Minimum wage and minimum wage: concept and size
The minimum wage is the amount of remuneration established by law that the employer is obliged to provide to each of its employees on a monthly basis. The main condition for payment of wages in at least this amount is the full fulfillment of work duties by the employee (Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, to obtain it:
- a salaried employee must complete full working hours for the month;
- an employee on a tariff or piecework basis - to fulfill the work standard established for him.
Note! The minimum wage has a federal scope, that is, absolutely all employers are required to adhere to it, regardless of industry and region of residence.
At the same time, a regional agreement (regional authorities, employers, trade union representatives) can establish a minimum wage level (MW), which cannot be lower than the minimum wage (Article 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is binding on employers only in a given region, unless the employer refuses to accede to the agreement.
The minimum wage is equal to the subsistence level of the population for the second quarter of the previous year. In 2021 it is 11,280 rubles. (Article 1 of the Law “On the Minimum Wage” dated June 19, 2000 No. 82-FZ). The minimum wage for 2021 is also equal to the subsistence level for the second quarter - already 2021.
Risks! Neglect of the established values of the minimum wage and minimum wage entails a negative consequence for employers in the form of administrative, criminal and financial liability (Parts 6, 7, Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Let's consider what payments are included in the minimum wage according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Responsibility of enterprises
Each participant in labor relations is obliged to fully comply with the established requirements of the law. Violation of working conditions and remuneration entails legal liability. You can hold a company accountable in the following ways:
- filing a complaint with the labor dispute commission;
- filing a complaint through the organization's trade union;
- sending a statement of claim to the court.
To protect interests, it is necessary to collect a complete package of documents confirming the violation on the part of the company.
In addition, companies are regularly inspected to identify violations of labor laws. If it is discovered that some employees receive profits below the minimum wage, the legal entity is held accountable. In 2021, the following types of sanctions apply:
- 30 – 50 thousand rubles fine for a single violation;
- 50 - 70 thousand rubles fine for repeated bringing to administrative responsibility.
In order to avoid liability, the employer must also take into account the fact that if, after calculating all salaries, allowances and compensations, the amount of wages does not reach 11,280 rubles, an amount is added to the current figure until the amount of payments reaches 11,280 rubles. If an agreement is signed with regional authorities, the minimum wage (MW) will have to be followed.
What does the minimum wage consist of according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
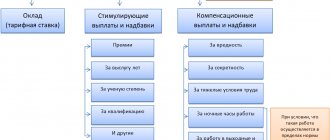
In Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines wages and indicates that it includes:
- salary;
- incentive payments;
- compensation payments.
Incentive payments are understood as material incentives for certain results or achievements of an employee. The most typical payment of this nature is a bonus. This category also includes bonuses for length of service, academic degree, qualifications, etc. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain an exhaustive list of incentive payments. The employer has the right to provide for any incentive bonuses in local regulations, as well as to develop the procedure and conditions for their accrual.
Compensation payments are compensation for any negative or difficult circumstances under which the employee is forced to work. These include allowances:
- for harmfulness;
- unfavorable working conditions;
- secrecy, etc.
Such payments should be distinguished from one-time compensation payments, which are not included in wages and are assigned solely to compensate for the costs incurred by the worker.
What does the minimum wage consist of? The salary is always included in the minimum wage and may well be less than it. The total amount that the employee will receive based on the results of the month worked, taking into account all additional payments, must be no less than this amount. In practice, many questions arise about which payments are included in the minimum wage and which are not.
An example of calculating additional payment up to minimum wage
Let us turn to the text of Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It states that a worker’s salary consists of the following payments:
- Remuneration for the performance of work duties (the amount will depend on the complexity of the work tasks, the qualifications of the employee, the conditions of the work performed, the quantity and quality of work).
- Various incentive payments (bonus payments, salary increases, additional payments and other incentive payments).
- Compensations (additional payments for work at night or on weekends, allowances for working in harmful and dangerous industries, performing labor functions in harsh climatic conditions, working in areas contaminated after radiation disasters, other additional payments and allowances of a compensatory nature).
But a logical question arises: “When actually calculating wages, the salary or the amount of the entire accrued income must be no less than the legally established minimum?” Let's find out what types of additional payments are included in the minimum wage.
Unfortunately, the law on the minimum wage itself does not provide clear explanations on this matter. Specific explanations are available in a special letter from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, published in 2009. According to this letter, the employer has the right to include bonuses, additional payments, allowances and other additional charges into the minimum established salary.
At the same time, the amount of the minimum wage should not include financial assistance and other one-time payments that are not directly related to the employee’s work activity.
Question
Question No. 1: What liability is provided for employers who ignore bringing wages to the minimum wage? (click to expand)
How should the additional payment to the minimum wage be calculated? namely: 1. What if an employee did not work for a full month and went on sick leave? Does he need to be accrued an additional payment up to the minimum wage in proportion to the time worked or does he not need to be accrued at all, since he did not work for the full period?2. Do I need to take into account sick leave, one-time bonuses, vacation pay, etc.?3.
Bonuses - monthly and one-time (annual, for holidays)
The procedure for paying bonuses is determined in the collective agreement or local regulations of the employer (for example, regulations on bonuses). They can be paid monthly, quarterly or annually, as well as on holidays. Bonus payments are a right, not an obligation of the employer.
Note! Monthly bonuses paid based on the results of work for the month are always included in the minimum wage.
In practice, the most difficult question is whether a one-time bonus is included in the minimum wage, and whether an annual bonus is included in the minimum wage. Labor legislation does not contain an answer to this.
The Supreme Court of the Republic of Karelia, analyzing whether a one-time holiday bonus paid to an employee for the New Year in accordance with the bonus regulations can be included in the minimum wage, came to the conclusion that such a payment should be included in the minimum wage (appeal ruling dated 06/05/2018 No. 33 -2448/2018).
Conclusion! Bonuses, ready-made or one-time, are included in the minimum wage.
Let's find out whether the minimum wage includes payment for holidays and weekends, as well as night hours.
What is included in the minimum wage when calculating wages in 2021
Before considering what the minimum wage is and what it includes in 2021, it is necessary to understand what this indicator is used for.
And also how a fixed minimum wage as a regulatory tool helps the state in ensuring the right of citizens to a specific level of income. The concept of minimum wage implies that the state provides a guarantee of wages to the employee to maintain an acceptable standard of living.
The lower limit of the “minimum wage” established by the state is an administrative and economic tool for regulating not only the actual amount of citizens’ incomes, but also socio-economic issues in society. By establishing a minimum wage, the state guarantees the employee protection from excessively low wages, which are often set by employers. It is also worth considering that the minimum wage depends on
Payment for holidays and weekends, as well as night hours
Work at night, on weekends and holidays, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is paid at an increased rate (Articles 153, 154). This is a kind of compensation to the employee for the lack of normal rest during periods intended for recuperation.
The question of whether payments for holidays and weekends are included in the minimum wage or whether they should be accrued above it is resolved in judicial practice in different ways.
Note! Most courts take the position that additional payment for night hours, holidays and weekends should be added to the salary and, in total, should not be less than the minimum wage.
This opinion is due to the fact that these payments relate to compensation (Part 1 of Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and are included in the salary, and, accordingly, in its minimum amount. Such conclusions are contained in the ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated August 30, 2013 No. 93-KGPR13-2, the resolution of the Presidium of the Altai Regional Court dated February 10, 2015 in case No. 44G-6/2015, etc.
At the same time, there are also opposing positions. For example, as set out in the ruling of the Perm Regional Court dated September 14, 2010 No. 33-8001.
The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation (letter dated September 4, 2018 No. 14-1/OOG-7353) and the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation also expressed their position on the issue of whether night and holiday work is included in the minimum wage. According to the Ministry of Labor, the inclusion of the above payments in the minimum wage depends on how the employee performed work at night or on weekends (holidays) - within the limits of working hours or beyond them. The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation insists that working at night, on weekends or holidays is a priori work beyond the norm, which means payment for such work should not be taken into account in the salary when compared with the minimum wage.
Conclusion! If the standard working time is exceeded due to work at night or on holidays, then additional payments should be accrued above the minimum wage.
What accruals are not included in the “minimum wage”
Why is incentives included in the minimum wage? The conditions for accrual of incentive payments are set out in local regulations of enterprises and organizations or collective agreements between the employer and employees. If bonuses are paid monthly, then the accrued amounts are constantly added to the minimum payment. However, the payment of incentives is not an obligation assigned to the employer, it is his right.
Are annual, quarterly, or one-time bonuses included in the minimum payment? In practice, this issue caused certain difficulties, since it did not receive an accurate interpretation in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Based on the ruling of the Supreme Court of Karelia No. 33-2448/2018 dated 06/05/2018, it was established that such payments are also subject to inclusion in the minimum wage component.
Let's see what other charges are included in the minimum wage. Compensatory additional payments for work on night shifts, weekends and holidays are calculated at increased rates and, accordingly, are accrued above the minimum wage. However, if this work is carried out within the framework of established duties and fixed standards of labor and working hours, then compensation is accrued within the “minimum wage”.
Additional payment for harmfulness refers to a compensation payment, which is determined by the work regime and special working conditions of employees (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Since this payment is a component of wages, it is calculated within the limits of the minimum wage.
When calculating the minimum wage, those payments that are not related to the payment of the main job, in accordance with established labor standards and working hours, are not taken into account.
Part-time work refers to work performed during free time from primary job responsibilities. The payment will be added beyond the minimum wage if the number of labor hours established by the standard is exceeded (Letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 14-1/OOG-7353). The same principle applies to overtime premiums.
Regional coefficient. This indicator is established for areas with unfavorable and severe climatic conditions (Article 148 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and implies an increased salary. Resolution of the Constitutional Court No. 38 of December 7, 2017 established that regional coefficients and additional payment for each year of work in the Far North and areas equivalent to it are not included in the “minimum wage” component.
This rule applies not only to the minimum wage indicator, but also to the minimum wage. If the minimum wage is already set above the federal minimum wage, northern additional payments are made based on the minimum wage, if it does not include them.
Additional pay for harmful work, overtime and combined work
Workers are often concerned about whether additional payments for hazardous work and overtime work are included in the minimum wage.
Additional payment for overtime work has been repeatedly analyzed by the courts from the point of view of the legality of its inclusion in the minimum wage. The courts were divided on this issue. One of the positions was that the salary can only include payment for fulfilling the labor standard, and everything worked by the employee outside the working time standard should be accrued from above (for example, the appeal ruling of the Perm Regional Court dated February 14, 2018 in case No. 33-1632/2018). However, there was also an opposite opinion (for example, the appeal ruling of the Tyumen Regional Court dated June 4, 2018 in case No. 33-2844/2018).
The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation put an end to this issue in paragraphs. 4, 5 Resolution No. 17-P dated April 11, 2019: payments for overtime work and work in hazardous conditions are payments in excess of the minimum wage.
A similar question arises when, in addition to the main job, the worker performs some part-time job function for the same employer. Decisions have been repeatedly made according to which the additional payment for part-time work should be included in the minimum wage as part of the salary (for example, the appeal ruling of the Trans-Baikal Regional Court dated 06/05/2018 in case No. 33-2256/2018). At the same time, there is another point of view (appeal ruling of the Smolensk Regional Court dated April 10, 2012 in case No. 33-894).
Conclusion! The Ministry of Labor expressed its judgment in the above-mentioned letter No. 14-1/OOG-7353, according to which any payments for work outside the established working hours should be calculated in excess of the minimum wage.
How does size increase occur?
The minimum wage in our country is established by the government. This is the federal minimum wage, which is determined by the level of inflation and the general economic situation in Russia. Ideally, it should be equal to the subsistence level, so it increases periodically.
Regional authorities, in turn, can adjust this indicator, but only upward. For example, in Moscow this minimum threshold today is not 7,500, as in many regions, but 17,561 rubles. The regional indicator is approved:
- local authorities
- trade union organizations or other employee representations
- union of employers: industrialists, entrepreneurs, etc.
Within 30 days after the publication of a regional decision on the minimum wage, private companies can express their disagreement to adhere to it. This refusal must be properly formalized and justified, and as practice shows, it is resorted to extremely rarely.
After increasing the minimum wage, all minimum wages must be increased to the established limit. The employer can increase both the salary and incentive parts by adjusting the amount of bonuses or compensation. The main thing is that together these parts reach the required size.
The Russian government plans to equate the minimum wage to the subsistence level by 2021, thereby establishing a balance between expenses and income of the population. It turns out that Russians don’t have long to wait for “ideal” salaries and benefits.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
We have a very low minimum wage, what is 7,500 rubles, this is life below the poverty line. It’s a pity that people in our country are not socially and economically protected at all.
The most interesting thing is that an increase in the minimum wage has a positive effect only on the remuneration of service personnel. This is good, but when a janitor or cloakroom attendant at a school earns more than a teacher (the salary of a primary school teacher is from 4,500 to 6,500 rubles), it becomes clear why we have a shortage of teaching staff and the quality of education leaves much to be desired.
Andrey, did you laugh? The service staff gets paid below par