One of the main tax fees levied on citizens of our country is personal income tax. In what budget this payment from the pocket of each Russian is credited is of interest to many, since all of us, of course, would like to see what favorable changes the money spent will contribute to. In addition, which budget to send personal income tax to is a predetermining question for each employing organization that withholds tax from its employees, and other organizations that need to independently pay tax on the income they receive.
Personal income tax: which budget is it included in?
Objects subject to personal income tax
According to Russian legislation, there are two main objects that are subject to personal income tax. First of all, this is the profit that a resident of Russia receives during the reporting period, regardless of where its source is located - within the country or outside it.
Another object is the profit of non-residents of the country, who, without changing, draw it from Russian sources. In addition to labor income, this includes:
- Money paid for work under an official agreement.
- Income from the sale of your property, shares in organizations, shares, and so on.
- Funds received for the exploitation of the author's rights to intellectual or other property.
- Renting out property located in Russia.
By law, you must independently declare your income:
- Persons conducting private practice (lawyers, private detectives, notaries).
- Persons who received unearned income from the sale or rental of property.
- Citizens whose income is transferred from sources outside the country.
- IP-schniks.
- People who received remuneration from a source that does not have the status of a tax agent.
- Heirs of the authors of inventions, works of science or art, receiving rewards.
- Citizens who have won money in risk-based games (lotteries).
An important point is that the annual deadline for self-declaring income is April 30th.
Where is the transferred personal income tax paid?
Where is personal income tax paid, to which budget? The conditions are completely simple, regardless of whether the calculation is made by the payer himself or his tax agent.
After filing a declaration of income received for the year, in accordance with the Tax Code, Art. 228 the declared amount must be paid before the middle of next year, that is, the deadline is July 15.
Provided that it is a day off, Art. 6.1 explains that it is possible to postpone it to the working day that follows.
Payment of tax by persons of any category who stopped working during the year has slightly different specifics. You need to immediately submit a declaration and deposit the required amount into the federal budget within two weeks.
Modern financial technologies offer several attribution methods:
- Non-cash transfer by bank transfer.
- By depositing cash into cash desks located in local administrations.
- By postal transfer.
- Transfer using a non-bank credit organization licensed by the Central Bank of Russia for such operations.
- Regional taxes
This category of tax revenue is also fixed by the legislation of our state and is also mandatory for all business entities.
The Tax Code strictly stipulates all the nuances of these taxes.
This is a determination of the deadlines for payment, rates and reporting forms of regional taxes, which are regulated by the laws of individual constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
These include the following regional taxes:
- Transport tax placed on the balance sheet of the enterprise.
- Taxation of property and funds belonging to a business entity.
- Calculation of tax on income received from running a gambling business.
- The amounts of tax revenues make it possible to fill the federal budget at this level. Federal laws regulate the general principle of forming the tax base and system.
- Regional administration allows you to set the rate and volume of benefits for this category of taxes.
Income that is not subject to taxation
Despite the fact that personal income tax is imposed on any funds that fit the definition of “income,” the Tax Code of Russia includes a specific list of income that is not taxed. Whether this income is received by a resident or non-resident of the country does not matter in this case. The list of such income includes:
- Cash benefits for pregnancy and childbirth, alimony.
- Pension accruals for persons who have reached the legally established age for retirement or who have been recognized as disabled by an examination.
- Compensation for damage to employee health.
- Gifts worth less than 4,000 rubles received by an employee or former employee (pensioner) from the employer.
- Financial assistance in the amount of less than 4,000 rubles received by an employee or former employee (pensioner) from the employer.
- Financial assistance to low-income families whose status is confirmed by the state.
- Payment from the employer's net profit for medical care for its employee or his family members.
- Rewards for blood donors.
- Compensation for damage to employee health.
- Compensation for the cost of vouchers to sanatoriums and other institutions related to the health of citizens (except for tourists).
- Expenses for improving the professional qualifications of an employee.
- Payment for retraining, education or professional training of an employee.
- Scholarships received by students of higher educational institutions.
- Grants for educational or scientific activities.
- Compensation in connection with dismissal, the amount of which is not more than three times the average monthly salary (six times the amount for residents of the Far North).
- Financial assistance to the family of a deceased employee.
- Financial assistance paid to citizens affected by a natural disaster or other emergency situation.
- Funds donated to victims of terrorist attacks.
- Compensation to an employee for the cost of paying interest on a loan for construction or purchase of real estate.
Changes to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation related to the implementation of social policy
Changes to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation aimed at implementing the main directions of social policy should be grouped separately:
- assistance to children left without parental care is not subject to personal income tax;
- funds, real estate and securities transferred for the formation and replenishment of the target capital of a non-profit organization and subsequently returned to the donor are exempt from personal income tax;
- When determining the financial result of transactions with securities received by an individual donor in the event of dissolution of the target capital, cancellation of a donation or other return of securities transferred to replenish the capital of an NPO, only those costs of transactions with securities that were incurred by the individual before the specified transfer (clause 13 of article 214.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- when transferring donations to charitable organizations and other socially oriented non-profit organizations, an individual has the right to receive a social deduction;
- When returning a donation to an individual, in connection with the transfer of which he applied a social deduction, he must include this deduction amount in the personal income tax base for the period in which the property or funds were actually returned to the donor.
It is advisable to highlight and analyze the main areas of taxation of personal income, which, in our opinion, mediate the increasing role of personal income tax in budget revenues:
- change in the composition of non-taxable income;
- increasing the amount of tax deductions;
- differentiation of the concepts of “dividends” and “wages”;
- development of a methodology for determining “impersonal” income received in kind. Let's look at each direction in more detail.
Personal income tax – what is it?
Individuals receiving income (cash) are required to give up part of it in favor of the state budget at a set rate. This alienated part is considered an income tax, which is direct and basic for the entire population of Russia.
Please note that this tax is paid not only by individuals, but also by legal entities.
The calculation of the amount due for payment to the state treasury is made on the basis of two basic values:
- tax (financial) base;
- tax rate.
Let's talk about these important concepts.
Characteristics of the tax base
For each type of income (object of taxation), such a characteristic as the tax base is used. It is necessary to measure such an object, to express it quantitatively. Essentially, the tax base is the set of incomes on which direct taxes are levied. At the end of each tax period (month, three months, year or other time frame), the tax base is determined.
There is a system - tax accounting, which summarizes data to determine the tax base. Each organization in the status of a tax agent independently creates such an accounting system. This is a necessity established by law. All paying organizations are responsible for the timeliness, reliability and transparency of tax information. According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there are two methods of accounting for the tax base: cash and cumulative. In the first case, actual income that has already been received is taken into account. The accumulative method takes into account not the money itself, but the rights to it. That is, if the organization has not yet received funds, but has the right to receive them, this fact will be taken as income.
According to Article 210 of the Tax Code of Russia, three forms of income of payers are included in the tax base: material, natural and monetary
In this case, for each form the financial base will be calculated separately, since each type of income has its own rates. The tax base is a value that helps in calculating the amount of income tax. To calculate it, you need to multiply the base by the tax rate.
Tax rates in the Russian Federation
The tax rate is the amount of tax assessments multiplied by the unit used to measure the tax base. This is a mandatory element and the main criterion for calculating any tax established by law.
Table 1. Tax rates in the Russian Federation
| Bid | Meaning |
| 13% | The standard 13% interest rate is levied on the income of individuals, no matter whether it is funds received as wages or money for the sale of an apartment. With the onset of 2015, this rate became valid for the payment of dividends. Please note that the financial basis for dividend deductions is determined separately from other incoming funds that are subject to tax at the standard rate. |
| 9% | 9% is taken from money received in the form of pre-2007 mortgage bonds. The same rate is valid for funds received by the founders of the union managing the mortgage coverage, which were acquired as a result of the purchase of mortgage participation certificates made before 2007. |
| 15% | Non-residents of the Russian Federation, who are individuals who have shares in companies located and operating in Russia, and therefore receive funds here, are subject to a rate of 15% of the amount of income received. |
| 30% | Other income of non-residents not included in the previous paragraph is taxed at 30%. |
| 35% | 35% is withdrawn from cash winnings received by citizens for participating in any kind of event, as well as from the percentage of the bank deposit made. |
What is the tax percentage?
The Federal Tax Service applies five personal income tax rates.
9% - the smallest percentage applies
- to dividends received before 2015;
- to interest on mortgage-backed bonds issued before January 1, 2007;
- to the income received by the founders of trust management of mortgage coverage.
13% - paid from salaries and other income of residents of the Russian Federation.
15% — dividends received by non-residents of the Russian Federation from Russian organizations are reduced by them.
30%- paid from salaries and other income of non-residents of the Russian Federation.
35% - subject to the highest tax
- winnings and prizes received in competitions, games and other events for the purpose of advertising goods, works and services;
- interest income on bank deposits;
- the amount of savings on interest when taxpayers receive loan funds;
- payment for the use of funds of members of a consumer credit cooperative, in other words, shareholders.
We correctly calculate the amount of personal income tax
To avoid imposing a fine for an incorrectly paid amount, it is worth figuring out how to calculate personal income tax. Some will say that the employer does this for most citizens, but at any time you may need to declare income on your own - when you receive winnings, money from the sale or rental of property.
Any payer can calculate the amount of tax
The first step is to quantify the income subject to tax. Next, find out the tax rate for each type of income and calculate the tax base. It was already mentioned above that depending on the type of income, a specific rate is applied, and each rate has its own financial base. The last step, when the named quantities are known, is simple calculations. You need to use the formula specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: multiply the tax base by the tax rate, as a result the total amount of personal income tax will be determined.
General aspects
Ordinary Russian citizens, for whom their main and only income is wages, rarely think about paying personal income tax.
Yes, they don’t need this, since wage taxes are paid for them by the employer, acting as a tax agent.
He independently calculates the amount to be withheld and transfers it to the budget. The employee already receives a “net” salary.
For citizens, the obligation to pay income tax arises when they receive income not related to official employment.
For example, a person can sell real estate or rent out an apartment. Tax on income not related to business is paid after the year of profit.
The absence of a requirement from the Federal Tax Service to pay taxes is not a compelling argument for ignoring the obligation to pay.
The taxpayer is required to independently calculate the tax, file a tax return and pay the required contribution.
The 3-NDFL declaration is submitted no later than April 30 of the year following the year in which the income was acquired. And the due amount must be paid before July 15 of the year of filing the declaration.
Failure to submit a declaration and non-payment of tax may result in a fine, which is paid in addition to the mandatory payment.
What it is
Personal income tax, or personal income tax for short, is a type of direct taxes in the Russian Federation, which is one of the main fees.
The basis for collecting tax is the receipt of taxable income. In this case, the tax base for calculating the payment amount becomes the total income of an individual, excluding documented expenses.
The tax amount is set as a percentage of the tax base. Moreover, depending on the category of payer, the rate varies.
The standard value for working Russians is defined as 13%. Non-residents pay tax at a rate of 30%. In addition, there are other betting options.
When establishing the tax base, all types of income acquired by the payer are taken into account, both in cash or in kind, and as material benefits.
Various deductions from income received, including those based on court decisions, do not reduce the tax base. The tax base is established for income groups corresponding to the same rate.
What do they pay for?
The objects of income taxation are income received by individuals:
Types of taxable income include:
- salary for official employment;
- payment for work performed under GPC contracts;
- dividends;
- insurance payments;
- income received from the disposal of property;
- income from the sale of real estate or other valuable assets;
- other income received from activities in Russia or abroad (for residents).
Certain types of income are not subject to personal income tax. Their list is determined by Article 215, Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. As a rule, such income includes social payments, benefits, subsidies and similar amounts.
Current standards
Personal income tax, or personal income tax, applies to absolutely all individuals. According to the law, individuals mean Russians and foreigners, adult citizens and minors, women and men, that is, absolutely everyone.
The essence of taxation comes down to the fact that once income has appeared, personal income tax must be paid. The procedure for collecting personal income tax is discussed in detail in Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, the legal framework for income tax includes the following standards:
- Federal Law No. 251 dated;
- Federal Law No. 281 dated;
- Federal Law No. 229 dated;
- Federal Law No. 279 dated;
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. ММВ-7-11/ dated .
Certain nuances of the calculation and payment of personal income tax are explained in the Letters of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Finance.
Money calculated and withheld
An employee's income tax goes through two stages before ending up in the government treasury. Every month, at the end of the reporting period, the accounting department accrues personal income tax. The funds will be transferred to the budget later, at the time the employees actually receive their wages. It turns out that in the first order the tax agent calculates (withholds) the amount allocated for the transfer, and in the second order he performs the calculation itself. In the accounting department of any company, settlement journals are kept, and each transaction has its own. They include information about the employee: his income, rates, accrued and withheld amounts.
The fact of the impossibility of transferring tax funds due to insurmountable reasons is also described in law. If a tax agent company finds itself in this situation, it is obliged to submit to the inspectorate the appropriate papers documenting what is happening as soon as possible.
Listed personal income tax and features of its formation
This tax is paid by almost all citizens of our country who receive active or passive income. Federal laws establish that numerous citizens of foreign countries who conduct active business activities are also required to pay personal income tax on an equal basis with our compatriots.
The state system has legislatively established not only the tax base, but also a graduated system of tax rates.
These are five levels of rates, each precisely corresponding to a certain type of income received.
In the period from 2014 to 2015 financial year, federal law established the accrual of personal income tax as follows:
- 9% tax deduction. Applies to dividends, income from a share of the work of organizations, % of mortgage-backed bonds, systemic trust management.
- 13% tax on labor activity and work as a highly qualified specialist in accordance with Federal Law of July 25, 2002 No. 115-FZ.
- Personal income tax of 15% is the basis for equity participation in the work of domestic enterprises in any field of activity.
- The 30% rate applies to income received by tax non-residents working in our country.
- 35% income tax applies to winnings, prizes received as a percentage of invested deposits, from ruble and foreign currency loans.
- The tax is extremely convenient for the control of the payer even in the absence of financial and economic education or certain skills.
Due to the fact that today the calculation of personal income tax is well developed, it has a flat scale, a minimum of benefits, simple calculation methods and determination of the tax base, this tax is the most convenient to manage and administer.
Personal income tax: document for reporting
Individual entrepreneurs and large companies that are legal entities still hire employees. This means that they are tax agents and must submit to the tax office the necessary documents, which indicate the labor taxes calculated and actually transferred to the state treasury. In this case, the main document is a certificate called 2-NDFL, which provides information on whether the tax agent has fully fulfilled its obligations to the Russian Federation.
Such a certificate in the accounting department is filled out for each employee separately; the basis for the specified data will be the fact that the employee receives wages or other income from the employer.
Important point! Each tax rate requires the completion of its own 2-NDFL certificate. If an employee receives a salary subject to 13% tax, and he also received money from the sale of a car, form 2-NDFL is filled out twice for him, each certificate reflects its own type of income and its taxation. In the example we indicated, the first certificate, about salary, will be prepared by the employer, the second, about personal income, will be prepared by the payer himself. The document must be prepared in two copies and submitted to the tax office for consideration no later than April 1 (at the end of the reporting period of the year). An example of filling out form 2-NDFL can be found in our article.
Who and how is personal income tax transferred to the budget?
Payers of income tax, according to Art.
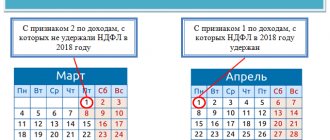
207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, individuals (residents and non-residents) who receive income from sources in the territory of the Russian Federation are recognized. The transfer of personal income tax to the budget is either carried out by them independently upon receipt of one-time or systematic revenues, or is entrusted to tax agents - the sources of payment of permanent income. The rules for calculating and paying income tax are reflected in Chapter. 23 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Tax agents pay personal income tax for employees no later than the day following the day they actually received income in the form of wages, and no later than the last day of the month in which vacation pay and disability benefits were paid (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Read more about these deadlines in the article “When to transfer income tax from salary?”
Tax payment by individual entrepreneurs and other individuals is made until July 15 of the year following the reporting year.
What happens if you don’t pay personal income tax?
The Russian Tax Code clearly establishes sanctions that will be applied to both the tax agent and the individual in the event that personal income tax is paid late or the transfer of funds to the state treasury is completely ignored.
Timely payment of taxes is controlled by law
Thus, tax agents who delay in transferring funds may receive a fine of 20% of the tax amount itself. The state will “charge” the same interest on top if the money is not transferred at all or the calculation is incomplete. Also, arrears and penalties may be withheld from the defaulter. But there is a nuance - if labor income is paid to employees in kind, it is impossible to collect taxes from them, and delay in tax payment, accordingly, cannot happen either. Another point is that the tax agent did not withhold personal income tax from the employees’ income. In this case, he will also face a fine, but without a penalty.
As for individuals, they may also receive a fine of 20% of the tax amount in case of incomplete payment or non-payment. But the law provides for another penalty for deliberate underestimation of taxable income. If an individual specifically indicates a smaller amount in the declaration, he will be subject to a fine of 40% of the actual amount. The law also exempts individuals from fines in case of late payment. But penalties for personal income tax for late payment will be charged.
Didn't manage to submit your declaration on time? Do you want to know what the consequences are for failure to submit reports on time? Read more about the statute of limitations for tax offenses and how to reduce the amount of the fine in our article.
Taxpayers and tax agents
Let us consider in more detail who and in what cases, in accordance with the provisions of tax legislation, refers to taxpayers and tax agents.
Taxpayers.
Based on clause 1 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the following are recognized as taxpayers of personal income tax (NDFL):
- individuals who are tax residents of the Russian Federation*,
- individuals receiving income from sources in the Russian Federation who are not tax residents of the Russian Federation.
*Tax residents are individuals who are actually in the Russian Federation for at least 183 calendar days over the next 12 consecutive months.
At the same time, the period of stay of an individual in the Russian Federation is not interrupted by periods of his travel outside the Russian Federation for short-term (less than six months) treatment or training.
Regardless of the actual time spent in the Russian Federation, Russian military personnel serving abroad, as well as employees of state authorities and local governments sent to work outside the Russian Federation, are recognized as tax residents.
Budget for personal income tax: regional or federal?
Income tax is a very significant fee for any country, not only Russia. Due to these payments, the state treasury receives very significant cash injections, which can be compared with revenues from income taxes or VAT. Let’s figure out what level the personal income tax in Russia should be assigned to.
The tax system of our country involves three types of taxes: federal, regional and local. Which classification the tax will be assigned to depends on the level of the government agency introducing mandatory payments. According to Article No. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax on labor income is federal. The principle of this classification is based on the fact that personal income tax is a fixed tax, the payment of which is carried out in the same and unchanged way in all settlements of the country without exception. This is the difference between taxes classified as federal and regional. The latter are legislatively prescribed very imprecisely, and local authorities can establish specific features and nuances of such payments, based not only on federal laws, but even on their own regulations.
However, personal income tax does not go entirely to the federal budget. According to the law, only 85% of the total tax funds paid goes to the budget of Russian constituent entities. An exception is made for taxes paid by foreigners who work in Russia under a patent - in this case, the money is credited to the subject budget 100%.
The remaining 15%, according to the Budget Code of Russia, must be credited to local budgets; then they will be distributed depending on the administrative structure of this subject. So, if the subjects have rural settlements divided into municipal districts, the former will receive two percent of the amount, the latter – thirteen percent. If the territory of the subject includes urban settlements, then ten percent of personal income tax will be transferred to their budget, the municipal districts within them will receive the remaining five percent.
By whom and how is personal income tax transferred to the budget?
According to the Tax Code of our country, income tax payers are citizens who receive funds from a source located on the territory of the Russian Federation. However, they can belong to two different categories:
Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 207. Taxpayers
A resident is a resident of our country who has a passport of a Russian citizen and permanent registration on the territory of the Russian Federation. At the same time, a resident receives or maintains his status by living in the country for at least 183 days a year. For residents of the Russian Federation, the so-called general rate applies to personal income tax, which is relevant at a given time. This year it is 13% of the income received.
Let's give an example: if a citizen, for example, has a monthly salary of 10 thousand rubles before deducting personal income tax, then he will receive 13% (that is, 1 thousand 300 rubles) less. It turns out that in the end there will be 10,000-1,300 = 8,700 rubles left for his expenses.
The most significant difference between the status of resident and non-resident is that representatives of each category pay completely different amounts to the state treasury from the income they receive in Russia
Based on the definition of a resident, one can easily say who he is – a non-resident. In fact, this is a person who left his homeland too often, and as a result did not accumulate 183 days of stay on its territory. The main difference between these two statuses in practice will be reflected in the amount of personal income tax paid.
If a person, due to a long and frequent absence from the territory of Russia, is recognized as a non-resident, then in this case the amount of income tax for him will be completely different.
Thus, the rate relevant for non-residents is 30% of income. Therefore, if our hero receives the same salary of 10 thousand rubles, even then after income tax he will have 30% (that is, 3 thousand rubles) less. Consequently, he will be able to manage the following amount: 10,000-3,000 = 7 thousand rubles.
Agree, the difference is quite noticeable. At the same time, in our example we consider an initially small amount of income. In those situations where this indicator is large, the citizen will have to give a much larger amount of money to the state treasury.
This tax must be paid only to those citizens who are employees of organizations located on the territory of our country, or who receive income from other sources also located on its territory.
Regardless of who the citizen is (non-resident or resident), in order for tax to be collected from him, it is necessary to have a source of incoming income on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Taxpayers can transfer tax revenue to the country’s treasury in various ways:
- in fact, without taking part in the process, through an intermediary - a tax agent, who is appointed by the employer organization of the individual;
- or independently, if the citizen receives funds systematically or one-time.
Payment “to addresses” and federal payments
There is no connection between the registration address of individuals and the transfer of personal income tax withheld from wages. However, most often the employer makes the payment based on the territorial affiliation of the company where the employee is employed.
Example. Individual entrepreneurs conducting two or more areas of activity, in one of them will report to the tax office at the place of their registration, in another - to a third-party inspectorate, according to the geolocation where the business is actually carried out. Then the personal income tax for employees will be distributed between different tax inspectorates if the employees are employed in different areas.
Where do payroll taxes go?
In accordance with Article 58 and Article 61 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation:
- 85% of taxes from wages go to the budget of the republic, region, territory, autonomous okrug or autonomous region of residence of the taxpayer;
- 15% of taxes are allocated to the municipality, i.e. go to the city budget.
Thus, the tax paid on an employee’s salary goes to the budgets of two levels.
Every year the budget distribution is planned, i.e. expenses, which reflect all the most important areas of life of a subject of the Russian Federation and a municipal entity, such as:
- education;
- social politics;
- healthcare;
- housing and communal services;
- National security;
- culture;
- physical education and sports, etc.
Is personal income tax counted towards other taxes?
We found out that income tax is federal. In this regard, the following questions may arise:
- Is it possible to cover the arrears associated with personal income tax by overpaying another tax, also federal?
- Is it possible to offset the excess of the transferred personal income tax (overpayment) into other missing payments?
If we consider organizations that have the status of tax agents (including individual entrepreneurs), the answers to both questions are negative. We are talking about specific labor income of employees, and personal income tax should be withheld from them. Even if within two to three months the employer makes overpayments or underpayments related to the same person, the tax agent may face fines. The law in this case is adamant - tax is withheld directly when specific money is paid to a specific person.
The above issues are simpler for an individual entrepreneur who pays income tax for himself. Individual entrepreneurs working under the general taxation system also pay VAT (this is also a federal tax), therefore, when submitting a corresponding application to the tax office at their place of residence, they will have the opportunity to make recalculations between these taxes. Such a scheme will help individual entrepreneurs recover overpayments.
Video - Regional and local taxes
Personal income tax: which budget is credited to, who makes the deductions
One of the main tax fees levied on citizens of our country is personal income tax. In what budget this payment from the pocket of each Russian is credited is of interest to many, since all of us, of course, would like to see what favorable changes the money spent will contribute to. In addition, which budget to send personal income tax to is a predetermining question for each employing organization that withholds tax from its employees, and other organizations that need to independently pay tax on the income they receive.
Personal income tax: which budget is it included in?
Summarizing
Every person living in Russia and having income subject to personal income tax is required to pay this tax. Since income tax is federal, all payments and their order are specified and carefully monitored by the tax office. This fact indicates the impossibility of evading tax deductions - this will not only poison life and work, but is also fraught with fines and penalties.
Understanding all the features of personal income tax payments, it is quite simple to protect yourself from troubles and numerous visits to the tax office. This material describes and reflects important points that may be useful to a person receiving income in the Russian Federation. The tax is calculated using a simple formula, and to make the calculations, you do not need to have any special professional knowledge. The country's tax code explains in detail everything about the nuances of income taxation, and filling out a certificate in form 2-NDFL does not take much time.
Distribution of income tax between budgets
Last update 2019-06-12 at 10:29
Income tax is levied on all citizens who earn income in Russia, and even foreigners cannot avoid this payment if they make a profit within the country. The massive scale of the income tax and the wave of revelations in government agencies make us think - to which budget is the income tax credited and how is the personal income tax distributed in the financial policy of the state? Read about the distribution of personal income tax between budgets in 2021 in our material.
Tax deductions for personal income tax
There are five types of personal income tax deductions: standard, professional, social, property and investment.
The standard deductions are listed in Section 218 of the Internal Revenue Code. According to it, all individuals with children have the right to receive a monthly deduction in the amount of 1,400 rubles. for the first child, 1,400 rubles. for the second child and 3,000 rubles. for the third and each subsequent child. “Children’s” deductions are provided up to the month in which the employee’s salary at a given employer, calculated on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year, exceeded 350,000 rubles.
Standard personal income tax deductions apply only to income received from one of the employers of the taxpayer's choice. In other words, if a person works two or more jobs, he can only take the standard deduction for one of them.
Professional deductions are available to individual entrepreneurs and those engaged in private practice. Also, the right to this type of deduction is given to persons performing work or services under contract agreements, and those who receive royalties (Article 221 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Professional deductions are equal in amount to documented expenses associated with the relevant activity. In fact, the determination of such deductions for individual entrepreneurs is similar to the determination of expenses when taxing the profit of an organization. If there are no documents confirming expenses, deductions are provided according to the standards (for entrepreneurs this is 20% of income received).
Social and property deductions for personal income tax will be of interest to those who have heard about the return or reimbursement of personal income tax - for example, about the return of personal income tax for education. Social deductions can be claimed by persons who spent money on education, treatment, charity, non-state pension insurance, voluntary life insurance and additional contributions to the funded part of a labor pension (Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Submit declarations for individual clients with a 50 percent discount Submit an application
Property deductions are provided to those who incurred costs in connection with the sale, purchase or construction of real estate (Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From January 1, 2015, the Code was supplemented with Article 219.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “Investment tax deductions”. An investment deduction is possible, in particular, in the amount of a positive financial result obtained from the sale (redemption) of securities traded on the organized market if they were owned by an individual for more than three years.