What it is?
According to Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an invoice is a document that serves as the basis for the buyer to accept tax amounts for deduction from the seller of goods, services, work, or property rights.
The invoice is issued in electronic or paper form: in the first case, both parties to the transaction must have compatible technical means and capabilities to receive and process invoices.
If, after drawing up the document, inaccuracies were revealed in it, namely: there was a change in the cost of services performed, goods shipped or their volume, quantity downward, then the seller issues an adjustment invoice to the buyer (in accordance with Federal Law No. 245-FZ dated July 19, 2011 .).
The adjustment document helps to make a recalculation taking into account errors and inaccuracies that were made in previous years.
IMPORTANT! Invoices are required to be issued by those selling companies that are VAT payers.
Therefore, the objectives of this document are:
- confirmation of the completion of work or delivery of goods;
- confirmation of the amount of VAT paid with the possibility of its further offset.
Filling rules
The detailed procedure for filling out is given in Resolution No. 1137 and Article 169 of the Tax Code. One of the mandatory details that the completed invoice contains is the serial number (clause 1, clause 5, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There are no special numbering rules.
IMPORTANT!
The document is signed by the head of the organization and the chief accountant or other persons authorized to carry out such actions by order or power of attorney from the organization. On behalf of the individual entrepreneur, another person has the right to sign on the basis of the entrepreneur’s power of attorney indicating the details of the certificate of state registration of the individual entrepreneur.
Invoices do not constitute:
- persons who are not taxpayers, exempt from fulfilling the duties of a taxpayer (clause 1, clause 3, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- for transactions that are not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation) on the basis of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- organizations, individual entrepreneurs working in the field of retail trade, public catering, performing work (providing services) for the population in cash, subject to the issuance of a cash receipt or other documents of the established forms (clause 7 of article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- organizations and individual entrepreneurs applying special tax regimes: Unified Agricultural Tax, simplified tax system, UTII, PSN, subject to some exceptions;
- in other cases.
What is the basic form approved by the government?
An invoice is a document of a strictly established format. The form of the invoice form is approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1137 of December 26, 2011 “On the forms and rules for filling out (maintaining) documents used in calculations of value added tax,” developed in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In 2021, two editions of this Resolution have already been published: No. 625 of May 25, 2017 and No. 981 of August 19, 2017, according to which the form of the form was modified.
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1137 approves the rules for filling out:
- Invoice used for VAT calculations.
- Adjustment invoice used for VAT calculations.
- Logbook of received and issued invoices.
- Purchase books.
- Sales books.
Errors in invoices affecting VAT deduction (Yudakhina E.)
VAT, No. 23
- VAT clarifications for the last half of the year, No. 19
- VAT deduction without sale: declare or transfer to the future - which is safer?, No. 19
- Errors in the invoice: important or not, No. 15
- Camera for VAT refunds: how to deal with documentary lawlessness, No. 12
- Is it possible to separately number advance invoices, No. 10
- Adjustment and Corrected Invoices: Feel the Difference, No. 10
- The price of one product rises, another falls: adjusting the invoice, No. 8
- New invoices: corrections, adjustments and more, No. 8
- Answers to the first questions about new invoices, No. 7
- Changing the cost of some goods: how to fill out an adjustment invoice, No. 7
- Is it necessary to submit a purchase book, No. 5, to the Federal Tax Service for VAT reimbursement?
- Price in foreign currency or USD.
Graphs that should be in the document
Each field of the completed invoice is checked by inspectors of the Federal Tax Service during on-site or counter inspections.
ATTENTION! The details of this document must be filled out correctly, otherwise the invoice will be sent for revision or there is a risk of denial of VAT deduction to the business entity.
If there are gross errors indicating distorted facts of economic activity, the organization may be subject to penalties.
The form of each invoice consists of lines and columns with numbering and letter designation.
For sale
The sales document uses the following lines:
- 1 indicating the serial number and date of preparation of the document. The number is assigned in individual chronological order, and if the organization has a separate division that sells goods (services, property rights), the dividing line “/” is used (more information about the rules for filling out the document by separate divisions can be found here).
- 1a is used to indicate the serial number and date of amendment to the document. Before any corrections are made, a dash is placed on this line.
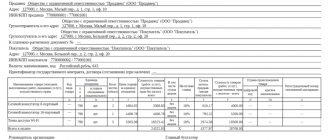
- 2 – indicate the name of the seller (legal entity, full name of individual entrepreneur).
- 2a – the address of the seller is indicated - a legal entity in accordance with the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or an individual entrepreneur in accordance with the entry in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs.
- 2b – the taxpayer’s TIN, as well as the taxpayer’s checkpoint, are filled in.
- 3 – full or abbreviated name of the shipper. If the seller and the consignor coincide, the line is filled in with the words “he”; when performing work (services), a dash is added.
- 4 – full or abbreviated name of the consignee (as in the constituent documents), his address.
- 5 – details of the payment order or cash receipt are indicated if an advance payment was received from the buyer.
REFERENCE. If the invoice is issued on the day the advance payment is received, a dash is placed in line 4. - 6 – full or abbreviated name of the buyer, which is indicated in the constituent documents.
- 6a – the buyer’s address is indicated in accordance with the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs (until 01.10.2017, the address had to be indicated as in the constituent documents).
- 6b – the TIN, as well as the buyer’s checkpoint, are indicated.
- 7 – enter the name of the currency and its code in accordance with the All-Russian Classifier of Currencies (read about whether it is possible to issue an invoice in the currency of another country, where to find out and display such a code here).
- 8 – indicates the identification number of the state contract for the supply of goods, works, services or an agreement to provide subsidies to a legal entity from the federal budget in accordance with ed. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 625 of May 25, 2017. If the organization does not have such contracts, a dash is placed in line 8.
The following fields are used in the sales invoice:
- 1 with the name of the product or service supplied.
- 1a – the code of the type of product is indicated in accordance with the unified Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity of the EEC. If the organization does not export goods outside the Russian Federation, a dash is placed in the column.
- 2 and 2a – the code and symbol of the unit of measurement are indicated in accordance with OKEI. If they are not there, a dash is added.
- 3 – quantity of goods shipped or a dash.
- 4 – price per unit of goods or tariff for services provided excluding VAT; if there is no indicator, a dash is placed.
- 5 – indicates the cost of the entire volume of services provided or quantity of goods without VAT.
- 6 – the amount of excise tax is indicated; if a non-excise product is sold, the entry “Without excise tax” is entered.
- 7 – tax rate is indicated. If goods are sold without VAT, a corresponding entry is made (clause 5 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- 8 – the amount of VAT charged to the buyer, based on the tax rate.
- 9 – the cost of the total quantity of goods shipped or services provided, including VAT, is entered.
- 10 and 10a - for goods produced outside the Russian Federation, the code and name of the country of origin of the product are indicated.
- 11 – an entry is made with the registration number of the customs declaration for goods released outside the Russian Federation.
From separate publications by our experts, you can also learn about the timing of issuing an invoice to the buyer, as well as the rules for filling out the document when returning goods to the supplier and when providing services.
Corrective
IMPORTANT! The adjustment invoice has details similar to the document for the release of goods, but the filling of some of them is different.
The form contains the following lines:
- 1 – number in general chronological order and date of the document.
- 1a – number of the correction made and its date.
- 1b – number and date of the document (or several documents) for which the adjustment invoice is drawn up, as well as the date of their correction.
- lines 2, 2a and 2b are filled out in accordance with the information entered in the same lines of the invoice for which the adjustment document is being drawn up.
- lines 3, 3a and 3b contain information about the name, location, tax identification number and checkpoint of the buyer.
- 4 – name and code of the currency.
- 5 – identifier of a government contract or agreement.
Column 1 of the adjustment document is filled out in accordance with the name of the goods, works, services indicated in the same column in the invoice for the adjustment. Column 1b is filled in with the code of the type of product according to the unified Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity of the EEC.
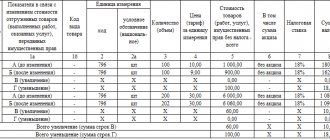
REFERENCE. The adjustment document contains information about the quantity and (or) price of goods or services, both original and changed.
The information is indicated in the lines under the letter designations:
- A – before the change.
- B – after the change.
- B – increase.
- D – decrease (cost, quantity).
The final lines (there are two of them) indicate the sum of lines B or D. In addition, the document contains information about the change in the cost of goods supplied or services performed without VAT and with VAT, as well as the difference between the amount of taxes.
Advance
When reflecting the received advance payment, the same form of invoice was developed as for sale. The preparation of an advance invoice has several differences:
- Consignor and consignee data are missing.
- The details of the payment document for the advance payment must be indicated in the appropriate line.
- With 100% prepayment, the unit of measurement, quantity and price of the goods are indicated; with partial payment, these data are missing.
An advance invoice is drawn up if there is a rate for VAT calculation of 18% or 10%. If the product is not subject to VAT or the rate is 0%, this document is not drawn up.
You will find more information about the rules for filling out an advance invoice in our special material.
Advance invoice
As a general rule, such a document is drawn up within 5 working days from the date of shipment of goods, performance of work (provision of services), transfer of property rights (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But in cases where the organization has received an advance payment, it is also obliged to prepare it. An advance invoice is issued in the same form as a regular “shipping” invoice.
The list of details to be filled out is set out in clause 5.1 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code.
Both advance and “shipping” invoices should be numbered the same way (>letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 10, 2012 No. 03-07-11/284).
If there is an advance invoice, the buyer claims a VAT deduction. For the seller, receiving an advance forms the basis for VAT.
Let's look at an example of an advance invoice:
Example 1. An organization received an advance payment on 05/04/2020 for future delivery of goods. The shipment was made to the buyer on 05/31/2020.
The earliest date is the date of receipt of the prepayment, so in May the organization will draw up two documents:
- No. 1 dated 05/04/2020 - advance invoice;
- No. 2 dated 05/31/2020 - “shipping” invoice.
The selling organization must reflect these documents in the sales book for May 2020. Advance invoice No. 1 dated 05/04/2020 is registered in the purchase book on the date when the goods were actually shipped, that is, 05/31/2020. As a result, for May only the amount of VAT reflected in the “shipping” document will be paid to the budget.
Example 2. The goods were shipped on May 31, 2020. Payment was received on June 10, 2020.
Since the earliest date is the date of shipment of the goods, one “shipping” invoice is drawn up.
Which of them are required to be filled out?
REFERENCE. Invoice details can be divided into mandatory ones, an error in which may lead to refusal to deduct VAT, and those, errors in filling in which do not imply refusal to deduct VAT.
Mandatory details, errors in which are “dangerous”:
- those that help identify both parties to the transaction as taxpayers: name, full name. seller and buyer;
- legal address of both parties indicated in the constituent documents (indicating the actual address is an error);
- TIN and checkpoint of the parties;
- information about the sender and recipient of the cargo (if this is the same person, it must be marked “the same person”);
- manager's signature;
- volume and cost of goods supplied;
- type of product and tax rate;
- details of the payment document for prepayment.
The above details are required to be filled out , but if they contain inaccuracies, the Federal Tax Service may accept VAT as a deduction if the errors do not interfere with identifying the parties to the transaction, as well as the name of the goods, works (services), their cost, tax rate and the amount of VAT.
Some details are considered additional (they are regulated by Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). These include: the unit of measurement of the product, which may be missing, as well as additional information that is necessary for the parties to the transaction and is indicated at the request of the seller.
Adjustment invoice
In cases of changes in the price (tariff) of goods and/or clarification of the volume (quantity) of shipment, an adjustment document is drawn up (clause 3 of Article 168, Article 169, clause 10 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The most common reasons for issuing an adjustment invoice are:
- an increase (decrease) in the cost of shipment, for example, due to the provision of a discount to the buyer or a change in the terms of the transaction;
- return to the seller of goods not accepted for registration by the buyer (>letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04/01/2015 No. 03-07-09/18053);
- disposal by the buyer (by agreement with the seller) of defective goods accepted for registration (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 13, 2012 No. 03-07-09/664);
- shortage or discrepancies in information about the quantity of goods (scope of work or services) indicated in the shipping documents and invoice (>Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 02/01/2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] ).
Adjustment invoices are drawn up only if there is a contract, agreement, or other primary document confirming the consent (fact of notification) of the buyer to change the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered).
IMPORTANT!
If new invoice forms contain a significant error, corrective documents are drawn up.
Significant drafting errors are those that prevent the taxpayer from receiving a VAT deduction. In other words, when the document does not meet the requirements established by Article 169 of the Tax Code. Such errors include arithmetic errors, errors in the address and/or name of the buyer or seller, etc.
Is it possible to delete or add new rows?
In accordance with clause 9 of Government Decree No. 1137 of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer has the right to enter additional information in additional columns and lines of the invoice, but when adding, the regulated form of the document must be preserved .
IMPORTANT! To prevent the Federal Tax Service from refusing a deduction in the event of a tax audit, it is safest not to add the necessary information between the lines and columns of the required details.
This may cause controversy. Columns and lines with mandatory information cannot be deleted.
Buyer and Seller Information
The first lines of the invoice provide information about the supplier and buyer of goods (works, services). They often cause complaints from tax inspectors. Therefore, upon receiving an invoice from the supplier, you need to check whether all details are filled out correctly. For example, is the name of the supplier indicated correctly and does it correspond to the constituent documents?
In addition, if the supplier’s details do not correspond to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, tax authorities begin to suspect the seller of dishonesty. Because of this, they may refuse to deduct VAT for the buyer.
Experts from the Russian Ministry of Finance also believe that the invoice must contain reliable information about the taxpayer (Letter dated July 29, 2004 N 03-04-14/24). From here, inspectors conclude that the buyer is obliged to check information about each supplier.
However, the Tax Code does not make the buyer's right to VAT refund dependent on the actions of the seller. There are examples of court decisions that state that if the fictitiousness of the transaction is not proven, then the lack of information about the state registration of the seller does not deprive the buyer of the right to deduct VAT. This conclusion is contained in the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated June 9, 2008 in case No. A44-2525/2007. A similar position of the arbitrators is expressed in the Resolutions of the FAS of the Ural District dated March 18, 2008 N F09-1522/08-S3 and the Volga District dated September 21, 2006 in case N A72-1233/06-16/8.
Therefore, if, during an inspection, inspectors find false information about the seller of goods (work, services) in the invoice, then the right to a deduction will most likely have to be defended in court. But if the judges do not see dubious schemes in your actions, they will reject the tax authorities’ claims.
Where should I indicate the contract number on the invoice?
9 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 N 129-FZ “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as the Accounting Law), these documents cannot be recognized as primary documents. In addition to this law, the term “Government Contract Identifier” is also used for treasury support of government contracts, agreements (agreements), which is provided for by federal laws dated December 14, 2015 No. 359-FZ “On the federal budget for 2021” and dated December 19, 2016 No. 415-FZ “On the federal budget for 2021 and for the planning period 2021” and 2021." respectively, orders of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 25, 2015 No. 213n and dated December 28, 2016 No. 244n). That is, for a legal entity,
We recommend reading: How to find out if accounts have been frozen
Name of the product (description of work performed, services provided)
When filling out an invoice, in column 1, companies indicate the name of the goods shipped or a description of the work performed or services provided.
Sometimes sellers do not decipher such names or write only the technical code of the product (article). For example, “R-10568” or “KL390/58”.
Tax inspectors are convinced that the name should make it possible to clearly determine what goods were shipped, work performed, or services provided. Therefore, generalization is unacceptable. For example, if several types of goods are shipped, the name of each type is recorded on the invoice on a separate line. Otherwise, VAT on such an invoice cannot be deducted.
However, the courts come to the conclusion that the name of the goods (work, services) can be indicated in general terms on the invoice. Moreover, without indicating their specific list and decoding their qualitative composition. And inspectors do not have the right to refuse a deduction in this case. As an example, we can cite the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated June 1, 2006 in case No. A56-10950/2005.
In addition, the FAS of the East Siberian District recognized that indicating the technical code of a product cannot serve as a basis for refusing a VAT refund (Resolution of November 27, 2003 N A74-153/03-K2-F02-3792/03-S1).
Similar disputes with tax authorities occur when companies use abbreviations in the names of goods (works, services). Inspectors say there should be no cuts. However, this approach does not find support in the courts (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga Region dated April 20, 2006 in case No. A55-15666/2005-31). The arbitrators indicated that the use of an abbreviation instead of the full name of the product is legal and not prohibited by Art. 169 of the Tax Code.
However, if you do not want to enter into litigation with the tax authorities, ask the seller to indicate the well-known name of the product in column 1. And only then its brand (for example: “Car tires 18.00-25 VF-76 BM BSK”).