Home / Labor Law / Responsibility / Material
Back
Published: 04/29/2016
Reading time: 8 min
0
6785
At every enterprise, regardless of the type of its financial and economic activities, there is an acute issue of compliance with the amount of material assets in its warehouses and the available documentation.
Ideally, these indicators should coincide, but in practice this happens extremely rarely.
- How is product shortage determined during inventory?
- How to register a shortage? Within the normal rate of natural loss
- As a result of uncontrollable circumstances
- As a result of theft
On what basis is inventory carried out?
Let's start with the fact that for many people, the concepts of shortages and inventory are inextricably associated with trade. This is a fundamentally incorrect judgment. Inventory is necessary at any enterprise, regardless of the area of activity, including budgetary organizations .
In essence, an inventory is carried out to identify excesses or shortages of inventory items listed on the organization’s balance sheet. This may include goods, cash, furniture and even accounting documentation. According to the method of conducting, inventory can be planned or unscheduled. In the first case, this procedure is regulated by the regulatory documents of the enterprise. The frequency of inspection is set by the manager, depending on the turnover and specifics of the activity.
Emergency incidents may serve as grounds for an unscheduled inventory. For example:
- Suspicion of theft of goods;
- Fire in the warehouse;
- Sale of the enterprise.
In addition, the availability of inventory items can be checked when the person responsible for storage changes.
Material liability of the employee
There is no doubt that the safety of the company's assets is ensured through the financial responsibility of its employees.
By virtue of Article 232 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee who causes damage to the employer shall compensate it according to the rules established by this code. These rules are established by Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Namely: the employee is obliged to compensate the employer for direct actual damage caused to him. At the same time, lost income (lost profits) cannot be recovered from the employee.
However, it is possible to recover damages without restrictions only if the employee is fully financially responsible. The relevant cases are listed in Article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Among them is a shortage of valuables entrusted to the employee on the basis of a special written agreement or received by him under a one-time document.
In accordance with Article 244 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a special written agreement must be understood as agreements on full financial responsibility - individual or collective (team). Examples of one-time documents include:
- a power of attorney issued to an employee to receive certain valuables;
- expenditure cash order for the issuance of funds to an accountable person for upcoming expenses;
- invoice for internal movement, transfer of goods, containers (according to the unified form No. TORG-13).
However, the head of the organization bears full financial responsibility by force of law - on the basis of the first part of Article 277 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For this reason, an agreement on the full financial responsibility of the manager is not drawn up.
In cases not expressly provided for in Article 243 of the Labor Code, the employee will bear financial liability for damage caused only within the limits of his average monthly earnings. The basis is Article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Such financial liability is called limited (letter of Rostrud dated October 19, 2006 No. 1746-6-1). According to the author, the remaining part of the amount of damage that cannot be recovered from the employee can be presented to the head of the company - of course, if there are legal grounds for this (clause 9 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated November 16, 2006 No. 52 “On the application by courts of legislation governing financial liability of employees for damage caused to the employer”).
What is called a shortage?
24114899
This definition hides the shortage of something previously put on the balance sheet of the enterprise and taken into account in the accounting documentation. This applies to funds, goods and materials in safekeeping. The amount of the shortfall is usually deducted from the salary of the person responsible or the culprit.
Here it is necessary to clarify that the shortfall also includes the profit lost by the enterprise. For example, if a product cannot be sold due to its breakdown. This may include the expiration of the shelf life, when products have to be sold at reduced prices. In this case, the shortage will be considered the difference between the actual and estimated cost.
Step-by-step instruction
It is not always possible to write off shortages that are discovered after recounting products. Then the collection procedure must be carried out according to the following algorithm:
- First, you will need to draw up and sign an official act, in which you need to clarify the results of the re-accounting of goods or money.
- Next, you should issue an official notice to the employee about the withholding of a certain amount.
- Finally, you need to deduct from his salary. The employer must take into account that more than 20% of the funds cannot be withdrawn from the employee’s funds.
The deficiency can be recovered from the guilty person even if the employment relationship with him was terminated for some reason. If, based on the results of the repeated accounting of valuables, violations were discovered, then a report on the theft of products should be drawn up as quickly as possible and the employee should be fired.
What could cause the shortage?
Here are the following factors:
- Re-grading. For example, the store sells Krasnodar and Dutch apples. They are similar in appearance, but differ in cost. If Krasnodar products are mistakenly sold instead of Dutch fruits, there will be a shortage.
- Production costs. This may include the fact that some goods may fall apart during the sales process, which will also lead to shortages.
- Insurmountable circumstances. For example, as a result of a flood, warehouses were flooded and some of the products became unusable.
- Theft. This is the fault of employees who, using their official position, appropriate funds or goods from the company.
Read also: What do you pay when you resign at your own request?
Reasons for surpluses and shortages
The inventory process helps to identify deviations in accounting data from the actual availability of property. Surpluses appear when an organization's cash assets exceed those recorded. Shortfalls, on the other hand, indicate a missing asset.
Reflection of inventory results in accounting depends on the reason for the discrepancies. The inventory commission draws up a statement of discrepancies and sends it to the manager to review the results of the inspection. The reasons for the formation of surpluses and shortages may be the following:
| Surplus | Shortages |
| Errors when taking inventory | Natural decline |
| Unaccounted deliveries | Errors in warehouse accounting |
| Excessive savings | Production costs |
| Errors in accounting for the release of materials and products | Theft |
| Excess supply | Incompetence or absence of financially responsible persons (MOL) |
How is a shortage investigated?
The inventory assets of an enterprise are never ownerless, and a specific person from among the employees is responsible for them.
If a shortage is identified, an explanatory note is taken from such an employee, which sets out in detail the reasons for what happened. Such a note is drawn up in free form, but is always certified by the signature of the person guilty or suspected of the shortage. The employee is obliged to explain the reasons for the shortage within 2 days from the moment such a demand is presented to him. The degree of guilt of the employee is determined by the head of the enterprise. He also has the right to apply legal sanctions to those responsible. For example, to recover the amount of damages or to fire an unscrupulous employee. If we are talking about dismissal, the culprit must be familiarized with the relevant order within three days.
Preparation of documents for write-off
Write-off of shortages must be carried out taking into account the norms of natural loss, as well as the policy of the institution. Natural loss is written off only after this amount has been calculated by the accounting department, and in addition, after the procedure for verifying the results by the management of the institution and an independent commission.
After this, a decision is made on the advisability of an official investigation to identify the perpetrators. Inventory shortage? What to do with the employees whose fault this happened? Let's figure it out first. An investigation is especially necessary in situations where the amount of the shortage significantly exceeds the norms of natural loss. The use of natural loss norms is provided for food products, in general for any quantitative, and, in addition, quality goods, excluding packaged products and those that come individually.
Registration of identified shortages
When registering a shortage, its reasons are always taken into account. In particular, losses may be caused as a result of the fault of third parties or unforeseen circumstances. The fact of production costs is also taken into account. Separate types of accounting entries apply to each situation.
Natural loss
Let's say that a store sells flour. During packaging, some of the goods fall apart, which is written off as production costs. Let’s assume that during the reporting period, the shortage amounted to 2,000 rubles, excluding the trade margin of 500 rubles.
The accounting entry will be as follows:
- Debit 94/Credit 41 - 1,500 amount of deficiency;
- Debit 94/Credit 42 - 5 00 the size of the trade margin for unavailable products;
- Debit 44/Credit 94 - 1,500 cost of shortage within production costs.
Unseen circumstances
Let’s assume that a concrete mixer worth 15,000 rubles burned down at a construction company. Accrued depreciation amounted to 2,500 rubles, the culprits of the fire have not been identified.
This is shown in the reporting documentation as follows:
- Debit 94/Credit 01 - 15,000 initial cost of equipment;
- Debit 02/Credit 01 - 2,500 accrued depreciation;
- Debit 91-2/Credit 94 - 15,000 amount of deficiency.
Theft has been committed
For example, taking advantage of her official position, a store cashier embezzled 12,500 rubles. The fault has been established, the shortage will be deducted from the cashier’s salary in equal installments of 1,250 rubles per month.
It will appear in the accounting entry as follows:
- Debit 70/Credit 73 - 1,250 deduction from salary.
Postings
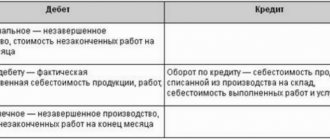
The account directly named as related to shortages is “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” (94), but it is not always used.
During a planned inventory, if there is a shortage, make an entry Dt 94 Kt of valuables accounts ; in case of force majeure (fires, natural disasters), it is included in profit and loss: Dt 99 Kt of valuables accounts .
If a shortage is identified when counting goods from counterparties, the Dt 94 Kt scheme for valuable accounts (within the limits of the volumes fixed by the contract). Volumes of shortages identified during the calculation that are larger than those provided for in the contract may give rise to claims. Then use the entry Dt 76 Kt of value accounts .
In account 76, a sub-account “Settlements for claims” is opened. The shortage is recorded depending on the type of goods and materials: Dt 94 Kt 01, 10, 41, 50. The detected shortage of fixed assets is recorded according to Kt 01 at the residual value, depreciation is written off separately: Dt 02 Kt 01.
Financially responsible persons are not obliged to compensate for shortfalls within the limits of natural loss. It increases the cost of production: Dt 20, 23, 44, etc. Kt 94 .
The shortfall in excess of the loss norms is repaid from the funds of the guilty employees: Dt 73/2 Kt 94. If the culprit is not found or there is a court decision in favor of the financially responsible person about his innocence, the excess shortfall is charged to other expenses of the company: Dt 91/2 Kt 94.
Briefly about the main thing
- The write-off of shortages during inventory is carried out depending on its reasons.
- The shortage within the limits of natural loss norms and compliance with the terms of the agreement between counterparties is taken into account in account 94 and written off to the cost of production. If the lack of material assets is higher than the norm, the company’s losses are compensated by the guilty employee from his own funds. If the culprit is not found or determined by the court, the shortage will be written off as other expenses.
- Shortages resulting from disasters and natural disasters are included in profit and loss (account 99), and in a situation where goods received from a counterparty have a shortage not provided for in the contract, account 76, subaccount “Settlements for claims”, is used.
- The norms of natural loss are established by separate documents of the ministries and are applied depending on the industry, business area, and inventory object by members of the inventory commission when calculating damage.
- It is very problematic to hold guilty persons accountable if a liability agreement has not been concluded with them.
- The manager always has financial responsibility to the company; such an agreement is not concluded with him.
Is it possible to write off the shortage?
The law provides for this possibility.
For example, a customer in a store accidentally dropped two bottles of expensive alcohol from the display case. This entails a shortage, but it will not be possible to recover losses from the buyer. Here, the store employee who was engaged in displaying the goods may be considered guilty. However, for each type of product there are certain standards, which are called distribution costs. If the amount of the shortfall does not exceed the established norms, it can be written off without any legal consequences. If, in the case of broken alcohol, distribution costs include the loss of 3 bottles, the shortage can be written off. However, this fact remains at the discretion of the manager.
Reasons for the undercount
Shortage is not only the theft by an employee of company property or his neglect of his official duties. The reasons for the shortage may also be the following factors:
- The impact on inventory items of emergency situations in the form of fire, flood.
- The occurrence of unforeseen situations at the enterprise, as a result of which material assets or money may be damaged or completely lost in the warehouse.
- Poor quality sorting of goods. For example, a store may confuse two similar-looking varieties of potatoes.
Each of the listed factors requires its own procedure for drawing up a document about a detected deficiency. Therefore, if a shortage of goods is detected, it is very important to find out the cause of the phenomenon.
Withholding the shortfall from the perpetrators
Typically, financial responsibility is negotiated during employment.
For example, a storekeeper will be fully responsible for the products in his warehouse. Department seller - for goods under his control. If a shortage is identified, losses are recovered from the salary of the responsible person. Here it is necessary to clarify that for shortages on particularly large scales, criminal prosecution is possible. However, this punishment does not exempt the culprit from compensation for losses caused. Read also: Calculation of vacation pay in 2021
Please note that financial liability can be personal or collective. The second option is often used in stores and supermarkets. For example, if a shortage is identified in the sausage department, the amount of the shortage will be covered by all employees who work here.
The amount is usually distributed in equal shares, regardless of whose shift the shortage occurred.
Circumstances excluding financial liability
When planning to recover damages, it is necessary to take into account the provisions of Article 239 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The fact is that the employee’s financial liability is excluded in cases of damage due to:
- force majeure, normal economic risk, extreme necessity or necessary defense;
- failure by the employer to fulfill the obligation to provide appropriate conditions for storing property entrusted to the employee.
We believe it would be appropriate to explain the regulatory grounds for exemption from liability.
Force majeure refers to extraordinary and unavoidable circumstances under given conditions (clause 3 of Article 401 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The requirement of emergency implies the exclusivity of the circumstance in question: its occurrence is not usual in specific conditions (clause 8 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 24, 2016 No. 7). Such circumstances include, in particular, natural disasters (earthquake, flood, hurricane), fire, mass diseases (epidemics), strikes, military operations, terrorist acts, sabotage (clause 1.3 of the appendix to the Resolution of the Board of the Chamber of Commerce and Industry of the Russian Federation dated December 23, 2015 No. 173-14). Obviously, such events do not depend on the will of the parties to the employment contract.
Normal economic risk may include the actions of an employee that correspond to modern knowledge and experience, when the set goal could not be achieved otherwise, the employee properly fulfilled his job duties, showed a certain degree of care and prudence, took measures to prevent damage, and the object the risk was material assets, and not the life and health of people (clause 5 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of November 16, 2006 No. 52).
note
Direct actual damage is understood as a real decrease in the employer’s available property or deterioration in the condition of said property, as well as the need for the employer to make costs or excessive payments for the acquisition, restoration of property or for compensation for damage caused by the employee to third parties (Part 2 of Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) .
In our opinion, an illustration of a normal economic risk is the shortage of goods due to theft by customers in the sales areas of self-service stores (decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 4, 2013 No. VAS-13048/13). In this regard, you can use the Procedure for approval and conditions for applying differentiated amounts for writing off losses of goods in self-service stores (departments, sections), approved by Order of the Ministry of Trade of the RSFSR dated July 8, 1984 No. 194. Moreover, such losses within the limits of natural loss norms are accepted for profit tax purposes ( letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 29, 2005 No. 03-03-04/1/392, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated July 18, 2013 in case No. A65-23469/2012).
And the infliction of harm by a person in a state of extreme necessity implies the elimination of a danger that directly threatens the personality and rights of this person or other persons, as well as the legally protected interests of society or the state, if this danger could not be eliminated by other means and if the harm caused is less significant than prevented harm (Article 2.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Part 1 of Article 39 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Finally, the state of necessary defense presupposes the protection of the personality and rights of the defender or other persons, the legally protected interests of society or the state from a socially dangerous attack, if this attack was associated with violence dangerous to the life of the defender or another person, or with an immediate threat of the use of such violence ( Part 1 of Article 37 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). Such situations are typical for robbery for the purpose of stealing someone else's property, committed with the use of violence dangerous to life or health, or with the threat of such violence (Part 1 of Article 162 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). Violence dangerous to life or health should be understood not only as violence that resulted in the infliction of grave and moderate harm to the health of the victim, but also infliction of minor harm to health, causing a short-term health disorder or a slight permanent loss of general ability to work (clause 21 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated December 27, 2002 No. 29 “On judicial practice in cases of theft, robbery and robbery”).
This “excursion” into jurisprudence is intended to show that resolving disputes about the financial responsibility of an employee requires a certain legal literacy.
How to properly contain shortages
If the loss does not fit into the distribution cost norms, it cannot be written off. In this case, deduction from the salary of the guilty or responsible person is applied. To ensure that everything happens within the framework of the law, the following rules are observed:
- A matching statement is prepared and a report on the fact of shortage is drawn up;
- The employee is given a written notice indicating for what and in what amount the deduction will be made from him;
- The form of compensation for losses is established: a one-time deduction or equal amounts, but not more than 20% of the total amount that the employee receives in hand.
Here it is necessary to clarify that recovery of damages is possible after the dismissal of the employee responsible for the shortage. However, such a procedure is performed only in court, and the employer will have to prove the employee’s guilt.
An audit will not replace an inventory
Internal control is carried out not only by the management bodies of the economic entity, but also by the audit commission (auditor) of the economic entity (clause 18.1 of Information No. PZ-11/2013).
In a corporate organization, the election of an audit commission (auditor) falls within the exclusive competence of the highest body of such an organization (Part 2 of Article 65.3 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
From the perspective of labor legislation, an economic entity is an employer. Article 20 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines an employer as an individual or legal entity that has entered into an employment relationship with an employee.
In cases provided for by federal laws, another entity entitled to enter into employment contracts may act as an employer. But the audit commission (auditor) does not have the authority to conclude employment contracts. Thus, in an LLC, the auditor is considered a body of the company and is elected exclusively by the general meeting of its participants. A person performing the functions of the sole executive body of a company cannot be a member of the audit commission of the company or an auditor (clause 6 of Article 32, subclause 5 of clause 2 of Article 33 of Law No. 14-FZ).
Based on Article 47 of Law No. 14-FZ, the auditor of the company has the right at any time to conduct inspections of the financial and economic activities of the company and have access to all documentation relating to the activities of the company. At the request of the auditor, the director of the company, as well as employees of the company, are obliged to give the necessary explanations orally or in writing.
note
Shortage is the physical absence of cash and material resources, including goods and fixed assets, identified as a result of control procedures, audits, and inventory (clause 172, section 2 “GOST R 51303-2013. National standard of the Russian Federation. Trade. Terms and definitions” , approved by order of Rosstandart dated August 28, 2013 No. 582-st).
Thus, shortages can also be identified as a result of an audit. However, the auditor does not have the right to take any action to recover damages from employees. Article 247 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation vests the corresponding powers only with the employer. It reads:
- before making a decision on compensation for damage by specific employees, the employer is obliged to conduct an inspection to establish the amount of damage caused and the reasons for its occurrence;
- To conduct such an inspection, the employer has the right to create a commission with the participation of relevant specialists.
Let us add on our own: such specialists can be members of the audit commission.
So, it is unlawful to equate an audit with an inventory, although the Ministry of Finance of Russia in its letter dated February 13, 2009 No. 03-03-06/4/4 did not see any difference between these activities. True, the letter is devoted to tax legal relations. Meanwhile, in the tax sphere, paragraph 1 of Article 11 of the Tax Code applies, by virtue of which the concepts and terms of civil and other branches of legislation of the Russian Federation should be applied in the meaning in which they are used in these branches of legislation, unless otherwise specifically provided for by this code.
As a result, we believe: following an audit that reveals a shortage, the manager is obliged to schedule an unscheduled inventory of the same assets.
Sample documents
Inventory order
Inventory order
Inventory report
Inventory report sample
Report of shortage of goods
Report of shortage of goods
Features of shortages during inventory
Let us consider the features of the various circumstances that caused the shortage.
Production costs
The following factors are taken into account:
- Methods of transportation and storage;
- Production technology;
- Climatic and seasonal conditions.
For example, if a company is engaged in the production of concrete, then natural losses of bulk materials are explainable and secured by local regulations. Such standards are reviewed every 5 years.
Re-grading
Offsetting can be used here, and the shortage is written off as natural loss, but only for certain types of products. At the same time, the concept of regrading is not always applied. To do this, it is necessary that the products have similar characteristics, quantity and name, and one person must bear financial responsibility for both types of goods.
Technical losses
This aspect is inextricably linked with production technology and is not regulated at the legislative level. Therefore, acceptable standards are determined by each enterprise individually. It should be clarified that the approved limits should be based on calculations that reflect the characteristics of the transportation of raw materials and production cycles.
Theft
Based on Article 22 of the Labor Code, heads of organizations have the right to hold their employees financially liable. Here, the fact of a shortage is revealed by an inventory, the reasons and culprits are established. All these nuances are documented, and deductions are made from the salaries of those responsible.
If there are no culprits
In such cases, the shortage is associated with the financial result and is reflected in the reporting documentation.
Inventory procedure
Before scheduling an event to count the organization’s property and assess the company’s financial obligations, a commission is convened. The absence of even one official included in the special council is the reason for the cancellation of the audit results. The composition includes representatives of the enterprise administration, accounting service, and other employees. The list of commission members is approved in advance on the basis of an issued order, which indicates the audit period and types of property. Inventory procedure:
- Setting the date for the recount of property.
- Checking existing values using a continuous or selective method.
- Drawing up an inventory sheet with entering data on the name of the product and its actual quantity.
- Displaying the final balance in monetary terms.
- Filling out a matching sheet to document shortages during inventory.
- Compilation of a report.
- Sending documentation to the head of the organization.
The reasons for conducting an inventory at the initiative of a company representative are the presence of data on theft, embezzlement, mis-grading, production of unaccounted for property, the fact of consumer deception, and deliberate destruction of goods. The main requirements for an audit include surprise, making up for shortages, getting rid of surpluses, and drawing up a matching sheet. The commission works in the presence of the director, manager, administrator, seller, merchandiser, cashier, storekeeper of the organization or their assistants. After the inventory, the manager has the right to assign a control check to check the correctness of the results.
Features of tax accounting
Let's look at the identified shortage through the prism of the Tax Code.
Income tax
Based on Article 265 of the Tax Code, the identified shortage is equated to non-operating expenses. If it is necessary to replenish inventories, this is taken into account as expenses in the period when the shortage was identified.
Read also: Meal compensation for employees