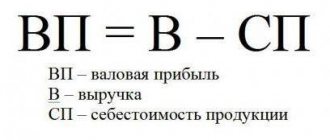When can input VAT be included in expenses?
Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation regulates these features.
- According to its first paragraph, taxes that are not included in the list of Article 270 are other expenses associated with the sale of goods and the process of their production. Art. 270 also indicates that the amount of taxes presented to the end consumer by the seller is not used to determine the amount of the tax base. Input VAT is taken into account as expenses for profit tax purposes if the taxpayer is exempt from VAT or pays it when purchasing goods. According to the article, these nuances are called “Other”. The article itself states that VAT paid by the taxpayer when purchasing necessary goods for the production process or when importing certain goods into the customs territory of the Russian Federation is not included in the expense column.
- If a taxpayer purchases goods for inclusion in fixed assets and production of goods, then the VAT paid for their purchase is deducted or calculated in the amount of fixed assets in the same proportion as these funds are used for production.
- Article 170 regulates the inclusion of input VAT in expenses, although in a large number of cases its payment is made at the expense of the taxpayer.
Example. The exporting company that sells household appliances did not provide documentary evidence of importation. In this case, she pays VAT, but the foreign buyer is not charged VAT directly. In theory, the amount of VAT should be classified as an expense, but according to Article 170, in which this situation is not stated as “Other,” the amount of VAT paid will be included in income. Although on the basis of Art. 270 it is by this amount that the company’s income must be reduced to calculate the tax on its profits.
- If VAT amounts attributable to the enterprise’s excess advertising costs are not approved for deduction, then they are not taken into account in the list of expenses. Standard advertising expenses are taken into account for calculating income tax and are deductible if they do not exceed 1% of revenue received from the sale of goods or services. The amount of VAT that is not deducted is paid from the taxpayer’s own funds. This is especially true in the case when the payer pays for goods purchased by him with his own property, and its value in the invoice is indicated lower than the market value.
- Taxes are taken into account in a special way when writing off loans and debts. If this is a debt that arose on the basis of budgetary relations, then the VAT amounts are not taken into account when calculating income tax. When the debt is written off for a long time, or if the creditor is liquidated, then such an amount will become non-operating income, and taxes on it will become a non-operating expense.
- Also, VAT is included in income tax expenses if the bank, insurance organization or private pension fund paid it when purchasing goods and services to maintain its operation.
- If the amount of VAT is paid during the calculation of it to pay a certain penalty, then such costs are included in non-operating expenses and are not used to calculate income tax (Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Important aspects about accounting for VAT in income tax can be learned from the video:
Write-off of VAT on costs under the simplified tax system
According to officials, simplifiers can write off VAT on expenses only after the sale of the acquired asset (letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 17, 2014 No. 03-11-09/6275 and dated September 24, 2012 No. 03-11-06/2/128).
The justification for this position is that, according to sub. 23 clause 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when calculating the tax base, one should take into account the costs of paying for the cost of inventory items acquired for subsequent sale (with their reduction by VAT amounts).
In accordance with sub. 3 p. 2 art. 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses for paying taxes of companies using the simplified tax system are accepted based on the amounts actually paid.
According to sub. 8 clause 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, simplifiers who use the “income minus expenses” scheme reduce their income by expenses in the amount of VAT on paid goods and materials and services.
According to the rules established by sub. 2 p. 2 art. 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses for paying the cost of inventory items purchased for subsequent sale are taken into account in the tax base as they are sold.
Summarizing the above, officials state that VAT on purchased goods under the simplified tax system can only be taken into account after their sale.
Is it possible for simplifiers to deduct VAT paid at customs when importing goods into Russia? Find out in ConsultantPlus. If you don't already have access to the system, get a free trial online.
How to confirm compliance with the conditions of release?
By the 20th day of the month following the 12th month of application of the exemption, you must provide the following to the Federal Tax Service:
Documents confirming that within 12 months the revenue was within 2,000,000 rubles. for every 3 consecutive calendar months (extract from the balance sheet/profit and loss account and sales ledger);
Notification of the extension of the use of the right to exemption over the next 12 calendar months or the refusal to use this right.
Expenses taken into account when calculating income tax
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation deals with expenses in Articles 253 (expenses related to sales and production), 265 (non-operating expenses) and 270 (not taken into account).
The list of expenses that are not taken into account when calculating tax is very extensive and specific. But you need to keep in mind that there are certain requirements for expenses. According to Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses are recognized as justified (that is, economically justified) and documented expenses that arise in the course of the enterprise’s activities. In addition, costs are recognized as expenses if they are the result of activities aimed at generating income. These are very important requirements for determining expenses.
In order to avoid unnecessary questions from the tax inspectorate, it is necessary that the organization can confirm that the costs attributed to expenses actually meet these requirements. True, the tax code does not explain in any way what exactly is meant by “economically justified” and “aimed at generating income.” In connection with this, in practice, many disputes often arise between the tax authorities and the organization. VAT when calculating income tax.
If an organization is a VAT payer, then the amount of this VAT is not taken into account when determining profit. That is, the taxpayer does not include VAT charged to customers in the amount of income, and does not take into account the VAT paid to suppliers in the amount of expenses. The exception is the cases described in Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which VAT is applied to the costs of production and sale of goods, works, and services.
If an organization is not a VAT payer, then by definition it does not charge VAT to its customers, which means it is not included in its income from the start. And VAT charged by suppliers is included in expenses, as in accounting.
I also offer you a comparison of income and expenses in tax and accounting for some operations (accounting entries are given for trading enterprises).
Income taken into account for tax purposes
| the name of the operation | Reflection of the transaction in accounting | Name of income in tax accounting |
| Revenues from sales | Revenue from sales is reflected (D62 K90.1) VAT is withheld from sales (D90.3 K68.VAT) | Income from sales (excluding VAT) clause 1 of Article 249 |
| Proceeds from the sale of fixed assets | Revenue from the sale of fixed assets is reflected (D62 K91.1). VAT is withheld from sales (D91.3 K68.VAT) | Not recognized as income |
| Receiving money or goods for free | The gratuitous receipt of money is reflected (D50 (51) K91.1) The gratuitous receipt of goods is reflected (D41 K98) | Non-operating income: property received free of charge (clause 8 of Article 250) (there are exceptions specified in Article 251) |
| Interest received under the loan agreement | Interest receivable accrued (D58 K91) | Non-operating income: interest received under a loan agreement (clause 6 of Article 250) |
| Fine from the counterparty for violating the terms of the contract | A fine has been accrued to be received from the counterparty (D76 K91.1) VAT has been withheld from the fine (D91.3 K68.VAT) | Non-operating income: sanctions recognized by the debtor (clause 3 of Article 250) |
| Surplus of fixed assets identified as a result of inventory | Surplus of fixed assets is included in other income (D01 K91.1) | Non-operating income: the cost of surpluses identified during inventory (clause 20, article 250) |
Income tax: calculation of the tax base
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
The figure below shows the procedure for calculating the tax base and income tax.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Why compare income based on profit and VAT?
The answer is very simple - the tax office does this, which means we, accountants, need to do this too =)
Tax officials compare VAT and profit returns to find income that the company forgot to charge with VAT.
In the simplest case (if we are analyzing the 1st quarter of the reporting period and we have no accounting difficulties), to reconcile we just need to carefully look at both declarations and check lines 010 + 020 (Sheet 02) in Profit and line 010 (Section 3) in VAT returns.
And this is quite easy to do.
Difficulties begin if we need to compare indicators over 9 months or over a year. Profit is easy to calculate - it is indicated in the declarations on an accrual basis. But with VAT there is already a problem - reporting is quarterly, which means we need to take all declarations from the beginning of the year and summarize their indicators.
Now let’s add some more truths of life:
- refunds to suppliers (increase the VAT base, but no profit)
- customer returns (reduce income in profit, but not in VAT)
- VAT-free income
- different periods of income recognition for export sales
All this leads to the need to understand the discrepancies between VAT and profit
- becomes a very difficult task, requiring a deep dive into accounting, drawing up additional tables and additional checks.
Specialists have a lot of experience in finding VAT and profit differences using Excel tables and “working weekends,” but we are tired of searching everything by hand. We used all our knowledge and experience and developed a special report that allows you to automatically check the convergence of the VAT and Profit base
and take into account common discrepancies. And we are ready to share our findings.
Important: in addition to the adequate reasons for the differences between VAT and Profit, we often find accounting errors that distort the tax base. Our report removes all “resolved” discrepancies and allows you to focus on the actual errors.
What is this?
Revenue represents the income that an organization or enterprise receives over a certain period of time through the sale of a number of goods or services. This is the final stage of the company’s commercial or non-commercial activity, and the calculation is made by multiplying the price of the product by the number of units sold.
Net sales revenue is recognized as profit minus indirect taxes . It is an indicator of the organization's performance.
Revenue from the sale of sales objects is divided into two types:
- Gross revenue is the total amount including taxation (excise taxes, customs duties, VAT).
- Net revenue is profit from sales of products, works or services without taxation.
You will learn about how such sales revenue is calculated in a special material.
The tax calculation looks like this: let’s denote the amount by the letter C, then VAT=C*18/100. According to this calculation, with revenue of 100,000 rubles, VAT will be 18,000.
Including tax
To make such a calculation, the amount including VAT is designated Sn. The calculation turns out like this:
Сн = С + С*18/100 = С*(1+18/100) = С*1.18.
Then, with revenue of 100,000 rubles, the result will be 118,000.
In the Russian Federation, an invoice document is used to calculate value added tax . The law establishes clear rules for filling out this form and its format.
Without him
To calculate the value of profit without this indirect tax, the same formula is used as a basis. When designating N=18/100, it turns out that Сн = С+ N*С = С*(1+N).
Thus, C = Cn/(1+N) = Cn/(1+0.18) = Cn/1.18.
If difficulties arise when working with formulas, then specialized online calculators simplify the work of taxpayers . With their help, data is calculated quickly and accurately.
Enterprise profit and the place of VAT in it
The profit of an enterprise is the difference between its income and expenses. It is determined after taking into account deductions and discounts that are due to the business entity. Where is the place of VAT in this case?
An organization operating on OSNO, operating on legal terms, is a registered VAT payer. In this case, the amount of VAT that it charges to the buyer is not indicated in the list of expenses, as is the amount of VAT that the organization pays to the supplier.
If an enterprise is not a VAT payer, then it does not receive income from it, since it does not present this amount to the end consumer. The calculated amounts of VAT that the organization paid to suppliers are taken into account in expense items.
VAT comes into contact with income tax in the cases specified in Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, where VAT refers to the category of production costs and sales of goods.
Income tax is a direct tax that affects the calculation of all indirect taxes and deductions made. The peculiarities of VAT accounting have a special place in the regulation of such processes.
So, income tax is calculated as follows: from the proceeds excluding VAT, subtract expenses without taking into account the amount of VAT, add non-operating income, subtract non-operating expenses and multiply the resulting number by the interest rate on the tax. In some cases, which are regulated by Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT paid can be classified as expenses, and with its help, a reduction in income tax can be achieved. But you need to make sure that you have the right to such a calculation. Such situations often become controversial for the taxpayer and the tax inspectorate and are resolved in court, but regulatory legal documentation, examined from the right angle, can help prove one’s case.
Income subject to income tax
What is the organization's income? This issue is covered in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in articles 249 (income related to sales), 250 (non-operating income), 251 (income not subject to taxation).
Income subject to taxation:
- from sales (revenue from sales).
- non-operating (all other income). The list of these incomes is long; it is better to read them in the original, that is, in the tax code.
Income not subject to taxation
There are also a sufficient number of them listed in Article 251, the most common:
- income in the form of property, property rights received in the form of an advance, pledge, deposit
- income in the form of property received free of charge from: a) an organization in which the recipient of income has a share in the authorized capital of more than 50%, b) an organization that has a share in the authorized capital of the recipient of more than 50%, c) an individual, if this person has a share in the authorized capital of the recipient more than 50%.
- VAT charged to buyers.