Features of accounting for land plots
The procedure for registering land transactions is regulated by the provisions of Chapter.
17 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the norms of the Land Code of the Russian Federation and the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as PBU 6/01 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n). You can buy land only on the basis of a purchase and sale agreement drawn up in writing (Article 550 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). There is no need to notarize the agreement. The contract must contain all the information about the restrictions or encumbrances of the land, as well as the location and price of the plot (Articles 554, 555 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The object of the transaction can only be land that has undergone state cadastral registration (Article 37 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
Ownership of land passes from the moment of state registration in Rosreestr (Clause 2 of Article 223 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The fee for state registration of land transactions for legal entities is 22,000 rubles. (Subclause 22, Clause 1, Article 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
According to accounting rules, land should be classified as fixed assets (FA) (clause 5 of PBU 6/01). The site is accepted for registration if the following conditions are met:
- the company will use it in its core business or rent it out;
- use will last longer than 12 months;
- resale of the plot is not planned - otherwise the land must be recorded in account 41 (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 23, 2009 No. 03-05-05-01/36);
- income is expected to be received from the acquired land (clause 4 of PBU 6/01).
When purchasing a land plot, it is taken into account at its original cost, formed from actual costs:
- payment to the counterparty for the site itself;
- the cost of information and consulting services, for example, the work of a realtor;
- intermediary remuneration;
- state duty and other non-refundable taxes;
- other expenses associated with the acquisition of land.
NOTE! The sale of land is not subject to VAT (subclause 6, clause 2, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Purchasing land is an expensive operation, so companies often take out a loan for this. Interest on the loan is included in the cost of the land until the site is transferred from a non-current asset to fixed assets (clause 7 of PBU 15/2008, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 6, 2008 No. 107n).
The company can also receive land:
- Free of charge - then it is accepted for accounting at the market price confirmed by an independent appraiser (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2015 No. 03-04-05/3074). Moreover, if the land was donated by the founder of the company, who owns more than half the share of the authorized capital (AC) of the recipient company, then the recipient does not generate income. Otherwise, gratuitous receipt is non-operating income for profit tax purposes (subclause 11, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Under an exchange agreement, the organization will accept the site in accordance with the value of the valuables transferred to another company in exchange (clause 11 of PBU 6/01, article 568 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- On account of the contribution to the management company - according to the assessment agreed upon by the founders.
The land is transferred to the OS when it is fully ready for operation and the initial cost has been formed. A company can accept a plot of land for accounting on account 01, without waiting for registration of ownership - then it is reflected in a separate sub-account of account 01 (clause 52 of the Methodological Guidelines for OS Accounting, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n).
Land plots are not depreciated either in accounting or in NU (clause 17 of PBU 6/01, clause 2 of article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There is no other way to include expenses for the purchase of land in the company’s expenses (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated March 14, 2006 No. 14231/05).
The costs of purchasing a land plot can only be taken into account when it is subsequently sold. Then, on the date of transfer of the plot to the buyer, the seller of the land reflects the income from the transaction, reduced by the cost of acquiring the plot and expenses for its sale (clause 31 of PBU 6/01, clause 1 of Article 271, clause 1 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
In a special procedure, expenses for the acquisition of land from state or municipal property on which buildings, structures or structures are located, or which is acquired for the construction of an operating system, are recognized for profit, under agreements for the acquisition of plots concluded from 01/01/2007 to 12/31/2011. Such costs can be (subclause 1, clause 3, article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Recognize evenly over the period chosen by the enterprise (at least 5 years).
- Accept as a reduction in profit in the reporting (tax) period a maximum of 30% of the tax base for the profit of the previous tax period until the entire amount is fully recognized. At the same time, a permanent tax difference arises in accounting, which we will consider below.
NOTE! Land can be used only in accordance with the type of permitted use given in the State Real Estate Cadastre (clause 1 of Article 263 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
A land plot is subject to land tax. Read more about the procedure for paying it in this article.
How to quickly reflect the acquisition and registration of a land plot
How can you quickly reflect the acquisition and acceptance of a land plot in 1C: Accounting 8, edition 3.0, without including additional costs?
The video was made in the program “1C: Accounting 8” version 3.0.65.72.
To simultaneously reflect the receipt and acceptance of land plots for accounting without including additional expenses in their cost, the document Receipt (act, invoice)
with the type of operation
Land plots
.
Quick access to this type of receipt document is provided from the OS and intangible
using the hyperlink
Acquisition of land plots.
Document form Acquisition of land plots
simplified as much as possible, since for land plots it is not required to indicate the method of reflecting depreciation expenses, depreciation group, service life, VAT rate and invoice from the supplier. In the tabular part you only need to indicate the name of the purchased object and its cost.
To quickly enter a new object, just enter the name of the land plot in the appropriate field and select the Create command:
.
In this case, the Fixed Assets
does not open, but the details are automatically filled in:
- OS accounting group
(the value
Land plots
); - Location
and
MOL
(the values indicated in the header of the document are substituted); - The procedure for repaying the cost
(the value
Cost is not repaid
- for accounting purposes); - The procedure for including cost in expenses
(the value
Cost is not included in expenses
- for tax accounting purposes).
After posting the document, accounting entries are generated:
Debit 08.01.2 Credit 60.01 and Debit 01.01 Credit 08.01.2
- on the cost of acquired land plots.
For tax accounting purposes for income tax, the corresponding amounts are also recorded in the resources Amount NU Dt
and
Amount NU Kt
.
If an organization applies the simplified taxation system (STS) with the object “income minus expenses”, then entries are made in special registers for the purposes of the tax paid in connection with the application of the STS.
In addition to movements in accounting and tax accounting, the document also generates entries in the periodic information registers of the OS accounting subsystem, reflecting information about the land plot.
In addition to accounting and tax accounting movements, the document also creates entries in periodic information registers that reflect information about the fixed asset.
For the purpose of calculating land tax, to reflect information on the state registration of land plots and their deregistration, a register of information is intended: Registration of land plots
.
Access to the specified register is carried out both from the fixed asset card (hyperlink Register
) and from the
Main
(
Taxes and reports - Land tax
-
Registration of land plots
).
Calculation and accrual of land tax is automatically performed at the end of the reporting period by a routine operation with the type Calculation of land tax
included in
the month end
.
Documentation of transactions with land plots
Operations with land can only be carried out if the agreement is drawn up in writing. The parties draw up 3 copies of the agreement: 1 for each participant in the transaction and 1 for Rosreestr.
The registration of the plot on account 08 is carried out on the date of actual transfer of land according to the transfer and acceptance certificate or the date of signing the agreement (if the agreement is equated by the parties to the transfer and acceptance certificate).
You can keep records of land plots using unified forms OS-1 and OS-6 or using independently developed forms compiled using mandatory details (Article 9 of the Law “On Accounting” dated November 22, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
When accepting a land plot from the founder, it is necessary to conduct an independent assessment of the land, as well as make changes to the company’s constituent documents.
How to do this, read the article “Accounting entries for contributions to the authorized capital” .
If the organization received the land free of charge, then the market valuation of the site is confirmed by an independent appraiser or cadastral registration data (Article 66 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
The company can lease the land. Then a lease agreement must be concluded and an act of acceptance and transfer of property to the counterparty must be drawn up. If the lease agreement is concluded for a period of more than a year, then it must be registered with the territorial branch of Rosreestr (clause 2 of Article 609, clause 2 of Article 651 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
For more information about the registration of lease transactions with land, read the article “Accounting for the lease of fixed assets (nuances)” .
Find out whether the sale of land by a member of a peasant farm is subject to taxes in ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the system and find out the answer to this and other questions for free.
Accounting for transactions with land plots: postings
Actual expenses for the purchase of land are collected on account 08 in correspondence with accounts 60, 76. Payment of the state duty and its inclusion in the cost of the land plot is carried out by entries:
- Dt 68 Kt 51 - the fee for registering land ownership has been paid;
- Dt 08 Kt 68 - the duty is included in the initial cost of the land.
Further accounting of land depends on the purposes of its use. If a company builds buildings on the territory, but at the expense of investors, then such an object cannot be recognized as OS - it will remain on account 08. Upon completion of construction, the accountant will make an entry:
- Dt 76 Kt 08 - land was transferred to the investor in connection with the completion of construction work.
If the owner uses the land for his own purposes and for his own money, then the site should be included in the OS by posting:
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - the land plot was accepted as part of the OS.
When purchasing land from the state for the construction of OS (under contracts of 2007-2011), a tax difference arises: in the NU, spending on land is recognized as an expense, but in the BU it is not. The accountant should reflect a permanent tax asset in accounting on a monthly basis until expenses are completely written off in tax accounting:
- Dt 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” Kt 99 subaccount “PNA” for the amount of Z / n / 12 months. × 20%,
Where:
Z is the initial cost of the site;
n is the number of years to write off expenses for the purchase of land.
The sale of land is recorded by the following records:
- Dt 45 subaccount “Transferred real estate” Kt 01 - the cost of land is written off;
- Dt 62 Kt 91 - revenue from the sale is reflected;
- Dt 91 Kt 45 subaccount “Transferred real estate” - the initial cost of the sold plot is reflected as part of other expenses.
We remind you that the sale of land is not subject to VAT.
When land is added to the company’s authorized capital, the accountant will make the following entries:
- Dt 75 Kt 80 - reflects the debt of the founder for the contribution to the management company;
- Dt 08 Kt 75 - a land plot was received on account of the founder’s contribution to the management company;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - land is accepted for accounting as an asset.
The transfer of land as a contribution to the management company of another legal entity is reflected in the following entries:
- Dt 58 Kt 76 subaccount “Settlements on deposits in the Criminal Code” - reflects the debt on deposits in the Criminal Code;
- Dt 76 subaccount “Settlements for deposits in the management company” Kt 01 - the plot was entered as a contribution to the management company.
If the initial cost of the transferred land differs from the estimate agreed upon by the founders, the difference should be attributed to the appropriate subaccount of account 91 in correspondence with account 76 (subaccount “Settlements for deposits in the management company”).
The accountant reflects the receipt of a land plot free of charge with the following entries:
- Dt 08 Kt 83 - land was received from the founder, whose share in the management company is more than 50%, while the company has no income;
- Dt 08 Kt 98 - land was received free of charge from other persons;
- Dt 08 Kt 01 - land plot put into operation;
- Dt 98 Kt 91 - income from the gratuitous receipt of a land plot is recognized.
If your company transfers a land plot free of charge, then the accounting entry is as follows:
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - reflects the cost of land donated to another company.
Income and expenses do not arise in tax accounting when transferring land free of charge (Articles 249, 250, paragraph 16 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But then a permanent tax liability is formed in accounting, which is taken into account simultaneously with the write-off of the cost of land and the costs of its transfer (clause 7 of PBU 18/02):
- Dt 99 subaccount “PNO” Kt 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” - reflected PNO due to the difference in accounting when transferring property free of charge.
When concluding an agreement for the exchange of wiring from a company transferring land and accepting other property in return, the following:
- Dt 08, 10, 41 Kt 60 - valuables were received under an exchange agreement;
- Dt 62 Kt 91—reflects income from the transfer of land under an exchange agreement;
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - the cost of the transferred land plot has been written off;
- Dt 60 Kt 62 - the obligations of the parties are fully repaid upon fulfillment of the terms of the exchange agreement.
The financial result from barter transactions in the accounting of transaction participants is zero.
In exceptional cases, a land plot may be withdrawn (Article 49 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). Government agencies are obliged to notify the owner of the land plot about this. The owner or user of land has the right to claim compensation in the amount of the market value of the land plot, the real estate located on it, as well as losses and lost profits from the seizure (Articles 56.8, 56.9 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). On the date of termination of ownership of land, the following entries are made:
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - disposal of land;
- Dt 76 Kt 91 - other income includes the amount of compensation for seizure.
Is this compensation included in the taxpayer’s income and is it necessary to pay taxes on it? Find out the answer to this question in ConsultantPlus by getting trial access to the system for free.
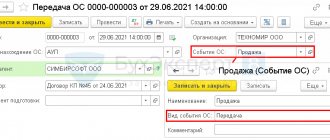
How to reflect in the 1C: Enterprise Accounting program ed. 3.0 rent in the lessee's accounting
Often companies need to lease property under a lease agreement - this could be an office, equipment, a car or a plot of land. Renting property is a common phenomenon in commercial activities, since renting property for a certain period is less expensive than purchasing it, and in relation to state property, such as a land plot, it is also impossible by law. Let us briefly consider the main points that you may encounter when leasing, and how to correctly reflect them in 1C: Enterprise Accounting ed. 3.0.
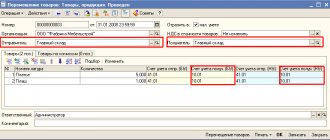
Since the leased property is not listed on the tenant’s balance sheet, it must be reflected in the debit of off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets” using a manual transaction. Payment of rent is made as a regular payment to the counterparty, through a bank or cash desk in correspondence with invoice 76.05 or 60.01. And also a receipt document (act, invoice) for services, on credit 76.05 or 60.01, on debit expense accounts 20,23,25,26,44. At the end of the lease, a reverse entry is made in the document “Operation entered manually” Kt 001.
If an organization leases property from an individual, then the “Receipt of Services (Act)” document will be missing; instead, we register the same transactions through a manual operation. In addition, the tax agent becomes obligated to withhold and transfer personal income tax to the budget. We add one more to our manual entries: Dt 76.10 Kt 68.01 for the amount of personal income tax. To reflect the tax in reports 6-NDFL and 2-NDFL (if this is our employee), we create a “Personal Tax Accounting Operation”: section “Salaries and Personnel - Personal Income Tax - All Documents on Personal Income Tax”. We fill out all the tabs except the last one, since the transfer to the budget will be reflected in the program as a write-off from the account.
To reflect inseparable improvements to the rent, if any, we draw up a receipt document (act, invoice). Costs are reflected on Dt 04/08/1. Next, we take into account the fixed assets for the amount of inseparable improvements as of 01.01 from 08.04.1. At the close of the month, depreciation will be charged. At the end of the lease, in addition to writing off the fixed assets in Kt 001, it is necessary to transfer inseparable improvements. We will draw up a document “Write-off of fixed assets”, in which depreciation will be accrued for the last month and written off for the entire period, as well as the initial and residual value will be written off.
Then we create a “VAT accrual reflection”, in the “Operation type code” field, select the value “10”, check the “Use as a sales book entry” and “Generate transactions” checkboxes, indicate the VAT account as 91.02, and issue an invoice.
The final touch will be the re-qualification of IT into PNO (in terms of the difference in depreciation) and the recognition of PNO (in terms of VAT) automatically at the end of the month in which the document “Write-off of fixed assets” was created. This can be seen by opening the postings of the routine operation “Calculation of income tax”.
If it is necessary to repair the leased property, a document for the sale of services and adjustment of the debt is drawn up, in which offset will take place. When repairs are carried out in-house, payroll documents and a “Demand-invoice” are drawn up to transfer repair materials to the same account, for example 23. When repairs are carried out by a third-party organization, a service receipt document for 91.02 is entered into the program.
In this article, we examined the main points that you may encounter when renting and their reflection in 1C. Like any other operations, their correct and error-free execution affects the formation of reliable reporting for the enterprise. Contact our 1C Expert Support Center. Our experts will easily and quickly solve any of your questions.
Work in 1C programs with pleasure!
Results
Features of land accounting are as follows:
- land is an OS object;
- the purchase and sale agreement is drawn up only in writing, taking into account the requirements of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- land ownership is subject to mandatory registration;
- sales of land are not subject to VAT;
- land cannot be depreciated;
- expenses for the purchase of land can only be written off when it is sold;
- In a special manner, plots acquired in 2007-2011 from the state for the construction of environmental protection are taken into account.
For more information about what kind of reporting should be submitted to the land owner, read the article “Reporting on land tax” .
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.