In times of crisis, organizations quite often need to sell receivables. Most often we are talking about the sale of overdue or unrealistic debt. The sale, as a rule, is carried out at a price lower than the one at which such debt is recorded in the organization’s records. In this article we will talk about the purchase and sale agreement for receivables in 2021, and consider other documents.
According to established practice, such a transaction is formalized by concluding an agreement for the assignment of the right of claim (cession). It is also possible to draw up a factoring agreement. According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, accounts receivable are defined as a property right. Guided by paragraph 4 of Article 454 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, dedicated to the purchase and sale agreement, some lawyers believe that when selling receivables, a purchase and sale agreement, rather than an assignment, can be drawn up.
How to transfer a debt
To transfer an obligation, the original debtor and the organization to which the debt is transferred sign a corresponding agreement.
And the creditor must put his mark on this agreement stating that he is not against the transfer. Such consent is required by paragraph 1 of Article 391 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Or you can enter into a tripartite agreement. The creditor's signature on it will mean his consent.
https://www.youtube.com/watch{q}v=https:accounts.google.comServiceLogin
By default, the original and new debtors are jointly and severally liable to the creditor. That is, the creditor can demand that the debtors fulfill the obligation jointly. He also has the right to make such a demand to each of them separately.
At the same time, in the debt transfer agreement, the parties may also provide for subsidiary liability. It assumes that if the new debtor does not fulfill the demand, then the original debtor is obliged to fulfill it.
It is possible to completely release the original debtor from the obligation (clause 3 of Article 391 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
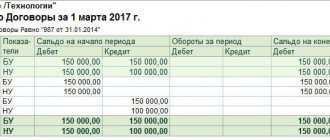
Accounts receivable.
Disputes regarding the assignment of the right of claim to third parties
Let us recall that in accordance with Article 825 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation: “As a financial agent, financing agreements for the assignment of a monetary claim may be concluded by banks and other credit organizations, as well as other commercial organizations that have permission (license) to carry out activities of this type."
Let us note that the arbitrators of lower courts can make a decision in favor of the debtors. As an example, we can cite the Resolution of the Federal Arbitration Court (hereinafter FAS) of the Ural District dated January 4, 2001 No. F09-1969/2000-GK.
However, higher courts do not agree with this point of view. Evidence can serve as: Resolution of the FAS Moscow District dated September 5, 2000 No. KG-A40/3920-00, Resolution of the FAS Volga District dated February 22, 2000 No. 6976/99-15, Resolution of the FAS Far Eastern District dated January 9, 2001 No. F03- A51/00-1/2430.
Transfer of accounts receivable to another organization in connection with the liquidation of the transaction
Depending on the reason for the delay, the debt may be: Doubtful, that is, the debt is not repaid on time and is not secured by guarantees or collateral.
Important It is possible that it will be repaid, but this is not known for certain. Hopeless When collecting a debt is almost impossible Write-off of a receivable debt means that it will no longer appear in the company’s assets. This will allow you to assess the real financial condition and amount of capital. But why write off debt? Every year, the organization is obliged to conduct an inventory of debts and identify overdue obligations of counterparties. A debt that cannot be collected must be written off.
And to make it easier for you to plan your affairs for the upcoming six-day work week and not forget anything, we present to your attention our weekly accounting reminders.
How to sell accounts receivable{q}
The sale of receivables is accompanied by the conclusion of an assignment agreement. Assignment - assignment of the right to claim a debt - an agreement according to which the original owner of the debt transfers to a new person the right to claim it. The original owner is called the assignor, and the new owner is called the assignee. As a result of concluding such an agreement, the debtor will repay its obligations to the original creditor to the assignee.
Dt 60 (last creditor) Kt 60 (old creditor), because according to Art. 384 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the sale of debt retains its legal basis.
Dt 60 (new creditor) Kt 51 (50).
The procedure for putting a lot up for auction
The sale of the debts of a bankrupt enterprise usually occurs at the stage of external management, as part of a plan to restore the solvency of the legal entity. The financial claim of each individual creditor is considered a separate lot at auction. The display and sale of lots occurs in the following order:
- The general meeting decides to sell the debts of a bankrupt company.
- The meeting draws up a list of lots and determines the starting price for each lot.
- The manager publishes a notice of upcoming auctions 30 days before they are held.
- On the appointed day, bidding takes place electronically , and winners are determined.
The auction takes place in the form of an auction - the winners are the persons who offer the highest price for the lot, which denotes a debt claim of a certain creditor for a specific amount against the debtor.
The starting price of lots is usually set in the region of 0.1-.05% of the claim amount.
Accounting: with the lender
Debit and credit using examples in the article: what is debit and credit in simple words.
Debit 62 (58, 76...) “New debtor” Credit 62 (58, 76...) “Original debtor” – reflects the amount of debt transferred by the debtor to another person.
This must be done on the effective date of the debt transfer agreement.
Debit 50 (51, 60, 76...) Credit 62 (58, 76...) “New debtor” – payment has been received (offset has been made) to repay the debt under the agreement from the new debtor.
This procedure follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 58, 62, 76).
Reflection in the accounting of transactions on the transfer of debt obligations from the party accepting receivables will be carried out according to the norms of PBU 19/02. Accounting rules require the attribution of amounts for repurchased debts from other legal entities to account 58 (clause 3 of PBU 19/02). Transactions on the assignment of the right of claim, drawn up by a legal entity that initially acted as a creditor and initiated the transfer of debt to a third party, are formalized as a sale of receivables.
By what principle is a unified base formed?
Is it legal to transfer data about payers to third-party agencies and its subsequent placement on resources? This became possible thanks to the relevant decision of the Supreme Court. If a person applies to a bank, he is obliged to sign an agreement that implies such conditions. A similar rule applies to enterprises. If a person refuses to sign the agreement, he will not be provided with funds.
Is there a single list of debtors? There are quite a few resources on the Internet where you can check for debt. However, the only official website that provides information of this kind is the Unified Credit and Debt System. It is for informational purposes only. If information is entered there, this does not entail any consequences for the debtor.
The situation is more complicated if enterprises, individual entrepreneurs or individuals are included in the Register of Debtors. This is evidence that a case has been opened against the person in court and the process of enforcement proceedings has begun. It is worth checking such a resource to see if it contains data about you. Sometimes a person may not know that a case has been opened against him. This is especially true for persons who do not live at their place of registration. Notifications about the start of a trial may simply not reach them.
It is worth keeping in mind that information can be published about any types of defaulters:
- Firms, companies;
- IP;
- Individuals;
- Enterprises.
It is worth considering that cases are often initiated without the participation of the debtor. This can lead to a person suddenly learning that his access abroad is blocked and his accounts are frozen.
The Unified Federal Service has created a data warehouse about persons against whom legal proceedings were initiated. Such a database can be called open only conditionally. To access the information, you need to know some information about the debtor. Some information is not published, as this violates the law on personal privacy.
Reflection of transactions under the assignment agreement with the debt buyer
In accounting, referring to clause 7 of PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization” (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 No. 32n), income from the sale of debt is taken into account as from the sale of other assets as part of other income. Proceeds from the sale of debt are credited to the account. 91 in correspondence with the other debtors account. At the moment of transfer of debt, the realized debt recorded in the assignor’s account is also written off. 62. Consequently, the following entries are made in the assignor’s accounting:
- Dt 76 Kt 91.1 - revenue from the sale of debt is displayed;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 62 - the amount of receivables sold is written off;
- Dt 51 (50) Kt 76 - funds were credited for the assignment of the right of debt.
According to Art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the transfer of rights is subject to VAT. Art. 155 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes the taxation procedure for this situation. Thus, during the initial assignment of debt arising as a result of the sale of goods and services subject to VAT, the original creditor charges VAT on the positive difference between the income from the assignment and the amount of the receivables sold. If the amount of the assignment is less than or equal to the buyer's debt, no VAT arises.
Dt 91.2 Kt 68.
We suggest you read: First vacation after getting a job
In the case of a subsequent assignment, the VAT basis is determined for its seller as the difference between the income received from its buyer and the amount originally spent on acquiring the debt.
The financial result from the assignment of debt is accordingly determined as the difference between credit and debit turnover on the account. 91, as a rule, it is negative.
The tax accounting of the debt seller will also include income and expenses. In this case, the date of receipt of income will be the date of signing the act of assignment (clause 5 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). When the assignment is unprofitable, the provisions of Art. 279 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, if the transfer of debt was carried out after the payment deadline established by the parties to the transaction, the resulting loss can be taken into account in the calculation of income tax in a total one-time amount on the date of assignment. If the assignment agreement was concluded before this period, to accept the loss you must be guided by clause 1 of Art. 279 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and accounting policies.
You can familiarize yourself with the procedure for normalizing losses and see an example in the material “Losses from the assignment of a claim from January 1, 2015 are taken into account according to the new rules.”
Dt 58 Kt 76.
The assignee takes into account the received receivable in the amount transferred to the assignor, taking into account all costs of acquiring the debt. If there is input VAT from the assignor, the tax can be deducted, observing the general conditions for deduction.
You can learn more about accounting for financial investments, including accounting for issued loans, investments in securities, and find out how financial investments are kept in a management company or a simple partnership in the article “Accounting for financial investments - PBU 19/02.”
Dt 76 Kt 51 (50).
The right of claim as a financial investment, according to PBU 19/02, is withdrawn at the moment of receiving money from the debtor or signing an assignment deed to another creditor. Clause 34 of PBU 19/02 in accordance with PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization” (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 No. 32n) classifies income from financial investments as other income if they are not the subject of the company’s main activity.
Accordingly, the receipt of money from the debtor is accompanied by the following accounting entries:
- Dt 51 (50) Kt 76 - amount received from the debtor;
- Dt 76 Kt 91.1 - income from the assignment of the right of claim is displayed;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 58 - reflects the amount spent on the acquisition of debt;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 68 - if the amount of debt repayment exceeds the amount transferred to the original creditor, VAT is charged on the excess amount.
Similar entries will be made if the debt is transferred to another creditor:
- Dt 76 Kt 91.1 - debt assigned;
- Dt 51 (50) Kt 76 - funds received from a new creditor;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 58 - the cost of the transferred right of claim has been written off;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 68 - VAT is charged (if there is a positive difference).
In tax accounting, execution from the debtor or income from the assignment, according to clause 3 of Art. 279 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the assignee recognizes upon receipt of money from the debtor or further assignment of the debt. The same date is the date of recognition of assignment expenses. If the debtor repays the debt gradually, then income is recognized in parts, and expenses are taken into account in direct proportion to them.
How to check whether a company or an individual has debts in the data bank?
Who may need information from the list of debtors? It is relevant if the bank has provided you with a loan. If you want to check whether enforcement proceedings have begun against you, it is worth visiting this resource.
Companies that are starting cooperation with a new counterparty can access the site. Before concluding a contract, it is worth checking companies for their reliability. Checking for any outstanding debts is one of the best ways to find out about your partner’s financial stability.
To obtain data, you need to perform the following algorithm of actions:
- If you are interested in enterprises or firms, you should select the “legal entities” section. To store information about citizens, a section “individuals” is provided;
- You will see a page called “Territorial Authorities”. If you need information about the individual, you must enter the place where the citizen is registered. If this is a legal entity (enterprises, companies), it is required to indicate the place of registration in accordance with the Federal Tax Service;
- Passport details are entered;
- You can simplify obtaining information if you are interested in debtors under writs of execution and you know the document number. In this case, you can go to the “Search by IP number” section and check all the necessary information.
By accessing such a site, you don’t have to worry that your individual data left in the search bar will be known to other people. This information is confidential and is not shared with third parties.
If a citizen applies to a bank to take out a loan and has uncovered obligations, information about them can only be published on the official website of the FSSP of the Russian Federation.
What information is included in the list?
Not the entire list of data is publicly available. However, you can get a lot of information from the resource regarding the enterprise, individual entrepreneurs, and individuals. In particular, the resource stores the following information:
- Basic information. For individuals, this is passport data, date of birth. If these are enterprises, indicate the name and place of registration;
- Date the debt was created. It is counted from the date when the judicial authority made the corresponding decision;
- Data on enforcement proceedings, the defendant of which is an enterprise or individual entrepreneur. The bank, most often, is the initiator of the business. Information about him is also provided. The management company or the person receiving alimony can also act as a creditor. We have already written earlier where you can see the list of alimony debtors. This section includes information about the case and the date of its initiation. The requirements for the debtor are also specified;
- Information about the territorial office of the FSSP, which conducts enforcement proceedings. The section includes the name of the unit and its place of registration. What is ID debt;
- If a person or company with uncovered liabilities is put on the wanted list, these sanctions are also prescribed, adopted by the judicial authority.
Not the entire list of data is publicly available.
Such an information bank provides rather limited opportunities. It does not publish a complete list of information, but the material provided is quite enough to detect debt in yourself or your partner.
Recommendations for debtors and companies that have found themselves in the Federal Database
What to do if companies or individuals discover that the bank has published information about their obligations? You must immediately contact the bailiff department. Let's consider the algorithm of actions for the debtor:
- Login to the FSSP resource;
- Search for the phone number and address of the institution that conducts enforcement proceedings;
- A call to the bailiffs, which will help to obtain more detailed materials about the sanctions taken against the person due to the debt.
In order to protect yourself from being included in the list of persistent defaulters, you need to close the loan correctly. To do this, it is not enough to give the required amount to the bank. You must sign an application to close your credit account. You should definitely ask for a copy of this document. In this case, you don’t have to worry that the bank will make any claims against you.
Differences between resources with information about debtors
There are two types of sites on which they publish material about debtors if enterprises or individuals have outstanding obligations:
- Bank of information on credit debtors. It receives material about those persons against whom a lawsuit has already been filed;
- General base. Such a bank is necessary to confirm the reliability of a person or enterprise. It allows you to find out your credit history. A database is compiled based on data from tax, insurance organizations, and banking institutions.
The first resource is relatively open, where you can get brief material about the debts of an interested person or enterprise. Access to the second site is limited. It contains confidential information about debt holders. This resource is used, for example, by banking institutions to check the reliability of a new borrower.
The debtor database allows you to find out your credit history.
Why do you need a resource that maintains a list of debts? Through it you can obtain materials about your debt and its current amount. This is an indispensable tool for lenders who need to check a debtor's credit history. To obtain the required information, you will need brief information about the debtor.
Watch the video instructions for checking debt in the FSSP debtor database:
This is not a completely open portal. If you find information about yourself in it, you should contact the bailiffs. To remove the material, you will need to cover the debt. Sometimes information gets into the database by mistake. In this case, an immediate contact with the bailiffs is also required to correct the error.
Accounting: with the original debtor
Debit 60 (66, 76...) Credit 76 – the amount of accounts payable transferred to the counterparty with the consent of the creditor is written off.
Debit 76 Credit 50 (51, 60, 62, 76) – payment has been made (offset) of the obligation under the debt transfer agreement.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Statute of limitations when transferring debt to collectors
This procedure follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 60, 76).
An example of reflecting debt transfer transactions in the accounting records of the original debtor
In June, Torgovaya LLC (creditor) sold materials to Alpha LLC (original debtor) for the amount of RUB 590,000. (including VAT - 90,000 rubles) according to the supply agreement. The payment deadline for the goods is July 30. On July 1, Alpha, with the consent of Hermes, transfers the debt to Proizvodstvennaya LLC (counterparty).
In Alpha's accounting, the accountant made the following entries.
Debit 10 Credit 60–500,000 rub. – materials were received from Torgovaya;
Debit 19 Credit 60–90,000 rub. – VAT is reflected for purchased materials;
Debit 68 Credit 19–90,000 rub. – accepted for deduction of input VAT on purchased materials.
Debit 62 Credit 90-1– 590,000 rub. – income from the sale of products to the “Master” is recognized;
https://www.youtube.com/watch{q}v=ytaboutru
Debit 90-3 Credit 68–90,000 rub. – VAT is charged on the cost of shipped products.
Debit 60 Credit 62– 590,000 rub. – debt transfer obligations are offset against payment for delivered products.
Accounting: for a new debtor
Debit 60 (76) Credit 76 – accounts payable to the original creditor and receivables of the former debtor are reflected.
Debit 76 Credit 50 (51, 60, 62, 76...) – the debt to the creditor is repaid.
An example of reflecting debt transfer transactions in the accounting of a new debtor
In June, Torgovaya LLC (creditor) sold materials to Alpha LLC (original debtor) for the amount of RUB 590,000. (including VAT - 90,000 rubles) according to the supply agreement. The payment deadline for the goods is July 30. On July 1, Alpha, with the consent of Hermes, transfers the debt to Proizvodstvennaya LLC (the new debtor).
The Master's accountant made the following entries.
Debit 10 Credit 60– 1,000,000 rub. – the receipt of products from Alpha is reflected;
Debit 19 Credit 60–180,000 rub. – reflected input VAT on purchased products;
Debit 68 Credit 19– 180,000 rub. – accepted for deduction of input VAT on purchased products.
Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements with Alfa LLC” Credit 76 subaccount “Settlements with Trading LLC” – 590,000 rubles. – obligations have been accepted to Torgovaya;
Debit 60 Credit 76 subaccount “Settlements with Alpha LLC” – 590,000 rubles. – offset of accounts payable to Alfa;
Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements with Trading LLC” Credit 51–590,000 rub. – the debt to Torgovaya was repaid.
Situation: how can a new buyer reflect in accounting the receipt of a fixed asset when acquiring the right of claim under a purchase and sale agreement{q} Ownership rights transfer after payment to the seller.
Reflect the receipt of property as part of fixed assets on the date of entry into force of the agreement on the assignment of the right of claim.
In this case, your organization assumes the rights and obligations under the purchase and sale agreement. Namely:
- repay the debt to the seller;
- actually receive property from the former buyer;
- receive ownership of the property after full payment.
As soon as the rights and obligations have transferred to you, the property will immediately be reflected as part of fixed assets. After all, all the conditions for this have been met. The moment of transfer of ownership does not matter (clauses 4 and 5 of PBU 6/01).
Debit 08 Credit 76 subaccount “Settlements with the former buyer” – accounts payable to the former buyer are reflected in the amount of money actually transferred by him to the seller for the fixed asset;
Debit 08 Credit 60 – accounts payable to the seller in the amount of the remaining payment for the equipment is reflected;
Debit 01 subaccount “Fixed asset in operation” Credit 08 – the fixed asset was accepted for accounting and put into operation at its original cost.
Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements with the former buyer” Credit 50 (51...) – the debt to the former buyer is repaid.
Debit 60 Credit 50 (51...) – the debt to the seller is repaid in the amount of the remaining payment for the equipment.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: New rules for registration of road accidents by the commissioner without payment
This procedure follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 01, 08, 60, 76).
Regarding VAT. The new buyer does not have the right to deduct tax. This is due to the fact that he will not have an invoice from either the seller or the former buyer. Firstly, the sale (shipment) of the equipment does not occur in this case, although in the future the ownership will be transferred to it. Secondly, the former buyer took advantage of the right to deduction (clause 2 of Article 171, clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Course 5: Making transactions made easy
You probably have a lot of real-life examples running through your head right now that you want to record in your accounting system.
but which accounts to choose? How to understand which account to put in Debit and which account to put in Credit of our accounting rules? In order to make it clear in which part of the accounting rule and when to put which accounting account, all accounting accounts were assigned the attribute: active accounting account or passive accounting account. I will separately mention accounting accounts, which in the chart of accounts are called active-passive. The duality in the name of such accounting accounts is due to the fact that at a particular point in time there may be a balance (either-or) on either a credit or a debit of this account. There is nothing wrong with this, it’s just that the same economic category, for example, suppliers of goods, may at a particular moment in time both owe us, and we may owe them, but in any case, this whole changing picture is taken into account only on one accounting account that we chose specifically for suppliers. For example, a supplier delivered goods to us in the amount of 100 rubles.
BASIC: income tax
For the creditor, replacing the debtor has no meaning. With the accrual method, sales revenue is already taken into account (clauses 1, 3, Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the creditor uses the cash method, then income must be recognized on the date of receipt of funds from the debtor's counterparty (new debtor) (clause 2 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the accounting of the original debtor, the costs of purchasing goods (work, services) must be reflected in the general manner, despite the fact that the payment debt was transferred to the counterparty (clause 1 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Using the accrual method, recognize the cost of purchased goods as expenses regardless of their payment (clause 1 of Article 271, clause 1 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If you use the cash method, then the goods are considered paid on the date of transfer of the debt (clause 2 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For a new debtor, the debt transfer operation itself will not be reflected when calculating income tax. That is, such an operation will not affect either income or expenses. After all, he simply participates in the calculations.
Methods for collecting debt obligations from a debtor
The main options for collecting debts from a debtor include:
- Making claims against the debtor. As a result, the creditor and debtor can begin to work on a netting scheme, which involves repaying the debt through the free transfer of products or services. The disadvantage of this method is that both parties do not receive additional funds, which in no way improves the financial position of the lender;
- Involvement of collection companies in the process. This method can significantly damage business relations between the borrower and the lender. This may subsequently affect the company's reputation, which will negatively impact future profits;
- Initiation of legal proceedings. The imperfection of our legislation often leads to the fact that courts drag on for many years. Even if it is possible to collect his obligations from the debtor, fluctuations in exchange rates, together with inflation, can “eat up” a large part of the debt, which makes this method impractical. Plus, the legal process requires certain costs;
- Resale of receivables. In general, this method has no obvious disadvantages, which makes it very popular today.
Nowadays, the most popular operations for resale of debt obligations, which can really help you get back all your receivables, are:
- Assignment procedure;
- Organization of the factoring procedure.
When are accounts receivable sold? Photo: myshared.ru
Each of the above transactions represents a process of complete transfer to another structure of its unreceived debt obligations for previously agreed upon financial compensation.
The result of such manipulations is that the company that sold its uncollected debts receives certain financial resources, while the acquirer of the debts has all the legal grounds for their further collection from the debtor.
There are a number of quite important differences between the assignment and factoring procedures. An assignment is an ordinary assignment of legal rights to a debt. Factoring is a specific method of financial security for receivables, which has some common characteristics with classic loans.
Because of this, such financial transactions are most often carried out by various types of credit firms and organizations that have special permitting licenses. In the case of the factoring procedure, various receivables of a fixed-term nature are often subject to assignment.
Assignment of financial obligations of debtors
Regardless of the type of transaction, it must be formalized in the form of a written agreement, which will contain all sorts of important points related to the joint commercial activities of the organizations. When drawing up contracts for the sale of services or goods, it is imperative that they stipulate:
- Deadlines;
- Total quantity of product delivery;
- Implementation of procedures for the provision of various services;
- Carrying out various types of work;
- Indication of payment terms.
Such a concluded agreement is the most important legal document, serving as confirmation that the client has certain debts of a material or financial nature to the seller.
At times, very serious situations arise in which the creditor urgently needs funds, and the deadline for fulfilling financial obligations is still very far away. Not every type of loan obligation can be assigned to another person acting as a new creditor.
Such obligations include various address-type payments that are addressed to a specific person:
- Alimony payments;
- Various awards;
- Compensation for damage caused, etc.
In the event that the very identity of his new creditor has some significance for the borrower himself, concluding an assignment becomes impossible.
At the end of the process regarding the approval of the final agreement on the resale of the claimable rights to financial assets or other type of property, you need to find a person who will act as a legal successor. Now there are certain commercial firms engaged in the purchase of this type of debt obligations.
Sale through assignment. Photo: myshared.ru
The parties to the agreement regulating the assignment of rights to debt are the lender and the recipient of the rights to debt obligations. The agreement is concluded and drawn up in writing with further notarization.
Pros and cons of an assignment agreement, as well as its risks
The main advantage of the assignment procedure is the ability to quickly collect your debts. Among the main disadvantages of the assignment, the low level of profit received by the creditor stands out.
Such a development of events may well provoke certain claims from the tax service. The deal itself may end up being unprofitable.
For the buyer of debt obligations, the main risk is the likelihood of non-receipt of funds on the loan from the borrower. In such cases, their relationship acquires civil legal status due to the initiation of legal proceedings by the creditor.
It is necessary to carefully study the assignment agreement, because if there are errors or inaccuracies in it, it will be declared invalid. The entire process of assignment of rights must be accompanied by an experienced lawyer.
What factoring is is discussed in this video:
Debt factoring procedure
The factoring procedure is the process of selling existing receivables to certain credit institutions or companies that have a special state license.
The main goal of this type of financial transaction is to find additional sources of finance, increase the amount of working capital, and stimulate the growth of overall sales volumes. In the factoring procedure, purchasers of debt obligations act as financial and economic agents.
All their obligations and legal options are fully specified in Chapter 43 of the current Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Like the assignment process, the factoring procedure is the assignment of debt obligations in favor of third parties. There are certain important differences between these operations:
- The main difference is that the agent has the opportunity to acquire not only existing debts under real contracts, but can also acquire debt obligations under proposed transactions that have not yet been completed. In this case, there is no possibility of selling overdue debts;
- Another important difference is that with factoring there is the possibility of assigning only monetary obligations, while the assignment allows the assignment of material rights;
- Also, with assignment, unlike factoring, there are no restrictions on enterprises that have a large number of borrowers with small debts. Such companies engaged in the production of narrowly specialized goods do not have the opportunity to use the services of financial agents.;
- Another difference is that during an assignment, any commercial structure has the right to purchase debt obligations, but during a factoring operation, only companies that have the appropriate permitting licenses have such rights.
The main advantages and disadvantages of the factoring procedure, as well as possible risks
Flaws:
- Due to the confusing tariffs and high rates of companies offering factoring services, such a procedure may turn out to be completely unprofitable for businesses;
- If a company regularly works with partners who constantly delay payments, the factoring procedure becomes meaningless.
What is factoring? Photo: myshared.ru
Advantages:
- Ensuring constant circulation of funds, without the influence of counterparties.
- Significant simplification of debt management;
- The possibility of providing the client with a certain deferment in payment, which is likely to increase the flow of potential clients.
It is necessary to carefully study all the clauses of the contract in order to minimize the likelihood of any friction arising between the parties to the contract. The entire process of concluding such an agreement must be accompanied by an experienced lawyer.
When signing a factoring agreement, it is necessary to take into account currency fluctuations, because if the ruble falls sharply, the parties may suffer huge losses, or, on the contrary, profits.
Promissory notes and bills of exchange
With the help of bills of exchange, it is possible to sell receivable-type debt obligations. The bill itself is a security, which presupposes the existence of unreasonable obligations of the drawer to pay the prescribed amount of money, together with the specified interest, in favor of the holder of the bill.
A commercial structure can issue a promissory note to another company, which will oblige it to pay certain specified financial resources after a certain time. Bills of exchange can be simple, transferable, as well as interest-bearing and with a certain discount.
The most common are promissory notes and bills of exchange:
- Promissory notes of a simple type involve the implementation, in accordance with obligations, by an organization or an individual, after the expiration of the time prescribed in the security, of payments of funds to another person. This paper acts as a valid confirmation of debt obligations. When the prescribed deadlines are exceeded, the bill is transferred to the immediate debtor. With this type of obligation, the lender can carry out settlements with its partners. The transfer of this type of securities is an operation similar to the assignment of receivable-type debts;
- A bill of exchange is an obligation requiring the debtor to transfer money to third parties. The debtor undertakes to transfer funds within the framework of its obligations to third parties specified by the creditor.
Main advantages and disadvantages, as well as risks associated with bills of exchange
Advantages:
- Payment of debts on bills of exchange is indisputable and does not even require any judicial confirmation;
- The demand for payment of debts on bills of exchange can be presented to any structure that is the owner of the securities;
- It is possible to sell the bill to third parties.
This video will tell you how to collect receivables:
Flaws:
- A bill is a security that does not have any collateral;
- The enforcement service can collect debt obligations from the debtor for years.
Today there is no trading platform or at least a single database of bills. This state of affairs leads to the fact that the potential buyer of the bill cannot know for sure whether he will receive his money or not.
The current economic situation in the country negatively affects the financial position of many commercial structures. In this regard, there are often delays in the payment of debt obligations.
As practice shows, the best methods of collecting obligations are based on their assignment. This is due to the fact that such methods can significantly save time and, in some situations, even money.
Results
The sale of receivables is accompanied by the conclusion of an assignment agreement. The procedure for the relationship between the parties when concluding this type of agreement is regulated by Art. 382–390 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Conducting transactions related to the sale of debt in the accounting of each party has its own nuances.
How the sale of receivables occurs in bankruptcy proceedings, what features this process has, can be found in the article “Sale of receivables in bankruptcy proceedings.”
simplified tax system
In the accounting of the creditor (seller), no special features will arise in connection with the replacement of the debtor under the obligation. After all, simplified organizations recognize income and expenses after their actual payment (clauses 1, 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, the seller will take into account the income when the new debtor pays off the obligation. That is, the same as if the payment obligation was fulfilled by the original debtor. Income from sales in this case arises on the date of receipt of funds from the new debtor (clause 1 of Article 346.15, clause 1 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When the debt is transferred, the original debtor's obligation to pay ceases. Therefore, he can recognize the cost of purchased goods (works, services) as expenses. After all, the obligation to pay them was fulfilled on the date of transfer of the debt (subclause 5, 8, clause 1, article 346.16, subclause 1, clause 2, article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 23, 2012 No. 03-11-06 /2/45, dated May 25, 2012 No. 03-11-11/169).
The new debtor simply incurs a debt to the creditor. But this does not need to be reflected in accounting. Expenses will arise only when such a debtor begins to pay the seller.