What is the main purpose of an invoice?
An invoice is a tax accounting document for VAT.
It is issued for relevant transactions (sales of goods, works, services, etc.) by persons under the general taxation regime, and in some cases, for example, when importing goods from abroad, and by persons using special tax regimes. The document indicates the amount of tax that must be accrued for payment to the budget from the transaction performed. The person who received the document, if he is a payer of the specified tax, can reduce the amount of VAT payable to the budget by the reflected amount of tax, because Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines an invoice as a document on the basis of which the buyer claims a VAT deduction. This is the main purpose of an invoice.
Should the agent organization reissue an invoice to the individual principal in the event of a purchase on behalf of the latter of material assets with VAT? Find out the answer to your question from a ConsultantPlus expert by getting free trial access to the system.
Buyers - individuals may or may not be VAT payers. It all depends on the availability of entrepreneurial status and the applicable tax regime. We will discuss in the next section when an invoice must be issued to an individual.
Invoice. Form and sample 2021. Adjustment invoice
An invoice is the most important document that is required for both parties to trade transactions. Entrepreneurs who constantly issue and receive invoices know how much depends on the correct and correct completion of this document.
Download the document for free
FILES Download a blank invoice form .xlsDownload a sample of filling out an invoice .xlsDownload a blank form of an adjustment invoice a sample of filling out a correction invoice .xls
If you already know what elements are included in the invoice and what will change in the new year, as well as the basic rules for filling it out, you will find useful information on how to avoid annoying misunderstandings and problems with tax deductions.
Why do you need an invoice?
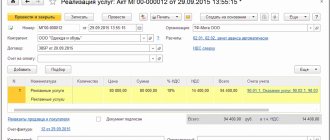
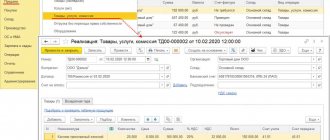
The document, which is drawn up on a standardized form that includes information required by the state, is needed by both sellers and buyers. When a trade transaction is carried out, confirmation is needed that the goods were actually shipped, services were provided, and work was done. An invoice is just such documentary evidence.
An error was made, what should I do?
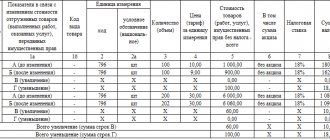
If the seller who issued the invoice finds errors in it, he has the right to make the necessary adjustments. The buyer does not have this right, but he can point out the error to the invoice issuer and ask for corrections. For this purpose, a special operation is provided - invoice adjustment .
Actions of the invoice recipient
If a corrected invoice was sent to the buyer, he must change the data in the purchase book, because the parameters of the defective invoice or erroneous data were indicated there. To do this, the buyer needs to use an additional sheet from the Book, only to match the tax period of the purchase. On this sheet, you need to make a record of the cancellation of a specific invoice and calculate the amount of purchases made before this invoice, thus determining the amount corresponding to the canceled invoice.
The buyer has the right to exercise the legal possibility of deducting VAT not only in the tax period when he made the purchase: it is only important that the document is registered on time.
What are the features of issuing an invoice to an individual if he is an individual entrepreneur on OSNO?
If the buyer is an individual - an individual entrepreneur who is in the general regime, then he will need an invoice to submit tax for deduction.
In order for an individual entrepreneur to receive a deduction, the seller must follow some rules:
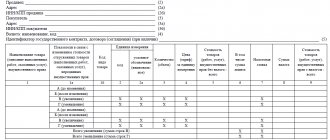
- The invoice must contain all the necessary details: number and date, names of the seller and buyer, TIN of both parties and addresses, name of the product (work, service), its quantity, price and value, tax rate and amount, etc.
NOTE! When filling out the line with the name of the buyer, it is advisable to indicate his entrepreneurial status, that is, it is better to write in the invoice: “Buyer: individual entrepreneur (or individual entrepreneur) Petrov Ivan Vasilyevich.” However, it is possible to obtain a deduction without such an indication.
- The invoice can only be signed by authorized persons.
- The document must be issued no earlier than the date of shipment of the goods within 5 working days from such shipment.
There are other invoice requirements. We talk about them in a special section.
If any errors or omissions are discovered, it is best for the entrepreneur to contact the seller with a request to replace the damaged document with a new one. Otherwise, problems will arise with the deduction.
What to do with issuing an invoice if the buyer is an individual entrepreneur on a special regime?
Entrepreneurs using special tax regimes, in general cases, should not charge and transfer VAT to the budget (with the exception of importing goods, performing the duties of a tax agent for a specified tax and issuing invoices by themselves when selling goods, works, services).
When completing a transaction, the seller and the buyer, an individual entrepreneur in a special mode, can agree on the condition of not issuing invoices (subclause 1, clause 3, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). You can also refuse them if the individual entrepreneur is on the general regime, but is exempt from paying VAT (for example, under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But if the agreement of both parties to the transaction to refuse invoices cannot be achieved, the seller will have to draw up all documents in the general manner.
IMPORTANT! The special regime person will not be able to exercise the right to deduct VAT on the basis of received invoices, even if he is obliged to pay tax to the budget (upon import or when he issues an invoice with the allocated tax amount). After all, the Tax Code grants this right only to VAT taxpayers (Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Document for yourself
At first glance, an organization should not issue invoices for non-cash payments to the population. Judge for yourself: for a “physics” buyer who bought a music disc in an online store or a book from a “mail” catalogue, this document is clearly of no use: he will still not accept VAT as a deduction! However, in order not to violate the requirements of the Tax Code, the seller in such a situation must issue invoices to each individual. And here's the reason.
Any company that sells goods, work or services is required to issue invoices (of course, except for those organizations that use special regimes). This is stated in paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The only exception to this rule is made for companies selling goods to the public for cash. Only they have the right not to issue invoices to customers, limiting themselves only to cash receipts or, if we are talking about services, strict reporting forms (clause 7 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It turns out that the selling company is obliged to issue an invoice to a client who pays for goods not in cash, but through a bank branch. Otherwise, tax authorities may fine the organization under Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for a gross violation of the rules for accounting for income, expenses and objects of taxation (the minimum fine under this article is 5,000 rubles). On the other hand, by issuing an invoice with a designated VAT amount, the taxpayer violates paragraph 6 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which does not allow the tax amount to be separately indicated in documents issued to the population. It turns out that the seller must issue invoices to individuals without allocating VAT to them. But even if the taxpayer violates this requirement, the tax authorities will not be able to punish him: the Tax Code does not establish liability for such a violation.
Is it necessary to issue an invoice for individuals without entrepreneurial status?
Individuals without entrepreneurial status are not VAT payers in any case. Therefore, the seller has the right not to issue invoices for them. How the buyer pays for the goods - whether he transfers money to the cash register or transfers it to a bank account - also does not affect the need for paperwork.
This is where sellers may have a question: how will the accrued tax data get into the sales book? The Ministry of Finance offers the following solutions:
- Compile for a certain period of time (for example, a day, a month, a quarter) all data on sales and accrued tax in an accounting statement and, based on it, fill out a sales book (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/08/2016 No. 03-07-09/6171). Instead of an accounting certificate, a consolidated invoice may appear here, drawn up in one copy, where the columns associated with the buyer (name, address, INN/KPP) are crossed out.
- Record cash receipts or strict reporting forms in the sales book (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 31, 2009 No. 03-07-09/38).
NOTE! The seller may, at his own discretion, issue invoices to individuals. The law does not prohibit this.
The procedure for filling out an invoice for an individual was explained step by step by ConsulttPlus experts. Get trial access to the system and learn how to properly prepare a document.
How to deal with VAT when working with individuals?
The original invoice is given in person, delivered by courier or sent by mail, a copy of the document can be sent by fax or email, and this is also a sufficient basis for payment.
Our lawyers know the answer to your question
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, then ask our duty lawyer online. It's fast, convenient and free!
or by phone:
- Moscow and region: +7-499-938-54-25
- St. Petersburg and region: +7-812-467-37-54
- Federal:+7-800-350-84-02
Results
With the help of invoices, buyers of goods (works, services, etc.) can exercise their right to reduce VAT payable to the budget. But not everyone has this right, but only VAT payers, for example, general-regime individual entrepreneurs. They need an invoice to confirm the deductions.
Individuals who have entrepreneurial status, but use special tax regimes, cannot claim a VAT deduction, so an invoice may or may not be issued to them as agreed by the parties to the transaction.
An individual without entrepreneurial status will definitely not need invoices, so the seller can refuse to issue them, thereby significantly saving his resources.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Everyone has their own shortcomings
It is not as easy to issue an invoice for an individual as for an organization. All details of a legal entity necessary to fill out this document are usually specified in the contract. But a private person, when placing an order, provides a minimum of information about himself - last name, first name and delivery address, and occasionally a telephone number. But a correctly executed invoice, in addition to these data, must contain one more mandatory detail - the buyer’s TIN. But it is precisely this information that is often missing.
What could happen to online stores and postal merchants if the invoices they issue do not include the buyer’s TIN? In our case, nothing. The fact is that an invoice that is missing some of the required details creates problems only for the buyer. According to such a document, he will not be able to deduct the VAT paid to the supplier (clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For the seller, the Tax Code does not provide for liability for incorrectly executed invoices. The main thing is that the company regularly displays them when selling goods, correctly calculates and pays VAT to the budget, and keeps books of purchases and sales. The Department of Indirect Taxes of the Federal Tax Service of Russia agrees with this. “Of course, formally the company violates the rules for issuing invoices by not indicating the buyer’s TIN,” the specialists of this department answered us. — But in this situation, goods are purchased by individuals who, to put it mildly, do not need input VAT. Therefore, during an audit, the tax inspector most likely will not find fault with the company.”
What if the company receives an advance payment from an individual, draws up an advance invoice and then, at the time the goods are sold, reflects it in the purchase book? Will the tax authorities accept this deduction if they notice that the invoice is missing one of the required details? The Department of Indirect Taxes of the Federal Tax Service of Russia assured us that nothing threatens the taxpayer here either. After all, the peculiarity of an advance invoice is that the seller does not present it to the buyer, but keeps it for himself, first charging VAT and then deducting it. And tax authorities are unlikely to refuse an organization a deduction for such an invoice.