How can the program reflect the reimbursement of expenses to an employee, made from personal funds for the needs of the organization, in the case where the money was not issued on account?
The legislation does not contain a direct prohibition on compensation of employee expenses in the interests of the organization. And at the same time, it does not provide specific recommendations for the execution of this operation. Moreover, this type of operation occurred at least once in every organization.
If for a specific issue of accounting (AC) the federal standards do not establish methods for maintaining accounting, then the organization itself develops an appropriate method (clause 7.1 of PBU 1/2008). Thus, the Organization needs to prescribe in its Accounting Policy the method and procedure for compensating employees for expenses incurred for the needs of the organization, including approval of the document on the basis of which compensation for expenses will be made to the employee.
In our opinion, the use of account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” is not appropriate, since the account is intended for settlements with employees for amounts issued to him on account (Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n ). And in this situation, the employee was not given accountable amounts.
To reflect settlements with an employee, in our opinion, it would be more correct to use account 73.03 “Settlements for other transactions”.
Since when purchasing goods at his own expense, the employee acted with the permission and in the interests of the organization, it is necessary to document that the organization approved such a transaction (Clause 1 of Article 183 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Such documents may be:
- An employee’s application for reimbursement of expenses, approved by the manager (the resolution on the application is “pay”).
- An approved report on the funds spent with documents for purchase and payment attached to it (sales receipt, delivery note, invoice, etc.), including in the form based on AO-1.
- An order on behalf of the manager to reimburse expenses to an employee.
Funds spent by an employee on the purchase of goods or services for the needs of the organization and reimbursed to the employee by the organization on the basis of supporting documents (checks, receipts) are not recognized as the employee’s income and, accordingly, are not subject to personal income tax (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 04/08/2010 N 03- 04-06/3-65). Also, this compensation is not subject to insurance premiums (clause 2, clause 1, article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In 1C, the operation is best documented with the following documents:
- Receipt (act, invoice);
- VAT write-off;
- Cash withdrawal or debit from current account . Type of transaction – Other expense , debit account – 73.03 “Settlements for other transactions”.
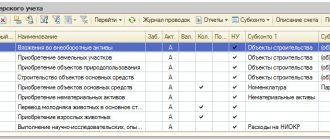
Receipt of material assets
The receipt of goods, materials, and services is documented using the document Receipt (act, invoice) from the section Purchases – Receipt (acts, invoice).
- Account for settlements with counterparties – 73.03 “Settlements for other transactions”;
- The invoice is not registered.
Postings according to the document
Analytics for account 73.03 “Settlements for other transactions” is not automatically entered into the document Receipt (act, invoice) . It is necessary, using manual adjustment, to substitute the name of the employee who incurred the costs.
Accounting methods for inventory items
Accounting methods are prescribed in Guidelines No. 119.
Varietal method
Accounting is carried out using grade-type cards. They record the presence of objects, as well as their movement. Paragraphs numbered 136-140 of the Methodological Instructions describe the features of the method. Accounting can be carried out in the following ways:
- Quantitative-sum. It is assumed that numerical and total accounting is simultaneously introduced in warehouses and accounting departments. In this case, inventory numbers of inventory items are used.
- Baldovy. It is assumed that exclusively quantitative accounting by type of inventory items is introduced in warehouses. Accounting uses total accounting. It uses monetary terms. Quantitative accounting is carried out on the basis of primary documentation. In this case, cards and books are used for warehouse accounting. After the end of the reporting year, the primary documentation must be submitted to the accounting department.
The varietal method is used when inventory items are stored by name and grade. In this case, the time of delivery of valuables and their cost are not taken into account. A separate inventory card is created for each item. One nomenclature differs from another in the following indicators:
- Product brand.
- Variety
- Unit of measurement.
- Colors.
The cards will be valid throughout the year. They must contain all the information about the accepted object. They must be registered in the appropriate register. After this, individual numbers are placed on the cards. Registration is required by employees of the accounting department. If the entire sheet of the card is filled, new sheets are opened. They must be numbered.
NOTE! All entries made on cards must be supported by primary documentation.
Pros and cons of the varietal method
The varietal method has the following advantages:
- Saving warehouse space.
- Quick management of inventory balances.
However, there are also significant drawbacks - difficulties in classifying goods of the same type at different prices.
Batch method
The batch method involves an accounting procedure similar to the varietal method. The difference is that each batch of inventory items is registered separately. The batch method is described in paragraph 242 of the Directions. It is used both in the warehouse and in the accounting department. Assumes separate storage of each batch. Each shipment must have a corresponding transport document.
IMPORTANT! Products that were transported by one transport, goods with one name and simultaneous receipt from a single supplier - all this can be considered a single batch.
The batch must be registered in the goods and materials receipt journal. She is assigned an individual registration number. It is used to make marks in expenditure documentation. The registration number is placed next to the names of inventory items. You need to open two party cards. One will be used in the warehouse department, the other in the accounting department. The shape of the card is determined by the type of product.
Pros and cons of the batch method
The technique has the following advantages:
- Determination of batch consumption results without inventory.
- Increased control over the safety of inventory items.
- Reducing enterprise losses.
But there are also disadvantages:
- Irrational use of warehouse space.
- There is no possibility of operational control of inventory items.
The choice of a specific method will depend on the priorities of the enterprise and the size of the warehouse.
VAT write-off
The Ministry of Finance believes that VAT can be deducted only on an invoice, the exception is if this is provided for in clauses 3, 6-8 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The Code does not provide for the specifics of deducting VAT on retail purchases.
Also, the specified VAT cannot be accepted as expenses for income tax purposes, since clause 2 of Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the possibility of taking into account in the cost of goods (work, services) VAT presented due to the lack of an invoice (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 24, 2017 N 03-07-11/3094).
Since the goods were purchased at retail and no invoice was issued, VAT is not deductible. Based on the Receipts document (acts, invoices), you need to create a VAT write-off .
Postings according to the document
Accounting for inventory items in production
Accounting for inventory inventories
The main question that is posed before starting inventory accounting is: How much and what kind of inventory balances do we have in stock at each warehouse now? Moreover, the emphasis is on the word now - at this moment, and not on the first of the month, not on Monday morning, or even on yesterday evening. Accounting for inventory items in production is necessary to obtain operational data on balances and transition to procurement scheduling.
It is obvious that new materials do not appear at the enterprise just like that. First they were ordered by suppliers. However, at this stage, inventory accounting will be limited to general information - counterparties and contract numbers entered by the supplier. Later, when the procurement management business process is launched, documents for the receipt of new inventory items will need to be linked to purchase orders. For now, let’s look at the desktop for the warehouseman role (the role is the same for both purchased warehouses and finished goods warehouses).
The main function for a storekeeper is a document register. It contains documents on all types of movement, thanks to which it is easier for him to carry out production accounting of inventories in the warehouse.
In a warehouse, inventory accounting is carried out according to the main documents, which are Receipt from the supplier and Requirements - Invoice for delivery to production departments. For a GP warehouse, the main documents are Delivery of products to the SGP and Shipment of products.
Watch a video on creating movement documents in production
Accounting for inventory in a warehouse involves the generation of new documents. To do this, headers are created first, then lines. After this, the document is posted.
When generating document lines Requirements-Invoice and any shipping documents, it is recommended to use the selection mode from existing balances (F9 in the Inventory and Materials field).
Inventory accounting card file
When accounting for inventory in a warehouse, after a high-quality and prompt count, the storekeeper and other responsible persons will be able to view current balances at the current moment.
For any card, you can view all movements since the card was created.
Standard document printing forms are available.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the sections on procurement management:
- Procurement planning. Card file of contracts and specifications for contracts.
- Production accounting
- Clobbi Solutions for Manufacturing
Checking settlements with an employee
To check mutual settlements with an employee, you need to create a Turnover Balance Sheet for account 73.03 “Settlements for Other Operations” section Reports - Standard Reports - Turnover Balance Sheet for an Account.
In conclusion, we would like to add that we do not recommend using this scheme all the time, preferring it to the good old reporting. The purchase of goods (works, services) by an organization with payment from the personal funds of employees may have problems:
- the acquisition may be considered by the tax authorities as expenses incurred in favor of employees with additional personal income tax (clause 2 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and subclause 2 of clause 1 of Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- in the absence of a purchase and sale agreement between the employee and the organization, the tax authority may not recognize expenses on documents issued to the employee for tax purposes.
If the documents confirming the purchase of goods and materials are issued in the name of the organization, then the organization will not have problems with recognizing costs and deducting VAT, as well as difficulties associated with settlements with employees.
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Business trip: daily allowance in excess of the norm, payment through a corporate card, purchase of tickets by an organization. This article is devoted to accounting for settlements with a business trip employee who received an advance…
- Purchase of fuel and lubricants by an accountable person for cash One of the usual, proven options for purchasing fuel and lubricants is purchasing through...
- Purchasing fuel and lubricants using coupons: transfer of ownership at the time of refueling Let’s consider the features of reflecting fuel and lubricants received using coupons in 1C -...
- Typical scheme for purchasing goods in wholesale trade in 1C This publication provides a complete standard scheme for carrying out operations for...
* * *
In conclusion, it remains to add that checking the completeness of revenue accounting is one of the favorite control procedures of the Federal Tax Service. However, practice has shown that auditors do not have a clear idea of what needs to be checked and in what sequence. Let's hope that the Regulations on control over revenue accounting developed by the Ministry of Finance will bring clarity. And, perhaps, then, due to cash transactions, disagreements will not arise between auditors and the persons being audited. Wait and see.
S.V.Bulaev
Journal expert
"Trade:
Accounting
and taxation"
Subaccounts 10 accounts
PBUs establish a list of certain accounting accounts in the Chart of Accounts that should be used to account for materials in accordance with their classification and item groups.
Depending on the specifics of the activity (budgetary organization, manufacturing enterprise, trade, etc.) and accounting policies, accounts may be different.
The main account is account 10, to which the following sub-accounts can be opened:
| Subaccounts to the 10th account | Name of material assets | A comment |
| 10.01 | Raw materials | |
| 10.02 | Semi-finished products, components, parts and structures (purchased) | For the production of products, services and own needs |
| 10.03 | Fuel, fuel and lubricants | |
| 10.04 | Container materials, packaging | |
| 10.05 | Spare parts | |
| 10.06 | Other materials (for example: stationery) | For production purposes |
| 10.07, 10.08, 10.09, 10.10 | Materials for processing (outside), Construction materials, Household supplies, equipment, Working clothes, equipment (in warehouse) |
The chart of accounts classifies materials according to product groups and the method of inclusion in a certain cost group (construction, production of own products, maintenance of auxiliary production and others, the table shows the most used ones).
Penalties for violations
Any deviations from the letter of the law are punishable by Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. It clearly states the fines that officials and legal entities face in case of violation of cash handling procedures.
So for officials the fine will be from 4,000 to 5,000 rubles, for legal entities - 10 times more: from 40,000 to 50,000. The information is relevant for 2021.
Important! Violation of cash discipline also entails the imposition of penalties.
These are the basic principles of cash circulation for individual entrepreneurs. Understanding these basics and knowledge of the legislative framework will help individual entrepreneurs conduct business successfully and legally.
Inventory accounting
Accounting is carried out on the basis of primary documentation drawn up in a unified form.
Admission
Accepted for accounting:
- Raw materials used in the production of goods.
- Products for subsequent sale.
- Assets for the needs of enterprise management.
The design will depend on the following factors:
- Places for receiving goods.
- Quantities of products, their quality.
- Compliance of the supply agreement with the accompanying papers.
Upon acceptance, an act is drawn up. It must be completed using form No. TORG-1. Upon receipt of goods and materials, employees must act in accordance with the following algorithm:
- Placing a purchase order.
- Reconciliation of the order with the standards.
- Statement.
- Acceptance of goods and materials by the storekeeper.
- Entering relevant information into the warehouse accounting system.
- Sending primary documentation to the accounting department.
- Reconciliation of accounting and warehouse records.
- Detection of shortages and batches without invoices.
The regulations must be recorded in the internal acts of the enterprise.
Postings upon receipt
When goods and materials are received from the supplier, the following transactions will be used:
- DT 10 CT 60.1. Receipt of valuables.
- DT 19.3 CT 60.1. Input VAT.
Inventory and materials can come not only from suppliers, but also from founders and other persons. In this case, the corresponding subaccount of account 10 is opened. The postings will be as follows:
- DT10 KT75.1. Receipt from the founder.
- DT10 CT 71. Receipt from an accountable person.
- DT10 KT20. Manufacturing of goods and materials at the enterprise itself.
If inventory items are received for resale, account 41 should be used.
Internal movements of goods and materials
By internal movements of inventory items we need to understand their movement within the boundaries of the enterprise. For example, the release of raw materials from a warehouse to a production workshop. As a rule, for internal movements, an invoice is issued. It is relevant in the following cases:
- The products produced will be used by the enterprise itself.
- The object is returned to the workshop or warehouse.
- Production waste and defects are handed over.
The invoice is drawn up, in accordance with Resolution No. 71a, in form No. M-11.
Write-off
Write-off of inventory items is a necessary procedure that ensures that the actual amount of valuables corresponds to that recorded in accounting documents. For registration, a write-off act is drawn up. The values indicated in it are not subject to further application. The document is approved by the manager. The act must indicate all information about the item being written off: weight, number, reason for disposal.
The accountant’s task is to reflect the value of the assets being written off. It can be determined by the following methods:
- At average cost.
- At the cost of an individual object.
- FIFO (at the price of the first batch received or manufactured).
IMPORTANT! If the write-off is made due to the fact that the value is obsolete, then the act is not drawn up.
Postings upon write-off
When writing off, the following entries can be used:
- DT20 KT10.
- DT23 KT10.
- DT25 KT10.
NOTE! Upon disposal, both the cost of the asset and the depreciation charges on it are written off from the balance sheet account.