To automatically include losses from the sale of fixed assets in expenses in 1C: Accounting 8, a special technique is recommended, which is outlined by methodologists in the proposed article using a specific example.
According to paragraph 3 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “Features of determining expenses when selling goods and (or) property rights,” if the residual value of depreciable property, taking into account the expenses associated with its sale, exceeds the proceeds from its sale, the difference between these values is recognized as a taxpayer’s loss, taken into account for tax purposes in the following order.
The resulting loss is included in the taxpayer's other expenses in equal shares over a period defined as the difference between the useful life of this property and the actual period of its operation until the moment of sale.
Step-by-step instruction
On June 29, the Organization sold a Nissan Teana car to the buyer Simbirsoft LLC at a price of RUB 240,000. (including VAT 20%). On the same day, the Nissan Teana car was deregistered with the traffic police.
Depreciation in accounting and for profit tax purposes was calculated using the straight-line method. The depreciation bonus for sold fixed assets was applied in the amount of 30%.
The residual value of the fixed asset (BU = 440,000 rubles, NU = 308,000 rubles) exceeded sales revenue.
The parties to the transaction are not interdependent persons.
Sales are made before the expiration of 5 years from the date of commissioning of the vehicle.
Its remaining useful life is 11 months.
On July 2, payment was received from the buyer to the bank account in the amount of RUB 240,000.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
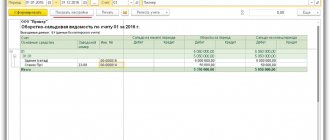
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| OS implementation | |||||||
| June 29 | 62.01 | 91.01 | 240 000 | 240 000 | 200 000 | Revenue from OS sales | OS transfer |
| 26 | 02.01 | 40 000 | 28 000 | 28 000 | Calculation of depreciation for the last month | ||
| 02.01 | 01.09 | 560 000 | 392 000 | 392 000 | Write-off of accumulated depreciation | ||
| 01.09 | 01.01 | 1 000 000 | 700 000 | 700 000 | Write-off of the initial cost of the OS | ||
| 91.02 | 01.09 | 440 000 | 308 000 | 308 000 | Write-off of residual value of fixed assets | ||
| 91.02 | 68.02 | 40 000 | VAT accrual on revenue | ||||
| Issuance of SF for shipment to the buyer | |||||||
| June 29 | — | — | 240 000 | Issuing SF for shipment | Invoice issued for sales | ||
| — | — | 40 000 | Reflection of VAT in the Sales Book | Sales book report | |||
| Deregistration of a car | |||||||
| June 29 | — | — | — | Removing a car from registration with the traffic police | Register of information Registration of vehicles - Deregistration | ||
| Reflection in the tax accounting amount of the loss from the sale of fixed assets | |||||||
| June 29 | 97.21 | 91.09 | — | 108 000 | 108 000 | Transfer of the amount of loss from the sale of fixed assets to the remaining private investment fund (NU) | Manual entry - Operation |
| Receipt of payment from the buyer | |||||||
| July 02 | 51 | 62.01 | 240 000 | 240 000 | Receipt of payment from the buyer | Receipt to the bank account - Payment from the buyer | |
| Accounting for the monthly amount of loss as part of indirect expenses for NU | |||||||
| July 31 | 91.02 | 97.21 | — | 9 818,18 | 9 818,18 | Accounting for the monthly amount of loss as part of indirect expenses (IO) | Closing the month - Write-off of deferred expenses |
For the beginning of the example, see the publications:
- Purchasing a car
- Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets with bonus depreciation
Example of transactions when selling a fixed asset
Titania LLC sells equipment (machine) for the amount of 500,000 rubles. (VAT is 90,000 rubles.) Initially, the machine was listed on the balance sheet at a cost of 650,000 rubles. Depreciation was charged on it in the amount of RUB 350,000. It was necessary to spend 20,000 rubles to dismantle the machine. What notes should the accountant of Titania LLC make?
- Debit 76, credit 91.1 – 500,000 rubles. – revenue from the sale of equipment is reflected.
- Debit 51, credit 76 – 500,000 rub. – receipt of funds from the buyer of the machine.
- Debit 91-2, credit 68, subaccount “Calculations for VAT” – 90,000 rubles. — VAT calculation.
- Debit 01, subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets”, credit 01 – 650,000 rubles. — the original cost of the machine has been written off.
- Debit 02, credit 01, subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” – 350,000 rubles. — the amount of depreciation accrued on the machine is written off.
- Debit 91-2, credit 01, subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” – 300,000 rubles. (650,000 - 350,000) - the residual value of the machine is written off.
- Debit 91-2, credit 10 (20, 23...) – 20,000 rubles. – the costs of dismantling the machine have been written off.
- Debit 91-9, credit 99 – 90,000 rub. (500,000 – 90,000 – 300,000 – 20,000) - the profit from the sale of the machine is determined.
OS implementation
Regulatory regulation
Sales are recognized as the transfer of ownership of goods (including fixed assets) on a reimbursable basis (Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, organizations must take into account the income and expenses associated with acquisitions and sales.
Income:
- In the accounting system, revenue from the sale of fixed assets is classified as other income and is reflected in the credit of account 91.01 “Other income” (clause 31 of PBU 6/01, clause 7 of PBU 9/99, chart of accounts 1C). Income is recognized at the moment of transfer of ownership of the fixed asset (clause 12 of PBU 9/99).
- In NU, income is the proceeds from the sale of fixed assets without VAT (clause 1 of Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The date of receipt of income using the accrual method is the date of transfer of ownership of the asset (clause 1, article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3 of article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Expenses:
- In accounting, this is the residual value of the fixed asset and the costs associated with its implementation (dismantling, transportation, evaluation, etc.) (clause 5, clause 9 of PBU 10/99). Expenses in the accounting system are reflected in the debit of account 91.02 “Other expenses” (clause 31 of PBU 6/01, clause 11 of PBU 10/99, chart of accounts 1C).
- In NU, the amount of expenses that reduce sales income, just as in accounting accounting, includes the residual value of the fixed asset and expenses associated with its sale (Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 1, clause 1, Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the sale of fixed assets is carried out, in respect of which a depreciation bonus was previously applied, then the bonus must be restored if:
- the object is sold to a person who is interdependent with the taxpayer earlier than after 5 years from the date of commissioning.
VAT
Sales of fixed assets are subject to value added tax on the date of shipment (transfer) of fixed assets (clause 3 of article 38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1 of article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subclause 1 of clause 1 of article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, article 147 of the Tax Code RF).
The date of shipment of the OS is recognized (clause 1, clause 1, clause 16, article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- date of drawing up the transfer and acceptance certificate (for example, OS-1) - for movable property;
- the date of transfer to the buyer according to the transfer and acceptance certificate, regardless of the date of state registration of the transfer of ownership - for real estate.
Features of calculating the tax base and the applied VAT rate depend on how input VAT was taken into account when purchasing fixed assets:
- VAT was not included in the cost of fixed assets (clause 1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): tax base - the contractual cost of the sold fixed assets;
- VAT rate is 20%.
- tax base - profit from the sale of fixed assets, representing the difference between the contractual value of the sold fixed assets and its residual value;
When selling fixed assets, it is not necessary to restore the VAT accepted for deduction upon purchase, even if the fixed assets were sold at a loss (clause 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 15, 2015 N 03-07-11/422).
The amount of accrued VAT is reflected in Dt 91.02 “Other expenses” in correspondence with Kt 68.02 “Value added tax”.
Accounting in 1C
The sale of fixed assets is documented in the document Transfer of fixed assets in the section fixed assets and intangible assets - Disposal of fixed assets - Transfer of fixed assets.
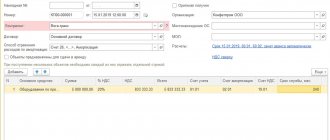
The header of the document states:
- OS event - description of the OS transfer event. In our example - Sale , which has an OS event type - Transfer ;
- Agreement - a document according to which settlements are made with the buyer, Type of agreement - With the buyer .
In our example, settlements under the agreement are carried out in rubles PDF. As a result of selecting such an agreement, the following subaccounts for settlements with the buyer are automatically established the Transfer of Assets
- Settlement account - 62.01 “Settlements with buyers and customers”;
- Advances account - 62.02 “Calculations for advances received.”
If necessary, accounts for settlements with the buyer can be corrected in the document manually or configured for the automatic insertion of other accounts for settlements with the counterparty.
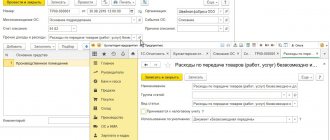
On the Fixed Assets , the following is indicated:
- Fixed asset - implemented by the OS, selected from the Fixed Assets directory;
- Income account - 91.01 “Other income”;
- Subconto - an analytical item for accounting for other income and expenses, selected from the directory Other income and expenses, Type of article - Sales of fixed assets ;
- VAT account - 91.02 “Other expenses”;
- Expense account - 91.02 “Other expenses”. For analytical accounting, the same Subconto as for other income.
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 62.01 Kt 91.01 - revenue from the sale of fixed assets;
- Dt 91.02 Kt 01.09 - write-off of residual value;
- Dt 91.02 Kt 68.02 - accrual of VAT on the sale of fixed assets;
- Dt Kt 02.01 - depreciation calculation for the month of disposal of fixed assets;
- Dt 02.01 Kt 01.09 - write-off of accumulated depreciation to determine the residual value;
- Dt 01.09 Kt 01.01 - write-off of the original cost to determine the residual value;
Control
Calculation of monthly depreciation amount:
Calculation of financial results:
Documenting
The organization must approve the forms of primary documents, incl. OS implementation document and an inventory card form for OS accounting. In 1C, the OS Acceptance and Transfer Certificate (OS-1) and the OS Inventory Card (OS-6) are used.
The form can be printed by clicking the Print button - Certificate of acceptance of the transfer of OS (OS-1) of the document Transfer of OS . PDF
Based on this act, a record of disposal is made in the inventory card of the sold fixed assets, which is attached to the act of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets (clause 81 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2003 N 91n).
the OS Inventory Card (OS-6) button in Fixed Assets directory . PDF
Income tax return
Starting from the half-year declaration, the loss from the sale of fixed assets will be reflected in Appendix 3 to Sheet 02: PDF
- line 010 - number of retired fixed assets;
- line 020 - number of retired fixed assets with a loss;
- line 030 - revenue from the sale of fixed assets;
- line 040 - residual value of fixed assets;
- line 060 - loss from the sale of fixed assets.
Accounting
Proceeds from the sale of an fixed asset are recognized as other income of the organization on the date of transfer of ownership of the fixed asset to the buyer (clause 7, paragraph “d”, clause 12, clause 16 of the Accounting Regulations “Organizational Income” PBU 9/99, approved By Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 N 32n, clause 31 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for Fixed Assets” PBU 6/01, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 N 26n). The specified income is recognized in the amount of the contractual value of the fixed asset (clauses 10.1, 6, 6.1 of PBU 9/99, clause 30 of PBU 6/01).
When an asset is transferred to a buyer, the accounting records of the selling organization reflect its disposal, and the cost of the disposed asset is subject to write-off from accounting (clause 29 of PBU 6/01).
The residual value of the disposed asset is reflected as part of other expenses (clauses 11, 16 of the Accounting Regulations “Organization's Expenses” PBU 10/99, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 N 33n, clause 31 PBU 6/01) .
Accounting records for the transactions under consideration are made in the manner established by the Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 N 94n, and are shown below in the table of entries.
Issuance of SF for shipment to the buyer
The organization is obliged to issue an invoice within 5 calendar days from the date of shipment and register it in the sales book (clause 3 of article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
You can issue an invoice to the buyer by clicking the Issue an invoice on the document Transfer of fixed assets . PDF
Invoice data is automatically filled in based on the document Transfer of Assets .
- Operation type code : “Sale of goods, works and services and operations equivalent to it.”
Documenting
You can print the completed invoice form by clicking the Print from the document Invoice issued or the document Transfer of Assets . PDF
Sales Book report can be generated from the Reports – VAT – Sales Book section. PDF
VAT declaration
The amount of accrued VAT is reflected in the VAT return:
In Section 3 p. 010 “Implementation (transfer on the territory of the Russian Federation...)”: PDF
- amount of sales revenue, excluding VAT;
- the amount of accrued VAT;
In Section 9 “Information from the sales book”:
- invoice issued. Operation type code "".
Value added tax (VAT)
Sales of goods (including fixed assets) on the territory of the Russian Federation are recognized as subject to VAT taxation (clause 1, clause 1, article 146, clause 1, article 38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The tax base is determined on the date of shipment of the fixed assets to the buyer based on the cost of the fixed assets established by the contract (excluding VAT) (clause 1 of article 154, subclause 1 of clause 1 of article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Taxation is carried out at a rate of 18% (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In general, the selling organization is obliged to present the amount of VAT for payment to the buyer and, no later than five calendar days from the date of shipment, issue the appropriate invoice (clauses 1, 3 of Article 168, clause 1, clause 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). For information about cases in which an invoice may not be issued, see the VAT Practical Guide.
Deregistration of a car
When selling a vehicle, it is necessary to deregister the vehicle with the traffic police. From the moment of deregistration, the collection of transport tax stops.
If the vehicle is deregistered during the year, then the advance payment for transport tax is calculated taking into account the ownership coefficient (clause 3 of Article 362 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Deregistration of a vehicle with the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate is completed in the register of information Registration of vehicles, type of operation Deregistration in the section Directories - Taxes - Transport tax.
The register indicates:
- Fixed asset - a vehicle that is deregistered;
- Date - the date of its deregistration with the traffic police.
Transfer of fixed assets to non-current assets
An organization cannot simply sell a fixed asset. First, you need to perform an important accounting operation: transfer the OS being sold to the appropriate section of the balance sheet, that is, to non-current assets intended for sale.
The PBU provides conditions, each of which must be met in order to make a transfer:
- profit is planned to be received precisely from the sale, and not from the use of the operating system;
- the fixed asset is fully prepared for sale, there is no need for any additional operations with it;
- The OS will be sold after the transfer no later than within a year, unless otherwise provided by the sales plan;
- the terms of sale do not contradict current regulations;
- the transfer is carried out under a specific sales contract or within the framework of a sales plan adopted by the company.
Valuation of non-current assets
Fixed assets transferred for sale must be valued at a certain balance sheet date. For evaluation, the value that is the lowest is selected:
- or residual book value (original minus depreciation);
- or the cost at which the asset will be sold (also called “net realizable value” or NVR).
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Net realizable value is the contractual selling price less costs to sell.
Reflection in the tax accounting amount of the loss from the sale of fixed assets
If the residual value of an asset, taking into account the costs associated with its sale, exceeds the proceeds from its sale, then the difference between these values is recognized as a loss.
The loss from the sale of fixed assets under NU cannot be fully taken into account at the time of sale of the fixed assets. It is included in indirect (other) expenses in equal shares over the remaining useful life of the asset, defined as the difference between the established useful life of the asset and the actual life of its operation until the moment of sale (clause 3 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The loss under the accounting system is fully taken into account at the time of sale (clause 31 of PBU 6/01).
Determining the amount of loss
The amount of loss subject to equal write-off in tax accounting can be determined using the report Register of information on financial results from the sale of fixed assets and intangible assets in the section Reports - Income tax - Tax accounting registers - Register of reporting data generation - Financial results from the sale of fixed assets and intangible assets.
Reflection in the tax accounting amount of the loss from the sale of fixed assets
There is no standard document for reflecting in NU the operation of accounting for the amount of loss from the sale of fixed assets in 1C.
Therefore, we propose to reflect the loss from the sale of fixed assets according to NU by posting Dt 97.21 Kt 91.09:
- in the debit of account 97.21 - the transfer of losses to the future is reflected to automatically include the loss in other expenses in equal shares over the remaining useful life of the fixed assets;
- on the credit of account 91.09 - the loss is excluded from the expenses of the current period in NU.
This operation is reflected using the document Transaction entered manually, the operation type Operation in the section Operations – Accounting – Transactions entered manually.
The document states:
- Date - date of implementation of the OS;
- The amount is not indicated, because in accounting, the loss was recognized at a time when the document Transfer of Assets .
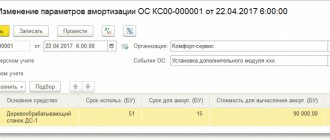
The reference book Deferred Expenses specifies the parameters for recognizing losses from the sale of fixed assets in the National Institution:
- Type for NU - Losses from the sale of depreciable property ;
- Amount - 108,000 , i.e. amount of loss according to NU;
The amount in the Deferred Expenses is indicated for reference only. To calculate the monthly loss amount, the amount indicated in account 97.21 is used, i.e. Amount NU Dt document Transaction entered manually .
- Recognition of expenses - By month ;
- The write-off period from to is the period during which the loss will be taken into account in other expenses for NL. Set starting from the month following the implementation, ending with the last month of the OS SPI.
Control
Service Temporarily Unavailable
Losses not written off in previous tax periods are transferred to it, and also losses of the current tax period are reflected as they arise. The tax register for accounting for losses from the sale of fixed assets may look like this:
| Object name | Implementation date | Amount of loss, rub. | Remaining useful life, months. | Monthly loss write-off amount, rub. | The loss in previous tax periods is written off, rub. | Subject to write-off in the current tax period, rub. | ||
| January | December | |||||||
Tax return
To reflect income and expenses associated with the sale of fixed assets, the tax return provides a special Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02 (lines 010 - 060). The amount of revenue (line 010) is included in the total line 340, the amount of expenses (line 020) is included in the total line 350, and the amount of loss (line 060) is included in the total line 360 of Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02:
| Fragment of Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02 | |
| Indicators | Line code |
| Number of objects for sale of depreciable property – total | |
| including objects sold at a loss | |
| Proceeds from the sale of depreciable property | |
| Residual value of sold depreciable property and expenses associated with its sale | |
| Profit from the sale of depreciable property (excluding objects sold at a loss) | |
| Losses from the sale of depreciable property (excluding objects sold at a profit) | |
| Total sales revenue from operations reflected in Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02 | |
| Total expenses for operations reflected in Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02 | |
| Losses on transactions reflected in Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02 | |
Then the data from Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02 is transferred to other applications and Sheet 02 in the following order:
— the amount of revenue from line 340 is transferred to line 030 “Proceeds from sales from operations reflected in Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02” of Appendix No. 1 to Sheet 02;
— the amount of expenses is transferred from line 350 to line 080 “Expenses for operations reflected in Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02” of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02;
— the amount of losses is transferred from line 360 to line 050 “Losses” of Sheet 02.
A loss from the sale of a fixed asset is reflected as it is recognized in the corresponding reporting (tax) period on line 100 “Amount of loss from the sale of depreciable property attributable to the expenses of the current reporting (tax) period” of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02.
Accounting
Due to the fact that a loss from the sale of a fixed asset is recognized in accounting on the date of sale, and in tax accounting the same loss is recognized over the remaining useful life, deductible temporary differences in the amount of the loss are formed in accounting.
The resulting deductible temporary differences (DTD) should be reflected in a special accounting register for accounting for differences on the date of sale of the fixed asset. In connection with the formation of foreign tax assets, deferred tax assets (DTA) should be accrued in accounting:
SHE = VVR x STnnp, where
STnnp – the current income tax rate.
The accrual (formation) of IT in accounting is reflected by the posting:
Debit 09 Credit 68, subaccount “Calculation of income tax.”
Gradually, as a loss from the sale of a fixed asset is recognized in tax accounting, deductible temporary differences (in the amount of the recognized loss) and, accordingly, deferred tax assets are written off:
Debit 68, subaccount “Calculation of income tax” Credit 09 – part of IT related to the loss recognized in tax accounting is written off.
The procedure for accounting for permanent and temporary differences, tax assets and liabilities is regulated by PBU 18/02 (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n).
Question
The organization submits a profit tax return monthly and pays tax based on actual profits. In February, we sold a fixed asset at a loss. We submitted a declaration for January-February 2015 and did not fill out Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02. We discovered an error in May, paid additional tax, and submitted an updated declaration for January-February. We are using the 1C program, the 1st quarter period is already closed.
In this regard, we have the following questions:
1. How to correctly reflect additional tax in accounting?
According to clause 5 of PBU 22/2010 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 28, 2010 No. 63n), an error in the reporting year identified before the end of this year is corrected by entries in the corresponding accounting accounts in the month of the reporting year in which the error was identified.
If an organization applies PBU 18/02, then the accounting records as of the date the error was discovered (that is, May 2015) should:
a) create deductible temporary differences in the amount of the loss (in a separate accounting register; no accounting entries are made);
b) accrue deferred tax assets in the amount of 20% of the amount of deductible temporary differences formed: Debit 09 Credit 68.04.2;
c) write off deductible temporary differences (in a separate register) and deferred tax assets attributable to the loss from the sale of fixed assets recognized in tax accounting in March–May 2015: Debit 68.04.2 Credit 09.
If the organization does not apply PBU 18/02, then in the accounting records on the date the error was discovered (that is, in May 2015), the arrears for income tax identified in the updated declaration for January-February should be accrued: Debit 99 Credit 68.04.1.
2. How to reflect in income tax returns, starting from March, on line 100 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02, a loss recognized in proportion to the months: on an accrual basis or not?
The tax base for income tax is the monetary expression of taxable profit, determined in accordance with Art. 247, (clause 1 of article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The profit of Russian organizations is recognized as income received, reduced by the amount of expenses incurred, which are determined according to the rules of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code (Article 247 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
According to paragraph 7 of Art. 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the tax base, profit subject to taxation is determined on an accrual basis from the beginning of the tax period.
The tax period for income tax is a calendar year (Clause 1, Article 285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, in income tax returns for 2015 on line 100 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02, the loss from the sale of fixed assets recognized in 2015 should be reflected on an accrual basis:
- in the declaration for the 1st quarter - a loss recognized in March;
- in the declaration for January-April - loss recognized for 2 months (March-April);
- in the declaration for January-May - loss recognized for 3 months (March-May);
- etc. until the end of the year.
If the amount of loss reflected on line 060 of Appendix No. 3 to Sheet 02 is not written off completely in 2015, then in the declarations for 2016 only the amount of loss recognized in 2016 should be reflected, also on an accrual basis (but only in this tax period) :
- in the declaration for January - the loss attributable to January 2016;
- in the declaration for two months - the loss attributable to January-February 2021;
- etc. until the end of the year.
Note! To correctly reflect in tax returns the amount of loss from the sale of fixed assets, the taxpayer is required to keep records of this loss in a special analytical tax register provided for in Article 323 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Receipt of payment from the buyer
At the time of sale of the fixed assets, the buyer’s receivables were reflected in accordance with Dt 62.01 “Settlements with buyers and customers.” When payment is received from the buyer, the receivables are repaid and the posting Dt Kt 62.01 (chart of accounts 1C) is generated.
Receipt of payment from the buyer is documented with the document Receipt to the current account; transaction type Payment from the buyer based on the document Transfer of fixed assets by clicking the Create button based on - Receipt to the current account.
Document Receipt to current account transaction type Payment from buyer can be:
- enter through the section Bank and cash desk – Bank – Bank statements – Receipt button;
- download from the Client-Bank program or directly from the bank if the 1C:DirectBank service is connected.
The document states:
- from - date of payment by the buyer, according to the bank statement;
- According to document No. from - the number and date of the buyer’s payment order, according to the bank statement.
- Payer - the buyer who transferred the payment;
- Amount - payment amount in rubles, according to the bank statement;
- Agreement - a document according to which settlements are made with the buyer, Type of agreement - With the buyer .
- An income item is a cash flow item. In our example, fixed assets are sold, so the Income Item is indicated with the Type of Movement - Proceeds from the sale of non-current assets (except for financial investments) .
Selecting the Income Item in the payment document from the buyer is necessary to automatically fill out the Cash Flow Statement.
Postings according to the document
Document we generate transactions:
- Dt Kt 62.01 – receipt of payment from the buyer.
Sale of uncommissioned OS
Situation: how to reflect the sale of a fixed asset for tax purposes if it has not been put into operation and is listed on account 08? The organization applies a general taxation system.
The sale of fixed assets that have not been put into operation refers to the sale of other property.
In tax accounting, proceeds from the sale of other property (minus VAT) are included in income from sales (clause 1 of Article 249, clause 1 of Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). When selling other property, the organization has the right to reduce the income received by the cost of its acquisition (subclause 2, clause 1, article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When selling fixed assets that have not been put into operation, problems may arise with VAT deductions. For more information about this, see Under what conditions can input VAT be deducted?
For information on how to reflect the sale of a fixed asset that has not been put into operation in accounting, see How to reflect the sale of fixed assets in accounting.
Accounting for the monthly amount of loss as part of indirect expenses for NU
Every month until the loss is written off in full, in the procedure menu Closing the month is a routine operation Write-off of deferred expenses .
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 91.02 Kt 97.21 - recognition in the current month of the monthly amount of loss under NU.
Control
The calculation of the portion of the amount of loss in the taxable income included monthly in other expenses is determined by dividing the entire amount of the unaccounted loss in the taxable income by the remaining useful life.
Income tax return
Starting from the half-year declaration, the monthly amount of the loss written off is reflected as part of indirect (other) expenses: PDF
- Sheet 02 Appendix No. 2 page 100 “Amount of loss from the sale of depreciable property.”
Test yourself! Take a test on this topic using the link >>