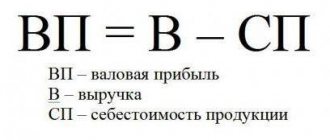Calculating profit is determining the difference between the amount of revenue received and costs. In order to understand the procedure, you need to know the decoding of each concept, which only at first glance seems to be synonymous. It is also important to know the formulas and methods of various types of calculations to obtain accurate results.
The following information will be interesting and useful for business representatives:
- Calculation of net profit
- Profit calculation formula
- Calculation of enterprise profit
- Calculation of gross profit
- Profit calculation methods
What is profit and how does it differ from income and revenue?
The financial condition of any enterprise can be objectively assessed by calculating economic indicators, which include profit. Its size allows us to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of the company’s current activities and prospects. A person who is well versed in business first of all judges the financial and economic condition of an organization precisely by how profitable it is.
According to the definition given by classical economic theory, profit is the difference between two indicators: the amount of funds spent by the enterprise on the sale of manufactured products and production costs. The term began to be used a couple of centuries ago, at a time when any enterprise had only two tasks: to produce goods and sell them.
Today, the economic activities of companies are more diverse. In addition to the main direction (product sales), modern business also has indirect sources of income (real estate rental, currency transactions, etc.), as well as a complex cost structure (logistics, marketing, advertising, obtaining a patent, etc.).
Depending on how much costs are taken into account in the calculation, profit can be of two types:
- accounting - for the calculation, the amount of external costs is taken, that is, the costs of production and sale of goods, including the payment of wages, taxes, rent, etc.
- economic (net) – the formula takes into account explicit and implicit costs (lost in exchange for explicit ones). That is, to calculate this indicator, you need to reduce accounting profit by the amount of implicit costs.
Revenue is the money that a company (or entrepreneur) receives from the sale of its goods or services. Simply put, this is the money that was earned from selling products.
A clear example of calculating the amount of revenue: a businessman sold 100 units. of their own goods, each worth 100 rubles. Revenue amounted to: 100 × 100 = 10 thousand rubles.
There are two types of revenue:
- gross is the total cash receipts from the sale of goods (provision of services, performance of work);
- net - the amount of money that remains after taxation (including VAT), loan payments, fines, etc.
Income is the difference between revenue and cost (purchase price) of manufactured and sold products. The cost includes tax payments, contributions to budgetary funds (for example, for social insurance), as well as material costs, that is, funds allocated for the purchase of raw materials, fuel, equipment, packaging, for auxiliary economic needs, etc.
An example of calculating the amount of income: a businessman produced products whose cost was 100 rubles per unit of goods. Having produced and sold 100 pieces at a price of 1,000 rubles/piece, he received an income in the amount of: 100 × (1,000 − 100) = 90,000 rubles.
Profit is the difference between total income (goods sold and other income) and expenses (production, sales, etc.).
Let's give a simplified visual example of the formula for calculating the profit of an enterprise: income from sales of products amounted to 100,000 rubles. Of this amount, 20,000 is the seller’s salary, and 13% after deducting wages is tax. Total amount: 100,000 − 20,000 − (100,000 − 20,000) × 13% = 69,600 rubles.
The main goal of any commercial enterprise or entrepreneur is to make the activity as profitable as possible, since it is this indicator that makes it clear how successfully the business is developing.
Profit includes the following elements:
- Receipts from the sale of goods (provision of services, performance of work).
- Funds that an organization receives from its auxiliary (non-core) activities. This category includes interest on deposits, rental of premises, etc.
- The difference between the amount received from the sale of products and its cost.
Why do you need to know what the company’s profit is:
- The indicator demonstrates the result of economic activity.
- If the difference between income and expenses is positive, then the funds received can become investments necessary to expand the business.
- The index is the basis for calculating the tax base.
You may also be interested in: Types of company profit: what are they and how to calculate
Principle of taxation
Individuals are required to pay Who and in what cases must pay income tax? Income tax (NDFL). More often, personal income tax is paid not by the citizen himself, but by the official employer, who automatically withholds a set percentage from the salary. The citizen receives a “net” salary, from which personal income tax has already been deducted and paid.
Legal entities are taxed according to a different principle - depending on the chosen form of taxation.
Property income is also taxed separately. The fee is fixed and amounts to 13%. It is paid upon the purchase and sale of real estate.
So that the tax authorities know about the amount of incoming funds, declarations are provided. They are filled out annually at the end of the reporting period and submitted to the regulatory authorities (local tax inspectorate offices).
The information should include:
- Accounts and the amount of funds in them that are opened in banks outside the Russian Federation.
- A citizen has securities, bonds, shares and other issuers that are issued by other states.
- Available real estate outside the territory of the Russian Federation.
Enterprise profit structure
The profit of an enterprise includes various economic indicators that demonstrate the results of each area of the company’s economic activity.
The structure includes the following sources of cash receipts:
- Sales of products (provision of services, performance of work).
- Sale or management of real estate that is at the disposal of the enterprise.
- Foreign exchange transactions, interest on stocks, bonds, etc.
- Financial transactions (investments, dividends).
Recommended articles on this topic:
- Pricing methods and recommendations for their use
- Doing business: from developing a plan to choosing software
- Methods for reducing costs in a company and enterprise without small sacrifices
The first item on the list is the main source of cash flow, since it has a greater impact on the profit received, and also serves as the basis for analytical and statistical calculations, forecasts, and strategic plans.
It is the production and sale of products that is the main channel for the receipt of funds that can be directed to business development or distributed among the founders (shareholders).
In order to optimize business activities and look for ways to improve its efficiency, financial statements are analyzed monthly and the costs and profits of the enterprise are calculated.
An experienced manager who is able to think strategically and knows how to operate with financial indicators can influence the size of each index, as a result of which the activity will become more profitable.
How to calculate average annual return
The tenure of assets can be several years. However, most assets do not grow by the same amount. Assets such as stocks can fall or rise by tens or hundreds of percent per year. Therefore, I would like to know how much your investments grew on average per year. How then to calculate the average annual return? The average annual return is calculated by taking the root using the formula:
Formula 1
where n is the number of years of ownership of the asset.
An example of calculating profitability if we owned the stock for 3 years: 3√125/100 - 1 ∗ 100% = 7.72%
Formula 2
Another formula for calculating average annual profitability is through exponentiation.
The profitability using this formula is very easy to calculate in Ecxel. To do this, select the POWER function, in the Number line enter the quotient of division 125/100, in the Power line enter 1/n, where instead of n enter the number of years, add -1 outside the brackets.
In the cell, the formula will look like this : =POWER(125/100,1/3)-1 . To convert a number to a percentage, select the Percentage cell format.
Who needs a net profit indicator and why?
First of all, let's understand the term. This concept is used to denote the part of the funds received that remain at the disposal of the enterprise after deducting from the total receipts from the sale of products, contributions to funds, taxes and other obligatory payments.
The net profit of an enterprise is an indicator, the calculation of which is required not only by the owner of the company, but also by other interested parties.
- Founders and shareholders. This indicator is information on the basis of which the business owner evaluates the current economic activities of the enterprise and draws conclusions about the existing management system. In addition, this is the money that will be distributed among co-founders or private investors (shareholders).
- Director. The responsibilities of a top manager include ensuring the financial stability of the organization. In order to make reasonable management decisions, he needs to analyze the current economic state, namely, assess the volume of available funds received and the profitability of the enterprise.
- Counterparties. Organizations that supply raw materials must understand whether the customer will be able to pay for the goods. Therefore, it is also important for them to know how financially stable the company is, since unprofitable activities may become grounds for terminating the supply contract.
- Investors. Companies and individuals who make deposits are interested in receiving the maximum amount of income. Therefore, it is important for them to understand what the company’s profit is, and therefore future income from investing in shares.
- Creditors. A credit institution (bank), which temporarily makes funds available, must know whether the borrower will be able to repay the loan amount on time. Stable profit shows the solvency of the company, that is, the likelihood that loan payments will be sent on time.
Net profit is an index, the value of which most accurately characterizes the company’s economic activities. If in the current period this amount increases in comparison with the previous one, it means that the company’s activities are profitable. If it decreases, then this indicates irrational management tactics.
You may also be interested in: Increasing enterprise profits: calculation, methods, examples
We calculate the income of individual agricultural producers
The income of entrepreneurs and producers of agricultural products who have switched to paying the unified agricultural tax (USAT) consists of proceeds from sales and non-sales income (clause 1 of article 346.5).
Under this taxation system, all transactions are recognized on a cash basis, i.e. at the moment of crediting funds to the cash desk of an individual entrepreneur or to his current account (clause 5 of Article 346.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The income that they received is equal to the total value of column 4 of KUDiR for individual entrepreneurs paying agricultural tax.
Types of enterprise profit and their calculation
According to the current Russian legislation, the following profit indicators are used in accounting to determine the taxable base:
- revenue;
- gross;
- proceeds from sales;
- balance sheet;
- clean.
Economic theory also describes contribution margin and operating profit.
Among all the indicators for calculating the profit of an enterprise, the key one is revenue from the sale of goods, since it reflects the volume of revenues from the main economic activities of the enterprise. Then the following indices are calculated: marginal, gross, sales revenue, operating, balance sheet and net profit.
General calculation formulas:
Revenue (TR – total revenue) = Unit price (P – price) × Quantity of goods sold (Q – quantity).
Margin (PM – profit margin) = Revenue (TR) − Variable costs (VC – variable cost).
Calculation of the gross profit of an enterprise (GP - gross profit) = Revenue (TR) - Technological cost of manufacturing goods (PC - production cost).
Proceeds from sales (PS – profit on sales) = Revenue (TR) − Cost (TC – total cost).
Calculation of the enterprise's balance sheet profit (BP - balance sheet profit) = Receipts from sales (PS) + Other income (OI - other income) − Other expenses (OE - other expenditure).
Operating (OP – operating profit) = Balance (BP) + interest payable (I – Interest).
Net (NP – net profit) = Balance Sheet (BP) − Taxes (T – taxes).
You may also be interested in: Profit maximization: the golden rule and methods of implementation
Calculation of safety factor
In order to assess how successfully the production (sales) plan is being implemented, the actual volume of production (sales) is compared with the volume that ensures break-even production (sales). This allows you to calculate the margin of safety (reserve for profitability, margin of financial stability), that is, to establish the percentage deviation of the actual volume from the threshold. Such calculations can be made using estimated (expected) production (sales) volumes.
If actual sales or production volumes are above the break-even point, then the enterprise can calculate the margin of safety (Zp) in advance using the following formula:
Salary = (OPfact - TBU) / OPfact × 100%,
where OPfact is the actual volume of production (sales);
TBU - production (sales) volume at the break-even point.
This formula can be used to calculate the safety zone based on cost indicators both for the enterprise as a whole and for one type of product based on quantitative indicators.
The percentage deviation of actual revenue from the threshold allows the company to know its margin of safety. The larger this reserve, the more stable the financial and economic position of the enterprise. If the market situation changes (demand decreases, a new competitor appears, prices decrease, etc.), then the enterprise will make a profit in all cases as long as its revenue is higher than the calculated financial stability margin. If the sales volume is lower, the company will be at a loss. Knowing the margin of safety, enterprise managers can more reasonably build their relationships with consumers using flexible pricing and competitive policies.
Example 6
Initial data: OPfact = 4250 t, TBU = 2750 t.
Let’s determine the salary: (4250 – 2750) / 4250 × 100% = 35.3%.
Thus, the financial stability of the enterprise is 35.3%, which indicates that the enterprise will make a profit in cases where its revenue decreases by less than 35.3%. If revenue decreases by more than 35.3%, then the enterprise will be unprofitable. With information, managers can take a number of measures to prevent such a situation.
Calculation of net profit of an enterprise
The business owner, shareholders, counterparties - for all of them, the economic performance of the company and profit, in particular, are important. The dynamics of key indices show what amount is at the disposal of the enterprise after deducting taxes and other mandatory payments.
Free cash (remaining after taxes and settlements with counterparties and shareholders) is a fund that can be used to develop and expand the business. Do not forget that profit also affects how much dividends interested parties will receive.
The formulas used to calculate key economic indicators were discussed earlier. However, there is another method for calculating the profit of an enterprise, which is based on accounting data.
Alternative calculation formulas:
- Addition of three types of profit - financial, gross, operating - and deduction of taxes.
- The amount of revenue is reduced by the amount of cost, expenses for administrative, commercial and other needs and the amount of tax payments.
- Tax payments are deducted from pre-tax profits.
These formulas are general. To get an accurate result, a corporate economist or accountant needs to adapt them to the company's activities, for example, adjust costs.
You may also be interested in: Profit maximization: the golden rule and methods of implementation
Methods for calculating future profits
Let us demonstrate how the planned profit of an enterprise is calculated.
- Direct counting method.
- Normative method.
- Extrapolation method.
- Analytical method.
It is calculated as the volume of planned revenue reduced by the amount of the full cost (including contributions to funds).
Profit generation based on a system of various standards, for example, for assets.
It is based on forecasting, that is, taking into account indicators of past periods.
The influence of various factors on the expected profit margin is taken into account: product sales volume, cost, selling prices, etc.
The results of the presented methods for calculating the profit of an enterprise depend on the direction of the company’s activities, the chosen strategy, and various external and internal circumstances.
Only a thorough analysis allows you to plan performance indicators, look for ways to optimize costs and ways to make your business more profitable.
Having decided on the amount of available funds, the entrepreneur should decide what to spend it on. You can not only scale up an existing business project, but also direct them to production or social needs:
- purchase new equipment to automate the technological process;
- introduce new technologies;
- make workers' working conditions safer;
- pay bonuses to staff or increase payroll;
- increase production capacity;
- use money for investment or invest in transactions with securities and currencies.
From all of the above, we can conclude that the enterprise needs to plan profits, and this task can only be accomplished through accurate accounting of all cash receipts and costs. Obviously, in order to achieve the maximum amount of available funds, the first ones need to be increased, and the second ones need to be optimized.
Let's imagine that a certain company engaged in the production of clothing received a negative profit at the end of the year. After analyzing current activities, the top manager came to the conclusion that the number of sewing machines should be reduced (based on the size of the forecasted figures) or replaced with new ones in order to reduce maintenance costs, but the control indicator for the volume of goods produced should be increased. All funds remaining after paying taxes and other payments will be used to implement the approved plan.
Profit + losses - how to add?
How to add up profitable and unprofitable periods?
Simple question. In the first year we made a profit of +10% . For the second loss -10% . How much money will there be in the end?
It seems like plus and minus equals zero. Ten there, 10% back.
We are at the same starting point.
In fact, we lost 1% (you can check it on the calculator).
Moreover, the sequence is not important. First there is a profit, then a loss. Or vice versa. The result will be the same.
How to quickly calculate?
- 10 percent profit - 1.1;
- 10% loss - 0.9.
Formula: 1- (loss for the period/100).
We multiply the numbers together and get the result.
In our case: 1.1 X 0.9 = 0.99. Or 99% of the initial capital.
Calculation of enterprise profit from financial statements
The accounting report on profits and losses (financial results of an enterprise) has the form of a table, where each line is assigned its own code. Therefore, key economic indicators can be calculated using a tabular method. To do this, all data is formed into a table, and the results are obtained by adding or subtracting the numbers indicated in specific cells.
Gross = Revenue – Cost.
Rows: 2100 = 2110 – 2120.
Receipts from sales = Revenue - Cost - Selling expenses - Administrative expenses.
Rows: 2200 = 2110 − 2120 − 2210 – 2220.
Balance sheet = Income from sales + Other income − Other expenses.
Rows: 2300 = 2200 + 2340 – 2350.
Operating = Balance sheet + Interest payable.
Rows: OP = 2300 + 2330.
Net profit = Balance sheet − Current income tax.
Rows: 2400 = 2300 – 2410.
You may also be interested in: Increasing company revenue: 24 ways
How to find out the income of an individual entrepreneur - for a bank, the Federal Tax Service, calculation of contributions
Bzhasso Tatyana, professional accountant
How to find out the income of an individual entrepreneur? What should an entrepreneur do if the bank asks to provide a certificate of income or needs to calculate the amount of an additional contribution to the Pension Fund?
Individuals confirm their income with a 2-NDFL certificate. Legal entities that apply the general taxation system submit a report on financial results (form No. 2), and those who have switched to a simplified tax system submit the Income and Expense Accounting Book (KUDiR) of the legal entity. What should an entrepreneur do?
The reporting form confirming the amount of income of an individual entrepreneur depends on the tax system used by him.
If an entrepreneur combines several types of activities, then his total income will be equal to the sum of all income received from all types of activities.
Calculation of enterprise profit using an example
Limited Liability Company "Cozy House", which is engaged in the production and sale of household goods, has the following financial statements at the end of two years (RUB):
| Index | Code | 2017 | 2018 |
| Revenue | 2110 | 130 000 | 70 000 |
| Technological cost | 2120 | 45 000 | 25 000 |
| Business expenses | 2210 | 6 000 | 4 000 |
| Management costs | 2220 | 18 000 | 13 000 |
| Other income | 2340 | 1 000 | 800 |
| Other expenses | 2350 | 2 000 | 3 000 |
| Percentage to be paid | 2330 | 6 000 | 4 000 |
| Income tax | 2410 | 12 000 | 5 960 |
- Calculation of marginal profit: PM = TR − VC.
2018 = 70 000 − 25 000 = 45 000.
2017 = 130 000 − 45 000 = 85 000.
- Calculation of gross profit: GP = TR − PC.
2018 = 70 000 − 25 000 = 45 000.
2017 = 130 000 − 45 000 = 85 000.
- Calculation of profit from sales: PS = TR − TC.
2018 = 70 000 − (25 000 + 4 000 + 13 000) = 28 000.
2017 = 130 000 − (45 000 + 6 000 + 18 000) = 61 000.
- Calculation of book profit: BP = PS − OI − OE.
2018 = 28 000 − 3 000 + 800 = 25 800.
2017 = 61 000 − 2 000 + 1 000 = 60 000.
- Calculation of operating profit: OP = BP + I.
2018 = 25 800 + 4 000 = 29 800.
2017 = 60 000 + 6 000 = 66 000.
- Calculation of net profit: NP = BP − T.
2018 = 29 800 − 29 800 × 0,2 = 23 840.
2017 = 60 000 − 60 000 × 0,2 = 48 000.
You may also be interested in: How to calculate sales profit and 55 ways to increase it
Calculating net revenue
A simple way to calculate net and gross profit using the formula.
How to take into account all the costs of an enterprise? Article navigation
- Net profit: definition
- Types of profit
- Formula for calculating net profit
- Methods for analyzing the net profit of an enterprise
- Factor analysis of net profit
- Statistical method for analyzing net profit
- Distribution of net profit
- conclusions
A significant indicator of the economic activity of an enterprise is profit. The future development of any business, its competitiveness, investment attractiveness, solvency and financial reliability depend on it.
Table for calculating enterprise profit in Excel
Often businessmen have to independently calculate key economic indicators. To ensure accurate results, the process can be automated using special programs. Below is an example of calculating enterprise profit in an Excel table.
The table is divided into 4 blocks:
- Tax rates (profit, VAT) – cells B1:B2.
- Sales volume, costs and value added tax - cells B4:B6.
- Calculation of the VAT amount - cells B8:B9.
- Gross, net profit and calculation of corporate income tax - cells B11:B14.
The first two blocks are used to enter existing ready-made data; in the other two, the result is calculated automatically based on the entered formulas.
Excel formulas that can be used to calculate the amount of profit of an enterprise:
- Formula for calculating the amount of tax liability:
=ROUND(B4*(B1/(1+B1));2) – the result obtained is rounded to the second digit.
- Formula for calculating VAT payable to the budget:
=B8-B6.
- Formula for calculating gross profit excluding VAT:
=B4-B8.
- Formula for calculating the amount of gross profit:
=B11-B5.
- Formula for calculating corporate income tax:
=ROUND(B12*B2;2) – the result obtained is rounded to the second digit.
- Formula for calculating net profit:
=B12-B13.
The presented table can be adjusted to suit the characteristics of your enterprise, and it will become a useful working tool. Such programs are universal, regardless of external factors. So, if changes occur in tax legislation, then the calculation formula can simply be adjusted, let’s say replacing the base coefficient. If you change numbers, for example, sales revenue or costs, the results will be displayed in the corresponding cells.
A spreadsheet makes it possible to check your assumptions, evaluate how justified new investments or technologies will be, etc. Not a single large company can do without modern automation programs, such as Excel, since they are required for accounting, and for maintaining statistics, and for forecasting.
You may also be interested in: Sales return formula: calculation example
What is Potential Annual Income?
Potential annual income is the value established by the regional government for levying tax on individual entrepreneurs. To put it another way, this is the projected (potential) amount of profitability that is used for business taxation. The actual profit of the organization does not affect this size.
For each region and each type of activity, its own potential annual income is established. This value may be revised annually.
Potential annual income is determined in two ways:
- If an individual entrepreneur operates without hired employees, the entrepreneur simply needs to find a rate for his region and his direction.
- If an entrepreneur has hired employees or has several taxable objects (transport, real estate), then the potential annual income can be further increased by regional authorities.
Calculation of potential profitability
Please note that, by law, the maximum potential profitability cannot increase:
- more than 3 times - forms of activity from paragraphs 9, 10, 11, 32, 33, 38, 42, 34 (clause 2., article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- more than 5 times - in areas with a patent system, if they are carried out in cities with a population of over 1 million citizens);
- more than 10 times - areas of activity from paragraphs 19, 45, 46, 47 (clause 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Analysis of profit and profitability of the enterprise
The goal of any commercial enterprise is to ensure that the activity is as profitable as possible, that is, all existing costs (for raw materials, labor resources, marketing and advertising, etc.) are repaid. Despite the fact that the company’s position is influenced by market conditions (presence of competitors, market factors), the financial condition must be regularly assessed to determine whether the costs incurred are bringing the expected results. You can draw conclusions about how profitable and successful a business is by considering two indicators, which include profit and profitability.
You can analyze the profit of an enterprise using various techniques.
The following types of analysis exist:
- structural,
- factorial,
- temporal,
- comparative,
- index.
Using structural analysis (analysis of the constituent elements in the profit structure), an entrepreneur can determine what share of total income is occupied by funds, the sources of which are both the main and non-core activities.
The amount of income can be calculated as follows:
Percentage of operating activities = Sales profit / Profit before tax.
Percentage from other operations = Profit from other operations / Profit before tax.
Changes in the profit structure allow us to draw conclusions about how profitable the operating activities are. If a company receives more free cash from auxiliary operations, then the existing business model is ineffective.
The factor analysis technique involves research showing how profit depends on the influence of various factors:
- cost of production per unit of production;
- the size of the wage fund;
- sales volume;
- selling price of the goods.
This method allows you to find relationships between different values of one variable. For example, find out how the gross profit of an enterprise will increase if revenue increases by 1 ruble, that is, understand how the increased sales volume will affect the final result.
You can also analyze profits from the point of view of analyzing changes in dynamics, that is, by comparing indicators in the current and past periods. For example, to track how the size of the company’s revenue has changed: to calculate it, you need to divide the revenue received in 2021 by the corresponding index for 2021. We can talk about growth if the resulting result is greater than one.
The essence of comparative analysis is that the key indicators of the economic activity of an enterprise are compared with similar values of competing firms.
Index analysis of the level of profitability gives an idea of how profitable the company's activities are. This technique also involves comparing the indicators of the planned and past periods, which allows us to draw conclusions about increasing business efficiency or stagnation. Profitability shows how much profit the company receives from each ruble spent.
Calculation of profit and profitability of an enterprise:
- Total profitability ratio = Book profit / Revenue × 100%.
- Gross Margin Ratio = Gross Profit / Revenue × 100%.
A similar calculation shows how profitable assets or capital are.
You may also be interested in: How to calculate ROI: formula, examples
Relationship between profitability and investment risk
The higher the profitability, the better, it seems obvious. This rule would work well among risk-free assets, but they simply do not exist. There is always a possibility of losing some or all of your investment - that is the nature of the investment.
Higher returns are much more often achieved due to an additional increase in risks than due to the higher quality of the instrument itself. This is confirmed by real data - when I conducted a study of 3000 PAMM accounts of Alpari, I found a strong relationship between the standard deviation risk indicator and annual profitability:
The X axis is the annual return, the Y axis is the standard deviation. The trend line shows that the higher the annual return, the higher the risks of the PAMM account in the form of the standard deviation indicator.
This relationship, in simple words, is a correlation, and quite a strong one. In a study of 3000 PAMM accounts, I calculated the correlation between the standard deviation indicator and profitability and received a value of 0.44, which means a strong dependence on such a large sample. In other words, the relationship between profitability and risk is confirmed mathematically.
The investor’s task is to find his own balance between profitability and risk, to more accurately determine his propensity for risky investments. For web investments, the minimum acceptable return is at the bank level, multiplied by two (a large bank itself is more reliable than a Forex broker). Then it depends on the investor - to concentrate on minimizing risks and receive x2-x3 from bank profitability or try to take on additional risks to earn more.
All the above formulas allow you to calculate the final return on investment - we invested, time passed, and we received money. If we talk about such investment tools as PAMM accounts, trading robots, copying trades - this is not enough, there are trading risks and many other pitfalls that can lead to unnecessary losses.
The investor must know what will happen to his money in the process, for this reason these instruments are always accompanied by profitability charts.
Factors affecting profit
Profit is influenced by various factors, which can be divided into internal and external.
Internal factors include management decisions and the policies of the enterprise itself:
- quality of manufactured goods;
- optimization of production costs;
- automation of technological processes;
- efficiency of sales policy;
- expansion of product range;
- marketing strategy.
Any enterprise is also influenced by external factors that cannot be influenced:
- location;
- state of ecology in the area;
- climate features;
- state policy regarding entrepreneurship support;
- economic and political situation in the region (city, region, country);
- provision of resources.
Methods 72
The seventy-two method allows you to quickly find out how many years it will take for your investment to double.
To do this, you need to divide the number 72 by the expected annual return.
For example, with an annual return of 7%, you will double your capital in about 10 years.
We increase the profitability to 14.4% - and every 5 years we get a profit of 100%.
In 10 years you will have four times more money, in 15 - 8 times, in 20 - 16 times.
Well, after “suffering” for 30 years, you will increase your capital by 64 times!!!
Method 72 does not shine with mathematical accuracy. There is always a small margin of error. But quickly calculating on the fly and getting an approximate result is the way to go.
By the way, the formula also works in the opposite direction.
An annual loss of 6% will halve your capital in about 12 years.
It is interesting to use this for inflation. How much does the purchasing power of money decrease?
The average inflation in the Russian Federation over the past ten years was 7.43%.
This means that the ruble has “shrinked” by 2 times in 9.5 years.