Account 51 “Current accounts” is intended to summarize information about the availability and movement of an organization’s funds in rubles on its current accounts opened with credit institutions. The debit of the account reflects the receipt of funds to the organization's current accounts. For a loan – writing off funds from current accounts. Important! When opening a current account, you do not need to notify the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund. In accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 94n dated October 31, 2000, account 51 corresponds with the following accounts.
| By debit | By loan | ||
| check | Name | check | Name |
| 50 | "Cash register" | 04 | "Intangible assets" |
| 51 | "Current accounts" | 50 | "Cash register" |
| 52 | "Currency accounts" | 51 | "Current accounts" |
| 55 | "Special bank accounts" | 52 | "Currency accounts" |
| 57 | "Translations on the way" | 55 | "Special bank accounts" |
| 58 | "Financial investments" | 57 | "Translations on the way" |
| 60 | "Settlements with suppliers and contractors" | 58 | "Financial investments" |
| 62 | "Settlements with buyers and customers" | 60 | "Settlements with suppliers and contractors" |
| 66 | “Calculations for short-term loans and borrowings” | 62 | "Settlements with buyers and customers" |
| 67 | “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings” | 66 | “Calculations for short-term loans and borrowings” |
| 68 | "Calculations for taxes and fees" | 67 | “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings” |
| 69 | “Calculations for social insurance and security” | 68 | "Calculations for taxes and fees" |
| 71 | "Calculations with accountable persons" | 69 | “Calculations for social insurance and security” |
| 73 | “Settlements with personnel for other operations” | 70 | "Calculations with accountable persons" |
| 75 | "Settlements with founders" | 71 | “Settlements with personnel for other operations” |
| 76 | Settlements with various debtors and creditors" | 73 | "Settlements with founders" |
| 79 | "Intra-economic settlements" | 75 | Settlements with various debtors and creditors" |
| 80 | "Authorized capital" | 76 | "Intra-economic settlements" |
| 86 | "Special-purpose financing" | 79 | "Authorized capital" |
| 90 | "Sales" | 80 | "Translations on the way" |
| 91 | "Other income and expenses" | 81 | “Own shares (shares) |
| 98 | "Revenue of the future periods" | 84 | “Retained earnings (uncovered loss) |
| 99 | "Profit and loss" | 96 | “Reserves for future expenses” |
| 99 | "Profit and loss" | ||
Money can be transferred to your current account in several ways:
- from the current account of another organization or individual entrepreneur (IP);
- in the form of cash from the organization’s cash desk;
- through the terminal from other organizations or individuals;
- using plastic cards;
- from the budget or extra-budgetary funds
In this case, the supporting documents for non-cash payments can be:
- money orders;
- payment requirements;
- payment orders;
- letters of credit;
- collection orders;
- checks
How is the receipt of proceeds from sales into the current account reflected in accounting?
In practice, most often, proceeds from sales are transferred to the company's bank account via non-cash means.
Counterparties pay for the goods received (products, semi-finished products, services, etc.) by the usual transfer of funds from their current account to the seller’s current account. This is the simplest, most economical and safest way to transfer proceeds to the company’s account. How to record an operation in accounting if non-cash proceeds from sales are received in the current account - what entry should be used for this?
At the time of shipment, the seller reflects the proceeds from the sale of goods (works, services) and the buyer’s receivables. This debt is paid off as soon as the money from the buyer arrives in the seller's account. The following entries are made in accounting:
Postings for recognizing revenue in accounting are made on the basis of shipping documents (invoices, acts, etc.). A document confirming the receipt of money into the account is a bank statement.
When reflecting the receipt of revenue in foreign currency into a bank account, account 52 “Currency accounts” is used instead of account 51 “Currency accounts”.
Learn about the nuances of accounting for foreign currency account transactions in this article.
Payment by bill of exchange
You can pay for goods and services not only in cash. To repay the debt, the company can issue a promissory note. For settlements on account 60, a subaccount “Bills” is opened. The wiring looks like this:
- Debit 60 Credit 60 “Bills” - a bill is issued to the supplier.
Then it is “extinguished”:
- Debit 60 “Bills” Credit.
When calculating interest-bearing bills, interest is accrued:
- Debit 91.2 Credit 60.
Example:
The organization purchased materials in the amount of 112,545 rubles. As payment, the supplier was issued an interest-free promissory note, which was paid in full two months later.
Postings:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 10.01 | 60 | Goods received from supplier | 112 545 | Packing list |
| 60 | 60 "Veselya issued) | A bill of exchange was issued to the seller | 505 | Bill issued |
| 60 “Bills issued” | Bill paid | 112 545 | Payment order |
Cash proceeds handed over to the bank: what entries to make in accounting
It is not always possible for a company to work exclusively with non-cash revenue. If the proceeds from customers are received in cash and the cash balance exceeds the established limit, the excess amount must be deposited into the current account.
We explain how the cash limit is set in this publication.
Cash proceeds from the cash register are transferred to the current account - what kind of entry can be used to record this operation?
The operation of depositing proceeds into a current account is accompanied by the execution of cash documents (cash expense order, announcement for cash deposits, etc.) and is reflected in accounting by posting:
If the proceeds are not delivered to the bank by a company representative (cashier or other authorized person), additional entries may be required.
Find out what operations are available when your account is blocked here.
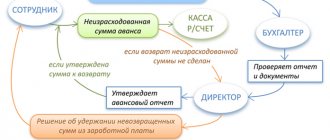
Is it possible to issue a loan from the cash desk in cash to the founder
For example, the permitted payments to employees are formulated differently (more specifically) (in the previous document it sounded like this: “other payments to employees”, “scholarships, travel expenses”).
This is discussed in paragraph 12. When issuing an interest-free loan, the borrower experiences savings in the form of savings on interest. But won't this specificity turn out to be unfavorable for the organization? Let's assume the business traveler spent personal (rather than accountable) funds. Can they be compensated from the proceeds received at the cash desk? Question... The founder gave the organization an interest-free loan. The funds were used to pay salaries to employees. Is cash discipline violated in this case?
Yes, it's broken. The Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated October 7, 2013, on the one hand, does not prohibit payments to employees included in the wage fund and social payments.
But, on the other hand, we are talking about cash for goods sold, services provided, work performed (revenue) or insurance premiums received. There are no other sources of cash that can be spent bypassing a bank account.
When additional entries are required to reflect the receipt of revenue into the current account
Proceeds from the company's cash desk can go to the current account through a special intermediary (bank collector). If the proceeds are handed over to the bank through a collector, what additional posting may be needed?
In this case, an additional entry appears in accounting, taking into account the presence of cash proceeds “in transit” from the cash register to the current account. The appearance of a collector in the chain of movement of proceeds from the cash desk to the bank requires recording the following set of transactions in accounting:
Additional posting to reflect revenue “in transit” is required in one more case: if the company’s cashier hands over the revenue to the bank through the terminal - read more about this below.
We will tell you in this article how to register the transfer to the current account of the authorized capital.
How to process the revenue of an online store if the buyer paid for the order with a card? The answer to this question was given by ConsultantPlus expert T. Bursulaya. If you do not yet have access to the system, get a free trial online access and find out how to make entries for an online store accountant.
Cash delivery by employee
Often, companies do not use the services of special collection services and transport money themselves to be credited to a bank account. In this case, how do you draw up documents and make accounting entries? The document confirming the fact of transportation of funds is the RKO. In the order, among other mandatory data, it is necessary to indicate the full name of the responsible employee; his passport details. When receiving cash, the employee must sign the order.
After the money is deposited into the account, the organization is issued a bank receipt. This form is attached to the RKO. There are two types of wiring:
- Upon receipt of funds to the account on the day of transportation - D 51 K 50.
- When cash is credited on the next working date - D 57 K 50 (at the time of transfer of funds to the employee), D 51 K 57 (at the time of transfer of funds to the account).
The proceeds were credited to the account through the terminal: we are sorting out the transactions
Banks can provide companies with a self-collection service. This method of transferring proceeds to a current account can significantly reduce the time between receiving cash proceeds and its crediting to a bank account.
Instead of making a daily trip to the bank to deposit cash, the teller deposits it into the bank terminal. To use this service, the company enters into an agreement with a banking institution and receives a special access code, which is entered into the terminal when depositing cash.
The proceeds deposited through the terminal almost immediately go to the company’s current account (minus the commission). A doubt may arise: is this extra posting necessary using account 57 “Transfers in transit” if the money goes straight to the account?
Wiring is still required. The terminal may not accept all banknotes in full, so to reflect the transaction of transferring proceeds to the account, it is safer to use account 57 “Transfers in transit.”
The wiring diagram in this case will be similar to that described above (when money is transferred to the bank through a collector). But the content of the operations will be somewhat different:
After accepting the proceeds, the terminal issues a document confirming the receipt of cash (order check, receipt, etc.).
Should I include in the revenue the tips that the client left to the waiter (or maid) after paying with a card, and is it necessary to withhold personal income tax from them? The answer to this question is in the ConsultantPlus system.
Get free trial access to K+ and watch the full version of the explanation.
This material will introduce you to other transactions on the current account.
Common questions about 51 accounts
Question. How to reflect the receipt of revenue on the current account if the buyer paid for services with a bank card?
Answer. In this case, make the following entries
- Debit 62 / Credit 90.1 – revenue paid by bank card is reflected
- Debit 57 / Credit 62 - posting is done if the money does not immediately appear in the organization’s current account
- Debit 51 / Credit 57 – amount credited to the organization’s current account
- Debit 51 / Credit 62 - posting is done if the money is immediately credited to the organization’s current account
Results
To reflect the receipt of revenue into a bank account, accounting entries are made to the debit of account 51 “Currency accounts” (52 “Currency accounts”) and the credit of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers.”
If cash proceeds are handed over to the bank by a cashier, account 50 “Cash” is credited in correspondence with account 51 “Cash Accounts” debited. When intermediaries (collectors, terminals) participate in the transfer of proceeds from the cash desk to the bank, account 57 “Transfers in transit” is additionally involved in the postings. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Algorithm for recording cash payments for goods at the cash register
- Revenues in rubles. When ruble revenue is received at the organization's cash desk, a primary document of the unified form KO-1 is drawn up - Cash receipt order. The cashier or accountant can write it out manually, or register it in the 1C program.
This document contains a detachable part - a receipt; it is certified by a seal and issued to the person from whom the money was received. If the cash received at the cash desk is revenue for goods, work, or services, it is necessary to use a cash register, i.e. In addition to the receipt for the receipt order, a cash receipt is issued.Typically, several such transactions are performed during a working day; in this case, it is enough to issue a cash receipt, and at the end of the day, issue one receipt order for the amount of total revenue. A receipt order executed manually must be registered in the Journal of Registration of Receipt and Expenditure Cash Documents (form KO-3), filed with the cashier’s report, and a corresponding entry made in the cash book.
- Foreign exchange earnings. According to the Law of 10.12. 2003 No. 173-FZ, Russian enterprises have the right to carry out foreign exchange transactions. In accounting, foreign currency earnings must be reflected at the exchange rate valid on the date of transfer of ownership, or on the date of receipt of the advance payment. If payment is made after shipment, the organization will experience exchange rate differences (positive or negative) due to the fact that the exchange rate changes regularly.
Exchange differences are reflected in non-operating income (expenses) in the debit of the account. 57 (91) – credit account. 91 (57).You will find more information on the repatriation of foreign currency earnings in a special material.
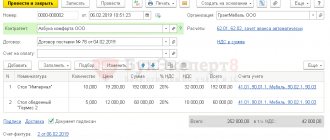
Turnover balance sheet for account 62 using an example
Let's consider an example of generating a balance sheet for account 62 from the 1C program:
What do we see from this SALT?
For example, the counterparty LLC Horns and Hooves made a payment in our favor for 2021 in the amount of 61,114.56 rubles, and we shipped him goods or provided services in the amount of 27,110.68 rubles. The final accounts payable to the buyer is 34,004.88 rubles.
Existing subaccounts
The current plan for analytical accounting does not provide for a hierarchical division of account 51. Thus, there are no officially approved sub-accounts.
Some programs used for accounting provide the function of entering your own subaccounts. However, using such a function to indicate postings to item 51 is not mandatory. In addition, the introduction of subaccounts can lead to errors. The most common is the differences between the final balances for Dt and Kt in different months.
Handing over money to a collector - example
Let’s assume that on April 2, a trading company sold products worth 315,000 rubles. The cash limit is set at 15,000 rubles; you need to deposit 300,000 rubles to the bank. To do this, the cashier prepared a bag with cash and filled out the accompanying documents according to the general regulations. In RKO for 300,000 rubles. on the line “Issue” the full name of the cashier transferring the means is indicated, on the line “Attachment” - the details of the receipt. Such recommendations of the Central Bank are contained in Letter No. 29-1-1-OE/4065 dated October 16, 2015.
The bag with cash and the enclosed statement is sealed. Then the cashier hands the bag to the collector along with the invoice. The receipt signed by the collector and the cash register remain with the organization.
Delivery of proceeds to the bank through a cash collector - posting:
- D 57 K 50 for 300,000 rubles. – on the day of transfer of cash to the collector.
- D 51 K 57 for 300,000 rubles. – on the day the funds are credited to the company’s account.
Accordingly, the delivery of money to the collector is always recorded as an accounting entry through an account. 57, and when transporting funds by a company employee, posting D 51 K 50 can also be used. But only if the cash is credited to the account by the bank on the same day.