the tax office will issue him a new certificate with the same TIN.
Find out the TIN of an individual (individual entrepreneur)
can be found on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia or on the Unified Portal of State and Municipal Services.
Find out the OGRN/GRN/TIN of a legal entity
In order to check yourself or a counterparty, you can visit the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
How to obtain a TIN of an individual or legal entity
The procedure for registering and deregistering organizations and individuals, as well as assigning a taxpayer identification number, is determined by the following regulatory documents:
TIN of an individual
The TIN of an individual is a sequence of 12 Arabic digits, of which the first two are the code of the subject of the Russian Federation, the next two are the number of the local tax office, the next six are the tax record number of the taxpayer and the last are a check number to check the correctness of the entry.
In order to obtain a taxpayer identification number (TIN) for an individual, you must contact the tax office (IFNS) at your place of residence. Tax registration is carried out on the basis of an application in form No. 2-2-Accounting, in which you need to indicate personal data: last name, first name and patronymic, date and place of birth, place of residence, passport details or other identification document, citizenship data .
Within no later than 5 working days from the date of receipt of the application, the tax authority is obliged to issue a TIN certificate, which is an A4 form indicating personal data and taxpayer identification number. Registration and deregistration are free of charge.
At the request of the citizen, a note about the TIN can be made on the 18th page of the passport indicating the name of the tax authority, its code and the date of entry.
Changes in information about individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs are subject to registration by the tax authority at their place of residence on the basis of data that the authorized bodies transmit to the tax office. If a citizen changes his location or place of residence, the change in place of registration occurs automatically. An individual is not required to report new data to the Federal Tax Service.