Are you switching from UTII? Connect Kontur.Accounting
45% discount in November: RUR 7,590 instead of 13,800 rub. per year of work
Easy bookkeeping
The system itself will calculate taxes and remind you of the deadlines for payments and submission of reports.
Automatic calculation of salaries, vacation pay and sick leave
Technical support 24/7, tips inside the service, reference and legal database
Sending reports via the Internet
Reports and KUDiR are generated automatically based on accounting data
Electronic document management and quick verification of counterparties
Documents, transactions, analytical reports, VAT reconciliation
Application of reduced tariffs when combining modes
The law allows for combining a simplified taxation system and a special regime in the form of UTII. However, it was possible to pay insurance premiums when combining UTII and simplified tax system at reduced rates only in the period from 2021 to 2021. In 2021, the benefit ceased to apply. Now businessmen pay contributions at the generally established rate. Previously, the total share of insurance premiums of persons on the simplified tax system listed in Art. 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and having revenue of no more than 79 million rubles per year, was 20%, now increased to 30%.
The following tariffs apply in 2021:
- in the Pension Fund of Russia - 22%;
- in the Social Insurance Fund - 2.9%;
- in the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 5.1%.
Reduced tariffs in the amount of 20% of contributions to the Pension Fund and 0% each to the Social Insurance Fund and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund until 2025 can be applied by non-profit organizations that conduct socially significant activities in the field of public services, science, healthcare, sports, education and charity.
It is not possible to combine the simplified tax system and UTII in 2021. From January 1, imputation will be cancelled. Choose a new tax system using our online calculator: enter your parameters to find the most profitable regime. We answered the most popular questions about the cancellation of UTII and insurance premiums in the article. If you don’t find the answer, ask your question in the comments, we will definitely answer.
Base for distribution of general business expenses
If activities within the framework of the simplified tax system and UTII are carried out in the same premises, such common expenses arise as:
- rent;
- payment for electricity, heat and water;
- payment for communication and Internet services;
- other general business services.
They relate simultaneously to the activities of the simplified tax system and UTII and for tax purposes require differentiation.
What is the basis for such a division? Officials of the Ministry of Finance and tax authorities express the following position on this topic - total expenses when combining regimes should be distributed in proportion to the shares of income received under the simplified tax system and UTII, respectively. The basis for this conclusion is clause 8 of Art. 346.18 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
This method is based on the use of the following calculation formulas:
- determination of the cost distribution coefficient from the simplified tax system (USN):
KUSN = DUSN / (DUSN + DENVD),
Where:
DUSN and DENVD - income from activities on the simplified tax system and UTII, respectively;
Attention! Hint from ConsultantPlus What income should be included in the calculation of the proportion This issue is not regulated in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In our opinion, you can include... in the calculation (see K+ for more details).
- calculation of the amount of general business expenses (OKH) attributable to activities under the simplified tax system (OKH STS):
OHR USN = OHR × KUSN.
At the same time, when determining a simplified tax (income minus expenses), only those expenses can be distributed and recognized that:
- paid,
- are included in the acceptable list of simplified taxation expenses.
“List of expenses under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” will introduce you to the list of allowable expenses .
When applying these formulas, it is necessary to take into account an important condition related to the period of distribution of expenses - learn about this in the next section.
Insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs
Individual entrepreneurs pay insurance premiums for themselves and for their employees. Entrepreneurs pay contributions for themselves in a fixed amount only to the Pension Fund and the Federal Compulsory Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. You can pay contributions to the Social Insurance Fund voluntarily, but you need to keep in mind that they will not reduce taxes.
The Federal Tax Service has determined the amount of individual entrepreneur deductions for itself; it is no longer related to the minimum wage. In 2021, the amount of payment to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund is 8,426 rubles. In the Pension Fund - 32,448 rubles, if your income is no more than 300,000 rubles. If the income is higher, then you must pay to the Pension Fund a fixed part of 32,448 rubles and 1% of the excess amount, but not more than 259,584 rubles (32,448 rubles eight times the amount). You can calculate contributions for a partial year using our free online calculator.
For his employees, an entrepreneur, like any organization, must make payments to the Pension Fund, the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, and the Social Insurance Fund.
Income for proportion
It is generally accepted that the right decision is to choose the proportion of revenue for each area of activity as income for calculating the proportion. Side income (Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, etc.) is not taken into account when determining it.
It is correct from a legal point of view to apply this approach to income from the sale of property that is no longer in use and other similar types of income.
Let us recall that the revenue indicator should be determined in this way:
- under the simplified tax system, the cash method is used;
- with UTII, the basis is accounting information, although the cash method is also not prohibited.
In addition, let us add that there is another tax regime - the unified agricultural tax, which also provides for the cash method when calculating the amount of income. Based on the foregoing, when combining this special regime and UTII, you can use the approach described above to determine the proportion.
Distribute “insurance” expenses
If you conduct several types of activities and combine simplification and imputation, then accounting for income and expenses must be kept separately according to special modes. This also applies to insurance costs. Distribute insurance payments by type of activity: part of them will be taken into account when calculating the single simplified tax, and the other - when calculating the imputed tax.
Distribute contributions for employees depending on the type of activity in which they are employed. If the employee is involved in two at once, it is necessary to divide payments in proportion to the income received for each type of activity. The same applies to all expenses that cannot be distributed. To compare income from simplification and imputation, you need to consider them for the entire year as a cumulative total. In addition to contributions for employees, individual entrepreneurs also distribute their own contributions.
How does the IP think?
Why should I keep any records, I don’t have to do it. Yes, I keep KUDIR on the simplified tax system, but why keep records on UTII if the tax is still not on real income? What's the result? But in the end, sooner or later there comes a time when separated information is required. The simplest example is that you need to divide your insurance premiums to reduce taxes on them. And without separate accounting data, you will not be able to do this correctly. To be honest, I don’t understand entrepreneurs who don’t keep any records at all. Even if you are on UTII and are not required to maintain KUDIR, you still need to record income/expenses for yourself.
Tax reduction for individual entrepreneurs without employees
An individual entrepreneur can reduce taxes by the amount of insurance contributions - these are his fixed contributions. An entrepreneur can reduce the tax under the simplified tax system by deduction, reduce the imputed tax, or distribute insurance premiums between UTII and the simplified tax system.
Please note: a simplified individual entrepreneur with the “income” object reduces the tax on contributions, and with the “income minus expenses” object, insurance contributions reduce the tax base. Taxes can be reduced down to zero, but only in the quarter in which contributions are paid. Therefore, pay your insurance premiums quarterly.
Briefly about each special mode
Both regimes generally do not require payment of VAT, income tax or personal income tax on the income of an entrepreneur , as well as property taxes (there are exceptions). Instead, a single tax is paid. The absence of the need to pay VAT in most cases is the reason why these systems are chosen.
USN, aka simplified
In a simplified system, a businessman can choose for himself at what rate to pay tax. There are two options:
- 6% from income excluding expenses;
- 15% from income from which expenses have been deducted.
Obviously, the first option is suitable for those types of businesses where the amount of expenses is small. This is primarily the provision of services or the performance of some work that does not require the cost of equipment and materials. Trade organizations and individual entrepreneurs more often use the simplified form with the object “income minus expenses.”
The tax is paid in advance for the first quarter, six months and nine months. At the end of the year, the results are summed up and additional payments are made, and a declaration is also submitted. Those who have chosen the simplified tax system at a rate of 6% can reduce the tax according to certain rules by the amount of insurance premiums paid.
Restrictions on the use of the simplified tax system are mainly related to the volume of business. The amount of income for the year, as well as the residual value of fixed assets, should not exceed 150 million rubles , and the maximum number of employees on an average annual basis is 100 people. There are additional restrictions for organizations - the absence of separate divisions, the share of participants - legal entities - no more than 25% and some others.
A new company can choose the simplified tax system at the time of registration or within 30 days after that. An existing organization or individual entrepreneur can switch to the simplified tax system starting next year by submitting a notification to the Federal Tax Service.
UTII or imputation
The single tax on imputed income exists until 2021, then it will be excluded from the Russian tax system. The beauty of imputation is that the amount of tax does not depend on the amount of income. On the other hand, if a loss is incurred, you will still have to pay.
Despite its profitability, UTII has a lot of limitations. Firstly, the system does not operate everywhere, but only where municipal authorities have approved it and adopted the corresponding local law . Secondly, UTII can be applied to strictly defined types of activities . The full list is given in paragraph 2 of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code. These are many services - household, veterinary, repair, motor transport, advertising, as well as retail and catering.
There are other conditions for the use of UTII: the maximum number of employees is 100 people , and the share of participation of legal entities is up to 25% . But there are no restrictions on the amount of income and the cost of fixed assets.
The object of taxation on UTII is imputed, that is, theoretical, income. It is calculated using a formula based on the basic profitability and physical indicator, which are shown in the table from paragraph 3 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, for small stores the physical indicator is 1 square meter of area. The basic profitability in this area is set at 1,800 rubles. That is, it is assumed that from each square meter of its retail space the store receives income in the amount of 1,800 rubles per month. Another example is the provision of veterinary services. In this area, the physical indicator is the number of employees, and the basic profitability is set at 7,500 rubles.
To calculate the tax base, the profitability is multiplied by the physical indicator, and the resulting value is adjusted by certain coefficients. Next, a tax rate of 15% is applied to the base, unless in a particular municipal district or city it is set at a lower level. You can then apply tax deductions for insurance premiums.
You need to report on personal income tax once a quarter, and pay taxes at the same frequency.
Tax reductions for the “profitable” simplified tax system and UTII with employees
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs with employees can reduce the amount of imputed and simplified taxes by half due to insurance premiums paid for themselves and for employees. However, when combining UTII and simplified tax system “income”, some features arise:
- If employees are engaged only in imputed activities. In this case, due to the contributions paid for all employees, the imputed tax can be reduced by 50%. The simplified tax system is reduced without restrictions due to contributions paid for individual entrepreneurs.
- If employees are engaged only in simplified activities. Then you can reduce the tax under the simplified tax system by up to half due to contributions for employees. In this case, UTII can be reduced by individual entrepreneurs’ contributions for themselves.
- If employees participate in all types of activities. Then both the imputed and simplified tax can be reduced by half according to the limitation. The simplified tax system is based on contributions paid for employees and individual entrepreneurs. UTII - from contributions paid for employees. The amount of contributions paid for employees is divided taking into account the distribution of employees according to the applicable regimes, and if this is not possible, in proportion to income.
We create methods of accounting for salaries (reflection of postings)
The next important step. Set up payroll accounting methods. These settings affect the formation of accounting entries.
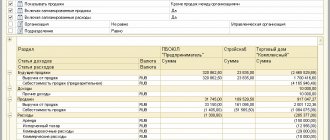
Go to the “Salary and Personnel” section and select “Salary Settings”:
Here we open the item “Salary accounting methods”:
Our task is to create in this directory three methods of accounting for wages: “Payment according to UTII”, “Payment for labor under the simplified tax system” and “Payment for labor under the simplified tax system-UTI”.
The first method is needed for the seller, the second for the photographer, and the third for the director (you remember that it is half on the simplified tax system and half on the UTII):
Here's how to fill out the salary accounting method “UTII wages”:
Here we have chosen account 44 as the cost account and indicated the cost items for each activity. We created these articles in the previous step.
Here's how to fill out the salary accounting method "STS":
Here we have chosen account 20 as the cost account and indicated the cost items for each activity.
Finally, here’s how to fill out the salary accounting method “Payment of the USN-UTII”:
We entered cost account 26 and again selected the appropriate cost items.
The general meaning of these methods is only to indicate the correct cost accounts and cost items we have created. Let's move on.
Accounting for insurance contributions under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” and UTII with employees
In this case, the amount of imputed tax can also be reduced to 50% by the amount of deductions for employees. As for simplification, it is not the amount of tax that is reduced, but insurance contributions that are taken into account as expenses.
- If employees are employed everywhere, then the costs of insuring themselves and employees fall into the expenses of the simplified tax system in full, in proportion to the amount of income received. UTII is reduced according to the half-limit of contributions paid for part of the employees and in a fixed amount in proportion to income. Distribute contributions wisely.
- If employees participate only in activities subject to imputed tax, it can also be halved through contributions for employees, and income under the simplified tax system is reduced by the entire amount of fixed payments for individual entrepreneurs.
- When employees are employed only in simplified activities, take into account all payments for employees and for yourself related to this activity as part of the expenses under the simplified tax system. You can reduce UTII only by fixed contributions for yourself.
Author of the article: Lyubov Evgrafova
If you combine modes, work in the Kontur.Accounting web service. The system itself will calculate taxes and help distribute contributions, and draw up reports based on accounting. Simple accounting, salary, reporting via the Internet and advice from our experts. Use the service for free for the first 14 days.
Why you shouldn’t abandon the simplified tax system, even when your activity is only based on a patent
A patent is a tax system that cannot exist on its own, only in conjunction with the main tax system (OSNO) or simplified tax system. STS and OSNO are basic systems on which you can conduct almost any activity and take into account almost any income. Therefore, when at least some income goes beyond the scope of activities on a patent, it is subject to taxation under the simplified tax system or OSNO. By the way, this income even includes regular cashbacks and interest on the current account balance. It is easier to report on such income using an inexpensive simplified tax system than under a complex OSNO with VAT, income tax or personal income tax.
If absolutely all income falls within the scope of the patent, according to the simplified tax system it will be enough to file a zero declaration and you will not have to pay tax. This is why we always advise leaving the simplified tax system as a safety net.