Field 33B Amount and currency
Filling out is required.
Indicated:
- Transfer amount – the amount of funds that the paying client transfers. The whole part of the amount is indicated without separators (including spaces). If the amount is presented only as an integer part, then two zeros (00) must be indicated after the decimal point.
- ISO currency code (see currency code reference). When transferring funds from the client's account in a currency different from the currency of the paying client's account specified in field 50a, the amount received as a result of converting the transfer amount at the rate agreed with the client is debited.
When transferring in Belarusian rubles (BYR):
- Amounts in Belarusian rubles are indicated without kopecks. Sberbank of Russia does not accept payments in which the transfer amount is indicated in kopecks.
Example
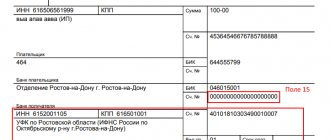
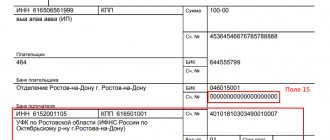
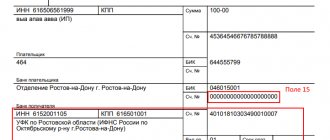
On June 1, 2021, IP Melnikov paid the Balance organization 100% of the delivery cost (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3
When selling the goods on 06/09/2020, no exchange rate differences arose; the exchange rate was taken on the date of payment.
The second option is if the payment arrived after registration. In this case, the goods are recognized at the exchange rate that was established on the date of transfer of ownership. At the time of sale, the seller’s accounting records reflect the amount of the buyer’s receivables in cu, as well as rubles, calculated at the exchange rate on the date of sale.
The amount of revenue will not be revalued, but accounts receivable expressed in monetary units will be revalued at each reporting date or at the time of full (partial payment by the buyer). Accordingly, exchange rate differences will be reflected as other income (expenses) in accounting and as non-operating income (expenses) in taxation.
Source:
Materials from the newspaper “Progressive Accountant”
Heading:
currency transactions 1C:Accounting 8
- Marina Ereyskaya, accountant-consultant Consultation lines
Sign up 9880
12350 ₽
–20%
Field 23E Instruction code
Filling out is optional.
Indicated:
- An instruction code that defines information about payment, the method of notification or payment (see the reference codes for instructions in field 23E).
- Additional information that can follow the instruction code and is indicated through a slash / after the codes: HOLD, PHON, PHOB, PHOI, REPA, TELE, TELB, TELI. (no more than 30 characters after the slash, format /30x).
Several instruction codes can be indicated in the field in the order specified in the directory of instruction codes of field 23E; the same directory defines codes that cannot be specified simultaneously.
Instructions can only be executed if the bank for which they are intended works with the specified instruction codes, and banks charge an additional fee for executing instructions.
When transferring in Ukrainian hryvnia (UHR): Field 23E is not filled in.
Sample of filling out a payment order for a non-resident (in Russian rubles)
The payment order is filled out for the transfer of Russian rubles, so its usual filling procedure is maintained in accordance with the documents and details of the counterparty, except for the currency transaction code, which must be indicated in the final field of the payment order. To do this, before the text in the “Purpose of payment” field, write VO in capital Latin letters, and then the five-digit transaction code from the table below. The code must be enclosed in curly braces.
Let’s assume that the Russian organization VESNA LLC needs to pay wages to its employee who works remotely from Kazakhstan and is not a resident of the Russian Federation. In this case, fill out the payment form as usual, and in the appropriate field write:
Field 50a Paying client
Filling out is required.
The details of the client making the funds transfer are indicated.
The following must be indicated on separate lines:
- Account number from which funds are debited during the transfer.
- Client data (4 lines, format 4*35x): Client name: full or short, as provided for in the client’s constituent documents.
- TIN (taxpayer identification number) for resident legal entities or TIN/KIO (foreign organization code) for non-resident legal entities.
- Address.
- City, country.
When transferring in Belarusian rubles (BYR):
- The account number and name of the payer are indicated.
- If there is no invoice, the payer's address must be indicated.
What currency transaction code should be indicated in the payment order?
Codes for types of foreign exchange transactions (KVVO) are contained in Appendix 2 to Bank of Russia Instruction No. 181-I dated August 16, 2011. They are indicated in settlement documents in some strictly defined cases:
- When filling out a certificate of currency transactions.
- When filling out a payment order for a transfer in the currency of the Russian Federation and in any foreign currency, if the transaction is foreign currency, when:
- the payer is a Russian organization, and the recipient of funds is a foreign company or citizen;
- the payer is a resident - when making transfers to his own accounts or to the accounts of another resident opened in a bank outside of Russia;
- the payer is a foreign organization or citizen;
- the payer is a financial agent (factor), the recipient is a Russian company (and vice versa), in the case of settlements within the framework of a financing agreement concluded between them for the assignment of a monetary claim (factoring) and (or) an agreement on the subsequent assignment of a monetary claim.
Field 56a Intermediary bank
The field is optional, but if field 57a contains the correspondent account number of the beneficiary's bank, field 56a must be filled in. The details of the bank in which the beneficiary's bank (field 57a) has a correspondent account are indicated.
The field is filled in one of three options:
- If you have a SWIFT code: SWIFT code and the corresponding name of the bank;
- City, country.
- national clearing code (see the reference book Structure of National Clearing Codes) and the corresponding name of the intermediary bank (full);
- name of the intermediary bank (full);
Field 57a Beneficiary's bank
Filling out is required. Indicate the details of the bank in which the beneficiary client's account is serviced (field 59a).
The field is filled in one of four options:
- If you have a SWIFT code: SWIFT code and the corresponding name of the beneficiary's bank;
- City, country.
- national clearing code (see the reference book Structure of National Clearing Codes) and the corresponding name of the beneficiary's bank (full);
Note: In this case, filling out field 56a is mandatory.
- the number of the correspondent account of the beneficiary's bank with the intermediary bank, which it is advisable to indicate without service separator characters (hyphen, space, etc.);
name of the beneficiary's bank (full);
- name of the beneficiary's bank (full);
When transferring in Ukrainian hryvnia (UHR):
- The code of the bank participating in interbranch turnover (MFO), assigned by the National Bank of Ukraine (NBU) to resident banks of Ukraine and their branches, is indicated. The MFO code is indicated in the Clear subfield. code in the form of a national clearing code (see the reference book Structure of national clearing codes): //UA6!n , where 6!n is a microfinance organization of a resident bank of Ukraine. For example: //UA300335.
When transferring in Belarusian rubles (BYR):
- The interbranch turnover code (MFO) of the beneficiary bank is indicated in the form of a national clearing code in the Clear field. code (see the reference book Structure of national clearing codes): //BY[6!n]3!n , where [6!n]3!n is the code of the MFO bank in the Republic of Belarus.
When converting into Kazakhstan tenge (KZT):
- The bank identification code (BIC) of the beneficiary's bank is indicated after the name of the bank with the designation BIC in the following form: BIC9!n , where 9!n is the BIC of the bank in Kazakhstan.
When paying in Chinese Yuan (CNY):
- If the country code is 156 CHINA and the bank is not part of the Bank of China group (the bank's SWIFT does not begin with BKCH), then in the Cor. account, you must indicate the bank's CNAPS code containing 12 or 14 characters.
Field 59a Client-beneficiary
Filling out is required.
The details of the client-recipient of funds are indicated.
On separate lines it is indicated:
- The client's account number at the beneficiary's bank (field 57a) can be indicated as an IBAN/BBAN number. When transferring funds to clients of banks in the European Union (EU) and European Economic Area (EEA), indicating the account number in the form of an IBAN number is mandatory. The IBAN/BBAN account format is presented in the IBAN/BBAN account structure directory, and the account format of some non-EU/EEA countries is presented in the National Account Number (DAN) structure directory. For a list of EU and EEA countries, see the note to section. A.2.5 "Identification codes".
- BEI code of the client (if available).
- Information about the beneficiary client (4*35x, no more than 140 characters): Client name (client's abbreviated name may be indicated if available).
- TIN for resident and non-resident legal entities (if available).
- address (if available).
Note: If the beneficiary client information exceeds the length limit (140 characters), the address may not be provided.
- City, country.
When transferring funds to the bank, the details of the beneficiary client are indicated:
- Internal account of this bank (if available), including in the form of an IBAN/BBAN number.
Note: If a bank's domestic account is specified along with its SWIFT code, then the same bank must be indicated in field 57a.
- SWIFT code of the bank in favor of which the funds are transferred (if available).
- Information about the beneficiary client (no more than 140 characters): Name of the bank in whose favor the funds are transferred.
- address (if available).
Note: If the beneficiary client information exceeds the length limit (140 characters), the address may not be provided.
- City, country.
When transferring in Ukrainian hryvnia (UHR):
- The beneficiary's account number must consist of no more than 14 digits (spaces, “/” and other symbols cannot be specified): 14n format.
- The taxpayer code (KNP) is indicated on a separate line before the client’s name in the following form: KNP8!n or KNP10!n, where 8!n is the KNP of a legal entity according to the Unified Real Estate Development Receipt; 10!n – KNI of an individual according to the “State Register of Individuals Paying Taxes and Other Obligatory Payments” for Ukraine. For example, KNP20262860.
When transferring in Belarusian rubles (BYR):
- The beneficiary's account (recipient of funds) must consist of 13 digits (spaces, / and other symbols cannot be indicated): format 13!n.
When converting into Kazakhstan tenge (KZT):
- The beneficiary's account is indicated (format 9!n). In Kazakhstan, the account is designated as IIK (individual identification number).
- The beneficiary's tax registration number (TRN) is indicated, which is assigned by the tax authorities to all residents of Kazakhstan, as well as non-residents of Kazakhstan carrying out permanent activities in the territory of Kazakhstan. Some non-resident banks that have correspondent accounts in banks of Kazakhstan do not have a TRN; then 12 zeros are indicated as the TRN. Indicated after the RNN designation in the following form: RNN12!n, where 12!n is the beneficiary’s RNN in Kazakhstan.
Comments: 11
Your comment (question) If you have questions about this article, you can tell us. Our team consists of only experienced experts and specialists with specialized education. We will try to help you in this topic:
Author of the article: Klavdiya Treskova
Consultant, author Popovich Anna
Financial author Olga Pikhotskaya
- Anton
08/12/2020 at 16:13 Which of the proposed methods did you use, i.e. What exactly has been verified by your own experience? For example, Skrill is mentioned, from which it is very problematic to withdraw funds, and it also has a confusing identity verification system. WU can also transfer from card to card, but this method is not mentioned at all. Sending and receiving via Russian Post, even within the Russian Federation, is quite a puzzle. Sending abroad using this method requires being a very serious fan of Russian Post.