In 2021, most businesses should switch to using online cash registers. Otherwise, the company or entrepreneur will face penalties. They are also possible in case of violations of the rules for using cash register equipment. In practice, the most common violation is failure to issue a cash receipt to the buyer. This happens either intentionally, when the seller does not carry the goods through the cash register, or due to inattention - the seller in a hurry or for another similar reason forgets to give the receipt. But any such violation may be grounds for administrative liability.
Obligation to issue a cash receipt
In accordance with the requirements of the law, in particular, certain provisions of Federal Law No. 54-FZ, the obligation of business entities to issue cash receipts to customers directly depends on their (the business entities) organizational and legal form, as well as the specifics of the activities they carry out, according to the constituent and registration documents.
At the same time, for some categories of sellers - both organizations and individual entrepreneurs - the use of cash registers is not a prerequisite for carrying out the target activity.
Cash receipts are not required to be issued by organizations and individual entrepreneurs paying taxes in a special regime (UTII or PSN). However, sellers belonging to this category are required, at the request of the client, to issue a handwritten sales receipt (payment receipt or similar document), which from a legal point of view is equivalent to a cash receipt.
Also, cash receipts are not issued by organizations and individual entrepreneurs engaged in certain types of activities, including:
- Sale of newspapers on paper, as well as sale of other goods through newsstands , provided that the share of printed products in the kiosk’s turnover is at least 50%, and the assortment sold is approved by the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
- Sales of: lottery tickets and securities; travel documents (conductor or driver) in public transport; food products in educational institutions.
- Trade: ice cream; soft drinks on tap; from tankers (milk, live fish, kerosene, etc.); seasonal products in bulk (including fruits, potatoes, melons); religious paraphernalia sold by official representatives of the Russian Orthodox Church.
- Retail trade at fairs, markets, exhibition complexes or other areas of similar purpose . An exception is specially equipped retail outlets located in designated areas and ensuring the display and safety of goods (shops, auto shops, pavilions, etc.).
- Hand-to-hand sales of food and non-food products outside the stationary retail network (with the exception of those subject to mandatory labeling and technically complex goods, respectively) on trains and on board aircraft.
- Repair and production of keys and metal goods; shoe repair and painting; acceptance of glass containers and waste materials (except for scrap metal, as well as precious metals and stones); sales of folk art products by manufacturers.
- Services: supervision and care (for children, the sick, the disabled, the elderly); cutting firewood and plowing vegetable gardens; cargo transfer (at auto, airport and railway stations, river and sea ports); rental of residential premises by owners.
In addition, organizations and individual entrepreneurs operating in hard-to-reach and remote areas, as well as pharmacies operating in paramedic and paramedic-obstetric centers located in rural settlements, have the right not to issue cash receipts.
If the business entity does not belong to any of the above categories, a cash receipt when carrying out the target activity should be issued to the buyer, regardless of the existing circumstances.
At the same time, the buyer’s refusal to receive this document is not a basis for non-issuance , nor are any other reasons.
For example, if the cash register is faulty, the seller has no right to accept money from customers for goods until the fault is eliminated.
Legal provisions for the use of online cash register receipts
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 2.1 of the Law “On the Application of Cash Register Machines...” dated May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ, enterprises and individual entrepreneurs working with cash register machines are required to punch checks when making payments using cash and payment cards. Payments refer to the receipt and issuance of funds.
Tax authorities, in accordance with Art. 7 of Law No. 54-FZ, have the right to monitor the correct application of cash registers and the completeness of revenue accounting for organizations and individual entrepreneurs. As part of the exercise of their powers, tax authorities can gain full access to the cash register, conduct checks on the correctness of its operation, and issue orders to impose penalties and eliminate violations. A fine for a check not cleared at the cash register may also be imposed in the event of a customer complaint to the consumer protection department.
What is a check for?
The document records the amount passed through the company's cash desk. At the end of the working day a report is drawn up. And if unrecorded proceeds are found at the cash register (the money was accepted, the check was not issued), this indicates a violation of the seller’s work and may lead to punishment during an audit by the tax authorities.
When is a fine imposed for a bounced check?
The absence of an administrative offense entails the termination of administrative proceedings. As well as the absence of an administrative offense event. Therefore, first about the composition.
The objective side of the offense under Part 6 of Art. 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation is expressed in inaction. Namely:
- failure to send a cash receipt or a strict reporting form in electronic form to the buyer (client) when using cash registers, or
- failure to transfer such documents on paper to the buyer (client) upon his request
When the subject of the offense does not use cash register equipment at all, he will be fined for not using cash registers. But when you didn’t send it electronically or didn’t hand over the check, then there’s a fine for a bad check.
In general, according to the Law of May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ, when making a calculation, the user is obliged to issue a cash receipt or a strict reporting form on paper and (or) if the buyer (client) provides the user with a subscriber number or email address before the calculation mail, send a cash receipt or a strict reporting form in electronic form to the buyer (client) to the provided subscriber number or email address (if it is technically possible to transmit information to the buyer (client) in electronic form to the email address). Exceptions are established by Article 2 of this Law.
For what violations of 54-FZ can individual entrepreneurs be fined?
An individual entrepreneur selling goods/services is required to work with cash registers. Conducting a business without an online cash register or errors in its use can lead to fines. Responsibility for failure to comply with cash discipline is determined by the norms of the Administrative Code.
What is the fine for?
- if you work without a cash register or have an outdated cash register;
- deadlines for providing documents and information on CCP to tax authorities were violated or data were not provided at the request of the Federal Tax Service;
- the procedure for registering a cash register, re-registration and deregistration has not been followed, or the procedure/conditions for using a cash register do not comply with the rules;
- if the cash register does not comply with the requirements of the law;
- the buyer has not been issued a check or BSO (a citizen whose check has not been punched has the right to contact the Federal Tax Service with a complaint, but he will have to prove the fact of payment for the product or service without a cash register).
The Code of Administrative Offenses provides a complete list of fines for entrepreneurs for online cash registers. The limitation period for liability is 1 year. Calculation occurs either from the time when the violation was committed or from the time when a continuing violation was established.
Amount of fine for a bounced check
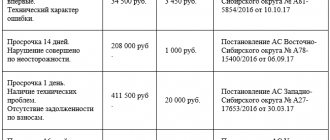
The amount of the administrative fine for a broken check is established by the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation as a fixed amount. For officials, and therefore, in order to bring them to administrative responsibility, and individual entrepreneurs - a warning or a fine in the amount of 2,000 rubles. For organizations, the fine will be 10,000 rubles. At the same time, the imposition of an administrative penalty does not relieve the person who committed it from fulfilling the duty for which he was punished for failure to fulfill it.
The person in respect of whom the protocol was drawn up under Part 6 of Art. 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation has the right to request a reduction in the amount of the administrative fine. To do this, it is necessary that the tax authority detects the offense during an automated audit. For the person to admit the violation before the ruling is made. And he was voluntarily eliminated (Parts 3, 4, Article 4.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). If these conditions are simultaneously met, the fine for a bounced check can be reduced to 1/3 of its size.
Case 2. The terminal does not issue checks - a fine of 10,000 rubles
At the Malina grocery store, a buyer topped up his mobile phone account for 100 rubles through a payment terminal and did not receive a cash receipt. The tax office found out about this and imposed a fine of 10,000 rubles on the store owner.
It should be. The payment terminal must be equipped with a cash register, which is registered to the owner of the terminal.
The store owner from the court case received a fine because she was the owner of the terminal. If she had rented out two square meters in the corner of the store for the terminal of IP Rybakov, the tax authorities would have fined IP Rybakov.
Jurisdiction of the offense
The tax authorities supervise the use of cash register systems. In particular, they have the right to freely access cash register and fiscal data, check documentation, and conduct audits. And, in fact, bring to administrative responsibility in the area of application of cash registers.
Thus, a protocol on an administrative offense is drawn up by the tax authorities. Moreover, as a general rule, regardless of which inspection the organization is registered with, unless otherwise established in the regulations of such inspection.
Deadlines, consequences of non-payment
The legal entity receiving the penalty is required to pay the fine specified in the order within 20 days from the moment it comes into force. For those who do not do this, the tax authority, within two months, decides to write off the fine from the LLC’s account.
If this deadline is missed, the tax authority has the right to go to court to demand the collection of a penalty payment. If there is a delay in payment, the tax office will charge a penalty in the amount of 40% of the fine , since such a violation is regarded as intentional (clause 1.3 of Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Application of strict reporting forms
From July 1, 2021, organizations can no longer issue printed BSOs. Now it is necessary to use BSOs created using an automated system, and they are equivalent to cash receipts. What should you pay attention to?
When providing services for which SSRs are established by executive authorities (for example, for organizations operating in the field of culture and the arts), you must issue the client a separate cash register receipt and a paper SSR or SSR printed using an automated system with details within 54- Federal Law, QR code, payment sign.
For example, it is not enough for a museum visitor to be given a paper ticket, as we are used to; a receipt must be issued for it. If you provide services for which there is no obligation to issue BSO, then now you can only provide clients with cash receipts indicating the name of the service. The taxi driver cannot limit himself to just a receipt; he must also give the passenger a cash receipt. Although it doesn't look very realistic yet.
Case 1. The bookmaker paid the winnings without a receipt - a fine of 632,577 rubles
The tax office conducted a scheduled on-site inspection at the bookmaker's office and found out that the office pays winnings to players, but does not clear cash receipts.
The bookmaker had a cash book and cash orders in which 361 payments of winnings were recorded in the amount of 832,000 rubles. All winnings were paid without checks: the bookmaker was sure that he did not need to punch cashier's checks, because paying out winnings was not a payment for a service.
The bookmaker's office was fined 632,577 rubles for failure to issue 361 cash receipts.
It should be. The law on cash registers states that a cash register receipt must be issued when settling with a buyer or client. Two transactions are considered settlement: when the client pays the seller and when the seller pays the client, for example, gives out winnings. It doesn’t matter how you pay: cash, card, online.
- Article 1.1, 54 Federal Law
The bookmaker in the case issued cashier's checks when he accepted bets, but did not do so when he gave away winnings. And he had to issue two checks: when accepting a bet - a receipt check, and when paying out a winning - an expense check.
Is it possible to avoid punishment
As the ancients said, dura lex (the law is harsh), but it is important to know that it is still possible to avoid severe punishment if you punch a correction check (with the date and description of the error), voluntarily report in writing to the tax office about the offenses committed and immediately get better.
We strongly advise you not to skimp on the quality of CCP; try to use modern technology, thereby reducing the risk of equipment failure and software failures.
In order not to incur an inspection by the Federal Tax Service, if suddenly your main cash register temporarily fails and you will not be able to submit fiscal reports for some time, get a spare device.
Which cash register should you choose?
The use of the following online cash registers is considered legal:
| Smart terminals Go to catalog | Autonomous cash registers Go to catalog |
| Fiscal registrars Go to catalog | POS systems Go to catalog |
| Mobile devices Go to catalog | Cash desks with acquiring Go to catalog |
Case 3. The farmer did not issue a check to the buyer, but was able to challenge the fine of 190,000 rubles
The tax office checked how the farmer complied with the law on cash registers. Upon inspection, it turned out that the farmer sold 80 cows, received 760,000 rubles in cash for them, but did not clear the cash receipt.
The farmer was found guilty and fined 190,000 rubles. He was not at the trial, because the city of Gorodovikovsk was indicated in the summons in the line “settlement”, although the case was heard in court at the address of the Republic of Kalmykia, the village of Priyutnoye.
The second court overturned the fine for selling without a receipt due to an error in the summons: the farmer could not defend himself in court because he did not know which court was dealing with his issue. But cases can be considered without a defendant only if he has been sent a normal notice.
It should be. At the time of the inspection, the farmer had no obligation to use the cash register if he was not engaged in retail trade, so he would have avoided the fine without an error in the summons.
How it happened that neither the tax office nor the first court noticed that the farmer had no obligation to use the cash register is unclear.
Payment Methods
It is possible to pay a fine:
- according to the details specified in the resolution, from the current account of the LLC;
- by bank card – through terminals, online banking.
Attention! An innovation from 2021 is the possibility of paying a fine for an LLC by another person. Read more about this in the explanation of the Federal Tax Service on the official website.
Information about the repayment of a fine is sent to a special system of state and municipal payments.
Material on the topic: How to make a payment using a QR code in Sberbank.
Normative base
The regulatory framework for the forced collection of a fine for a check not issued to the buyer is as follows:
- Article 32.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation “Execution of the decision to impose an administrative fine”;
- Article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation – collection of a fine at the expense of the perpetrator’s funds;
- Article 47 of the Tax Code “Collection of taxes, fees, insurance premiums, as well as penalties and fines at the expense of other property of the taxpayer (tax agent, fee payer, insurance premium payer) - organization, individual entrepreneur.”
Author: Viktor Sukhov, editor-in-chief. October 19, 2021.