The amount of land tax directly depends on the cadastral value of the land plot. At the same time, planned revaluation of real estate is carried out rarely and en masse, which leads to unreasonable overestimation or underestimation of prices. In this case, the owner has the right to file an application for review, justifying his claims and providing the necessary package of documents.
How often does the price of land change, is annual revaluation possible?
The procedure and conditions for cadastral valuation of land are regulated by Federal Law No. 135-FZ of July 29, 1998 (hereinafter referred to as the Law).
The cost of land plots within populated areas may change by decision of executive authorities during a planned recalculation or at the request of the owner. There are a significant number of factors that positively or negatively affect the price and are taken into account when forming or changing it:
- location of the land plot, surrounding infrastructure;
- area, building materials, soil fertility and quality;
- land surveying, presence of completed construction projects, their age;
- purpose, category of land;
- significant change in market value (read about market value and its differences from cadastral value);
- prospects and plans for the development of the settlement;
- errors or changes in the original assessment data.
Changes can be made no more than once every 3 years according to Art.
24.12 of the Law. For federal settlements this period is 2 years. The maximum term without cost adjustment is 5 years. During this period, the price according to the cadastre must be revised at least once. The assessment is made before January 1 of the year in which the changes are made.
Revaluation of land for previous years
A massive revaluation of land was carried out back in 2014 , and the result was such that in some regions the calculated figure significantly exceeded the market value of the plots.
This situation led to the fact that the owners of many plots, who did not agree with this fact, considered the increase to be unjustified, and initiated a large number of legal proceedings to challenge the value established at the state level.
An equally significant change in the cadastral value was the amendments to the laws introduced in December 2016 , when there was a significant increase in indicators for all categories of land plots.
Reasons for the increase
The cadastral value of real estate during a planned assessment is not calculated locally, but is carried out by appraisers based on publicly available sources of information and average market prices. As a result, the final markup can be up to 30% and may not correspond to the actual condition of the land plot. For several:
- regional programs to improve settlements, infrastructure development (opening schools, kindergartens, services);
- incorrect or inaccurate definition of the category of permitted use;
- low frequency and mass revaluation, averaged data;
- making changes to the state register in connection with an increase in area, construction of buildings and engineering facilities on the site;
- directive from executive authorities to increase the tax base for calculating land tax.
The last circumstance is the subjective opinion of some experts, but it is not without reason. It is based on the value of the land according to the cadastre that the tax levy is calculated, which increases proportionally.
An increase in the average market value of similar real estate in a locality or nearby regions may also have an impact on the increase.
What does the adjustment affect?
The value of the cadastral value has a significant impact on the following points :
- Calculation of payment for land lease under certain conditions;
- The amount of land tax, which is determined as a percentage of the cadastral value.
The most significant in this case is the impact on tax calculation, since almost every owner of a land plot, with rare exceptions of preferential groups, is obligated to make such transfers to the country’s budget.
It is on the basis of the cadastral value of one square meter of land that the total price of the plot is determined by multiplying the land area by a unit of indicator.
The tax is also calculated on the basis of a percentage determined for each individual category of land, while the average rate is at the level of 0.3% and can fluctuate significantly both up and down.
By whom and on what basis is the recount carried out?
In any case, a written statement from an authorized person or organization is required to re-evaluate or change the cadastral value of the land plot. These include the owner of the property (individual or legal entity), municipality or territorial executive authorities.
The municipality can make relevant claims only if the land plot is in its ownership.
According to Art. 9 of the Law the grounds are:
- agreement between the appraiser and the individual or legal entity that owns the land plot;
- determination of a district, arbitration or arbitration court;
- resolution of territorial executive authorities.
It is possible to initiate a revaluation or change in value if the property undergoes a planned revaluation by the State Cadastre, land surveying is established or the boundaries of the territory are changed, the type of permitted use or category of land changes.
The owner has the right to submit a corresponding petition in connection with other circumstances that objectively affect the assessment (decrease or increase in soil fertility, natural disasters, cadastral and audit errors).
Not only full owners, but also persons with the right of indefinite residence, inheritable ownership and tenants (with the consent of the owner, if the housing is not social) have the right to apply for a revaluation or change in the cadastral value.
Commonly owned plot
If the land plot is in common shared ownership, then the cadastral value of the part of the land plot owned by the organization is determined in proportion to its share in the common property. To do this, use the formula:
| Cadastral value of part of the land plot owned by the organization | = | Cadastral value of the entire land plot in common shared ownership | × | Share of a land plot owned by an organization by right of ownership, percentage |
Such rules are established by paragraph 1 of Article 392 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If the land plot is jointly owned, then the cadastral value of the share owned by the organization is determined in equal shares (clause 2 of Article 392 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For example, if the owners of a land plot are three organizations, then each of them owns 1/3 of this plot. This means that the cadastral value of the share owned by each organization will be equal to 1/3 of the cadastral value of the entire plot.
If an organization acquires a building (except for an apartment building) and the ownership of that part of the land plot occupied by this object is transferred to it, determine the cadastral value in proportion to the organization’s share in the ownership of this land plot (paragraph 1, clause 3, article 392 of the Tax Code RF).
If the owners of the building are several organizations (citizens), then determine the cadastral value in proportion to the share of ownership (in area) of this building (paragraph 2, paragraph 3, article 392 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the owners of the building are both a commercial organization and a state (municipal) institution, then the cadastral value is determined by the commercial organization. A similar rule applies if the owners of the building are both a commercial organization and a government enterprise. In this case, the state enterprise does not determine the cadastral value. For example, if a building simultaneously belongs to a commercial organization on the right of ownership, a state institution and a state-owned enterprise on the right of operational management, then the state institution and the state-owned enterprise in this case have a limited right to use the land plot (clause 3 of Article 36 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, a commercial organization must determine the cadastral value and pay land tax, since an institution (enterprise) that has the right of limited use is not recognized as a payer of land tax (clause 1 of Article 388 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the owners of the building are both a state-owned enterprise and a state (municipal) institution, then the cadastral value is determined by the one that owns the largest area of the building (clause 4 of Article 36 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). For example, if a building belongs to three state-owned enterprises, then the cadastral value and land tax will be determined by the one to which the land plot belongs with the right of permanent (perpetual) use (clause 1 of Article 388 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the right of permanent (indefinite) use will belong to the enterprise that owns a large area of the building (clause 4 of article 36 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). The remaining enterprises have only the right to limited use of the land.
An example of calculating the cadastral value of a part of a land plot occupied by a building. A commercial organization owns part of this building by right of ownership
The organization owns 150 sq. m of building. The total area of the building is 1500 sq. m. m. The cadastral value of the entire land plot, which is in common shared ownership, is 335,000 rubles. Cadastral value of part of the land plot owned by the organization: RUB 335,000. × 150 sq. m: 1500 sq. m = 33,500 rub.
Situation: how to determine the cadastral value of a land plot if a commercial organization is the owner of one of the floors of the building?
Determine the cadastral value of a part of the land plot in proportion to the organization’s share in the common shared ownership of this building (paragraph 2, paragraph 3, article 392 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The title documents confirming the size of its share are the purchase and sale agreement and the certificate of state registration of land ownership (Article 17 of the Law of July 21, 1997 No. 122-FZ, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 11, 2006 No. 03-06 -02-02/37).
To calculate the cadastral value of part of a land plot, use the formula:
| Cadastral value of part of the land plot owned by the organization | = | Cadastral value of the entire land plot in common shared ownership | × | The area of the building owned by the organization | : | Total building area |
If the land plot is located on the territory of several municipalities, then determine the cadastral value separately for each part of the land plot. To calculate, use the formula:
| Cadastral value of part of the land plot | = | Cadastral value of the entire land plot | × | The area of part of the land plot located on the territory of the corresponding municipality | : | Total land area |
This procedure is provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
To obtain information about the area of land falling within the territory of a particular municipality, contact the territorial office of Rosreestr.
How to change the indicator?
First of all, check the current cadastral value through the Unified State Register of Real Estate (USRN) extract (how to get an extract?). It is necessary to apply for a review if errors are identified in the assessment data or if it is necessary to establish a market price. It is also possible to form an appeal if the characteristics or condition of the property change.
Where to go for review?
The procedure must be initiated by personally contacting the territorial bodies of Rosreestr. The application is considered by a collegial commission, which includes:
- regional executive authorities;
- delegates of the Union of Entrepreneurs (monitoring the situation on the real estate market);
- qualified appraisers;
- accredited by a self-regulatory organization (SRO).
The petition is sent to the chairman of the commission. Documents and applications may be submitted to the MFC if available in the region.
Statement
The application is drawn up in any form in printed text on an A4 sheet, indicating the full name and address of the applicant, as well as the full name of the chairman of the commission. Indicated:
- link to article 24.19 of the Law;
- view;
- address and cadastral number of the property;
- basis for review.
The appendix contains a list of documents confirming the applicant’s rights and arguments. Consideration will be refused if the necessary documents are missing or the five-year statute of limitations has been missed (Article 24.18 of the Law).
Documentation
The application form is provided at Rosreestr . It can also be found on the official website of the institution. If a third party acts on behalf of the owner, it is necessary to provide a notarized power of attorney. List of documents:
- an extract from the Unified State Register on the cadastral value of the land plot;
- documents confirming the unreliability of the information used for assessment (if necessary);
- report on establishing the market value of the land;
- receipt of payment of state duty.
There is no need to attach title documents to the application.
In some cases, other written evidence supporting the applicant's arguments is allowed. For example, the conclusion of a geological examination about a change in the chemical composition of the soil, if the reason is a decrease in fertility.
How much does the procedure cost and when is it performed?
- According to Part 6, Clause 1, Art. 333.19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the state fee when challenging the cadastral value by individuals in court is 300 rubles. Legal entities will need to pay 4,500 rubles.
- The work of the appraiser is also paid by the owner, where the price of the service varies between 3-10 thousand rubles.
- If necessary, the services of legal intermediaries and consultants are paid (15-20 thousand rubles).
- Making changes to the state register will cost 350 rubles for individuals and 4,000 rubles for organizations.
The application is considered within 1 month, and the applicant is informed about the date and time of the meeting within 7 days from the date of application.
The owner is notified of the results within 5 working days from the moment the decision is made (Article 24.18 of the Law).
Presentation of results by a special commission
Upon a positive decision of the commission, within 10 days the information is sent to the Unified State Register of Real Estate with prior notification of the owner.
Changes are registered in the database and posted on the official website of the institution within another 10 days.
Within the same period, the applicant has the right to challenge the commission’s decision in court if there is a refusal and the requirements are not fully satisfied.
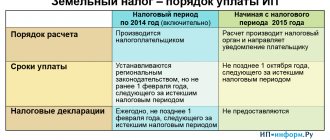
Tax rates
Tax rates for land tax are established by local regulations by which land tax is introduced on the territory of a particular municipality (clause 2 of Article 387 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax rates for land tax established by local legislation cannot exceed:
- 0.3 percent in relation to lands provided (acquired) for housing construction, personal subsidiary plots, gardening, vegetable farming, livestock farming, summer cottage farming and occupied by housing stock and housing and communal facilities, agricultural lands. This rate also applies to lands restricted in circulation due to their use for defense, security and customs needs. At the same time, the procedure for confirming the status of such sites is determined by the Russian Ministry of Economic Development. This was stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 29, 2014 No. 03-05-04-02/25629;
- 1.5 percent for other land plots.
Tax rates can be differentiated depending on the category of land and the type of permitted use of the land.
Such rules are provided for in Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, failure to develop a land plot acquired (provided) for housing construction is not a basis for refusal to apply the reduced land tax rate provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 8 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 23, 2009 No. 54 ).
In relation to land plots acquired (provided) in ownership for housing construction, land tax (advance tax payments) must be calculated by multiplying the tax rate by two. This must be done during the first three years of construction until state registration of rights to the constructed property. This is stated in paragraph 15 of Article 396 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, this rule does not apply to land plots provided to an organization on the right of permanent (indefinite) use for housing construction. That is, there is no need to apply increasing coefficients when calculating land tax. This was stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 10, 2007 No. 03-05-06-02/40.
To calculate land tax at the end of the year (during the first three years of construction), use the formula:
| Land tax | = | Cadastral value of the land plot (if there is a benefit in the form of a tax-free amount - minus this amount) | × | Land tax rate | × | 2 |
To calculate the down payment, use the formula:
| Advance payment for land tax | = | 1/4 | × | Cadastral value of the land plot (if there is a benefit in the form of a tax-free amount - minus this amount) | × | Land tax rate | × | 2 |
The double tax rate must be applied starting from the date of state registration of rights to the land plot.
If housing construction on a land plot continues for more than three years, the tax rate must be increased fourfold. The four-fold rate is applied from a period exceeding the three-year construction period until the date of state registration of rights to the constructed property.
If a residential building is built (registered as property) in less than three years, the land tax (advance tax payments) paid in double amount is recalculated based on the regular rate. Excess amounts of tax (advance payments) paid can be returned or offset against future payments.
Such rules are established by paragraph 15 of Article 396 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. They are used when calculating land tax starting from 2015. When taxing land plots in previous tax periods, different rules were applied.
Situation: at what rate should I pay land tax on a basement that is located in a residential building and is the property of an organization?
If the basement belongs to the housing stock, then apply the rate set at 0.3 percent for land plots occupied by the housing stock. If the basement is transferred to non-residential premises, then the rate can reach 1.5 percent.
The land tax rate must be established by local legislation and cannot exceed 0.3 or 1.5 percent (Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The basement belongs to the housing stock, as it is a room for auxiliary use in a residential building (subclause 1, clause 2, article 19 and clause 2, article 16 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation).
The tax rate established in relation to land plots occupied by housing stock cannot exceed 0.3 percent (paragraph 3, subparagraph 1, paragraph 1, Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the organization has transferred the basement from residential to non-residential in accordance with Chapter 3 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, pay land tax at a rate of 1.5 percent (unless local legislation establishes a lower rate) (subclause 2, clause 1, article 394 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation: at what rate should I pay land tax on an agricultural plot? The organization leases one part of the plot for agricultural production, the second part is not used
For plots classified as agricultural land and partially used for their intended purpose, apply a rate of no higher than 0.3 percent, regardless of who uses the plot.
Reduced rates for agricultural land (0.3 percent) apply only to those land plots that simultaneously meet two criteria:
- refer to agricultural lands (lands within agricultural use zones in populated areas);
- are actually used for agricultural production.
This is stated in subparagraphs 1–2 of paragraph 1 of Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
As for the partial use of a land plot for its intended purpose, the legislation does not provide for the application of different tax rates to different parts of the same plot depending on their actual use. Separate determination of the tax base is allowed only for those parts of the land plot that are located on the territory of different municipalities or are in the common shared ownership of several owners. This follows from paragraphs 1–2 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is confirmed by arbitration practice (see, for example, decisions of the FAS of the North-Western District dated September 22, 2009 No. A56-39782/2008, dated March 21, 2008 No. A56- 27820/2007).
Taking into account this position, as well as based on the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 12, 2012 No. 03-05-04-02/03, an organization using only part of a land plot in agricultural production has the right to apply a reduced land tax rate to the entire plot as a whole .
For tax purposes, it does not matter who exactly uses the plot for agricultural production: the owner or the tenant. Therefore, even if an organization has leased the entire land plot to an agricultural producer, it has the right to pay land tax at a reduced rate. This follows from letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 14, 2008 No. 03-05-05-02/12, dated March 26, 2007 No. 03-05-05-02/14, dated August 8, 2006 No. 03-06 -02-04/119 and is confirmed by arbitration practice (see, for example, decisions of the FAS of the North-Western District dated September 26, 2007 No. A56-50713/2006, Moscow District dated February 12, 2010 No. KA-A41/553- 10).
The dependence between the right to apply a reduced land tax rate and the nature of the use of the land plot is confirmed by letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 16, 2014 No. 03-05-04-02/34879 (sent to tax inspectorates for use in their work by letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 30, 2014 . No. BS-4-11/14944), dated January 12, 2012 No. 03-05-04-02/03 and arbitration practice (see, for example, the determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated April 9, 2008 No. 4872/08, resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated April 22, 2010 No. A66-10150/2009, dated February 8, 2008 No. A56-11088/2007 and dated June 6, 2008 No. A56-19758/2007). From these documents it follows that the tax rate of 0.3 percent applies only to those plots that are actually used in agricultural production.
If an organization owns agricultural land but does not use it in agricultural production, it is violating current legislation. The list of signs by which the composition of such an offense is determined is given in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 23, 2012 No. 369. Having discovered an offense, the territorial division of Rosselkhoznadzor can make a decision to recognize the site as unused for agricultural production. From the beginning of the year in which this decision was made and until the beginning of the year in which the violation was eliminated, the organization must calculate land tax at a rate of 1.5 percent on the entire area of the site. This was stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 16, 2014 No. 03-05-04-02/34879.
Recalculation of land tax
According to Art.
391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the cadastral value of real estate acts as a tax base for calculating land tax, and accordingly entails a revaluation of its value. There is no need to submit a written request to the Federal Tax Service, since the recalculation is carried out automatically. The amount of tax will change for the reporting period in which the owner filed an application with the court or collegial commission. The procedure is carried out from the moment of registration of changes in the state register.
Reasons for overestimating cadastral value
Those who are interested in why the cadastral value of land was raised should know that this may be due to imperfections in the assessment methodology or to errors made during its implementation.
Thus, the priority method for determining the CL of lands is the method of mass assessment. It assumes that real estate objects within specific territories are subject to grouping by types of permitted use. Then the objects are grouped by price zones, on the basis of which a specific indicator of cadastral value is derived, applied to each plot, based on its area.
This approach does not require inspection and study of a specific site, as a result of which its individual characteristics are not taken into account. Thus, the CZP derived as a result of this assessment method is no more than the average cost of 1 m2 of land in terms of the area of a particular plot. It is logical that such an indicator will have a significant error.
The second reason for increasing the CSA is the use of incorrect information about the site:
- incorrect area indicators;
- unreliable intended purpose or type of use;;
- irrelevant data when making calculations;
- ignoring significant defects in the area, and so on.
If the appraiser makes such mistakes, the final SPV may increase several times. The presence of inaccuracies in cost calculations is a legitimate reason for revising the valuation results.
How to reduce the rate?
Reducing the cadastral value is relevant when the usefulness of the land decreases, as well as in a number of other cases:
- damage to the fertile soil layer, drought, natural disasters;
- formation of a swamp, ravine, landslide;
- establishment of a gratuitous easement;
- transfer of land into the ownership of several persons.
The application must be submitted to the city cadastral chamber in accordance with the general procedure. Documents confirming the applicant's arguments are attached to it.
How to reduce CVS
The only way to reduce the cadastral value of a plot is to challenge it. As mentioned above, for this you need to submit an application for review to the commission at Rosreestr or go to court.
The most commonly used strategy is to determine the CSC based on market value: according to , if a market value is established for an object, it is accepted as a cadastral value.
Market value is the result of an individual assessment, taking into account all the significant characteristics of a particular object, from the area to the installed communications.
This indicator is the most objective, and therefore should be determined on the same date as the CPS. To determine the market value, the interested party:
- Contacts a private independent appraiser.
- Concludes an agreement with him and provides the necessary access.
- Receives an appraisal report with objective market value.
- Together with the report and a package of documents, it is sent to the commission at Rosreestr or to the court.
Important: in order for the assessment to be as objective as possible, you should contact qualified appraisers with a good reputation in the market.
Objectivity of the assessment is the main criterion for successfully challenging an inflated SSC. If the court has any doubts, it will appoint an independent forensic examination and select an appraiser. As practice shows, in this case the results of the judicial assessment are 20-50% higher than the results presented by the applicant.
How to challenge it in court?
The claim is filed in the district court at the location of the defendant. The plaintiff is the landowner, and the defendant is Rosreestr.
The decision of the commission is similarly contested within 10 days from the date of its issuance. A copy of the defendant's statement of claim is certified by a notary and sent to the address of the territorial office with a notification of delivery and a list of attachments. Thus, the cadastral value of a land plot can be challenged in several cases when the condition and characteristics of the property change.
An application for a change in value must be submitted to the territorial department of Rosreestr or the MFC, having collected the necessary package of documents. The appeal will be considered within 1 month, and then within another 20 days it will be registered in the state register if the decision is positive.
Possible changes in legislation 2021
Considering the current mood in society and the position of the authorities, an increase in the cadastral value in 2021 most likely will not happen. For the first time, even the president himself spoke out about the imperfections of the cadastral assessment and the resulting CAS. In his message to the Federal Assembly, he negatively assessed the facts of a significant excess of the cadastral value over the market value.
The President noted that property taxes should be affordable for the population, and the mechanism for determining cadastral value involves obtaining inflated figures. In this regard, to improve the methodology for determining the KSZ.
At the time of preparation of this publication, it is unknown whether the methodology has changed - there have been no official reports. Experts are unanimous in their opinion that it is impossible to make a cadastral valuation error-free.
Is it possible to calculate land tax paid by legal entities online?
How to calculate land tax online? This is a completely natural question with modern automation of settlement processes. Services for calculating tax amounts using an online calculator are offered by many websites.
But you can take advantage of these offers if the tax calculation algorithm is quite simple (for example, there are no benefits, and the site is located on the territory of one municipal district). Otherwise, you will not be able to find a universal calculator.
As practical experience shows, it is better to calculate land tax using a formula you created yourself (automating the process using Excel spreadsheets or other proprietary computer developments).
And for individuals and individual entrepreneurs, a special service is available on the Federal Tax Service website, which will calculate the amount of tax online. See here for details.
From what age is it paid?
The indicated tax is charged to the landowner. In order for a person to take ownership of land property, he must reach the age of majority. This logic is elementary, but in reality circumstances do not always develop the same way. Accordingly, there are often cases when the owner of a plot is a child or teenager. Such precedents may arise in relation to the receipt of inherited plots or by receiving them as a gift. Today, situations are quite relevant when parents register purchased real estate in the name of their own children.
These situations are based on a full legal basis, according to which there are rules for resolving them. If the landowner has not reached the age of majority, then the land tax for the land owned by him is paid by:
- Parents.
- Adoptive parents or guardians.
- Other persons acting as their legal representatives.
If a minor is a pupil of a specialized institution, then certain conditions may exempt him from paying tax completely. The tax authority issuing a notice of payment must be aware of who the actual payer is, until financial capacity is achieved, the owner of the site. The notice must be issued in his name.
Who calculates the tax amount?
The land tax from individuals is levied in favor of local self-government bodies, since they are the economic entity in relation to the lands entrusted to them by federal entities. Naturally, the proceeds from the tax received from citizens are sent to the regional fund. The payment is calculated in relation to the region in whose territory the site subject to taxation is located. For its accrual, the following reasons are required, that is, the site:
- Is property.
- Belongs by right of permanent (perpetual) use.
- Refers to lifelong inherited ownership.
Cities of federal significance, such as Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol, are governed by local tax acts; they create their own legislative framework that determines the principles of taxation.
Calculations are the responsibility of the local tax office, which carries them out based on regulations and acts, and using specialized calculation methods. The basic fundamental element of the process is Article 388 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation .
Individuals are forced to be content with ready-made data on the amount of tax amounts imputed to them, which is indicated in the tax notice. It is transferred for payment by resolution of the local branch of the Federal Tax Service, no later than 30 days before the end of the payment period.
However, if you doubt the correctness and adequacy of the calculations made, you have the right to double-check their accuracy yourself, and if the amount presented for payment is unlawful, submit a written claim with the calculations made yourself.
Necessary grounds
Revaluation of cadastral value is carried out at least once every 5 years after an audit of lands by the authorized commission of the State Property Committee. After the revaluation has been carried out, the cadastral value of the land is changed in the records of the state register.
During this period, individual citizens and interested parties have the right to receive information about changes in the value of their plot. Landowners who have claims to the established assessment amount have the right to put their claim in writing and submit it to the cadastre and cartography department at the location of the land plot.
This procedure is given a period of 6 months , after which the accounts become stable and cannot be changed.
Revaluation at the initiative of citizens during this period is carried out on the basis of statements that indicate the reasons for the change in the value of the site, that is, on the basis of indicating information that was not taken into account by the commission during the planned revaluation of land. These applications are subject to consideration and satisfaction at the discretion of the State Committee for Human Rights.
After a certain period, revaluation can be carried out on an individual basis according to existing needs or in the case when the owner of the plot was informed of an inadequately inflated (underestimated) value.
There are often cases when, after landscaping the territory as a result of the construction of a high-rise building, the cadastral value increases as a result of accounting activities on the part of the State Property Committee or on the initiative of the developer, who subleases the site under the house to participants in shared construction.
This allows him to significantly increase his profit income while the rent remains the same.
Such cases of increasing cadastral value are carried out on the basis of changes in the quality of land, bringing a previously unkempt site to balance in the general urban planning context.
Such procedures require the efforts of a group of independent appraisers who establish new regulations for the value of land due to changed circumstances.
Based on the examination, a revaluation of the cost of the storage unit may be carried out in the direction of reducing the cost. If the lands have fallen into disrepair or the fertile layer of soil has been damaged for reasons beyond the control of the right holder, their cadastral value can be significantly reduced. To carry out a revaluation in this case, an expert opinion confirming the decline in land quality will be required.
These cases are especially important for individual entrepreneurs with vast areas of land. In the event of a decrease in fertility or damage to plots, they will have to spend money on paying land taxes without much return. Such cases may arise as a result of fires, natural disasters or damage to land by a nearby industrial enterprise.
Life is rich in various examples when a landowner finds himself in a difficult situation, regardless of the degree of his responsibility. For such situations, options are provided for possible support from the state, including through a reduction in the cadastral value of land as a result of their revaluation. Do you want to know more about where to look at the cadastral value of a land plot or how to change the cadastral value of a land plot? Click on the highlighted phrases.
How to calculate land tax taking into account the benefits?
Benefits contained in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation or established by regional law can exempt a company from paying land tax in whole or in part (Article 395 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If municipalities have provided a benefit for a company's land plot, the tax is calculated taking into account this benefit.
Let's continue our example of calculating land tax: a company has located a scientific center on its land plot (it occupies 20% of the area and is used for its intended purpose), and local authorities have provided tax exemption for land plots used to house scientific institutions.
The land tax will then be calculated as follows.
- Let's determine the tax base:
(980,000 rub. – 980,000 rub. × 20%) = 784,000 rub.
- Let's determine the amount of tax at a tax rate of 1.5% and coefficient (Kv) = 0.9167 (previously calculated as 11/12):
784,000 rub. × 1.5% × 0.9167 = 10,780 rubles.
For more information about the benefits established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, read the article “Object of taxation of land tax”.