Features and differences
The main difference between reporting by an entrepreneur and a legal entity is the independent management of document flow by the business owner, and not by a separate accounting department. Therefore, an individual entrepreneur is given 5 calendar days, not working days, to issue an invoice.
The starting point is the day of receipt of property rights to the goods, the date of shipment, receipt of services, acceptance of work or receipt of an advance. In cases of prepayment, an invoice is drawn up twice, upon receipt of the advance payment and upon fulfillment of the terms of the transaction. You can find out how an advance invoice is prepared here.
Reference. Invoices are drawn up in the form approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1137 of December 26, 2011. The main requirements for the document details are given in Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains the basic requirements for indicating to an individual entrepreneur the features of a transaction in an invoice:
- Number, date of compilation and corrections.
- TIN and other data to identify the parties to the transaction.
- Address for delivery of goods or provision of services.
- Invoice or advance invoice number to confirm the amount.
- Names and units of measurement of transferred goods.
- The number of goods, works or services transferred in the specified unit of measurement.
- Settlement currency.
- Country of origin and customs declaration number for imported goods. Read about import and export invoices here.
- The cost of each specified unit.
- Total transaction amount.
- Tax rate and excise duty amount.
- Calculated tax amount.
Important! Reliable and correct indication of all the listed information in the invoice gives the individual entrepreneur the right to receive a tax deduction when transferring the purchase book to the tax service.
More information about what an invoice is and the features of using the document can be found here.
What is an invoice
An invoice is a document containing the following information:
- the cost of goods shipped or work performed;
- the amount of VAT on the sale of goods;
- the amount of VAT giving the right to a tax deduction.
Simplified taxation system
The invoice form (s/f) contains the most important information that allows you to uniquely identify the customer and the contractor in order to avoid fraud. For reinsurance, both parties appearing in the document must make sure that their opponent is registered as a legal entity or individual entrepreneur with the tax authorities.
Note! An invoice is a form of financial reporting, but it can also be convincing evidence in court. You need to enter everything without errors to avoid problems in the future. Additional information that the seller and buyer decide to add does not change the authenticity of the document.
Do you need a document?
Clause 4 of Article 169 and Clause 7 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicate cases in which the individual entrepreneur seller is not required to draw up an invoice. For transactions between private entrepreneurs, in the areas of retail trade, provision of services and hired work, invoices are not required.
Also, there is no obligation to draw up such securities in case of cash payment and sale of securities, provided that the parties to the transaction are not intermediaries or brokers.
An individual entrepreneur should not issue invoices when making a transaction with an LLC, individual entrepreneur or a company operating under a special tax regime with simplified taxation.
Lawyers' answers (2)
How to fix. Switch to the general regime from 2021. At the same time, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows non-payers to issue VAT invoices under the simplified tax system, but then you must submit a declaration and pay the resulting VAT to the budget.
Client clarification
But if I purchase goods from legal entities that work with VAT and accordingly indicate it in the invoices, does this not affect my activities in any way? Shouldn't I be reimbursed for this tax? After all, I am not a VAT payer.
24 April 2015, 13:56
Some clients are reluctant to cooperate because of this. I am in sales. Tell me how you can solve this issue? Alexander
I recommend that you conduct a seminar on VAT for your clients. Just kidding, of course. But there is some truth in this joke and here's why. If a client organization works with VAT, then it should not make a difference to it from whom it buys goods: from you without VAT or from some other organization or individual entrepreneur with VAT. This has absolutely no effect on anything. The most important thing is the price of the product.
Let me give you an example for clarity: “Romashka LLC (this is your client) works with VAT and purchases goods in the 1st quarter of 2015. for 118 rub. (including VAT 18 rubles) and sells goods for 354 rubles. (including VAT 54 rub.). As a result, Romashka LLC will pay 36 rubles to the budget based on the results of the 1st quarter. (54 - 18). Now let’s imagine that during the 1st quarter two suppliers approached Romashka LLC with an offer to buy their goods: one works with VAT, the other without VAT. The product from both suppliers is identical. The cost of the product is 40 rubles. Both suppliers increased their profitability by 20% and their product cost was 50 rubles. The supplier who works with VAT will charge Romashka LLC the cost of the goods at 59 rubles. (including VAT 9 rubles), and the one that works without VAT will charge Romashka LLC the cost of the goods 50 rubles. (without VAT). If Romashka LLC wants to buy goods from a supplier with VAT, the Company will transfer 9 rubles. more from the current account, but these 9 rubles. can be taken for deduction based on the results of the 1st quarter of 2015. and then the amount of VAT payable to the budget will not be 36 rubles, but 27 rubles. (36 - 9). If Romashka LLC wants to buy goods from a supplier without VAT, the Company will transfer 9 rubles. less from the current account and then the amount of VAT to be charged will remain 36 rubles. As a result, none of the suppliers is more or less profitable and Romashka LLC makes no difference with whom it works.”
Can I issue a VAT invoice? Alexander
According to clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if an invoice with the allocation of the amount of VAT is issued to the buyer by a person who is not a VAT payer, or by a person exempt from the duties of calculating and paying tax, this person is obliged to calculate and pay this tax. Thus, you have the right to issue VAT invoices to another organization. In this case, you have the obligation to transfer the VAT, which you indicate in the invoice, to the budget.
You will also need to submit a VAT return electronically using the TKS on a quarterly basis.
Should I issue a document if I work without VAT?
The obligation to issue an invoice under the conditions of the seller’s exemption from VAT, in accordance with paragraph 5 of Article 168, occurs in cases provided for in Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. We are talking about individual entrepreneurs with revenue of less than 2 million rubles per quarter, who do not work with excisable goods.
Such entrepreneurs, after notifying the Federal Tax Service, are exempt from VAT for 12 calendar months, unless conditions arise for the cancellation of such a right. The exemption is then reviewed and updated annually.
In other cases, the taxpayer has the right, but not the obligation, to draw up an invoice , and can use it solely for his own convenience.
An example of such a situation is the exemption from tax of part of the consignment indicated in the invoice together with goods subject to tax. Also, an optional invoice for tax-free goods will help maintain consistency in document numbering.
Read about when you need an invoice without VAT here.
Basic information ↑
It is quite obvious that the preparation of invoices should be carried out by those business entities that pay VAT to the treasury.
Therefore, many entrepreneurs are concerned about the question of whether the individual entrepreneur issues this document, especially when it comes to simplified tax regimes.
Here, first of all, mention should be made of those entrepreneurs who are exempt from the obligation to prepare invoices.
These include (Articles 168-169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- companies engaged in retail trade;
- Individual entrepreneurs engaged in the field of catering and the provision of services for cash;
- entities engaged in the sale of shares and bonds.
You can add to this list those individual entrepreneurs who sell their goods (work or services) to entities using preferential tax regimes.
All other individual entrepreneurs are required to issue an appropriate invoice within 5 days after the transaction.
So, if a small company works on an advance payment basis, then it will have to draw up this document twice:
- for advance funds;
- on the total cost of goods shipped to the buyer or services provided.
Basic definitions
An invoice is a payment document that is drawn up by the seller of goods (services or works) and then transferred to the buyer. In general, each party to the transaction receives one copy of the invoice.
This document, important for calculating VAT and deductions for this tax, can have two forms (RF Government Decree No. 1137):
- electronic;
- paper
In this case, both options have equal legal force. There are also adjusting invoices, invoices for advance payments and invoices for invoices. The electronic version of the document must be certified with an electronic digital signature (EDS).
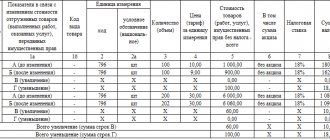
All invoices are reflected in such summary journals as:
| Book of purchases | This is a special register that provides information about those invoices received by the company during the acquisition of goods (works, services) and has already paid VAT on them |
| Sales book | This is a consolidated log of invoices issued to customers, on the basis of which the company has the right to receive VAT deductions |
Nuances depending on the tax system
It was previously noted that the preparation of invoices is mandatory only for those companies that pay VAT to the treasury.
However, it is important to take into account some of the nuances of various taxation regimes, in particular (Articles 168-169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
| For AHF | Individual entrepreneurs are required to issue invoices within 5 days after shipment of products to customers |
| Under special taxation regimes (USN, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax) | Individual entrepreneurs do not pay VAT to the treasury and submit appropriate reports. However, they have the right to issue an invoice without VAT or a zero invoice (Article 346.11, Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
If a company issues an ordinary document, then it will have to pay tax and prepare reports for the Federal Tax Service.
Thus, for simplified entrepreneurs, the answer to the question whether such a company issues invoices is an affirmative answer.
However, if this payment document is zero, then the invoice will only play the role of paper certifying the relationship with the buyer.
Normative base
Issues related to the preparation and submission of invoices by buyers are discussed in detail in such Russian legislative acts as:
| Art. 168-169 Tax Code | Which consider all issues of drawing up invoices, the possibility of issuing them electronically, as well as those types of activities that do not require the mandatory generation of these documents |
| Art. 346.11 and 346.26 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | They establish the fact that individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system and UTII are not obliged to issue set invoices |
| Federal Tax Service Order No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] | Sets new standards for invoicing, both electronically and in paper form |
It should be emphasized that the new form of invoice, which individual entrepreneurs are required to use in their activities, began to operate in the first quarter of 2021.
For transaction codes in invoices, see the article: codes in invoices. Read about the buyer's adjustment invoice here.
How to display?
In paragraph 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation it is stated that when issuing an invoice, an individual entrepreneur must personally sign it and indicate his own details of state registration of himself as an individual entrepreneur. Details mean a certificate of state registration of an individual entrepreneur to identify the taxpayer. Unlike an LLC, an entrepreneur cannot delegate this responsibility to a trustee.
Note! Although the right to participate in relations of an authorized representative is confirmed by paragraph 1 of Article 26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it also states that it may be limited by other legislative acts.
Therefore, the legal representative can conduct the transaction, but cannot sign the invoice on behalf of the individual entrepreneur.
Nuances of activity that arise for individual entrepreneurs
Any invoice must be certified by a signature, which is located after all the required details, usually in its lower right part.
The individual entrepreneur has the right to sign personally, as stated in Article 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, indicating information about the number and date of registration of the status. Delegation of the right to sign invoices to third parties by orders or other internal regulations is not permitted. This obligation makes it difficult for those persons who are not permanently present at the place of business to timely transmit invoices to customers.
One of the options for executing the instruction is to provide a notarized power of attorney to the responsible person, who is an accountant. In the power of attorney, indicate which documents the representative is allowed to visa. The best option would be to purchase an electronic signature and endorse documents with it online, if necessary.
The presence on the invoice of the details of the certificate of state registration and the date of its issue is not a mandatory requirement if such data is contained on the seal impression.
The invoice must be certified with a “live” or electronic signature of the individual entrepreneur and must have a seal with all the necessary parameters, with the obligatory indication of the certificate number and the date of its issue.
The changes that came into force at the beginning of 2021 concern information in the invoice, as well as the calculation and payment of VAT:
- The VAT declaration is submitted no later than the 26th day of each month following the reporting period only in electronic form.
- Before submitting the declaration to the Federal Tax Service, it is necessary to summarize the amounts in the Book of Purchases and Sales.
- If an individual entrepreneur issues zero invoices on USP, he is not required to provide a declaration.
It is necessary to draw up documents correctly and provide accounting and tax reporting on time. Remember that errors identified by the audit are not always critical, but may serve as grounds for refusal of compensation.
Timely adjust the procedure for maintaining accounting, management and tax accounting when the legislative framework changes. Each entrepreneur must competently substantiate his position and optimize costs during negotiations with tax authorities or by defending his rights in court.
Good afternoon. I have an individual entrepreneur, I work without VAT on the simplified tax system Income minus expenses. Some clients are reluctant to cooperate because of this. I am in sales. Tell me how you can solve this issue? Can I issue a VAT invoice? and how to fix the situation in general?
Filling rules
To send a VAT deduction to the buyer to the tax service, the supplier, along with the invoice, must issue an invoice (in which cases the invoice and invoice are needed, read here). In addition to the fact of having the document, you need to fill out the invoice correctly. The law has introduced the following procedure for compiling the title part of the form:
- Document number in the supplier's accounting and date of completion. 1a is intended for dating the corrective version and is left blank during the initial drafting.
- Full name of the entrepreneur. 2a IP registration address. 2b TIN of an individual.
- The name of the shipper may duplicate the data in line 2.
- Name and address of the buyer-receiver.
- Number and date of the payment receipt, in cases of prepayment.
- 6a, 6b – data about the buyer, identical in form to lines 2 and 3.
- Name and code of the settlement currency. The code can be found out from the classifier, for example, the ruble is numbered 643.
Next, the form contains a table where for each product from the invoice you must enter:
- Name;
- quantity;
- unit of measurement;
- price;
- amount and rate of VAT;
- final price.
The document is filled out in two copies and signed personally by the entrepreneur, if drawn up on behalf of an individual entrepreneur. The invoice is not stamped.
- You will learn more about correctly filling out an invoice in this article.
Option with VAT
When receiving invoices from contractors who are individual entrepreneurs, the buyer should especially carefully monitor their authenticity and especially the presence of the signature of the entrepreneur himself. The main difference from receiving a document from an LLC is the requirement for a personal visa.
Important! The absence of one of the key details, such as a personal signature or duplication of data in column 3, is grounds for refusal of a deduction during an inspection.
If an entrepreneur has issued an invoice, but the form contains an error, then it will be impossible to obtain a VAT deduction even through the court.
In case of tax exemption
Drawing up an invoice for goods “without VAT” is possible in 2 variations:
- If all the goods in the batch have such a mark, then in line 8 of the form with the total tax amount this mark is duplicated, and such a tax document is not considered.
- If some services or goods are exempt from tax, then column 8 indicates the actual amount excluding these data.
An invoice without VAT is filled out in accordance with the general rules for the preparation of this document, since Government Decree No. 1137 of December 26, 2011 was updated by Appendix 2 to the resolution, dated February 1, 2021. It is enough to enter the entry “excluding VAT” in the appropriate section of the table. The mark can be made separately, in a printed document by hand, for example, when signing a document.
VAT declaration and reporting
All participants in the payment of VAT (it should be noted that these are both taxpayers and tax agents) must submit a tax return to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration.
Since 2014, the declaration of value added tax takes place in the form of electronic document management using the taxpayer’s UKEP. Declarations submitted on paper are not accepted and are not considered submitted.
When filling out the VAT return, you need to take into account every ruble
It should be taken into account that the VAT declaration is filled out in rubles (without kopecks), kopecks are rounded according to the arithmetic rule.
The main reporting document for VAT - the declaration - must be submitted no later than the 25th day of the next month of the quarter.
Attention! If the taxpayer fails to submit a tax return to the tax authority within 10 days after the expiration of the established period, transactions on the accounts may be suspended (clause 3 of Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation
https://www.nalog.ru/
In addition to blocking the account, for late submission of the declaration, individual entrepreneurs can be fined from 5 to 30% of the VAT amount or charged from 1000 rubles. (the fine also includes a larger amount). In this case, sanctions will apply for each month of delay.
Table: registration of VAT declaration by sections
| Sheet number/section | Who submits, in what case it is filled out |
| Title page and first section of the declaration | All VAT payers, including those whose VAT base is zero |
| Sections No. 2—12 | Only if necessary operations are available |
| Sections No. 4—6 | If the activities of an individual entrepreneur are subject to a VAT rate of zero percent |
| Sections No. 10–11 | If a contract is issued and (or) received when carrying out business activities in the interests of another person (commission agreements, agency agreements, etc.) |
| Section No. 12 | If payers are exempt from VAT or are not payers |
Photo gallery: VAT declaration pages
The first section must be completed by all VAT payers
Some sections are completed only if there are operations
Section No. 12 is filled out by those who are exempt from VAT
If necessary, additional sheets can be added to the declaration
Invoice journal
In addition to the declaration, there is another VAT reporting document - the invoice journal. This form is regulated by paragraph 5.2 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It applies to intermediaries: developers, contractors, agents, freight forwarders, who are not recognized as VAT payers, but allocate it in accounting documents when providing their services.
Just like the VAT return, the invoice journal report is submitted based on the results of each quarter. Thus, based on the results of the first quarter of 2021, the journal must be submitted by 04/20/2018. If the intermediary did not receive or issue tax invoices with VAT in the past quarter, then there is no need to report on the journal.
Reports on accounting of invoices must be submitted through the portal of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation using electronic document management.
Table: deadline for submitting VAT reports
| Regularity | View | Deadline | Where/in what form |
| Quarterly | VAT declaration at the end of each quarter | Until the 25th of the first month of the next quarter | Federal Tax Service / EDF |
| Quarterly, when carrying out activities subject to VAT | Invoice journal | Until the 20th of the month of the next quarter | Federal Tax Service / EDF |
When to pay VAT
Each VAT payer can choose one of two payment options: quarterly or annually. In any case, the tax regulator has allocated 25 calendar days after the end of the payment period.
The main rule of timely payment to the state budget is to avoid delays. In order not to fall under sanctions, it is recommended to transfer the tax 2-3 days earlier than the deadline established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Delays in paying tax to the federal budget are punishable by a fine on the entrepreneur - from 20 to 40% of the VAT amount.
Table: current budget classification codes (BCC) for VAT
| Payment Description | KBK for tax transfer (contribution, fee, other obligatory payment) | KBK for transferring penalties for taxes (fees, other obligatory payments) | KBK for transferring a fine for a tax (fee, other obligatory payment) |
| VAT on goods (work, services) sold in Russia | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| VAT on goods imported into Russia (from the Republics of Belarus and Kazakhstan) | 182 1 0400 110 | 182 1 0400 110 | 182 1 0400 110 |
| VAT on goods imported into Russia (payment administrator - Federal Customs Service of Russia) | 153 1 0400 110 | 153 1 0400 110 | 153 1 0400 110 |
Video: VAT return
Actions after issue
When receiving an invoice from the entrepreneur's authorized representative, the buyer has a high chance of being denied a deduction from the tax service and will have to go to court. The judge will check the authenticity of the transaction and, most likely, will grant the request to annul the refusal on a formal basis, but this will take the buyer time and money.
To avoid legal costs and other unpleasant moments associated with the incorrectness of this document, the nuances of issuing an invoice should be specified in the supply agreement. In any case, the supplier is not responsible for issuing an invoice, unless otherwise specified in the contract.
Consequences of errors in invoices
Like any document, an invoice should not, but may contain “technical” errors.
Paragraph 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation clearly defines on the basis of which errors a VAT refund can be refused, and which are not recognized as significant and do occur.
The task of the tax authorities is to control the timely receipt of taxes to the budget, increase their amount, prevent non-payment and reduce the amounts subject to deduction. If a specialist from the department identifies inaccuracies or typos, he will form a negative conclusion and no VAT deduction will be made.
If an employee of the Federal Tax Service was able to identify the participants in the transaction by name or tax identification number, type of product or service and their cost, amount and amount of tax, then I have no right to refuse a VAT deduction.
The signature on the documents must be affixed with your own hand; the use of a facsimile may be regarded as an error in the preparation of the document. Judicial practice proves the opposite; however, to save time on communicating with the tax service, endorse the documents yourself or by third parties, if they have the authority.
Of course, subsequently, after identifying any errors, it will be necessary to make changes to the counterparty’s registration card in order to avoid misunderstandings and controversial situations with government agencies in the future.
Looking for an answer? It's easier to ask a lawyer!
to our lawyers - it’s much faster than looking for a solution.
More on the topic:
- CJSC consultant lawyer Consultant-Lawyer, CJSC Consultant-Lawyer, CJSC registered at Tambov, N. Virty St., 2A, 392018. Director of the organization CLOSED JOINT STOCK COMPANY “CONSULTANT-JURIST” Zaikin […]
- Tarot card of divorce Online fortune telling on gypsy cards Tarot “Divorce” Layout on gypsy cards Tarot “Divorce” is indispensable in a situation where the family is close to divorce, and the fortuneteller is interested in whether there is a possibility [...]
- Article 116-117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation Question: According to Art. 116-117 of the Labor Code, workers whose working conditions in the workplace, based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, are classified as harmful conditions (2, 3 or 4 degrees), are provided […]
- Magistrate Court of the Avtozavodsky District Precincts of justices of the peace of the Avtozavodsky District of the city of Nizhny Novgorod C debny plot No. 1 of the Avtozavodsky Judicial District of the city of Nizhny Novgorod, Nizhny Novgorod Region 603950, Nizhny […]
- Lists of children in kindergarten 2021 Lists of children who got into kindergartens in Vologda will be published on April 7. This year, lists of children who got into kindergartens will be published earlier, the head of the education department said […]
- Law 13 on mortgages Law of Ukraine “On Mortgages” The Law on Mortgages in Ukraine regulates the relationship between the mortgager and the mortgagee, as well as all related issues. Ukrainian legislation on mortgages […]