There are certain cases when the seller must calculate VAT on the amount of income at the estimated rate. This is stated in paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of Russia. Such cases include operations on the assignment of property rights provided for in Article 155 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Can the buyer deduct this VAT, since formally the amount of tax was not presented by the seller? And does the latter have the right to take this amount into account as expenses? Let us consider these issues in more detail using the example of the assignment of the right of claim under a sales agreement.
From January 1, UPD and invoices can only be issued in the new format
The Federal Tax Service has approved a new format for primary documents, invoices and UPD. All organizations that exchange electronic documents should switch to it.
What's changing
Until January 1, 2021, electronic primary documents, UPD forms and invoices can be created in two formats:
- in the old one, which is enshrined in the order of the Federal Tax Service dated March 24, 2016 No. ММВ-7–15/ (hereinafter referred to as order 155),
- and the new one, which was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated December 19, 2018 No. ММВ-7–15/ (hereinafter referred to as order 820).
On January 1, 2021, Order 155 will no longer be in force; it will be possible to create invoices and UPD only in a new format. In the old format, they will not comply with the requirements of the law (clause 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The Federal Tax Service will accept documents in the old format that you submitted before January 1, 2020 until the end of 2022. In 2023, receiving complexes will no longer process electronic invoices and UPD with invoices in the old format. You will only be able to submit a printed form of the document.
Labeling changes
Product codes can be recorded in electronic UPD forms using the new format. For traceable imported products, fields are allocated for the registration number of the product batch and its quantity.
One document can contain either traceable or tagged goods, since the corresponding prefix is indicated in the file name.
Changes related to procurement
The Federal Treasury authorizes all expenses of recipients of budget funds. To track payment for purchases, the documents indicate, in particular, contract information.
In the format according to order 155, this was only the identifier of the government contract (Table 5.9). In the new UPD format, a new block has appeared (Table 5.10), where the date and number of the government contract, the seller’s personal account number, the name of the territorial body of the Federal Treasury and other details are entered.
Changes affecting document processing
It is easier for EDI users and regulatory authorities to work with primary documents in the new format. Transaction participants can agree on the structure of information fields and fill out documents according to this structure. It has become more convenient to reflect the date of provision of services, completion of work or delivery of goods. The characteristics, grade, article and code of the product were placed in separate fields - now the EDI system can automatically process this data.
All format changes and completion requirements are reflected in Order 820.
Sample of filling out an invoice in 2021
In order to correctly fill out the invoice in 2021, take the information from the primary shipping documents - invoices, acts. If there was an advance payment, payment details will be required for line 5 (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 02/06/2018 N 03–07-14/6704).
You can fill out the invoice form in 2021 with a VAT rate of 20 percent:
The rules by which invoices must be filled out in 2021 are given in Government Decree No. 1137 dated December 26, 2011. These rules also did not change in any way in 2021 (this is logical, because the invoice form itself has not undergone amendments). At the same time, we recall that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has established a number of mandatory requirements for the preparation of invoices. They are contained in paragraphs 5, 5.1, 6 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Here is the general approach and rules for filling out invoices in 2020:
- Fill in the lines about the consignor and consignee when shipping goods; put dashes in invoices for work or services. If the shipper is a seller, write “He” on line 3;
- The government contract identifier is needed only for shipments under government orders.
- a product type code is needed when exporting to the EAEU - select it from the HS reference book;
- Take the code and designation of the unit of measurement from Sect. 1 or 2 OKEYS, for example, “796” and “pcs”. If there is no price per unit in the contract or your units of measurement are not in these sections of OKEI, put dashes in columns 2, 2a, 3 and 4.
- the registration number of the customs declaration, the name and code of the country from OKSM is indicated by the importer of the goods. If you resell the goods, column 11 does not need to be filled in.
- number invoices in chronological order. However, violation of the numbering is not critical - it does not deprive the buyer of the right to deduction (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 12, 2017 N 03–07-09/411).
- The invoice is signed by the director and chief accountant or other employees authorized by order or power of attorney (clause 6 of article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An invoice is a document on the basis of which the buyer can accept for deduction the amount of VAT presented by the seller of goods (works, services), property rights (clause 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This is the main purpose of the invoice, so it plays a big role for VAT payers.
Having received from the seller a correctly drawn up invoice, in which there are no errors that would prevent the tax authorities from accurately identifying the seller, the buyer, the name of the goods (work, services), their cost, the tax rate, the amount of tax charged to the buyer, the latter will have the right to accept the amount indicated in the invoice. invoice the amount of VAT to be deducted or include the tax in the cost of purchased goods, works, services (clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Provided that there are also documents confirming their acceptance for registration, for example, a delivery note or an act (clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the buyer receives an incorrect invoice from the seller, you have the right to ask the seller to make appropriate corrections.
Sample invoice for goods in 2021
Sample invoice for advance payment in 2021
Sample invoice for services in 2021
Please note that one person can sign the invoice for the director and chief accountant. To grant him such powers, it is enough for the director to issue one order or issue one power of attorney. This was confirmed by the Ministry of Finance in a recent clarification (letter dated July 24, 2019 No. 03–07-11/55067).
The Tax Code does not require that invoices be signed exclusively by the director and chief accountant of the company. These may be other persons whom the director authorized by order or power of attorney (clause 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code).
It is not necessary for one person to sign for the director and another for the chief accountant. You can issue one general power of attorney for the right to sign invoices for both the manager and the chief accountant. Give it, for example, to the manager so that the director does not waste time signing documents. Instead of a power of attorney, you can draw up an order.
Warn the manager to put not one, but two signatures - both with a transcript. Additionally, let him indicate the number and date of the power of attorney or order. Then counterparties will not have any unnecessary questions regarding the preparation of documents.
Has the manager gone on vacation? No problem. Transfer the right to sign invoices to another employee.
invoices 2020
Download
How to reflect the VAT returned by the bank in accounting
If you sued the bank and sued it for an excessively transferred amount of VAT, then in tax accounting this amount is recognized as non-operating income in accounting - other income on the date of the court decision. The transactions will be reflected in the following entries (we use our example data here).
Of course, all of the above is true not only for situations where the seller is a bank or property received as compensation or under a pledge agreement is sold. After all, VAT is calculated on the difference between prices also when selling:
- agricultural products and products of their processing, which
— purchased from individuals who are not entrepreneurs;
— included in the List of agricultural products and their processed products, approved by the Government
- cars purchased specifically for resale from individuals who are not entrepreneurs
Before signing a property purchase and sale agreement with the bank, you should clarify how VAT will be calculated: in the usual manner or based on the inter-price difference. Subsequently, this can save the company from claims from tax authorities and litigation with the seller.
In addition, VAT on the inter-price difference is calculated upon the sale of property used to conduct VAT-free transactions, the cost of which is formed taking into account the tax in accordance with the separate accounting methodology adopted in the organization
In these cases, the amount of VAT paid to the seller in excess of the amount calculated from the inter-price difference will also be recognized as unjust enrichment
At the same time, decisions are known in which judges came to the conclusion that with such a scheme the state is unjustifiably deprived of the difference between the amount of VAT received from buyers and the amount listed in the budget. The seller does not have the right to retain part of the amount of VAT charged to buyers, regardless of how the tax was calculated
With the beginning of the spring-summer season, many trade and catering organizations purchase products grown by the population on their plots. When selling it, VAT is calculated on the difference between the sales and acquisition prices. But this is not the only case when the tax amount is determined in this manner.
S.V. Knyazeva, UNP expert
The Tax Code provides for two cases when VAT must be calculated not from the full cost of sales, but from the difference between the sales price and the acquisition price or residual value (clauses 3, 4 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Please note: in both cases, when calculating VAT, the sales price is determined according to the rules of Article 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The first case is the sale of agricultural products purchased from individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs and their processed products (clause 4 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This procedure applies only to products included in the List approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 16, 2001 No. 383.
Example 1.
A trading organization purchased 50 kg of radishes from an individual at a cost of 10 rubles. per kilogram. The selling price of 1 kg of radishes was 30 rubles. The entire batch of goods was sold at retail in one tax period.
The following entries will be made in accounting:
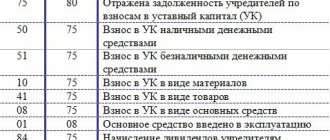
Debit 41 Credit 76 - 500 rub. (10 rub. x 50 kg) - goods are capitalized;
Debit 76 Credit 50 - 500 rub. — the goods have been paid for;
Debit 50 Credit 90-1 - 1500 rub. — revenue for radishes sold in retail trade is reflected;
Debit 90-2 Credit 41 - 500 rub. — the cost of goods sold is written off;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 - 90.91 rub. ((1500 rubles - 500 rubles) / 110% x 10%) - VAT is charged, payable to the budget on the price difference.
The second case is the sale of property subject to VAT accounting (clause 3 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Example 2.
The organization sells a car, which is listed on its balance sheet along with VAT. Selling price - 30,000 rubles. The residual value of the car is 10,000 rubles. (initial cost - 50,000 rubles, accrued depreciation - 40,000 rubles). The tax base for VAT will be determined as the difference between the sales price and the residual value of the car.
The accounting records will include:
Debit 62 Credit 91 - 30,000 rub. — revenue is reflected;
Debit 91 Credit 68 - 3050.85 rub. ((30,000 rub. - 10,000 rub.) : 118% x 18%) - VAT payable to the budget has been accrued;
Debit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” Credit 01 - 50,000 rubles. — the original cost of the car has been written off;
Debit 02 Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - 40,000 rubles. — accrued depreciation is written off;
Debit 91 Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - 10,000 rubles. — the residual value of the car is written off.
When selling property accounted for VAT, the invoice is drawn up with some features (see, for example, letter of the Department of Tax Administration of Russia for Moscow dated November 6, 2003 No. 24-11/62363). In column 1 you need to make o. Column 5 reflects the difference between prices, including VAT (in our example - 20,000 rubles). Column 7 indicates the estimated VAT rate (18/118). Column 8 shows the amount of VAT payable to the budget (RUB 3,050.85), and column 9 reflects the cost of the property sold (RUB 30,000).
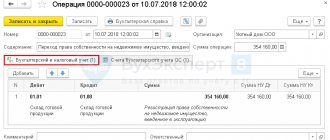
Good afternoon. 1C:Enterprise 8.3 (8.3.13.1644). How to reflect VAT on the inter-price difference when purchasing a car from a dealership? So that the purchase book is filled out correctly. We have an invoice from LLC in the amount of 330,000 thousand rubles. VAT on the inter-price difference is 50,000, VAT rate 20/120 RUB 8,333.33.
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
When is the document used?
An invoice is a document that serves as the basis for the tax authority to accept the buyer for deduction of VAT presented by the seller. When selling goods, providing services, performing work or transferring property rights, sellers charge VAT by issuing an invoice (what is an invoice for?).
Invoices are registered in the Journal of issued and received invoices (books of purchases and sales), and the displayed VAT amounts are subsequently taken into account in tax returns, and at the end of the reporting period, based on the entries made, the amount of tax payable to the budget is calculated.
All comments (3)
Good afternoon. I had a question about purchasing a car, not selling it. It is necessary to reflect the entries in the purchase ledger.
Good day, Natalia. If I understand correctly, then the supplier issued you an invoice with VAT, which was not calculated on the entire amount. From this we can conclude that the supplier purchased this car from an individual. As a buyer, you record the invoice in the purchase ledger as usual. In this situation, the Federal Tax Service will not have any questions for you.
Access to the “Ask a Question” form is only possible if you have fully subscribed to BukhExpert8. Submit an application on behalf of Legal Entity. or Phys. faces you can here >>
By clicking the “Ask a Question” button, I agree with the BukhExpert8.ru regulations >>
In what cases is an invoice not needed?
There are situations when issuing an invoice is not necessary, and the transaction is confirmed by other documents: an invoice for payment, invoices, etc. You don’t have to worry about an invoice if:
- the transaction is not subject to VAT (Articles 149, 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the enterprise sells goods to individuals at retail for “cash” (for such transactions, a strict reporting form or a receipt from the cash register is sufficient);
- entrepreneurs are under special tax regimes (simplified taxation, imputation, unified agricultural tax, have a patent);
- a legal entity gives the goods to its employee free of charge (based on letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 8, 2021 No. 03–07-09/6171);
- delivery of goods is planned, and an advance has been received for it (in this case, this product is produced no longer than six months, or the buyer does not pay VAT, or the transaction has a zero rate for this tax, for example, the product is being exported).
VAT calculation
The creditor, for a certain fee, assigns the right of claim under the sales agreement, which he acquired (purchased) earlier. At the same time, the seller must pay VAT on the difference between the income from the assignment and the costs of acquiring this right. In accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in this situation a calculated rate of 18% / 118% is applied. Let's assume that the rights were acquired for 100 thousand rubles, and later assigned for 110 thousand rubles. VAT on the inter-price difference of 10 thousand rubles amounted to 1,525.42 rubles.