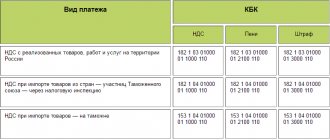
Changing the procedure for submitting financial statements
On January 1, Federal Law No. 444-FZ dated November 28, 2018 “On Amendments to the Federal Law “On Accounting” comes into force. Now most organizations will no longer have to submit their financial statements to Rosstat. In accounting, from 2021, the principle of “one window” will operate, namely the tax service, which will collect reports. The deadlines for submitting annual financial statements will not change.
An exception will be organizations whose reports contain information classified as state secrets, and some other organizations determined by the Government of the Russian Federation.
The Federal Tax Service of Russia, based on financial reporting data, will create an information resource to which interested parties will have access. Access will be paid for everyone, with the exception of government agencies and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Labor legislation
Expanded opportunities for remote work. If previously only permanent remote work was prescribed in the Labor Code, now there are three options: permanent, temporary and mixed. The Labor Code also clearly spells out the rights of remote employees. Thus, they cannot have their salaries cut just because they are working remotely, and the employer must compensate for the use of personal equipment (Federal Law No. 407-FZ of December 8, 2020).
The obligation to keep paper work books has been abolished. If in 2021 you hire an employee without a work permit for the first time, you no longer need to create a paper record for him. If an employee comes in who already has it and has not yet given it up, you need to keep a labor report. For all employees with personnel changes, a SZV-TD report must be sent to the Pension Fund.
A new minimum wage has been established. In 2021 it will be 12,392 rubles. (Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 542n dated August 28, 2021). This amount must be taken into account when calculating wages (if the employer has not joined the regional minimum wage agreement) and benefits.
Changing the procedure for submitting tax reports
From 2021, Federal Law No. 63-FZ dated April 15, 2019, which amended the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, cancels the submission of calculations for advance payments of corporate property tax. In addition, when calculating the amount of the advance payment for corporate property tax, you can use a different cadastral value that differs from the cadastral value as of January 1 of the year that is the corresponding tax period.
A taxpayer who is registered with several tax authorities at the location of his real estate on the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation may submit a tax return for property tax for all objects to one tax authority of his choice. The notification form on the procedure for submitting a tax return to the tax authority on the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 19, 2019 N ММВ-7-21/ [email protected]
Termination of UTII from 2021
Companies applying the UTII regime this year are not required to submit any applications for deregistration . This process will be carried out automatically by the tax office.
If the taxpayer does not notify the Federal Tax Service of the choice of a new tax regime by December 31, 2021, then the company will by default be transferred to the OSNO regime, the individual entrepreneur will be recognized as a personal income tax payer (see in more detail Which tax regime to switch to after UTII?)
Such clarifications are contained in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated August 21, 2020 No. SD-4-3/13544.
Changing forms of accounting and tax reporting
The forms of financial statements themselves have been changed since January 1 by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 19, 2019 N 61n, which amended the order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 N 66n “On the forms of financial statements of organizations.” In the header of all accounting forms in the line “Type of economic activity” the word OKVED is replaced by OKVED.2 - the actually used classifier of types of economic activity.
Also, in balance sheets and other forms, the possibility of using a million as a unit of measurement is excluded. Now all reporting will be compiled in thousands of rubles. The amendment is aimed at ensuring comparability of reporting indicators from period to period and bringing it into uniformity for all organizations (large, medium and small).
A new line “Accounting statements are subject to mandatory audit [YES/NO]” has been added to the balance sheet form. In it, organizations for which an audit is mandatory will disclose the name of the audit organization or full name of the individual auditor, INN and OGRN or OGRNIP of the auditor, if at the time of submission of the reports the audit has already been conducted and an audit report has been issued. At the same time, the audit report itself, as now, can be submitted to the Federal Tax Service along with the reporting or within 10 working days from the date of issue of the audit report, but no later than December 31 of the year following the reporting year.
In the financial statements on changes in capital, on cash flows and on the intended use of funds, the OKUD codes have changed:
- Report on the intended use of funds - 0710003;
- Statement of changes in capital - 0710004;
- Cash flow statement - 0710005.
From 2021, the financial statements of organizations not related to the public sector are considered to be compiled after they are signed by the head in paper or electronic form.
Changes in tax accounting
Federal Law No. 379-FZ dated November 28, 2019 clarified the list of property of organizations subject to tax based on cadastral value. In accordance with the amendments to Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the types of real estate for which the tax base for property tax is determined as cadastral value now include:
- Living spaces,
- garages,
- parking spaces,
- unfinished construction projects,
- residential buildings,
- garden houses,
- economic buildings or structures located on land plots provided for private farming, gardening, horticulture or individual housing construction.
Federal Law No. 255-FZ of July 30, 2019 clarifies the date for recognition of non-operating income in the form of a positive difference between the amounts of excise taxes accepted for deduction and accrued amounts. Legal entities that carry out transactions with excisable goods may generate income in the form of the difference between the amounts of excise taxes accepted for deduction on individual transactions with excisable goods and the amounts of excise taxes accrued by it on these transactions. The date of recognition of income is the date of submission of the excise tax return in respect of the relevant transactions.
Federal Law No. 166-FZ dated July 18, 2017 established that from January 1, 2021, income in the form of property rights to the results of intellectual activity identified during the inventory carried out by the taxpayer is taken into account when determining the tax base for income tax. Until now, property rights to the results of intellectual activity identified from January 1, 2018 to December 31, 2021 inclusive as a result of an inventory of property and property rights were not taken into account when determining the tax base.
Expenses for the creation of social infrastructure facilities, transferred free of charge into state or municipal ownership, are now included in non-operating expenses when calculating corporate income tax.
Value added tax
Since October last year, VAT has not been charged on leasing agreements related to the turnover of vital medical products and on tickets to the aquarium.
The State Duma is considering a draft law allowing the use of a zero VAT rate in cases where exported goods are purchased by a foreign citizen.
Federal Law No. 83 in Article 6, paragraph 3, determines that from the beginning of 2021, Article 164 of the Tax Code, paragraph 6, will no longer be in force. Therefore, from this moment on, services for domestic air transportation of passengers and baggage between regions of the Russian Federation, which were previously taxed at a reduced rate, are subject to taxation under normal conditions. In this case, VAT will be 18 percent.
Changes in accounting provisions
On January 1, 2021, the following come into force and begin to apply with reporting for 2021:
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 20, 2018 N 236n “On amendments to the accounting Regulations “Accounting for calculations of corporate income tax” PBU 18/02”,
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 4, 2018 N 248n “On introducing amendments to the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for State Aid” PBU 13/2000”;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2002 N 66n “On approval of the Accounting Regulations “Information on Discontinued Activities” PBU 16/02.”
In particular, PBU 18/02 changed the terminology of permanent tax asset/liability to permanent tax income/expense. The standard also clarifies the concepts of temporary differences and the definition of the accounting procedure for calculating income taxes by participants (including the responsible participant) of a consolidated group of taxpayers.
In addition, the new edition of PBU 18/02 clarifies the concept of income tax expense (income). Income tax expense (income) is reflected in the income statement as an income tax that reduces (increases) the pre-tax profit (loss) of the reporting period. It consists of current and deferred income taxes.
Changes to PBU 13/2000 “Accounting for State Assistance” are aimed at bringing the rules for accounting for state assistance in accordance with IAS 20 “Accounting for Government Grants and Disclosure of Information on State Assistance”. In particular, it is now possible to recognize government assistance in accounting at the time of actual receipt of money.
When accounting for budgetary funds for capital expenditures, costs incurred from the budget are written off as depreciation accrues over the life of the capital expenditure item. When budget funds are allocated to compensate for costs previously incurred by the organization, they are included in the financial results of the organization.
The amendment to PBU 16/02 is aimed at bringing the standard into compliance with IFRS 5 “Non-current assets held for sale and discontinued operations”. A new concept has been introduced: “long-term asset for sale.” This is an asset (fixed asset or other non-current asset), the use of which is suspended for the purpose of its further sale. If the decision to sell is made or a sale agreement is concluded, the asset is transferred to current assets and its further valuation is carried out according to the rules for valuation of inventories.
When accounting for long-term assets for sale, the accountant must describe in the explanation:
- long-term assets themselves for sale;
- the circumstances of the sale or just the intention;
- financial result from the sale of an asset;
- an item for reflecting this result in the financial results statement;
- a reportable segment that includes indicators related to a long-term asset available for sale.
Trend analysis, what to expect next
If you look at such changes as a whole:
- total introduction of a system for electronic transmission of data on cash payments to the Federal Tax Service through online cash desks;
- transfer to the Federal Tax Service of the entire complex of salary taxes and fees;
- bringing the chart of accounts and report lines into a specific format;
Tax accounting, a priority from the point of view of state regulation, is transferred under the full control of the tax authorities. Moreover, most likely, an attempt will be made to remove tax calculations from the competence of the enterprise itself. All calculations will be attempted to be carried out by the Federal Tax Service on the basis of incoming information and reports from the payers themselves for control reconciliation. It is not for nothing that at SKB “Kontur”, which is going to become an operator of fiscal data, the development of the corresponding software is carried out by a department that also deals with the EGAIS system. In EGAIS you can see the entire chain of movement of goods from sellers to final sale to consumers. Now they are trying to achieve the same for all other (non-alcoholic) goods.
Based on this, it is possible that in the future we should expect:
- Separation of tax accounting from accounting with the transfer of many functions for tax calculations and control to the Federal Tax Service.
- Simplification of accounting methods and methods for those enterprises whose statements are not subject to audit. There will be several reasons for this:
- Uniformity of accounting policies will help the Federal Tax Service to simplify the processing of incoming data on the activities of these firms.
- Unification of the procedure for accounting for income and expenses will allow for better control and automation of the calculation of taxes payable based on this procedure. It is possible that additional changes will be made to the laws that exclude options for choosing an accounting method at the initiative of the enterprise, like a closed list of expenses accepted for tax reduction under the simplified tax system.
Read more about international standards in the IFRS .
- Taxpayers will also continue to need the services of accountants to maintain management accounting necessary for making management decisions and planning activities (including in the field of tax issues, for example, choosing a taxation system).
Read more about management accounting in the section “Management Accounting” .
These are the trends. Whether the reform in the accounting sector will follow this path - practice will show.
Application for granting an organization a tax benefit
On January 1, 2021, the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 25, 2019 N ММВ-7-21/ [email protected] , which approved the application form for granting an organization a tax benefit for transport and land taxes. Taxpayers-legal entities must send to the Federal Tax Service if they apply to the tax authority for a tax benefit for transport tax and (or) land tax, including the provision of tax deductions, as well as the use of other grounds established by law that exempt them from paying these taxes.
The same order establishes the procedure for filling out the application form.
Simplified taxation system
In the coming year, individual entrepreneurs and legal entities using the simplified system will need to make use of serious changes. The changes will affect the procedure for filling out the Book of Receipts and Expenses. Section V will appear in the KUDiR form; it is required by tax payers from Moscow on the simplified tax system “Income” who pay the trade tax.
The modernized KUDiR form is publicly available and is voluntarily used by many taxpayers. But in the coming year its use is mandatory.
Insurance premiums
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 6, 2019 N 1407 changed the income limit of an individual from whom insurance contributions for social and pension insurance are paid. As a result of indexation by 1.054 times, the following maximum base value for calculating insurance premiums was established:
- for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity - 912,000 rubles cumulatively from the beginning of the year;
- for compulsory pension insurance - taking into account the average salary increased by 12 times, and the increasing coefficient applied to it in the amount of 2.2 - in the amount of 1,292,000 rubles on an accrual basis.
Deflator coefficients
Accountants calculating taxes on UTII and PSN in 2021 are required to apply new deflator coefficients. They were established by order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 2017 No. 579. The K1 coefficient, which adjusts the basic profitability indicator on UTII, was increased. Now it is 1.868.
The deflator coefficient used for the purpose of applying the PSN was also increased. Now, when calculating the potential annual income of an individual entrepreneur on a patent, you need to use a deflator equal to 1.481 (previously - 1.425).
Non-financial organizations
Directive of the Bank of Russia dated May 22, 2019 N 5149-U changed the procedure for reflecting accounting items of individual non-financial organizations in the accounting accounts. This applies to those NFIs that are not required to publish their accounting (financial) statements, whose shares or debt securities are not publicly traded, and which are not in the process of issuing such securities for trading on the open market (national or foreign stock exchange or OTC a market that allows the circulation of securities among an unlimited number of persons).
A procedure has been established for reflecting the transfer of means of labor received under compensation and collateral agreements into investment property, as well as for including the amount of VAT in the cost of inventories.
Application of FSBU
Since 2021, a number of federal accounting standards for public sector organizations have been applied. When maintaining budgetary and accounting records, they must apply the following Federal Accounting Standards:
- "Stocks";
- "Concession agreements";
- “Long-term contracts”;
- “Reserves. Disclosure of information about contingent liabilities and contingent assets";
- “Budget information in accounting (financial) statements”;
- "Non-produced assets";
- "Information about related parties."
Starting from reporting in 2021, the provisions of the Federal Accounting Standards Authority “Cash Flow Statement”, which regulates the reflection of information on derivative financial instruments, are applied.
Results
Innovations in legislation affecting accounting policies in accounting and tax aspects lead to further separation of accounting from tax accounting.
At the same time, what is related to the calculation of taxes, fees, and insurance premiums completely falls within the competence of the Federal Tax Service, with the improvement of the Federal Tax Service’s receipt of operational information on the activities of payers. Accounting and information prepared on its basis fall into the scope of providing information to interested parties: management and shareholders of the enterprise, investors and creditors. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.