What is a currency transaction type code?
KVBO is a five-number value indicating the type of transaction. The code is selected depending on the purpose of the payment and the content of the documents accompanying the transaction. If the payment order and code do not match, the payment is rejected. The list of QVBOs is contained in Central Bank Instruction No. 181-I dated August 16, 2021.
How to make a foreign currency payment and what documents to submit to the bank ?
Where should I put the code? If this is an order for a transaction in rubles, you need to put it before the text about the purpose of payment. In other banking documents, KVVO is indicated in a line specially designated for this. The code is both alphabetic and numeric values. There is no need to put spaces or other symbols between letters and numbers.
KVVO consists of two parts. The first indicates the class of the transaction, the second – its essence. Let's look at an example. Operation code – 10100. Its components:
- 10 – indicates the export of products from the territory of Russia.
- 100 – indicates that the buyer made an advance payment.
the bank's commission for currency control in accounting and tax accounting ?
The very presence of this code means that this is a transaction with a foreign counterparty.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Sometimes an accountant encounters problems when choosing a KVBO.
There are a lot of codes in the Central Bank instructions. It is not always easy to decide which one is suitable for a particular operation. If an accountant is afraid of making a mistake, he can ask a representative of the servicing bank for advice.
Results
To correctly fill out a payment form in foreign currency, you need to:
- declare the transaction against payment to the bank and issue a PS;
- determine the details of a specific payment;
- fill out the transaction order according to the bank form - either in the client bank or manually according to the sample.
All actions involving the transfer of foreign currency funds outside the Russian Federation must be checked for compliance with the currency legislation of the Russian Federation.
Sources: Bank of Russia instruction No. 181-I dated August 16, 2017
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Code groups
The KVVO group is the first 2 digits that reveal the class of the operation. Let's look at these groups and their meaning:
- 01 and 02 – non-cash conversion payments.
- 10 and 11 – payment for export or import of products.
- 12 and 13 – payment for products without import and export.
- 20 and 21 – payment for services, work, rights to intellectual activity.
- 22 and 23 – payment under mixed type agreements.
- 30 – payments for real estate.
- 32 – payment under an agreement for assignment of claims.
- 35 – other payments.
- 40 and 41 – issuance of loans.
- 42 and 43 – payment of loans and interest on them.
- 57 – payment under trust agreements.
- 58 – payment under brokerage service agreements.
- 70 – transactions not related to trade (for example, transfer of salary or pension).
- 90 – other operations.
The next three numbers reveal the contents of the operation. Example: code 70 affects a non-trading transaction. The last numbers indicate which transfer was made. For example, this could be the payment of travel allowances.
Possible errors when making payments to a counterparty
The value of the list of the most common errors makes it easier to check and identify shortcomings in specific payment orders. These mistakes are very often made:
- Incorrect TIN. If in all other respects the order is completed correctly, then the regulatory authorities do not have the right to demand clarification of the details.
- The basis for payment is incorrectly specified. This is also a minor error. The funds will be sent to the recipient. In this case, it makes sense to contact the recipient. His response clarifying the basis for the payment is attached to the order. This must be done, as otherwise there may be confusion. It can lead to difficulties in the work of accountants and tax representatives.
- Allocation of VAT if the order concerns counterparties under a special tax regime. For example, the counterparty may use the simplified tax system. In this case, he does not need to pay VAT. Accordingly, there is no need to highlight VAT in the payment order. If this is done, you need to send a clarifying letter to your bank. The latter sends a notification to the bank servicing the counterparty. The error must be corrected. Otherwise, the counterparty will have to pay tax at an increased rate.
- Incorrect designation of payment purposes. For example, the funds were actually transferred as an advance for the service. However, the order specifies a loan as the purpose. In this case, you also need to notify the bank about the error. If this is not done, the company will not receive a deduction for the advance payment.
- Incorrect information about the counterparty. The counterparty's details may be changed. However, the company does not always send out notifications about this. That is, the payment is sent using the old details. In this case, the transferred funds will be kept in the banking institution until the information is clarified. On the sixth day, the funds are returned to their sender. When making such an error, the company has two courses of action: submitting updated information to the bank or receiving funds back on the sixth day and then re-issuing the order.
Errors that can be fixed
Let's look at correctable errors and the procedure for eliminating them:
- The purpose of the funds is incorrectly indicated. You need to perform a tax reconciliation with the Federal Tax Service, and then fill out a reconciliation report. It is signed by an accountant, as well as a representative of the Federal Tax Service.
- Inflated payment amount. There are several ways to proceed. First: redirection of funds. The overpaid money will be used to pay the next payments. Second: processing a refund of payment to the company’s bank account.
The listed errors are considered insignificant. They are relatively easy to fix.
Errors that cannot be corrected
Let's consider significant errors that cannot be corrected:
- Indication of the wrong BCC. For example, the code numbers are indicated incorrectly or the old KBK is taken. In this case, the payment is considered unclassified. The tax will be considered unpaid. That is, the payer will have to pay penalties and fines for late payment. To correct the situation, you need to send an application to the Federal Tax Service. It specifies a request to offset the transferred funds. A copy of the incorrect order and a bank statement are attached to the application.
- Underpayment. The tax is also not considered paid. To correct the situation, you need to add the missing amount to the budget.
- Indication of the BCC, which relates to another tax. In this case, you can act in several ways. This is, firstly, a return of funds to the payer’s bank account. Secondly, this is a repeated payment of the payment. What will happen to the old payment? It is credited under another tax, to which the KBK applies. An overpayment is created for this tax, which will be offset against the next payment.
- Invalid recipient account. This is the most difficult mistake. The money will have to be sent again. A penalty will be charged for late payments.
- The name of the banking institution is incorrect. Also an irreversible error.
- Indication of a non-existent BCC. A refund is being issued. The payment is sent again.
There is a big difference between a significant and an insignificant error. In case of correctable errors, the payer only needs to send a clarification. In this case, the payment will be considered paid. Errors that cannot be corrected mean that taxes or payments to counterparties are not considered paid. That is, fines and penalties will be imposed on the payer.
Errors when sending payments to the budget
A payment order for payments to the budget has many fields, which is prone to errors. However, among these fields there are those that control structures pay little attention to. Specifically, these are the following lines:
- Taxable period.
- Tax payer status.
- Order number and date.
- Reason for payment and its type.
If errors are made in these lines, it is not necessary to correct them. The line “priority of payment” is also unimportant. An exception is that orders are sent by companies whose activities involve financial difficulties: restrictions on expense transactions, insufficient funds in a bank account. If these circumstances are present, the “priority” line is checked first.
KVBO for operations
Here are the codes that usually accompany operations:
- 10100. Prepayment for the export of a batch of products from the territory of Russia.
- 10200. Deferred payment for a shipment transported out of the country.
- 11100. Advance payment to a foreigner for products imported into the country.
- 11200. Settlements with a resident if he is given a deferred payment for a consignment imported into the country.
- 12060. Payment for goods sold by a non-resident. It is assumed that the products were sold abroad, without import into the Russian Federation.
- 13010. Payment from a foreigner to a resident for goods sold in Russia.
- 20100. Prepayment of services or goods in favor of a resident.
- 20200. Payment between a non-resident and a resident for services or work.
- 20400. Payments under agreements on assignments, guarantees to the resident.
- 20500. Payments under guarantee agreements to a non-resident.
- 21100. Advance payment for services or work in favor of a foreigner.
- 35030. Payment to the resident for other actions.
- 35040. Payment in favor of a foreigner for other actions.
- 41030. Lending to a resident by a non-resident.
- 42015. Payment of the principal debt to a non-resident, if the resident has corresponding obligations.
- 61100. Movement of currency from one account to another.
- 61135. Transfer of currency from a resident’s account to an account in another bank.
- 70060. The resident transfers remuneration to the foreigner for work.
- 99090. Other actions and translations not listed above.
This is a list of the most common KVBOs. The remaining codes are in Central Bank Instruction No. 181.
Other operations
KVBO is also needed when working with foreign currency:
- 01010 – sale of currency for rubles.
- 01030 – purchase of currency for rubles.
Code usage example
Products were purchased from a non-resident. It was transported to Russia based on the provisions of a foreign trade agreement. The required code depends on the selected payment type:
- 10100 – for prepayment.
- 10200 – postpaid.
What to do if the goods of a non-resident are located in Russia? Code 13010 is used. The validity of its use is confirmed by an invoice with the Russian address of the product location.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Code 13010 is not suitable for fuel and other resources for vehicle operation. The purchase of fuel is accompanied by these KVBO: 22110 (prepayment transaction) and 22210 (postpayment).
Features of filling out a payment form
A payment order to a non-resident in rubles is filled out in the usual manner. As a rule, it is drawn up on the basis of an invoice sent by a foreign counterparty, or according to the terms of an agreement concluded with a non-resident. These documents contain all the details by which funds will be transferred. The entry in the “Purpose of payment” field when transferring an advance payment by a resident to a non-resident may have, for example, the following form:
“{VO11100} Transfer of advance payment for goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation. Agreement No. 63 dated 08/10/2020, invoice No. 12/125 dated 08/10/2020.”
The explanation for the payment must be written in as much detail as possible, then the payment transaction will be carried out without complications. It is recommended to indicate the contract or invoice number, document details, name of goods or services, payment method according to the contract.
Employers should also remember that, according to Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 5286-U dated October 14, 2019, when transferring wages or other income to individuals, incl. non-residents, from June 1, 2021 in the “Name” field. pl." payment cards indicate one of three codes for the type of income (we talked about this in more detail in our article).
Sample payment order for a non-resident individual
Code when paying wages to a non-resident
The company's staff may include non-residents. A non-resident is any person without a Russian passport or citizenship. Within the framework of currency control, it does not matter how long the foreigner lived in Russia. In any case, he is considered a non-resident. When paying remuneration to a foreign person, codes are also used.
Payments in favor of a non-resident are indicated by code 70060. But to use this KVBO, it is not enough to provide only a payment order to the bank. Most likely, you will also need an employment agreement with a foreigner and a copy of his passport.
Remuneration for an employee is not only salary, but also other payments. And each payment is assigned its own code:
- 70200 – payments according to the advance report (for example, travel expenses).
- 70030 – social payments (for example, financial assistance).
- 70120 – payments made by court decision.
Upon payment, accompanying documents are sent to the bank. Their list depends on the type of operation. For example, a non-resident is accrued travel allowances. In this case, a business trip order is sent to the bank.
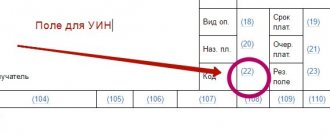
Currency payment order form
IMPORTANT!
The codes located on the left (for example 33B, 52a, etc.) correspond to a specific field of the SWIFT format in the international ISO system. According to SWIFT standards, such payments do not allow the use of characters like: №, %, #, $, &, “ “, =, @, \, { }, [ ], ;, *,!, _, < >.
The correctness of the details is important for both the payer and the bank for the purposes of:
- reducing the risk of erroneous execution of orders for payment in foreign currency;
- acceleration of currency control procedures and greater efficiency of payment;
- reducing translation costs by reducing the number of investigations into unaccepted or erroneously accepted payments;
- fulfillment of obligations to the counterparty without additional costs, including due to failure to meet payment deadlines.
Consequences of mistakes made
Payment orders must be drawn up carefully. Even if the error does not lead to the loss of funds, it will still take a lot of time to correct it. Let's look at the consequences of the error:
- Not paid taxes on time. Consequences: accrual of penalties, fines, risk of repaying the full amount of tax.
- The tax is considered unpaid. Consequences: penalties, fines.
- The payment went to another fund. There is no offsetting of amounts between different funds. Therefore, you will have to pay the tax in full again.
The error will have to be corrected. And this entails separation from employees’ activities, the need to draw up additional documents, and legal proceedings.