What are insurance premiums
Insurance contributions are mandatory payments for pension, medical and social insurance of employees and individual entrepreneurs. From 2021, control over the calculation and payment of contributions has again been transferred to the Federal Tax Service, which until 2010 was already collecting such payments under the name Unified Social Tax (UST).
Chapter 34 has been added to the Tax Code, which regulates the calculation and payment of contributions for:
- compulsory pension insurance;
- compulsory health insurance;
- social insurance in case of temporary disability and maternity.
These types of contributions must be paid not to the funds, but to your tax office. Contributions for injuries for workers remained in the introduction of the Social Insurance Fund; nothing has changed regarding them.
Among the payers of insurance premiums listed in Chapter 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, individual entrepreneurs are also named. An individual entrepreneur has a dual status - as an individual and as a business entity. An individual entrepreneur is his own employer, so the responsibility to provide himself with a pension and health insurance falls on him.
Payment
KBK
Why is the BCC of a regular Pension Fund for exceeding 300 tr.
coincide with 2021? We have been paying for one BCC since 2021 - they are the same (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 04/07/2017 No. 02-05-10/21007).
KBC are correct here.
From February 22, 2021, a new BCC was introduced for payments over 1% of insurance premiums - 182 1 0210 160 (order No. 255n dated December 27, 2017). However, then it was canceled (order dated February 28, 2018 No. 35n). For the additional percentage, the BCC does not change.
| Payment type | Until 2021 (for any year - 2021, 2015, etc.) | After 2021 (for any year - 2021, 2021, 2021, etc.) |
| Insurance contributions for pension insurance of individual entrepreneurs for themselves in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation in a fixed amount (based on the minimum wage) | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Insurance contributions for pension insurance of individual entrepreneurs for themselves in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation with income exceeding 300,000 rubles. | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Insurance premiums for medical insurance for individual entrepreneurs for themselves in the Federal Compulsory Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund in a fixed amount (based on the minimum wage) | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0213 160 |
How long should payments be kept?
Within 6 years after the end of the year in which the document was last used for calculating contributions and reporting (Clause 6 of Part 2 of Article 28 of the Federal Law dated July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ) or 5 years (clause 459 Order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia dated August 25 .2010 N 558)
Methods
Attention! Starting from 2021, the new KBK and the new recipient of contributions are not the Pension Fund of Russia, but the Federal Tax Service. Even contributions for December must be transferred according to the new BCC to the Federal Tax Service (except for contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for injuries). Here you can find out the details of your Federal Tax Service.
There are four ways:
- Through Sberbank in cash. Completed three Sberbank pension receipts (xls). PF data must be taken from their payment slips. Then you need to provide copies of receipts to the pension fund.
- If you have a bank account, then you can use it for Samples of payment orders for 2016-2017 and the Free Business Pack program to generate them for instructing the bank to make transfers through a bank account.
- Via Internet banking. For example, Tinkoff is one of the most convenient.
- You can combine these methods or use any of them in any order.
Article 113 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the three-year limitation period does not apply to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation! For such contributions, the requirement for payment is made “no later than three months from the date of discovery of the arrears” (Article 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Arrears can be identified for any period. Therefore, keep your bills for the rest of your life.
If I am an individual entrepreneur and at the same time an employee in another organization, can I not pay Pension Fund contributions as an individual entrepreneur?
Contributions will need to be paid both here and there. Taxes and contributions of individual entrepreneurs and employees are in no way connected and there are no benefits.
What kind of income must be on the simplified tax system for 6% income in order to deduct the entire amount of the Pension Fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund from the simplified tax system?
Individual entrepreneurs (not employers) can reduce the simplified tax system (if income is simplified tax system) to 100% (employers reduce it to 50%) In 2021, we will divide 23,153.33 rubles. rubles by 0.06 and we get 385,888.83 rubles. income for the year, or 32,157.40 rubles. per month (if it is less, the simplified tax system is not paid). In 2021 we will divide 27,990 rubles. rubles by 0.06 and we get 466,500 rubles. income for the year, or 38,875 rubles. per month (if it is less, the simplified tax system is not paid). In 2021 we will divide 32,385 rubles. rubles by 0.06 and we get 539,750 rubles. income for the year, or 44,979.17 rubles. per month (if it is less, the simplified tax system is not paid).
With such income or less, an individual entrepreneur without employees is always more profitable than the simplified tax system, because then the tax is simply not paid. Unlike OSNO, UTII, PSN.
Return
You can return the funds if:
- Paid more by mistake
- If you were given the maximum for a failed return
- If you did not take into account expenses under OSNO and simplified tax system, income and expenses
See return application
Who should pay insurance premiums
The procedure for calculating and paying mandatory insurance premiums causes a lot of controversy. Entrepreneurs who do not conduct business or do not receive profit from it believe that paying mandatory insurance premiums in such situations is not justified. The state proceeds from the fact that a person who continues to be listed in the state register of individual entrepreneurs, despite the lack of activity or profit from it, has his own reasons for this. Relatively speaking, no one is stopping him, due to lack of income, from stopping his business activities, deregistration, and, if necessary, re-registering.
We recommend: Registration of individual entrepreneurs online
Courts, including higher ones, always indicate that the obligation to pay insurance premiums arises for an individual entrepreneur from the moment he acquires such status and is not related to the actual implementation of activities and receipt of income. An exception is the choice of the NAP regime, in which the payment of contributions for oneself occurs on a voluntary basis.
Payer accounting
Before starting to work, according to the provisions of Article 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, each organization (individual entrepreneur) must submit an application for registration as a taxpayer. But to start transferring money to social insurance, in most cases you do not need to register. Article 419 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation specifies all categories of contribution payers. These include, in particular, individuals who must pay fixed amounts for themselves and for those individuals who work for them:
- citizens registered as individual entrepreneurs who hire workers for their activities as individual entrepreneurs;
- lawyers in private practice;
- notaries engaged in private practice;
- arbitration managers;
- appraisers in private practice;
- patent attorneys in private practice;
- mediators.
All of the above persons calculate contributions both for themselves and from all remunerations in favor of other citizens, and are obliged to comply with the deadline for paying contributions to the Pension Fund with a salary for future pensions, social and medical services. And the Federal Tax Service receives information that they are payers from other sources (at the time of registration of individual entrepreneurs or from authorized federal executive bodies exercising functions of control (supervision) over the activities of self-regulatory organizations of insolvency practitioners, appraisers or mediators).
At the same time, international organizations and individuals who pay amounts as a mediator are required to register with the tax authority. Special forms of applications for registration were approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service No. ММВ-7-14 / [email protected] dated January 10, 2017. Another case when you will have to contact the tax office is the granting of powers to a separate division (deprivation of powers) to accrue and make payments and rewards in favor of individuals. In this case, the message form should be taken from the Federal Tax Service order No. ED-7-14 / [email protected] dated 09/04/2020.
Calculation of insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs for themselves
An individual entrepreneur is obliged to pay insurance premiums for himself as long as he has the status of a business entity, with the exception of grace periods for non-payment.
Article 430 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows individual entrepreneurs not to pay insurance premiums for compulsory pension and medical insurance if they temporarily do not operate in the following cases:
- military service under conscription, caring for a child under one and a half years old, a disabled child, a disabled person of the 1st group, elderly people over 80 years old;
- living with a spouse who is a contract military serviceman in the absence of employment opportunities for a total of up to five years;
- living abroad with a spouse sent to diplomatic missions and consulates of the Russian Federation (also no more than five years).
The absence of activity during such periods must be documented, and the suspension of payment of contributions must be reported to your Federal Tax Service. If an individual entrepreneur has the right to a benefit, but continues to receive income from business activities, then he must pay insurance premiums on a general basis.
And now the most important thing - what amounts of mandatory individual entrepreneur contributions are we talking about? In 2021, an individual entrepreneur must transfer payments for himself only to compulsory pension and health insurance. The transfer of social insurance contributions for sick leave and maternity benefits is made by individual entrepreneurs on a voluntary basis.
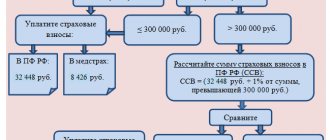
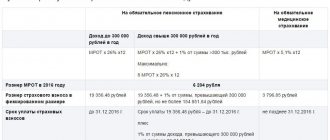
Insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs in 2021 no longer depend on the size of the minimum wage (minimum wage), but are fixed amounts approved by the Government:
- Contributions for compulsory health insurance (CHI) - 8,426 rubles per year.
- Contributions to compulsory pension insurance (OPI) are partially differentiated and consist of a fixed amount of 32,448 rubles and an additional contribution.
- An additional contribution is paid if the income of an individual entrepreneur is more than 300 thousand rubles per year. It is calculated as 1% of the amount of income exceeding this limit.
Insurance premium calculator for 2021:
It is necessary to pay insurance premiums in the amount of: - r.
The payment consists of:
| Purpose of payment | Sum | Payment date |
| Fixed contributions for compulsory pension insurance | - R. | Pay by December 31, 2021 |
| Additional contributions for compulsory pension insurance | - R. | Pay by July 1, 2021 |
| Fixed contributions for compulsory health insurance | - R. | Pay by December 31, 2021 |
✐ Example ▼
Let's assume that an entrepreneur received income in the amount of 1,200,000 rubles in 2021. Let's calculate the amount of insurance premiums payable by individual entrepreneurs:
- Pension insurance contributions will be calculated as follows: 32,448 + ((1,200,000 – 300,000) * 1%) = 41,448 rubles.
- Health insurance premiums will remain at the same level and amount to 8,426 rubles at any income level.
Total: the total amount of insurance premiums for yourself in this example is 49,874 rubles.
An upper limit on the amount of contributions to compulsory pension insurance has also been introduced - in 2021, this amount cannot exceed 259,584 rubles.
The above formulas show the calculation of the cost of a full insurance year; if the entrepreneur was not registered at the beginning of the year or ceased activity before its end, then all calculated amounts are proportionally reduced. In these cases, it is necessary to take into account only full months and calendar days (if the month is incomplete) in which the person had the status of an entrepreneur.
Let's summarize:
- In 2021, individual entrepreneurs’ contributions for themselves with an annual income not exceeding 300 thousand rubles, including in the absence of activity or profit from it, will amount to 40,874 rubles, based on: 32,448 rubles of contributions to compulsory health insurance plus 8,426 rubles of contributions to compulsory medical insurance .
- If the amount of income exceeds 300 thousand rubles, then the amount payable will be 40,874 rubles plus 1% of income exceeding 300 thousand rubles.
What has changed compared to 2021
In 2021, the insurance burden on individual entrepreneurs who pay premiums “for themselves” will generally remain at last year’s level. Let us remind you that at the end of 2021, individual entrepreneurs must pay personal medical contributions in the amount of 8,426 rubles, and pension contributions in the amount of 32,448 rubles. plus 1% of the amount of income that exceeded RUB 300,000.
Changes will occur for entrepreneurs who work in industries affected by coronavirus. For them, the amount of fixed pension contributions for 2021 was reduced by 12,130 rubles. and amounted to 20,318 rubles. For more details, see “For individual entrepreneurs affected by the coronavirus crisis, contributions for oneself have been reduced.” This relaxation does not apply in 2021.
REFERENCE
For 2022 and 2023, the amount of personal contributions of individual entrepreneurs will be increased. Fixed medical contributions for 2022 will be 8,766 rubles, for 2023 - 9,199 rubles. Pension contributions in a fixed amount will increase to 34,445 rubles in 2022, and to 36,723 rubles in 2023. Such contribution amounts are set forth in paragraph 1 of Article 430 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What is considered income when calculating insurance premiums?
Determining the base for calculating individual entrepreneur contributions depends on the chosen taxation system:
- on the simplified tax system Income - income from sales and non-operating income excluding expenses;
- on the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” - the difference between income and expenses.
In our service, you can prepare a notification about the transition to the simplified tax system for individual entrepreneurs absolutely free of charge (relevant for 2021):
Create an application for the simplified tax system for free
- in the patent taxation system, the potential annual income on the basis of which the cost of the patent is calculated;
- on the unified agricultural tax - income taken into account for tax purposes, without deducting expenses;
- on OSNO - income received from business activities, minus professional deductions.
If an individual entrepreneur combines tax regimes, then income from different regimes is summed up.
To choose the most profitable tax system specifically for your business, we recommend taking free advice from professionals who will help you choose a regime with minimal payments.
Free tax consultation
Individual entrepreneur taxes
A taxation system or regime is understood as a special procedure for calculating tax deductions. Tax regimes differ from each other in the following elements of taxation: the object of taxation and the tax base, the tax rate, the tax period, the procedure for calculating and paying the tax.
Find out about tax holidays for individual entrepreneurs in your region
Most often, individual entrepreneurs choose one of the special tax regimes. These regimes are preferential, and to work on them you must comply with the restrictions and requirements established by law. There are several such regimes in Russia:
- simplified taxation system (STS);
- patent tax system (PTS);
- single agricultural tax (USAT);
- professional income tax (PIT).
The choice of taxation system is the basis of tax optimization, i.e. legal actions of an entrepreneur to reduce the tax burden. An individual entrepreneur can choose a tax system himself, but if he cannot meet the necessary requirements or does not declare his choice in a certain order, then his activities will be conducted within the framework of the general (main) taxation system - OSNO.
To avoid a situation in which you will not be able to apply a preferential tax regime, you should carefully consider the choice of OKVED codes for individual entrepreneurs, since the tax office does not allow reporting under special regimes for a number of activities. For those who need help choosing permitted codes, we can offer a free selection of OKVED codes.
Free selection of OKVED
We recommend: What types of activities are subject to licensing
To ensure that an individual entrepreneur’s taxes do not become the main item of his expenses, it is worth asking yourself a few questions.
1.Will the expected income be constant or will its size change?
There is a direct connection between the irregularity of income and the choice of tax system, and based on this, it is worth making a calculation of expected income at least a quarter in advance. In the simplified tax system, unified agricultural tax, NPD and OSN regimes, the tax base, i.e. the amount on which taxes will be calculated arises only when the entrepreneur begins to receive real income. In the PSN regime, the basis for such calculations are other indicators, therefore, in these cases, the individual entrepreneur must pay taxes regardless of the amount of income received, including if there is no income at all.
2.Will hired labor be involved and how many workers will be needed?
The number of employees when choosing a taxation system can become a limiting factor, for example, for the PSN the number of employees should not exceed 15 people, and for the simplified tax system - 100 people. The cost of a patent will also depend on the number of employees, in those regions and for those types of activities that take this indicator into account. The presence of employees will also be important in cases where an individual entrepreneur has the opportunity to reduce the tax payable at the expense of paid insurance premiums.
3.What proportion of income will be expenses, and will you be able to document them?
When choosing between the options of the simplified tax system “Income 6%” or the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses 15%”, you need to imagine the size of the expected expenses. In cases where possible expenses will exceed 65% of income, you should choose “Income minus expenses,” but only if you can document the expenses. If there are no supporting documents, or the share of expenses is less than 65% of income, then the “Income” option is most likely more profitable.
4.What types of activities in your region are included in the lists of types for PSN?
The types of activities on the PSN are determined by regional laws, but within the limits permitted by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. You can apply for an individual entrepreneur patent for many household services, retail trade, and small-scale production.
It may be difficult for you to compare all these criteria now, but later we will look at each regime in more detail, which will clarify the issue of choosing a taxation system.
And for those who prefer an individual approach, we can offer a free consultation with a tax specialist who will help you choose a tax regime taking into account the specifics of your business and region.
Free tax consultation
Individual entrepreneur taxes on the simplified tax system
Let's start with the most popular system among small businesses and individual entrepreneurs - the simplified taxation system (STS). Entrepreneurs working on a simplified basis are tax payers, which replaces for them the payment of personal income tax on business activities and property tax used in business. The object of taxation on the simplified tax system is income or income reduced by the amount of expenses, so here you can choose the option “STS Income” or “STS Income minus expenses”.
Not only receipts from the sale of goods and services are recognized as income, i.e. revenue, but also some others, called non-operating. Expenses include not those that the entrepreneur himself considers justified, but a closed list of them, given in Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It must be said that this list is quite extensive and for the most part recognizes the real expenses of individual entrepreneurs. In addition to the expenses themselves, the code also specifies the procedure for their recognition; in particular, expenses can only be taken into account after payment. You also need to take a responsible approach to documenting expenses, because... Violation of the requirements for supporting documents may lead to their non-recognition by the tax inspectorate.
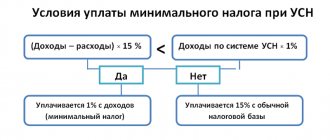
The tax base for the “Income” option is the monetary value of income. For the “Income minus expenses” option, the tax base will be the monetary value of income reduced by the amount of expenses. To calculate the amount of tax payable, you need to multiply the tax base by the tax rate, which is 6% for “Income” and 15% for “Revenue minus expenses.”
To develop certain types of activities and attract investment in the regions, local authorities can reduce the standard tax rate from 15% to 5%. You can find out what rate and for what activity is approved in your territory, in the regional law on the establishment of differentiated tax rates of the simplified tax system. Thus, if your region has a reduced tax rate and you can confirm your expenses, then individual entrepreneur taxes when applying the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” can be minimized.
But even taking into account the costs, it is important not to overdo it, because... here the individual entrepreneur has the obligation to pay the minimum tax. What does it mean? If you worked at a loss, i.e. expenses exceed the income received, you will have to pay a minimum tax of 1% of the income received.
The Income option can be a particularly attractive opportunity to reduce your assessed tax on premiums paid. At the same time, individual entrepreneurs without employees can reduce the tax on the entire amount of contributions, and with small incomes, a situation may arise that there will be no tax payable at all. Individual entrepreneurs with employees can reduce the tax due to the amounts of insurance premiums paid both for themselves and for their employees, but not more than 50%.
On “Income minus expenses” it is not allowed to reduce the tax calculated for payment by the amount of insurance premiums, but insurance premiums that an individual entrepreneur pays for himself and for his employees can be taken into account as expenses when calculating the tax base. This also reduces the tax payable.
Let's finish our acquaintance with simplified restrictions that must be observed to work on this system. For individual entrepreneurs there are few of them - the number of employees should not exceed one hundred people, the simplified tax system is not allowed in the extraction and sale of minerals, except for commonly occurring ones, and in the production of most excisable goods. In addition, an individual entrepreneur may lose the right to simplification after his income for 2021 exceeds the established limit.
If you find the simplified system beneficial and convenient for yourself, then you can prepare an application for transition to the simplified tax system 2021 absolutely free:
Create an application for the simplified tax system for free
Individual entrepreneur taxes on PSN
The patent tax system or IP patent is the only tax regime intended only for individual entrepreneurs. A patent can only be obtained for the type of activity specified by the law of the subject of the Russian Federation where it is planned to conduct business.
The permit is valid only on the territory of the municipality where it was issued, so the individual entrepreneur must submit an application to the Federal Tax Service at the place where the patent is valid. For cargo transportation and distribution trade, it is allowed to use one patent when providing services throughout the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation. Restrictions for this regime relate to the number of hired workers - no more than 15, and the loss of the right to use PSN will occur if the annual income exceeds 60 million rubles.
Calculating the annual cost of a patent is quite simple. To do this, you need to know the “potentially possible annual income” for the chosen type of activity and multiply it by 6%. You can also find out the amount of potential income from the regional law on PSN. Another option is the Federal Tax Service calculator to calculate the cost of a patent. A patent is issued for any period within a calendar year. An individual entrepreneur can have several patents and calculate its value for each of them.
Payment for a patent occurs as follows:
- A patent issued for a period of up to six months must be paid in full no later than its expiration date;
- If the patent validity period is from six months to a year, then one third of its full cost must be paid no later than 90 days after the start of validity, and two thirds - no later than the expiration date of the patent.
Individual entrepreneur taxes on Unified Agricultural Tax
The unified agricultural tax is intended for agricultural producers, i.e. those who produce, process and sell agricultural products. This also includes fisheries organizations and entrepreneurs. The main condition for the Unified Agricultural Tax is that the share of income from the sale of agricultural products or catch must exceed 70% of total income from goods and services.
Agricultural tax is calculated according to the same principles as the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”, but the tax rate is 6% of income reduced by the amount of expenses. In addition, from 2021, payers of the Unified Agricultural Tax are required to remit VAT, but an exemption from it can be obtained.
Individual entrepreneur taxes on OSNO
And finally, if the individual entrepreneur has not chosen any of the special modes, then he will work on the main tax system. In addition to VAT at a rate of 20%, 10% or 0%, you must pay personal income tax (PIT) at a rate of 13%. The tax base for individual entrepreneurs under this regime will be income from business activities, to which it is allowed to apply so-called professional deductions - documented and economically justified expenses. If expenses cannot be confirmed, then income received can only be reduced by 20%.
Insurance premiums for OSNO can be included in expenses in full, both for yourself and for employees. It is worth choosing OSNO if the majority of your customers will be VAT payers, who will benefit from working with you, because they will have the opportunity to take into account input tax.
Individual entrepreneur taxes on NAP
The tax on professional income has been valid in all regions of the Russian Federation since 2021. Activities are limited to the provision of services, performance of work and sale of self-made goods. Workers cannot be hired for NAP, and annual income should not exceed 2.4 million rubles. But the tax rate in this regime is very low - only 4% if payment for services comes from individuals. If the NPD payer works with legal entities, the rate is 6%. Insurance premiums for yourself are transferred on a voluntary basis.
Deadlines for payment of insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs
The entrepreneur must pay insurance premiums for himself in terms of income not exceeding 300 thousand rubles (i.e. the amount of 40,874 rubles) by December 31 of the current year. At the same time, it is worth taking the opportunity to reduce, in some cases, the amount of accrued taxes by paying insurance contributions quarterly, which will be discussed in more detail in the examples.
Please note: there is no such thing as “insurance premiums of individual entrepreneurs for the quarter.” The main thing is to pay the entire amount of 40,874 rubles by December 31 of the current year in any installments and at any time. The division of the indicated amount into four equal parts is used only for conditional examples.
For example, if you don’t expect to have income in the first and (or) second quarter using the simplified tax system, then there is no point in rushing to pay your contributions. It may be more profitable for you to pay 3/4 or even the entire annual amount in the third or fourth quarter, when significant income is expected. And vice versa - if the main income is expected only at the beginning or middle of the year, then the main amount of contributions must be paid in the same quarter.
An additional amount equal to 1% of annual income exceeding 300 thousand rubles must be transferred before July 1, 2022. But if the limit is exceeded already at the beginning or middle of the year, then these additional contributions can be made earlier, because they can also be taken into account when calculating taxes.
Or maybe it’s more profitable to be self-employed?
Starting from January 1, 2021, individual entrepreneurs will be able to completely avoid paying their own contributions to the Pension Fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. To do this, it will be enough to switch to a new special regime for the self-employed. To do this, their annual income should not exceed 2.4 million rubles. In the special regime for the self-employed, you will not have to submit a declaration and pay pension contributions for yourself.
Here is a list of regions where registration of self-employed people will be allowed from January 1, 2021:
- Saint Petersburg;
- Voronezh region
- Volgograd region;
- Leningrad region;
- Nizhny Novgorod Region;
- Novosibirsk region;
- Omsk region;
- Rostov region;
- Samara Region;
- Sakhalin region;
- Sverdlovsk region;
- Tyumen region;
- Chelyabinsk region;
- Krasnoyarsk region;
- Perm region;
- Nenets Autonomous Okrug;
- Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug-Ugra;
- Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug;
- Republic of Bashkortostan.
4 regions where a pilot project for the self-employed is already underway also remain on the list of permitted ones:
- Moscow;
- Moscow region;
- Kaluga region;
- Republic of Tatarstan.
Read also
29.07.2020
Insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs and employees
Having become an employer, in addition to contributions for himself, the entrepreneur must pay insurance premiums for his employees.
Read more: How can an individual entrepreneur organize accounting?
In general, the amount of insurance premiums for employees under employment contracts amounts to 30% of all payments in their favor (except for those that are not subject to taxation for these purposes) and consists of:
- contributions to compulsory pension insurance for employees of public pension insurance companies – 22%;
- contributions to compulsory social insurance OSS – 2.9%;
- contributions for compulsory health insurance compulsory medical insurance – 5.1%.
But from April 1, 2021, due to the coronavirus epidemic, employers belonging to small and medium-sized businesses pay contributions for payments to employees above the minimum wage at lower rates.
Additionally, a contribution is paid to the Social Insurance Fund for compulsory insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases - from 0.2% to 8.5%. Under civil contracts, remuneration to the contractor is subject to mandatory insurance contributions for compulsory health insurance (22%) and compulsory medical insurance (5.1%), and the need for social insurance contributions must be provided for in the contractual terms.
Unlike individual entrepreneurs’ contributions for themselves, insurance premiums for employees must be paid monthly, no later than the 15th day of the month following the billing month.
If you need help in selecting types of activities that require the lowest insurance premiums for workers, we advise you to take advantage of a free consultation with our specialists.
Free selection of OKVED
Calculation
The service guarantees confidentiality and protection of personal data. Only numbers are used for calculations - no personal data needs to be entered.
For individual entrepreneurs throughout Russia, insurance premiums are calculated the same (there are no regional laws) depending on the type of activity. There are no benefits or categories, except for benefits for some industries affected by coronavirus in 2021..
Online accounting in which you can calculate individual entrepreneur payments and other taxes and send reports via the Internet. (advertising)
How to reduce the amount of taxes payable through insurance premiums
It is possible to reduce the accrued tax itself only in the “Income” and PSN modes, and to reduce the tax base, i.e. the amount from which the tax will be calculated can be used on the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”, unified agricultural tax and on OSNO.
Our specialists can help you choose the most favorable tax regime and tell you how to properly reduce your insurance premiums.
Contributions of individual entrepreneurs to the simplified tax system with the object of taxation “Income”
Entrepreneurs in this regime who do not have employees have the right to reduce the accrued single tax by the entire amount of contributions paid (Article 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There is no need to notify the tax authorities about this, but the paid contributions must be reflected in the Book of Income and Expenses and in the annual tax return under the simplified tax system. Let's look at a few simplified examples.
✐Example ▼
1. An individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system “Income” and working independently received an annual income in the amount of 380,000 rubles. The calculated tax was 22,800 rubles. (380,000 * 6%). During the year, 40,874 rubles were transferred. insurance premiums, i.e. only a fixed amount (an additional contribution of 1% of income over 300,000 rubles will be transferred by the individual entrepreneur until July 1 of the next year). The entire amount of the single tax can be reduced by the contributions paid, so there will be no tax payable at the end of the year at all (22,800 - 40,874<0).
2. The same entrepreneur received annual income in the amount of 800,000 rubles. The accrued tax amounted to 48,000 rubles (800,000 * 6%), and contributions paid quarterly during the year - 45,874 rubles, based on (40,874 + 5,000 ((800,000 - 300,000) * 1%). The amount of tax payable will be only (48,000 – 45,874) = 2,126 rubles.
3. If an entrepreneur uses hired labor in this mode, then he has the right to reduce the accrued single tax at the expense of the amounts of contributions paid (contributions for himself and for employees are taken into account) by no more than 50%.
The individual entrepreneur discussed above with an annual income of 800,000 rubles. has two employees and paid 120,000 rubles as contributions for himself and for them. The accrued single tax will be 48,000 rubles. (800,000 * 6%), however, if there are employees, it can only be reduced by 50%, i.e. for 24,000 rub. The remaining 24,000 rubles. the single tax must be transferred to the budget.
Free tax consultation
Individual entrepreneur contributions to the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”
Entrepreneurs in this mode take into account the transferred contributions in expenses, thereby reducing the tax base for calculating the tax. Expenses can include both individual entrepreneurs’ contributions for themselves and contributions for employees. They cannot reduce the tax payable itself, so the amounts saved will be less than under the simplified tax system “Income”.
Individual entrepreneur contributions on the general taxation system
These entrepreneurs include paid contributions in their expenses and thus reduce the amount of income on which personal income tax will be charged.
How to correctly determine the amount of income from which contributions are paid?
In order to correctly enter into the appropriate window of the calculator the key indicator on which the amount of mandatory insurance payments will depend, you need to know exactly what financial results fall under the concept of “income of an individual entrepreneur” and are the basis for this calculation.
If the size of the contribution itself does not depend on the tax system, then this is decisive for determining income.
- Entrepreneurs under the general taxation system must pay contributions on the same income on which they pay personal income tax (not to be confused with the tax base; unlike the amount of income, it is reduced by tax deductions).
- Under the simplified tax system (USN), for calculating contributions, income is taken that is not reduced by the amount of expenses, even if the tax is paid according to the “income minus expenses” scheme.
- When using UTII, income for calculating insurance premiums is considered imputed, which must be calculated according to a specially provided formula, including basic profitability (it is determined by the Tax Code depending on the indicators of the object), multiplied by corrective indicators.
- The patent system takes into account potentially real income established by regional laws, and it is taken as an insurance base.
- When combining several tax systems at the same time, the amounts of income to take into account the amount of insurance premiums are added up.
Individual entrepreneur reporting on insurance premiums
An individual entrepreneur who does not have employees does not have to submit reports on the payment of insurance premiums for himself. In 2021, the individual entrepreneur must submit the following reports, reflecting the amounts of contributions transferred for his employees:
- to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation monthly, according to the SZV-M form - no later than the 15th day of the month following the reporting month;
- to the Social Insurance Fund quarterly in form 4-FSS - no later than the 20th day of the month following the reporting quarter;
- to the Federal Tax Service on a quarterly basis in form 6-NDFL - no later than the end of the next month after the end of the reporting quarter;
- to the Federal Tax Service on a quarterly basis in the form of a single calculation - no later than the 30th day of the next month after the end of the reporting quarter.
Also on the topic: How is the pension of an individual entrepreneur calculated?
How to use the calculator
Select the period for which you want to calculate contributions. This can be a full year or part of it; the calculator will automatically recalculate the amount of fixed contributions in accordance with the term.
If you worked as an individual entrepreneur for less than a full year, indicate the start and end date of your activity:
- start of activity - date of registration in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs;
- end of activity - date of exclusion from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs.
In the “Income” field, enter the amount of income for the year. For amounts exceeding 300,000, 1% must be transferred to the Pension Fund. We will discuss how to determine income below.
After entering the data, the calculator will automatically calculate the amount of contributions to be paid and display it at the bottom.
We will answer complex questions about calculations below.
Responsibility of payers for violation of deadlines
Contributions are collected from legal entities - policyholders and individuals with individual entrepreneur status, in order to financially ensure the implementation of the rights of insured persons to receive compulsory insurance of the appropriate type. Violation of the terms of transfer entails liability under the provisions of Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if we are talking about pension, health insurance or contributions in connection with temporary disability and in connection with maternity.
The Ministry of Finance spoke about the procedure for bringing violators to justice in letter No. 03-02-07/1/31912 dated May 24, 2017. Officials indicated that the provisions of Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are fully applicable to late payment of amounts of insurance premiums correctly calculated and reflected in the calculations timely submitted by payers to the tax authorities. But they are applied taking into account the position set out in paragraph 19 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 57 dated July 30, 2013 - only with the collection of penalties (without imposing a fine).
As for violations with payments to the Social Insurance Fund, the provisions of Article 19 of Federal Law No. 125 of July 24, 1998 provide for the possibility of imposing a fine of 20% for unintentional and 40% for intentional failure to pay the calculated amounts for injuries. But these sanctions are applied only if there is no payment due to:
- understating the base for accrual;
- incorrect calculation or unreasonable application of a reduced tariff;
- other unlawful actions of the policyholder.
If the reason for violating the transfer deadline is disorganization, then the violator only faces the accrual of a penalty.