Why do you need 70 count?
The accounting account is used to collect information about payments to personnel. Based on the loan, the accounting department calculates salaries, increasing the company's debt to the staff. And the debit reflects payments, reducing the amount of debt to employees. Also, debit 70 of the account records the deduction of personal income tax from wages.
Account 70 has a credit balance at the end of the month, since salary accrual occurs on the last day of the month, and payment occurs in the next month, for example, on the 5th or 10th. A debit balance on account 70 is also possible, for example, if an employee’s salary was transferred more than what was accrued.
What is reflected in account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”
This account is intended for carrying out business transactions for settlements with employees of the organization in accounting.
Detailed information about account 70 can be found in the Chart of Accounts, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n. The account reflects calculations for:
- wages,
- vacations,
- social or pension insurance benefits,
- one-time and regular rewards,
- dividends,
- other employee benefits.
Account 70 records business transactions for settlements exclusively with employees of the organization for remuneration. Settlements with other persons are not reflected here. Moreover, it is methodically incorrect to reflect settlements with individuals under GPC on account 70.
Analytical accounting for account 70 is carried out for each employee. Advanced analytics can be conducted by department, territorial basis, projects, etc.
It is possible to open subaccounts for this account in accordance with the chart of accounts approved by the organization. For example, account 70.1 can be used in settlements with employees of branch A, account 70.2 - in branch B, etc.
What is Deposited Salary?
There are situations when the salary was accrued, but the employee was not given it on time due to his absence.
Now this is rare, since most people receive their salary on a bank card, but such situations do happen. The reasons why an employee was unable to collect his salary from the cash register on time are different, for example, he was admitted to the hospital and he was unable to appear at the organization’s cash desk. In this case, his salary is deposited, that is, it is reflected as not received in the primary documents. To do this, do the wiring:
Dt 70 Kt 76. Settlements on deposited amounts
When the employee receives the deposited salary, the following posting is made:
Dt 76 Kt 50
Salaries are deposited for up to 3 years. If during this time the employee does not show up for it, then it is subject to inclusion in the company’s income.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
What does account credit 68 show?
The credit balance of account 68 shows that the taxpayer has arrears in paying taxes. The credit balance is reflected in the liability side of the balance sheet in line 1520 (clause 20 of PBU 4/99).
According to the credit of account 68, all mandatory taxes and fees paid by this taxpayer are calculated. So, in correspondence with account 99 the amounts of income tax are credited, with account 70 - income tax, etc. Postings for the credit of account 68 look like this:
Subscribe to our newsletter
Yandex.Zen VKontakte Telegram
- Dt Kt 68 - tax assessment on land acquired for construction;
- Dt Kt 68 - expenses for paying taxes when procuring materials are reflected;
- Dt (23, 26, 29, 41, 44) Kt 68 - taxes and fees have been accrued;
- Dt 51 (55) Kt 68 - return of overpayment/reimbursement of taxes to the taxpayer’s account;
- Dt 70 () Kt 68 - income tax on employee earnings (dividends of founders) is withheld;
- Dt Kt 68 - calculation of VAT and excise tax on the sale of inventory items;
- Dt (98) Kt 68 - assessment of taxes on types of activities that are not the main ones;
- Dt Kt 68 - calculation of income tax.
How to reflect the additional charge and payment of VAT based on the results of a tax audit? ConsultantPlus experts have prepared up-to-date and detailed material on this topic for you. If you don't already have access to the system, get a free trial online.
Which accounts does account 70 correspond to?
Account 70 corresponds with many expense accounts. For convenience, we have collected everything in a table.
| Account 70 corresponds by debit with | Account 70 corresponds for the loan with |
|
|
The state of an enterprise's payments is the most important indicator of the enterprise's performance. An enterprise can operate with a profit on the balance sheet, and at the same time have a large amount of accounts payable for suppliers ( account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” ), for settlements with the budget (account 68 “ Settlements for taxes and fees ”) and for settlements with extra-budgetary funds ( account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security ”). A clear indicator of the state of an enterprise’s settlements is a comparison of accounts receivable under account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” with accounts payable under account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”. and accounts 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” and account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security”. If an enterprise constantly has an excess of accounts receivable on account 62 over accounts payable on accounts of settlements with suppliers, with the budget and extra-budgetary funds, then the enterprise is in good financial condition. If, on the contrary, accounts payable for settlements with suppliers and with the budget and extra-budgetary funds exceed accounts receivable under account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” (i.e. debt of buyers and customers), then the enterprise has a poor financial condition. Accounts 60,62,68 and 69 are active-passive. The company’s settlements, in addition to the above accounts, are also recorded in other accounts, namely: - 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”, passive account - 67 “Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings”, passive account - 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees ", active - passive account - 69 "Settlements for social insurance and security", active - passive account - 70 "Settlements with personnel for wages", active - passive account - 71 "Settlements with accountable persons", active - passive account - 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations”, active - passive account - 75 “Settlements with founders”, active - passive account - 76 “Settlements with various creditors and debtors”, active - passive account - 79 “Intra-business settlements”, active - passive account As can be seen from the above, settlement accounts are mostly active-passive accounts, i.e. The balance of these accounts can be either debit or credit.
What does the balance on these accounts indicate? Let's consider the main settlement accounts from the point of view of the formation of balances, namely:
Account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” reflects on credit receipts of inventory items (inventory items) and services from suppliers, i.e., constantly during the operation of the enterprise, entries are made for such operations according to Kt-u account 60 with attribution of received inventory items and services to the debit of the corresponding accounts, namely: Dt 10,20 and 26. If payment is made for supplies of goods and materials and services to suppliers, then posting is made Dt 60 and Kt 51 (Cash account by bank transfer) or from the credit of accounts 71 and 50 (by cash). Thus, if in the context of a specific supplier we have a credit balance, then this indicates that our enterprise is indebted to this supplier for supplies of goods and materials, services or energy resources (for light, for water, etc.). If with this specific supplier we have a debit balance, this indicates that we overpaid for delivered goods and materials or services, or with scheduled payments, this indicates that goods and materials were not delivered on time, or the delivery date did not arrive, but we made the payment.
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” reflects by debit the arising debt of our buyers and customers for work and services performed by our enterprise. In the process of work, each enterprise, depending on the nature of its activities, produces products, sells goods and materials or some of its services to third-party enterprises - buyers and customers, and in the process of work, entries are constantly made to reflect sales on the credit of account 90 “Sales” (the volume is formed sales), with simultaneous debiting of account 62 , i.e. debt of buyers and customers to our company is formed. The receipt of funds for sold products or inventory items is reflected in the debit of accounts 50.51 (cash is credited to the cash register and to the current account) and account 62 , i.e. the debt of the buyer or customer to our company is written off. Thus, based on the above, the debit balance on account 62 for a specific buyer and customer indicates that he owes our company for work performed, services or for goods and materials sold to him. The credit balance on account 62 indicates that the customer overpaid our company, or made an advance payment for work, services not yet performed by our company, or for an unshipped batch of goods and materials.
70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” Payroll is calculated on the credit of account 70 with the debit of production accounts 20,23,26. , in this way a credit balance is formed on account 70, and it indicates the wage debt of the enterprise to its staff. The debit of account 70 reflects wage payments to staff / in correspondence with the debit of accounts 50 or 51. The debit of account 70 also reflects the withholding of personal income tax (NDFL) in correspondence with the credit of account 68 (sub-account for personal income tax accounting), according to the debit of account 70 may also reflect other deductions from wages provided for by the current legislation on wages. For example, debit 70 of the account reflects deductions on writs of execution, loan amounts at the request of the employee, etc. It should be noted that wages are always calculated on the basis of timesheets at the end of the month, and wages for the current month are issued in the first half of the month following the current one. Therefore, on the 1st day of each calendar month there is always a credit balance on account 70, i.e. current wage arrears of the enterprise to its staff. If the wage arrears, in the form of a credit balance on account 70, are listed for more than a month and increase every month, then we can talk about overdue wages. A debit balance on account 70 may be allowed due to excessively paid wages (Dt 70 Kt 50), as a result of a technical error in deducting the excess amount of personal income tax from wages (Dt 70 Kt 68), as a result of other erroneously made deductions from wages (Dt 70 Kt 73, 66.76) According to the economic content of account 70, for each employee there should be only a credit balance, since wages cannot be issued and deductions from wages made more than accrued under account credit 70 to a specific employee .
For account 68 (sub-account for personal income tax) and for account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security”, the credit balance is formed simultaneously with the calculation of wages with the following entries: Dt 70 Kt 68 (sub-account for personal income tax), Dt 20, 26 Kt 69. Thus, in the same way as when calculating wages, “on the 1st day of each calendar month, a current debt arises for taxes Kt 68 (sub-account for personal income tax) and contributions to extra-budgetary funds (Kt 69), because The payment deadline for the current month is the 15th day of the month following the current one. The debit balance on these accounts indicates an overpayment of taxes and fees from the payroll fund, since when paying, accounts 68 and 69 are debited in correspondence with the current account.. (Dt 68.69 Kt 51)
Thus, balances on active and passive accounts carry a semantic load , and not just a numerical value. Understanding the economic meaning of account balances allows you to “read” the balance sheet, so to speak.
At enterprises, when accounting for receivables and payables, work is underway to reduce receivables on account 62, i.e. measures are taken to ensure payment by customers and buyers for work and services performed or goods and materials sold. On account 60, work is underway to reduce accounts payable, i.e. debt to suppliers. This work is carried out on a daily basis and is expressed in the form of drawing up Reconciliation Reports, both for reporting dates and during inter-reporting periods. Situations arise when your partner is both a Buyer and a Supplier in relation to your company. Let’s say Lyutiki LLC owes your company 1,500 thousand rubles for work performed (accounts receivable for account 62), while at the same time Lyutiki LLC sold you materials in the amount of 500 thousand rubles as a supplier. (Accounts payable on account 60). In such cases, Settlement Certificate . In our example, the receivables of our partner, as the Buyer, will remain on account 62 in the amount of 1000 thousand rubles.
Calculation accounting documents
Accounting for settlements with debtors and creditors is carried out on various accounting registers. However, there is a boom. accounting documents that are used, as a rule, in all sectors of the economy.
1. For accounts 62 and 90, the formation of the volume of sales and receivables of Buyers is carried out on the basis of Certificates of completion of work (for work and services) , on the basis of the requirements of invoices or waybills (for the sale of goods and materials), with the simultaneous issuance of invoices . It should be noted that there is no single standard Certificate of work performed and services; however, in some industries, on the basis of industry legislation, Certificates of work performed are applied only in legal forms. So, for example, in construction, for work performed, a Certificate of Completion of Work, Form 2 - KS, is drawn up, with a certificate “On the cost of construction and installation work performed” Form 3 - KS attached. It should be noted the special role of invoices; the invoice form itself is standard and is constantly changing and supplemented; it must be drawn up with all the details of this document correctly filled out.
2. When accounting for accounts payable under account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, i.e. When accounting for debt to the Supplier, the same documents are used as for account 62, but the documents will be drawn up by the Supplier of services, works or goods and materials. It should be noted the special role of invoices presented to you by the Supplier, because According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the Supplier’s VAT can be deducted only if there is an invoice, and it must be drawn up without errors.
3. Accounting for settlements with personnel regarding wages is carried out on the basis of monthly wage accruals made monthly by the accounting department on the basis of the staffing table (with a time-based wage system) and timesheets. With a piecework labor system, accrual is made depending on the employee’s output on the basis of work orders - orders, certificates of completed work, etc., as well as on the basis of time sheets. In this case, wages are calculated using payroll or payslips. in this case, a credit balance is formed on account 70. Based on the data from cash documents on the issuance of wages, accordingly, this accounts payable is reduced and arises again at the next payroll.
Accounting for calculations and postings
In general, accounting for debts on taxes and fees is reflected in Kt-accounts 68 and 69, namely:
Dt 20.26.70.91.99 Kt 68.69;
As the payment is made, the debt decreases to zero or an overpayment is allowed (Debit balance),
Dt 68.69 Kt 51;
For accounts 62 and 60, the essence of the postings is described above. But when considering accounting for these calculations, one point should be discussed. Value Added Tax (hereinafter referred to as VAT) is charged to the budget , and when accounting for settlements with Suppliers, the Supplier's VAT is taken into account, which at the end of the reporting period is accepted for “deduction” when paying VAT. Let's consider this point on the wiring.
1. Dt 62 Kt 90-1 - formation of sales volume and Buyer's debt.
Dt 90-3 Kt 68 (VAT sub-account) - simultaneously with the first posting, this posting is made to calculate VAT payable to the budget on sales volume. During the quarter (quarter reporting period for VAT), VAT accruals are accumulated according to Kt-u account 68 (VAT sub-account). These two entries are made on the basis of an invoice - an invoice issued by the enterprise to the Buyer for goods, materials, works or services sold to him.
2. Dt 10,20,26 Kt 60 - formation of debt for goods and materials supplied by Suppliers, works and services. At the same time, an entry is made to register the Supplier's VAT for subsequent deduction at the end of the reporting period.
Dt 19 Kt 60 - taking into account the supplier’s VAT, both postings are made on the basis of the Supplier’s invoice.
3. At the end of the reporting period, a VAT declaration is drawn up, the accumulated VAT for deduction of the Supplier (according to Dt account 19) is written off to reduce the debt for accrued VAT on sales (according to Kt 68 VAT sub-account). In this case, a posting is made: Dt 68 (VAT sub-account ) Kt 19, and the final debt due for payment of VAT to the budget is displayed. The debt payable will be listed under Kt 68 (VAT sub-account) . It should be noted that Kt-e balance in account 68 (VAT sub-account) . A situation may arise when the amount of Supplier's VAT collected under Dt account 19 for the reporting period exceeds the amount accrued under Kt-u account 68 (VAT sub-account) , then when posting Dt 68 (VAT sub-account) Kt 19 , under account 68 (sub-account VAT) a Dt-e balance arises and the enterprise submits a VAT return with the result of a VAT refund from the budget, and not for payment as usual.
Standard entries for accounts receivable and accounts payable:
Account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” corresponds with the accounts:
debit 60 with credit accounts - 50 Cash, 51 Current accounts, 52 Currency accounts, 55 Special accounts in banks, 60 Settlements with suppliers and contractors, 62 Settlements with buyers and customers, 66 Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings, 67 Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings, 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors, 79 On-farm settlements, 91 Other income and expenses, 99 Profits and losses
on credit 60 with debit of accounts - 07 Equipment for installation, 08 Investments in non-current assets, 10 Materials, 11 Animals for growing and fattening, 15 Procurement and acquisition of material assets, 19 Value added tax on acquired assets, 20 Main production, 23 Auxiliary production, 25 General production expenses, 26 General business expenses, 28 Defects in production, 29 Service production and households, 41 Goods, 44 Selling expenses, 50 Cash, 51 Current accounts, 52 Currency accounts, 55 Special accounts in banks, 60 Settlements with suppliers and contractors, 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors, 79 On-farm settlements, 91 Other income and expenses, 94 Shortages and losses from damage to valuables, 97 Deferred expenses.
Account 76 “Settlements with various creditors and debtors” corresponds in the same way as account 60. At many enterprises, it is used for accounting with other suppliers of works, services and inventory items, that is, settlements with suppliers for non-core activities or for general business expenses are taken into account. For example, in a construction organization, this account may account for utility bills for the office, office rent, etc. However, the account has a number of sub-accounts for specific transactions. For example, subaccount 76 for accounting for VAT on advances. This subaccount accumulates VAT payable accrued by your company from the amounts of advances received for the reporting period for certain works and services, posting Dt 76 (subaccount for accounting for VAT on advances) Kt 68, subaccount for VAT. Upon completion of work 100% on objects or types of work for which advances were received, the amount of VAT accrued on advances is written off from account 76, posting Dt 68 (sub-account for VAT) Kt 76 (sub-account for accounting for VAT from advances) is made. Account 76 takes into account settlements with budgets for the rental of space in buildings owned by local municipalities and a number of other operations. Due to the brevity of the course, these operations are not covered.
Account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” corresponds with the accounts:
by debit 62 with credit accounts - 46 Completed stages of work in progress, 50 Cash, 51 Current accounts, 52 Currency accounts, 55 Special accounts in banks, 57 Transfers in transit, 62 Settlements with buyers and customers, 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors , 79 On-farm accounts, 90 Sales, 91 Other income and expenses.
on loan 62 with debit accounts - 50 Cash, 51 Current accounts, 52 Currency accounts, 55 Special accounts in banks, 57 Transfers in transit, 60 Settlements with suppliers and contractors, 62 Settlements with buyers and customers, 63 Provisions for doubtful debts, 66 Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings, 67 Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings, 73 Settlements with personnel for other operations, 75 Settlements with founders, 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors, 79 On-farm settlements.
Application of the balance sheet for account 70
The balance of the loan from the turnover in account 70 ends up in the balance sheet. When formed on the reporting date, it is reflected in the line “Accounts payable” in Section V “Short-term liabilities” (clause 20 of PBU 4/99 “Accounting statements of an organization”).
If the account balance 70 is active-passive, the data will be reflected in both the asset and liability of the balance sheet. The active balance must be entered in the “Accounts Receivable” line of Section II “Current Assets”. In financial statements, it is prohibited to offset data by reducing liabilities and assets (clause 34 of PBU 4/99).
Indicators that have a significant level should be displayed in a separate line and reflected separately (clause 11 of PBU 4/99, Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 07-02-18/01 dated 01/24/2011):
- in the liabilities side of the balance sheet this will be the line “Debt to the organization’s personnel” in the “Short-term liabilities” section;
- in the asset - the line “Advances issued to employees” in the “Current assets” section.
However, for all its “usefulness”, the turnover on account 70 does not disclose to users such important nuances as the type of accruals (salary, personal income tax, benefits, deductions), the source of financing (from the reserve, cost, net profit), the type of payment (cash, non-cash payments etc.).
For this data, it is better to refer to the payroll sheet, the summary of accrued salaries, or disclose the turnover on account 70 and other related accounts.
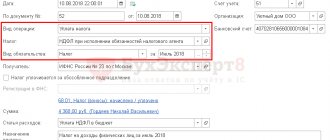
How to create a balance sheet for account 70
Let's look at this with a practical example.
Example
Romashka LLC pays salaries to its employees twice a month: Stepanov F.P. - 40,000 rubles; Ilyin I.F. - 30,000 rubles; Fedorova A.P. - 20,000 rubles.
At the beginning of November, the company had a debt to employees for accrued salaries for October: to Stepanov F.P. - 14,800 rubles; before Ilyin I.F. - 11,100 rubles; in front of Fedorova A.P. - 7,400 rubles.
For each employee in November, the accounting department made the following entries:
Dt 70 Kt 50 - wages paid for October (14,800 + 11,100 + 7,400) = 33,300 rubles.
Dt 70 Kt 50 - advance payment for November (20,000 +15,000 + 10,000) = 45,000 rubles.
Dt 44 Kt 70 - wages accrued for November (40,000 + 30,000 + 20,000) = 90,000 rubles.
Dt 70 Kt 68.01 - personal income tax is withheld from the salary 13% (5,200 + 3,900 + 2,600) = 11,700 rubles.
Now, based on the transactions, we will create a statement for November:
| Check | Balance at the beginning of November | November turnover | Balance at the end of November | |||
| Employees of organizations | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit |
| Type of wage accrual | ||||||
| Account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” | 33 300 | 90 000 | 90 000 | 33 300 | ||
| Stepanov Fedor Petrovich | 14 800 | 40 000 | 40 000 | 14 800 | ||
| Ilyin Ivan Fedorovich | 11 100 | 30 000 | 30 000 | 11 100 | ||
| Fedorova Anna Petrovna | 7 400 | 20 000 | 20 000 | 7 400 | ||
| Total | 33 300 | 90 000 | 90 000 | 33 300 | ||
Characteristics of account 68
Based on the results of their economic activities, organizations and entrepreneurs must transfer part of their funds to the budget. The same responsibilities apply to individuals.
Tax accrual for legal entities reflects account 68 in the accounting department. Transactions for the payment of budget obligations are also formed by accounting account 68.
The records contain data on accrued and paid tax liabilities of the organization itself, reflect the status of taxes withheld from employees, and provide data on indirect taxes, including those declared for deduction.
Account 68 in accounting
Tax liabilities based on the results of economic activity are calculated using account 68. Each type of tax that an organization must transfer has its own subaccount.
According to the methods of calculation, the following types of taxes are distinguished:
- Property. They are paid for the ownership of any object - transport, land, property on the organization’s balance sheet. Taxes are calculated based on the value of the taxable base and do not depend on the results of the company’s activities.
- Indirect taxes are included in the cost of goods or services provided (VAT, excise taxes, customs duties). The final payer is considered to be the direct consumer.
- Taxes based on the results of economic activity. Calculated based on the profit received.
The credit of account 68 shows the accrued amounts that must be transferred to the budget. The data must coincide with the results of tax reporting - declarations, calculations. Debit 68 of account shows transactions to pay off debt or reduce the amount of tax liabilities.
Analysis of account 68
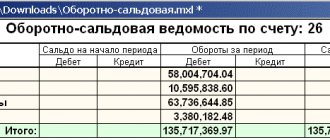
The status of tax payments for an enterprise can be seen in more detail by analyzing the subaccounts to account 68. Each tax or fee corresponds to a separate subaccount, and calculations are also carried out separately from each other. The current list is fixed in the accounting policy of the subject; the chart of accounts 68 account can be divided as follows:
- 68 01 accounting account reflects the status of personal income tax payments for employees;
- 68 02 - invoice reflecting accrued VAT;
- 68 03 - excise taxes;
- 68 04 - income tax;
- 68 06 - land tax;
- 68 07 - transport tax;
- 68 08 - tax on property of organizations;
- 68 10 - other payments to the budget;
- 68 11 - UTII;
- 68 12 - tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified tax system.
Subaccounts 68 of the accounting account are used depending on the type and nature of the activity of the economic entity. The presented list can be expanded or shortened.
The balance sheet for account 68 contains summary information and can be considered both as a whole for the organization’s obligations, and separately for each type.