O.I. Prokhorova author of the article, Ascon consultant on accounting and taxation
All organizations are required to conduct an inventory before drawing up annual financial statements (Part 2, Article 11 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ, clauses 26, 27 of the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 N 34n (hereinafter referred to as Regulation No. 34n), clause 27 of the Guidelines for inventory of property and financial obligations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 N 49 (hereinafter referred to as Guidelines for Inventory), clause 38 PBU 4/99, Appendix to the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 01/19/2018 N 07-04-09/2694, Appendix to the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 01/09/2013 N 07-02-18/01).
The purpose of the annual inventory is to identify the actual availability of property, compare it with accounting data, check the completeness of the reflection of liabilities in accounting, ensure the reliability of accounting data and financial statements (clause 1.4 of the Inventory Guidelines).
When an inventory is NOT necessary
At the end of each year, you should check whether the accounting data corresponds to the actual presence of assets and liabilities. Property and liabilities recorded off the balance sheet are also subject to inventory (paragraph 2, clause 1.3, clause 3.7 of the Inventory Guidelines).
In fact, property located in the organization that is not accounted for for any reason is also subject to inventory and subsequent acceptance for accounting (paragraph 2, clause 1.3 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory).
However, before drawing up annual reports, it is not necessary to check the condition of property, the inventory of which was carried out after October 1 of the reporting year. In this way, the inventory can be evenly distributed over the entire fourth quarter. Or an unscheduled audit due to a change in the financially responsible person may be accepted for the purpose of summing up the results of the year.
In addition, an inventory of fixed assets can be carried out once every three years, and of library collections - once every five years. For example, if an organization checked fixed assets in the 4th quarter of 2019, you don’t have to do this again until the 4th quarter of 2022 (clause 27 of Regulation No. 34n and Inventory Guidelines).
Drawing up inventories
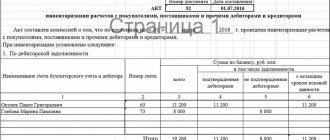
Information about the organization's property and liabilities obtained during the inventory is entered into inventory records (or acts).
Standard forms of inventories and acts are given in Appendices 6-18 of the Methodological Instructions and differ depending on the type of property (liabilities) being inspected.
Inventory lists are compiled taking into account the following features:
- number of copies of the inventory - at least 2;
- Filling out on a computer or by hand is allowed;
- when filling out by hand, use ink or a ballpoint pen;
- they must be filled out clearly and clearly, without blots or erasures;
- errors are crossed out and the correct version is written above them;
- leaving blank lines is not allowed;
- lines on the last pages are crossed out;
- on each page the serial numbers of material assets and their quantity are indicated in words;
- on the last page a mark is placed on the verification of prices, taxation and calculation of results signed by the persons who carried out this verification.
- Separate inventories are drawn up for property held in custody, rented or received for processing.
The completed inventory list is signed by the members of the commission and transferred to the accounting department.
Inventory procedure
The inventory before drawing up the annual financial statements is planned and is carried out in the manner established by the internal documents of the organization. This may be an inventory provision, which is part of the accounting policy in accordance with clause 4 of PBU 1/2008, or another administrative document signed by the head (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 01/09/2020 N 07-01-09/73).
The inventory regulations usually indicate:
- when an inventory is required;
- timing of inventory in the context of property and liabilities;
- document forms used to document inventory results.
When conducting an inventory before preparing annual financial statements, the following general procedure should be followed:
- drawing up a schedule of control activities;
- execution of an order for the appointment of a working inventory commission indicating the place, time and volume of inventory (Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 N 88 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording cash transactions, for recording inventory results”);
- receiving receipts from financially responsible persons (clause 2.4 of the Inventory Guidelines);
- checking the presence and condition, as well as assessing assets and liabilities using the continuous method (clauses 2.7, 2.8 of the Inventory Guidelines);
- checking the availability and storage conditions of documents confirming the location of assets in the ownership or disposal of the organization, as well as technical documentation (clause 3.2 of the Inventory Guidelines);
- identification of assets subject to write-off (clauses 3.6, 3.25, 3.26 of the Inventory Guidelines);
- checking assets for impairment (clause 35 of PBU 4/99);
- identification of doubtful and bad debts (clause 3.8 of the Inventory Guidelines);
- summing up the inventory and processing documents (Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 88);
- reflection of inventory results (clause 5.5 of the Inventory Guidelines).
How to take inventory of an organization's property
The whole procedure should look like this:
- Preparing for the process. At this time, the head of the company issues an order, resolution or other legal act, which indicates how, by whom and in relation to what the inspection will be carried out. Its deadlines are also set here.
- Conducting an audit. The group responsible for the inventory records the presence or absence of specific material and technical means in the specified locations.
- Filling out standardized papers. Their number depends on what exactly is being described, usually two copies are enough.
- The information received and recorded is compared with what was indicated in earlier accounting reports. If shortages or surpluses are identified, procedures are prescribed to bring the documentation back to normal.
- A final report is prepared. Surpluses are written off, shortages are recorded in accordance with write-offs or using other mechanisms.
Summing up the inventory
To formalize the results of the inventory, it is necessary to fill out inventories, acts, statements, using standardized forms (clause 2.10 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory, Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 88). Identified surpluses or shortages are entered into the comparison sheets (forms INV-18 and INV-19) and the list of results identified by the inventory (form INV-26). Based on the results of the annual inventory, the commission usually draws up a protocol.
The presence and correct execution of inventory documents is necessary both to reflect the results in accounting and to resolve disputes if they arise.
The results of the annual inventory are reflected in the annual financial statements (clause 5.5 of the Inventory Guidelines).
Accounting for inventory results
The result of the inventory can be:
- surplus - the excess of the actual quantity of inventory items over accounting data;
- shortage - a physical shortage of goods and materials, a discrepancy between the actual quantity of goods and materials and accounting data.
The procedure for recording inventory results depends on various factors.
If you are a subscriber to the BukhExpert8: Rubricator 1C Accounting system, then read additional material on the topic:
- Inventory of goods and materials
- Restoration of VAT when writing off inventory items
- Surplus inventory
- Guide Write-off of goods
- Shortage of goods and materials. The culprit has been identified
- Deduction of damages from wages for shortages
- Shortage of goods and materials. The culprit was not found, confirmed by a government document
If you are not yet a subscriber to the BukhExpert8 system:
Activate demo access for free →
or
Subscribe to Rubricator →
After subscribing, you will have access to all materials on 1C Accounting, recordings of supporting broadcasts, and you will be able to ask any questions about 1C.
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Universal report on financially responsible persons of fixed assets In this article we will talk about how, using...
- Sales of goods in an online store: payment via the Internet This article discusses the retail sale of goods through an online store, shipment…
- How to make adjustments to documents without re-closing the month Still wondering if it’s possible to make changes to...
- How can I add the ability for a user with Sales Manager rights to work with a Universal report? ...
Capitalization of surplus
Assets found to be in surplus are subject to capitalization and credited to the financial results of the organization (clause 5.1 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory).
In tax accounting, surpluses are included in non-operating income at market value (clause 8, clause 20 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 11, 2020 N 03-11-06/2/80113). The market value is determined taking into account the provisions of Art. 105.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 5 and article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 28, 2020 N 03-03-06/1/75787). Depreciation can be calculated on capitalized fixed assets, but bonus depreciation cannot be applied.
Inventory and materials are taken into account as usual. This property may be written off or sold. As for sales, the income received as a result of such transactions is reduced by the amount of the market value of the property being sold (accounted for as non-operating income), at which it was accepted for accounting (clause 2, clause 1, article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 23 .2011 N 03-03-06/1/583, dated 02/11/2011 N 03-03-06/1/88, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region dated 02/21/2013 in case N A40-2055/12-20-9).
What is included in the inventory of assets and liabilities
Property inventory includes checking the actual availability of:
- fixed assets;
- Inventory and materials: goods, stocks, inventory, finished products, raw materials, other materials;
- animals and young animals, incl. cattle;
- cash in the cash register, bank, monetary documents, strict reporting forms;
- intangible assets (IMA);
- work in progress.
An inventory of existing liabilities includes:
- checking settlements: accounts receivable and payable, mutual settlements with the budget, personnel; loans and credits received, settlements with founders;
- inventory of reserves for upcoming holidays, payments, expenses, estimated reserves, deferred expenses (FPR);
- audit of financial investments.
Write-off of shortages
Shortages within the limits of the norms approved by law are written off by order of the manager as production and distribution costs (clause 5.1 of the Inventory Guidelines).
In tax accounting, non-operating expenses take into account shortages of material assets in production and warehouses, at trading enterprises in the absence of culprits, as well as losses from theft, the culprits of which have not been identified. In these cases, the fact of the absence of perpetrators must be documented by an authorized government body (clause 5, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not contain instructions on what specific documents need to be obtained in order to confirm the absence of guilty persons, and thus does not limit the taxpayer in confirming the legality of accounting for relevant expenses (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 8, 2017 N 03-03-06/ 1/81919).
Documentary evidence may be, in particular, a copy of the resolution of the investigator of the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation on the suspension of the preliminary investigation in a criminal case due to failure to identify the person to be brought as an accused (clause 1, paragraph 1, article 208 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation, Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia from 16.12.2011 N 03-03-06/4/149, dated 03.08.2011 N 03-03-06/1/448).
If the guilty person is discovered, then a claim for compensation for losses from the theft of funds can be presented by the organization to the guilty person in accordance with the civil legislation of the Russian Federation. Amounts received to compensate for losses are non-operating income (clause 3 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and the cost of lost property is an expense (clause 20 of clause 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 27, 2014 N 03- 03-06/1/42717).
Purposes of property inventory
In addition to the tasks already mentioned above that this procedure allows you to solve, there are other reasons for its implementation. Here are the main ones:
- Preparation of accounting reports for regulatory authorities, including tax authorities.
- The need to rent out or sell the property.
- If facts of theft, intentional or accidental damage are detected.
- Reorganization activities in the company.
- Emergency incidents or natural disasters that led to the loss of a significant part of the material and technical resources.
- Appointment of a new responsible person.
The direction of the form in which the inventory will be carried out and what specific values it will affect is given by the head of the company or the person acting as director.
Write-off of bad debts
Bad debts are written off on the basis of an inventory of payments (form INV-17) and an order from the manager (clause 77 of the Accounting Regulations No. 34n, Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 27, 2018 No. 03-03-06/1/ 95709, dated 10/13/2017 N 03-03-06/1/67057, dated 07/11/2017 N 03-03-06/1/43877).
Uncollectible accounts receivable are subject to write-off against the allowance for doubtful debts. If the reserve is not enough, the remaining debt goes to expenses (Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 16, 2018 N 03-03-06/2/1551). In accounting, all organizations are required to create such a reserve; in tax accounting, this is the right of the organization (clause 70 of Regulation No. 34n, Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 31, 2020 No. 03-03-06/2/76195).
The receivable is subject to write-off as expenses along with VAT (Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 21, 2008 N 03-03-06/1/596). According to the Ministry of Finance, when writing off debts on advances issued, the VAT accepted for deduction from this advance payment must be restored (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 28, 2020 N 03-07-11/5018).
After write-off, bad receivables are reflected in off-balance sheet account 007 for five years (clause 77 of Regulation No. 34n).
Under the simplified tax system, written-off receivables are not taken into account either in expenses or in income (Letters of the Ministry of Finance dated 02/20/2016 N 03-11-06/2/9909, dated 07/22/2013 N 03-11-11/28614).
Bad accounts payable are taken into account as income under both the OSNO and the simplified tax system (clause 78 of Regulation No. 34n, clause 2, clause 1, article 248, clause 18, article 250, clause 1, article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If an organization uses the simplified tax system to write off the creditor for the advance received from the buyer, then no income will arise, because income is reflected as the advance payment is received (clause 1 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 14, 2016 N 03-11-06/2/14135).
Writing off accounts payable to the supplier does not oblige the buyer to restore VAT previously accepted for deduction (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated June 21, 2013 N 03-07-11/23503). When a creditor writes off an advance received, the VAT calculated on it cannot be deducted. There is no need to include it in income or expenses (Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated December 7, 2012 N 03-03-06/1/635).
Why do you need an inventory of material and technical assets?
It is mainly carried out in order to verify the reality of the situation presented in the accounting documentation. This allows you to avoid sudden problems with regulatory services. Additional tasks include:
- Quality control, especially when it comes to wholesale or retail sales. Goods must be properly packaged, have an attractive appearance, and meet established sales requirements.
- The ability to detect shortages and identify their cause.
- Tracking of all company assets from the moment of receipt and with each further movement.
- Control of correct storage and use.
The tasks in each specific organization may be different. This is related to its main activity and the frequency of such inspections largely depends on it.
Features of the annual inventory in 2021
When conducting an inventory before preparing reports for 2020, you should take into account the latest changes in accounting legislation.
From 2021, a new accounting standard will be mandatory.
Two standards have been approved, the application of which is mandatory from reporting for 2022, but if you wish, you can switch to the new rules earlier: FSBU 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” and FSBU 26/2020 “Capital Investments” (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 17, 2020 N 204n ).
This may require the organization to take a more thorough approach to checking and reflecting balances in accounting and reporting.
In addition, at the end of 2021, settlements with accountable persons and inventory of balances on account 71 deserve special attention.
This is due to the forced cancellation of business trips due to coronavirus restrictions and the need for many taxpayers to adjust their plans.
Recognition of loss.
According to paragraph 15 of the Federal Accounting Standards “Impairment of Assets”, an impairment loss on an asset is recognized in accounting when its residual value at the annual reporting date exceeds its fair value less the costs of disposal of such an asset. Once an impairment loss on an asset is recognized at the annual reporting date, it is recognized as a lump sum expense for the reporting period.
That is, identifying an impairment loss and recognizing it will now be one of the results of the inventory!
However, the application of these provisions of the standard gives rise to a difficult situation. On the one hand, an asset impairment loss is recognized as a lump sum as part of the expenses of the reporting period. That is, at the end of the year, “in one fell swoop,” expenses for the reporting period will be increased by the amount of impairment losses. In other words, the institution’s expenses at the end of the year will increase “out of thin air.” On the other hand, the question arises of covering such losses. How will these costs be covered? What will be the source of funding?
For example, last year, by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 13, 2017 No. 1101, changes were made to the procedure for forming state assignments. Now the state task must take into account the annual amount of planned (calculated) depreciation for particularly valuable movable property (VTsDI) used in the process of providing public services. That is, depreciation of fixed assets is financed, but there is no impairment loss yet. Although the loss itself, according to the Federal Accounting Standard “Impairment of Assets,” the Ministry of Finance already proposes to reflect in accounting.
The resolution of this situation should probably be reflected in the regulations of the Government of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Finance. It can be assumed that changes will be made to the procedure for forming state assignments by the Government of the Russian Federation, taking into account the provisions of federal standards. It is possible that the impairment loss will somehow be taken into account in the subsidy for the government task.
Penalty for failure to take inventory
The tax inspectorate or other government agencies cannot fine an organization simply because it did not conduct an annual inventory. There is no such fine in the law.
However, without inventory:
- it is impossible to obtain a positive audit opinion;
- accounting statements may be unreliable, which entails fines both for the organization itself and for its officials (Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
- errors in tax accounting, additional charges of taxes, penalties and fines are possible (Articles 75, 120, 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).