Adjustment invoice (ACF) refers to tax primary documents. The scope of its application, as well as the primary invoice, is VAT and calculations related to this tax. The need to draw up a corrective invoice arises in the event of changes in indicators that affect the calculation of VAT on a transaction: prices, quantities of goods and materials shipped, etc.
Such invoices are compiled and used in accounting by analogy with ordinary ones. In the event of actual changes in indicators that affect the calculation of VAT, the accountant first of all faces a dilemma: draw up an adjustment document or make corrections to the original one.
How to correct errors on an invoice
Corrected is a new invoice with the correct data filled in line 1a. In essence, this is a clarified document.
Important: 1. Line 1 indicates the number and date of the invoice with errors.
2. Line 1a indicates the serial number and date of correction of the original (erroneous) invoice (“correction No. 1 dated “__”_____2019).
The remaining lines and fields are filled in as in the original invoice, but with the correct values.
The corrected invoice is drawn up in two copies: for both the buyer and the seller.
If a defective invoice was recorded in the purchase book (from the buyer) and in the sales book (from the seller), it should be canceled and a corrected one should be registered.
Design rules
Five days are allotted for the preparation and delivery of an adjustment invoice to the buyer from the date of the decision to make changes and its documentation. The CSF must be drawn up in two copies.
If prices or quantities change for several items of the primary document, then information for each item must be indicated separately.
The Tax Code allows you to issue one adjustment invoice for several shipping invoices issued to one buyer (clause 13, clause 5.2, article 169). In this case, information about identical goods (works, services), the shipment of which was documented in several documents at different times, can be indicated in total. This is possible if the shipment was made at the same price and the following has changed:
- delivery quantity;
- the price is the same amount compared to shipping.
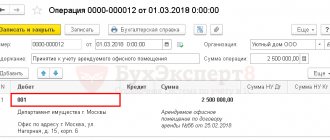
An example of compiling a CSF
On March 26, LLC "Company" shipped goods to JSC "Buyer". On May 25, it was agreed to change the price for “Colored Pencil” from 10 to 9 rubles. Also, when recalculating the delivered goods, it was discovered that “Ballpoint pen” was supplied in the amount of 202 pieces, that is, 2 more than indicated in the shipping documents. 05/28/2018 LLC "Company" exhibits KSF.
In line 1 we indicate the date and number of the CSF, and in line 1b - the details of the document being adjusted.
Lines 2–4 contain the details of the parties to the transaction, as well as the currency of the document.
In the tabular section we indicate changes for each position separately.
At the end of the form, do not forget to sign the responsible persons.
Reflection of corrections in accounting and reporting
1. If the correction occurs in one quarter:
The seller cancels the entry for the erroneous invoice in the current period's sales ledger and records the corrected invoice. Cancellation will be carried out by re-registering the document in the sales book with negative indicators.
The buyer makes similar entries in his purchase book.
2. If an invoice drawn up in the previous period is corrected , then the seller and buyer make the same entries, but only in additional sheets to the sales book (purchase book) of the period in which the erroneous (initial) invoice was registered. And also two entries are made in the additional lists: the previous invoice is canceled and the corrected one is registered.
If, as a result of corrections, the final data of the sales book (purchase book) has changed, you must submit an updated declaration. And if the amount of VAT payable for the corrected period increases, you need to pay additional tax and penalties.
Working with Corrective Invoices
1. Procedure for making corrections to invoices
Resolution No. 1137 provides for the procedure for correcting invoices, including adjustment invoices. Corrections are made by drawing up new copies of invoices, i.e. new copies of invoices with the changes made are issued (paragraph 2, clause 7 of the Rules for filling out invoices, clause 6 of the Rules for filling out a correction invoice).
Corrections to invoices drawn up before the date of entry into force of Resolution No. 1137 are made by the seller in the manner established on the date of preparation of such invoices (Article 2 of Resolution No. 1137).
2. When to make corrections to invoices
Corrections are made if:
- The price has changed due to:
- — a technical error that arose as a result of incorrectly entering the price or quantity of goods shipped, work performed, services rendered;
- - arithmetic error.
In this case, it is necessary to make corrections to the “shipping” invoice drawn up indicating the planned prices, since the calculation of the price of goods does not change (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2011 N 03-07-09/45).
Corrective invoices are issued in the same way if errors are found in them that do not allow the tax authorities to identify (clause 7 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, clause 6 of the Rules for filling out a corrective invoice) the following details:
- - seller, his address, TIN;
- — buyer, his address, TIN;
- — name of goods (works, services), property rights and their value;
- — tax rate;
- — VAT amount.
Attention: If corrections are made to an invoice for which an adjustment invoice was drawn up (or several such invoices), then in this case the corrective invoice is drawn up without taking into account the changes specified in the adjustment invoices (paragraph 1 clause 7 of the Rules for filling out an invoice).
3. Rules for filling out a correction invoice
The new (corrected) copy of the invoice indicates:
- in line 1a the serial number of the correction and the date of correction (clause “b”, clause 1, paragraph 3, clause 7 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, clause 6 of the Rules for filling out an adjustment invoice).
- in line 1 (for an adjustment invoice - in line 1b) you need to indicate the data of the original copy (number and date) (paragraph 3, clause 7 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, clause 6 of the Rules for filling out a correction invoice).
The remaining rows and the tabular section contain data with new correct values.
4. Who signs the corrective invoice.
The corrective invoice is signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization (other authorized persons) acting on the date of issuance of the corrective invoice, or by an individual entrepreneur who also indicates the details of the certificate of registration as an individual entrepreneur (paragraph 5, clause 7 of the Rules for filling out the invoice - invoices, paragraph 3, clause 6 of the Rules for filling out an adjustment invoice).
When an organization prepares an invoice in electronic form, the indicator “Chief Accountant or other authorized person” is not formed (clause 8 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, clause 7 of the Rules for filling out an adjustment invoice).
5. The procedure for registering a corrective invoice in the book of purchases and sales
ATTENTION! To reflect in the book of purchases and sales for the buyer and the seller, it does not matter whether the amount of VAT on the corrective invoice has increased or decreased.
Changes in previous tax periods:
Buyer:
- 1) in the additional sheet to the purchase book for the corrected tax period, cancels the invoice (paragraph 2, clause 9 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase book). The total values are indicated with a minus sign.
- 2) Registers the corrected invoice also in an additional sheet for the corrected tax period to the purchase book.
- 3) Submits an updated tax return for the corrected tax period with completed Appendix 1 to Section 8 “Information from additional sheets of the purchase book.”
Salesman:
- 1) in the additional sheet to the sales book for the corrected tax period, cancels the invoice (clause 11 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book).
- 2) in an additional sheet to the sales book for the corrected tax period, registers the corrected invoice.
- 3) submits an updated tax return for the corrected tax period with completed Appendix 1 to Section 9 “Information from additional sheets of the sales book.”
Changes in the current tax period:
- Buyer: in the purchase book of the current tax period, cancels the invoice. To do this, the invoice is registered again, but only in columns 4 - 9 the value with a minus sign is indicated. The corrected invoice is then registered by the buyer as normal.
- Seller: in the sales book of the current tax period, cancels the invoice. To do this, the invoice is registered again, only in columns 4 - 9 the value with a minus sign is indicated. The corrected invoice is then registered by the seller in the normal manner.
According to para. 2 clause 1.1. Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation upon receipt of an invoice by the buyer from the seller of goods (work, services), property rights after the end of the tax period in which these goods (work, services), property rights were registered, but before the submission deadline established by Article 174 of this Code tax return for the specified tax period, the buyer has the right to deduct the amount of tax in respect of such goods (work, services), property rights from the tax period in which the specified goods (work, services), property rights were registered.
6. Procedure for submitting an updated VAT return
On the title page of the updated declaration, fill in the “Adjustment number” field. If the updated declaration is submitted for the first time, then the number 1 is indicated, if the second time - 2, etc.
In sections 8–12 of the declaration, fill in line 001 “Indication of the relevance of previously submitted information.” In line 001 the value 0 or 1 must be indicated. The number 0 means that the company is making corrections to the section. If the company indicates 1, then the section data is correct and does not change.
You can clarify the declaration in two ways (this procedure is described in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 21, 2016 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] ):
The first is to put a 0 in the appropriate section (8 or 9) and transfer all the information from the primary declaration as it was submitted
The second is to put sign 1 in the corresponding section (8 or 9), and leave the remaining lines of the section blank.
The second option is more convenient and the file size is smaller.
Thus, according to the second option it turns out:
The company is correcting an error in the purchase book. Based on the additional sheet to the purchase book, the program will generate appendix 1 to section 8. In line 001 of this appendix you need to put 0, and in section 8 on the same line - 1, while the remaining lines of section 8 are left empty.
The company corrects an error in the sales book. Based on the additional sheet to the sales book, the program will generate Appendix 1 to Section 9 of the declaration. In line 001 of Appendix 1 you need to indicate the value 0, and in section 9 - 1, while the remaining lines in section 9 are left empty.
Correcting errors in the invoice journal
If errors are detected in the invoice journal, the organization resends all data from the invoice journal. If an error is found in part 1 of the journal, that is, in the list of issued invoices, then the company will send the entire section 10 in the updated declaration, and if in part 2 of the journal, that is, in the list of received invoices, then the entire section 11. In the line 001 must be set to 0.
The rules for maintaining an invoice journal, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137, do not provide for the company to draw up additional sheets to it. The Federal Tax Service of Russia recommends correcting the journal by adding a new line to the accounting journal for the reporting quarter, in which incorrect indicators should be canceled. The cost of goods and the amount of tax should be indicated with a minus sign. Then reflect the correct data in the next line.
Correction of accounting errors associated with incorrect reflection of invoice data
If in tax accounting the cost data from the supplier's invoice is entered incorrectly and is inflated, you can cancel the original entry in the additional sheet of the purchase book by indicating the cost data with a minus sign. In the next line of the additional sheet, indicate the correct data, form Appendix 1 to section 8, indicating the value 0 in line 001, and in sections 8 and 9 in this line indicate 1. Before submitting the updated declaration, pay additional tax and penalties.
If in tax accounting the cost data from the supplier's invoice is entered incorrectly and is underestimated, you can add a VAT deduction in the purchase book for subsequent reporting periods.
If an error has occurred in tax accounting that is not related to the value indicators of the invoice (for example, the supplier’s TIN was entered incorrectly):
- 1) you can cancel the initial entry in the additional sheet of the purchase book by indicating the cost data with a minus sign, and indicate the correct data in the next line of the additional sheet. Create Appendix 1 to section 8, indicating the value 0 in line 001, in sections 8 and 9 indicate 1 in this line;
- 2) do not correct the error, since it does not affect the VAT amount. If the Federal Tax Service identifies an error and asks for clarification, the correct values can be sent in the form of a table.
Response to a request for clarification
If the company receives a request for clarification, it must respond with a receipt. The period is six working days from the date when the request was sent by the Federal Tax Service (clause 5.1 of Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The request will contain a table with those entries from the sales book, purchase book or invoice journal that the Federal Tax Service considered erroneous (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 7, 2015 No. ED-4-15/5752). In addition, the request will contain a possible error code:
- - your declaration contains an entry for an invoice, but the counterparty does not have a similar entry,
- - in your declaration there is a discrepancy between the data from the purchase book and the sales book,
- — in the intermediary company’s invoice journal, the data on received invoices differs from the data on issued invoices,
- — The Federal Tax Service requires clarification of the indicator of a specific column in the purchase book, sales book or invoice journal. The number of this column will be given after the error code in square brackets. For example, like this: 4 [3].
Explanations must be sent within five working days (clause 3 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This period is counted from the next day after the company sends the receipt of acceptance of the request. Explanations can be compiled in tabular form, which was developed by the Federal Tax Service and is listed on the website nalog.ru in the “VAT 2015” section.
This form has two tables. Table 1 must be completed if the company wants to report that there is no error in the declaration. In this table you need to show, without changes, the entry from the sales book, purchase book or invoice journal that is contained in the request.
Table 2 must be completed if the company agrees that there is an error in its declaration. In the “Difference” line, you must indicate without changes those entries that require correction. And in the “Explanations” line, provide the correct data. This line can only be completed in those columns that the company has decided to correct.
If the company discovers an error that affects only the amount of tax, then it is necessary to submit an updated declaration; there is no need to submit a tabular form of explanations.
Tax audit from 12,000 P
New list of objects subject to taxation at cadastral value in Moscow
New list of objects subject to taxation at cadastral value in Moscow
The Moscow government established a new list by resolution No. 1425-PP of November 27, 2021.
Statutory and initiative audit
Statutory and initiative audit
Mandatory and initiative audit service for organizations of all forms of ownership. We have been working for more than 20 years, our specialists have extensive experience.
Symmetry is also important for minor errors.
It is possible that a cautious buyer will insist that the seller make a correction to the document even in the event of a minor error in the invoice.
Important: even if these are technical errors (number, date of the document, etc.), the seller must register the corrected document in the sales book. So that the corrected invoice information from the sales ledger is included in the tax return.
Otherwise, the ASK VAT-2 verification program will reveal a gap and the buyer will be denied a deduction.
Please note: the Ministry of Finance in letter dated May 6, 2021 N 03-07-11/32905 admitted that if the seller corrects an insignificant error (shortcoming), he may not register the invoice in the sales book. But in order to apply the deduction to the buyer, the mirror image of current invoices must be observed.
To be on the safe side, it is useful to request from the seller certified copies of the relevant sheets from his sales book.
Such an unconventional UPD
If your counterparty uses a UTD (universal transfer document), be sure to make sure that the document received from him in the part in which it replaces an invoice:
- fully complies with the invoice format approved by current legislation,
- it contains all the necessary details,
- and they are indicated correctly.
The UPD form was approved 6 years ago by letter of the Federal Tax Service dated October 21, 2013 N ММВ-20-3/ [email protected] Since then, a lot of significant changes have been made to the rules for filling out invoices, approved by Resolution No. 1137. The UPD form is lagging behind. And no one is in a hurry to update it.
The Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service in their letters advise independently supplementing the UPD, which combines the form of an invoice and a primary accounting document, with the indicators necessary to fulfill the requirements established by Article 169 of the Tax Code and the Rules for filling out an invoice used in calculations of value added tax , approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation N 1137. (letters of the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service dated April 22, 2021 No. ED-4-15/7638, dated September 14, 2021 No. ED-4-15/18322.
Advice: if you use UTD, it is worth reworking its form, bringing it into line with the current invoice form. And fix the form of this primary document in the annex to the accounting policy.
If the seller has issued you an UTD, carefully check the document to ensure it corresponds to the current invoice form. And each of its details.
Otherwise, the tax office will cancel the VAT deduction based on the UTD using an outdated form with incomplete indication of details.
Correcting an error in an invoice should not be confused with the procedure for issuing a correction invoice.
For VAT purposes, correction of an error and adjustment are two completely different concepts. And it is necessary to clearly understand when it is necessary to correct a previously issued invoice, and when to prepare an adjustment for it.
Why do you need an invoice?
The document, which is drawn up on a standardized form that includes information required by the state, is needed by both sellers and buyers. When a trade transaction is carried out, confirmation is needed that the goods were actually shipped, services were provided, and work was done. An invoice is just such documentary evidence.
VAT and invoice
When paying for the transaction, the seller is charged value added tax. It is the document that we consider (invoice), as confirmation of VAT payment, that is registered by the buyer in a special book. Based on this document, he fills in the corresponding indicators in the VAT return. According to the law, the buyer has the right to a tax deduction under this taxation article (Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), if everything is completed correctly and accurately.
There are situations when VAT is not charged, for example, for entrepreneurs working under the simplified tax system. But often the buyer, despite this circumstance, asks for an invoice, even without VAT. This is not the seller’s responsibility, but sometimes it is still worth meeting the buyer’s request and issuing an invoice, just indicate in the document that it is without value added tax, without filling out the corresponding line of the form.
IMPORTANT! If you are not a VAT payer, you should not indicate a 0% rate on your invoice instead. Even zero percent shows the real rate to which you are not entitled in this case. Specifying a rate that does not correspond to reality can create many problems for the recipient of the document, starting with a fine and ending with the accrual of the standard 18% rate.
Correction and error correction are two very different things
Completely different operations with completely different grounds, their own rules of documentation and reflection in accounting and reporting.
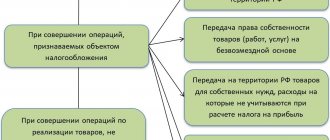
So, the adjustment conditions:
1.Adjustment - only if the cost changes.
An adjustment invoice is issued only when the cost of goods already shipped, work performed, services rendered, or transferred property rights is changed.
A change in price may be caused by:
- shortage of goods was detected,
- after shipment, the seller provided the buyer with a retro discount,
- sale of goods at a preliminary price with subsequent recalculation,
- changing the price in court at the request of one of the parties.
2. The adjustment must be formalized as a primary document. By which the parties agreed to reduce or increase the price of the product, or specified its quantity.
This may be a change (addition) to the contract, agreement, or other document confirming the fact of notification of a change in the terms of the transaction and confirming the buyer’s consent.
Important: The date of these documents must be later than the date of shipment. They confirm the fact that the change occurred after shipment.
Primary documents may be, for example, 1) an act on establishing a discrepancy in quantity and quality when accepting goods and materials in form No. TORG-2, 2) an act on price changes signed by the parties, 3) a court decision that has entered into legal force, and others
If there is no primary basis document, there is no need to issue an adjustment invoice. This is what the Ministry of Finance thinks in its letter dated February 9, 2021 No. 03-03-06/1/7833.
If, when issuing an invoice, inconsistencies or errors were initially made, including arithmetic, in value, in amount, such documents are not issued. Issuing an adjustment invoice in this case will be unlawful. To correct the error, a corrected invoice is issued.
When not needed
There is no need to compile a CSF in the following situations:
- The supplier offered the buyer a bonus for a large order. For example, a regular customer placed an order for 500 liters of milk. According to the contract, in this case, the farm is obliged to provide the wholesale buyer with a premium, which will not in any way affect the calculation of VAT or the price of goods. The agreed amount is usually transferred to the buyer’s account.
- If an incorrect address or name is found and a corrected invoice can be issued.
Invoice changes
Adjustments are made if clarification is required by the cost or quantity of goods. And corrections can be made if there is an error in the data that does not affect the price and amount of VAT.
Reflecting adjustments - according to your own rules
So, documents on changes in the value of previously shipped goods have been drawn up, the buyer’s consent to the change in value has been received, and an adjustment invoice has been issued.
The task is to correctly reflect the adjustment in accounting.
And the basic rules are:
- The accounting reflects the difference .
- The tax base of the current period . Regardless of the period in which the goods were shipped. The tax base calculated at the time of shipment is not subject to adjustment.
If the cost of shipped goods has increased, then in the current period (adjustment period):
- the seller includes the resulting difference in the tax base of the current period, regardless of the period in which the goods themselves were shipped;
- the buyer declares for deduction the difference between the VAT amounts calculated before and after the adjustment.
If the cost of shipped goods has decreased, then in the current period (adjustment period):
- the seller declares for deduction the difference between the VAT amounts calculated before and after the adjustment;
- the buyer recovers the VAT amount in the amount of the difference between the VAT amounts before and after the adjustment.
Some people remember that before 2013, adjustment invoices had to be registered in additional lists. Moreover, for the period when the shipment took place. This necessitated the submission of updated tax returns to the tax authority for the period of shipment of goods. Pay the difference in VAT and penalties.
As of July 1, 2013, this is no longer required. Now the differences that arise are reflected in the tax base of the current period . Therefore, the declarations do not need to be clarified, and no penalties will be charged.
What is CSF
The document contains the following mandatory information:
- price, quantity, cost of goods (services, etc.), VAT amount before adjustment;
- similar information after adjustment;
- the resulting differences in indicators - to decrease or increase.
Let us note that the legislation does not contain a single form of the document that is the basis for registration of the CSF. These can be primary documents signed by both parties to the transaction: acts, invoices, and additional agreements to the contract, as well as any other documents confirming the consent of the partners.
The details have changed, what about the adjustment?
If, from the moment of initial shipment to the moment of adjustment, the basic details of the seller or buyer, for example, address, have changed. In this case, the adjustment invoice indicates new details - those that are valid at the time the adjustment invoice is issued.
Advice: when signing their agreement to change the price, it is advisable for the buyer and seller to clarify their details. If the obligation to notify about this is not fixed by the terms of the contract.
Results
After a shipment has already been made, it may be necessary to adjust the data on the quantity or price of goods sold in connection with reaching an agreement to change 1 of these indicators. In this case, an adjustment document is drawn up reflecting the original shipment data, their new value and the amount of change. Such a document is not used to correct errors made during registration.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
About a single (consolidated) adjustment
The Tax Code provides for the possibility of generating unified (consolidated) adjustment invoices - invoices. Naturally, they were issued to the same buyer.
The seller can collect invoices that are subject to adjustment and enter data on them into a single adjustment invoice. At the same time, there will be only one adjustment invoice, and there will be only one entry for it in the books of the seller and the buyer.
Issuing a single adjustment invoice is not an obligation, but the right of choice of the seller . For some this is convenient. To reduce the number of documents and simplify accounting.
You can combine both options for issuing adjustment invoices - separate or single. There is no need to fix the choice option in the accounting policy.
A single adjustment invoice may indicate that the cost has increased for some items and decreased for others. In this case, it is necessary to separately summarize the data and reflect them separately in the final lines “Total increase (sum of lines B)” and “Total decrease (sum of lines D)”. The seller and buyer register such an adjustment invoice twice : in the purchase books and sales books, respectively.
Adjustment after adjustment
Adjustments to the cost of goods can be made repeatedly . In this case, for each subsequent adjustment, the seller issues an adjustment invoice to the buyer, which includes the data from the previous adjustment invoice. And it reflects the difference (increase or decrease) between them.
The number and date of the previous adjustment invoice are entered in line 1b of the subsequent (new) adjustment invoice.
A new adjustment invoice is also recorded in the current period for the amount of the difference. Entries on the previous adjustment invoice are not canceled and remain as they are in that period.
Display of purchases and sales in the ledger
If the CSF is incorrectly reflected, VAT deductions may be withdrawn, so it is important to prepare the document correctly. When reaching an agreement to reduce the price, the seller needs to make the following transactions:
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 62 | 90/1 | Decrease in revenue | 456000 |
| 90/3 | 68 VAT | VAT calculation | 43000 |
The buyer's transactions look like this:
| Debit | Credit | |
| 19 | 60 | Difference between original and adjustment invoice |
| 10 | 60 | Debt reduction |
| 19 | 68 | VAT surcharge |
Note! You can adjust or correct an invoice an unlimited number of times.
Disputes may arise between the customer and the supplier. The buyer may want to return part of the product or the entire shipment. An adjustment account allows you to issue a VAT deduction and reflect changes in the cost of goods or the volume of services provided.
Return of goods
From April 1, 2021, returns of goods - both full and partial - are issued only with adjustment invoices.
Why: by government decree No. 15 of January 19, 2021, amendments were made to paragraph 3 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, eliminating the obligation for the buyer to issue invoices for goods accepted for registration in the event of their return to the seller.
For the return of goods, the seller (!) must issue an adjustment invoice. It is he who will accept VAT for deduction on adjustment invoices.
The Ministry of Finance, in a letter dated April 10, 2021 No. 03-07-09/25208, warned: if, when returning goods accepted for registration, the buyer issues an invoice in the old manner, the seller will lose the right to deduction. Therefore, be careful!
Regarding the return, there is another letter from the Ministry of Finance dated April 8, 2021 No. 03-07-09/24636: if the return is formalized by an independently concluded purchase and sale (or supply) agreement, then VAT can be deducted on the invoice of the returning buyer product. In this case, in the contract, the original buyer must be the seller, and the original seller must be the buyer.
An example of reflecting an increase in the price of a product by a supplier
In August, the seller, Gamma LLC, delivered a batch of 30,000 chocolate bars to the buyer, Delta LLC, at a price of 20 rubles. (without VAT).
Party cost (excluding VAT):
30,000 bottles * 20 rub. = 600,000 rub.
VAT charged to Delta on shipment:
30,000 bottles * 20 rub. * 18% = 108,000 rub.
Cost of the lot including VAT
600,000 rub. + 108,000 rub. = 708,000 rub.
In September, Gamma, in agreement with Delta, increased the cost of products and issued an adjustment invoice. Each candy bar has increased in price by 2 rubles. excluding VAT.
Price with tax: RUB 25.96. (incl. VAT - 3.96 rubles)
Total cost of the batch: RUB 778,800. (including VAT - 118,800 rubles).
The Gamma accountant prepared the following entries:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Sum |
| August: sales revenue reflected | 62 | 90 subaccount Revenue | 708000 |
| VAT charged | 90 | 68 subaccount VAT calculations | 108000 |
| September: price for sold products increased | 62 | 90 subaccount Revenue | 70800 |
| additional VAT charged | 90 | 68 subaccount VAT calculations | 10800 |
The Gamma adjustment invoice was registered in the sales book for the third quarter.
Delta's accountant prepared the following entries:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Sum |
| August: goods received | 41 | 60 | 600000 |
| input VAT reflected | 19 | 60 | 108000 |
| accepted for deduction of VAT on capitalized goods and materials | 68 subaccount VAT calculations | 19 | 108000 |
| September: reflected increase in the cost of purchased products | 41 | 60 | 70800 |
| additionally submitted input VAT is reflected | 19 | 60 | 10800 |
| reflected increase in tax deduction | 68 subaccount VAT calculations | 19 | 10800 |
Delta registered an adjustment invoice in the purchase book for the third quarter (in September).
What happens if you issue an adjustment invoice instead of a corrected one?
Since the rules for registering adjusting and corrected invoices in the purchase books and sales books, as well as the procedure for applying tax deductions on them, are significantly different, both the buyer and the seller bear the risks.
Let's figure it out.
Yes, it’s possible that adjustments are convenient: you don’t need to plow through past periods, fill out additional sheets and prepare clarifications. In what period the document was received - in the same period it was reflected in the accounting.
But according to the rules established by law, an adjustment invoice can be issued subject to three conditions : 1) after shipment, the cost of the transaction changes 2) the parties have agreed on this 3) the primary document is available - the basis for the adjustment.
If one of the conditions is not met, the previously issued invoice must be corrected. Issuing an adjustment invoice will be illegal. And recognizing deductions on its basis is risky . The Ministry of Finance warned about this in a letter dated December 18, 2021 No. 03-07-11/84472. The same explanations are contained in numerous other letters from the controllers of the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service.
Seller's risks.
1. If, as a result of correcting the error, the cost of shipment has decreased - in the case of an incorrectly issued adjustment invoice - the seller faces refusal of a tax deduction for the amount of the difference between VAT, additional tax assessment, and penalties for tax liability for incomplete payment of tax.
2. If, as a result of correcting the error, the cost of shipment is increased - in the case of an incorrectly issued adjustment invoice - the seller faces additional tax, penalties and a fine due to underpayment of VAT for the shipment period.
3. For violation of the accounting procedure and the absence of corrected invoices, the seller may be brought to tax liability under Article 120 of the Tax Code and to administrative liability under Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses for gross violation of the rules of accounting and taxation objects.
Buyer's risks.
If, as a result of correcting the error, the cost of shipment is increased , the buyer - based on an incorrectly issued adjustment invoice received from the seller - loses the right to deduct the positive difference between the VAT amounts in the period of making the adjustment.
Therefore, require the seller to correct errors by issuing corrected invoices rather than corrective ones. In compliance with the correct order of their reflection in accounting registers and tax reporting.
Unreliable supplier
The carelessness or inattention of the supplier can seriously let the buyer down and leave him without a deduction.
More than once, businesses have tried to challenge in court the constitutionality of the provisions of the Tax Code, which make the taxpayer’s right to receive tax deductions dependent on compliance with tax legislation by its counterparties. But, unfortunately, the judges of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation did not find anything unconstitutional in these norms.
Russian judicial practice confirms that business liability is limitless. Checking potential counterparties is already a duty. With severe penalties for non-compliance: 1) accusation of complicity and 2) refusal to reduce the tax base and recognize deductions.
Of course, you can argue. But given the budgetary position of the courts, this is not always productive.
Therefore, it is important to calculate the risks and take timely measures to ensure the safety of your business. Be in the trend of current events. Know the tricks and understand the right moves.
In a fresh letter dated May 6, 2021 No. 03-07-11/32905, the Ministry of Finance once again warned that a corrected invoice that is not registered by the seller in the sales book deprives the buyer of the right to deduct VAT.
Making your legal right to a deduction dependent on the integrity or mood of the supplier is imprudent and risky. It's worth insuring yourself. It is useful to include in an agreement with a supplier - both a trusted partner and one chosen for the first time - a mandatory condition on the exchange of documents - the presentation by the seller of certified copies:
— additional sheets of the sales book (in case of correction of invoices) and
— current sheets of the sales book (in case of issuing adjustment invoices).
And further. It is advisable to include in contracts with suppliers other additional measures of responsibility that invigorate the counterparty. Eg:
- introduce a condition on a penalty for failure to submit properly executed documents within the established time frame: invoices, certified copies of sales book sheets and others;
- include in the contract a condition on assurances about the circumstances (in accordance with Article 431.2 of the Civil Code);
- stipulate in the contract the responsibility of the counterparty to compensate for property losses resulting from its violation of the law or obligations and guarantees under the contract. In this case, the contract must indicate the basis for compensation for losses;
and other useful conditions given in the article “Agreement with the counterparty. We manage risks."
If the counterparty is decent, he will not persist in accepting additional terms to the agreement. For him, these conditions do not entail any complications or problems.
If the counterparty avoids submitting documents or refuses to sign the proposed version of the contract, this is a reason to think about the reasons for his opposition and evaluate the advisability of choosing this particular counterparty to execute the contract.
If an unscrupulous seller delays in submitting documents, additional liability measures will help recover damages from him in a civil dispute. Without waiting for a tax audit and its results.