What are shipping costs?
Transport costs represent the costs of an organization associated with the provision of services for the delivery of various goods: goods, materials, fixed assets.
Depending on the method of transportation, type of goods, as well as places of departure and destination, the list of documents justifying expenses may vary. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a taxpayer can take into account expenses when calculating income tax if they have:
- documenting;
- economic justification.
Thus, in order to display transport costs as expenses when determining the tax base for income tax, it is important to have their real confirmation on paper.
Read about the peculiarities of tax accounting for transport expenses in the material “Transportation expenses when calculating income tax .
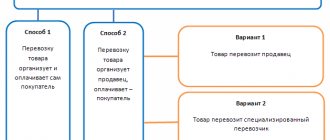
The most common type of transport service is the delivery of goods from the supplier to the buyer. The party who bears the costs themselves is determined by the terms of the sales contracts. Costs may be incurred:
- seller of goods;
- buyer.
In this case, transportation can be carried out by the following persons:
- by the seller himself;
- by the buyer using his own vehicle;
- a third party company with which either the seller or the buyer enters into an agreement.
Next, we will consider the features of documenting delivery costs carried out by the seller and buyer when transporting goods independently or with the involvement of an intermediary.
Read more about how the seller and buyer take into account transport costs in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you don't have legal access, a full access trial is available for free.
On the classification of transport costs for tax accounting purposes, see the material “Transportation costs - are they direct or indirect costs?” .
Settlement of disputes
In the event of a dispute, it is recommended to include in the contract a clause on resolving conflicts between the parties out of court.
As a rule, the document states the obligation of counterparties, before going to court, to inform the partner about their claims in writing and provide him with a certain period of time to consider them and prepare a response.
The parties also have the right, within the framework of the agreement, to enter into an agreement to resolve disputes in arbitration. In addition, they can change the territorial jurisdiction, for example, by providing for the possibility of filing a claim against the counterparty in arbitration or a court of general jurisdiction at the location of the plaintiff.
What documents do you need to have when delivering goods?
When selling goods, the seller is obliged to provide to the buyer:
- invoice (exception - the use of a special regime);
- waybill in the form TORG-12;
- other shipping documents - waybill (Bill of Lading) and bill of lading (BW).
TORG-12 is a primary document drawn up by the seller in 2 copies (one for himself, the other for the buyer). It contains information about the assets being sold and is confirmation of the transfer of ownership of them from the seller to the buyer.
TN (Appendix 4 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 15, 2011 No. 272) fixes the cost of transportation services, i.e. the amount of transportation costs. It contains information:
- about the parties to the transaction;
- transported goods and materials;
- additional documents;
- delivery vehicle;
- point and date of loading/unloading of goods;
- date of cargo delivery;
- other data.
At the same time, the technical document is not a document on the basis of which goods can be capitalized, but serves as a primary document for justifying transportation costs.
As for the TTN (Form 1-T), it is the primary document that not only confirms the organization’s transportation costs, but also reflects the information necessary for writing off and capitalizing inventory items.
It is with TTN that claims from regulatory authorities are most often associated. You can familiarize yourself with the main controversial issues and find arguments for a dispute with the inspectors in the Encyclopedia of Controversial Situations from ConsultantPlus. Trial access to the system can be obtained for free.
The CTN contains two parts - commodity and transport, and also includes the following details:
- TTN number;
- the date of its preparation;
- information about the product;
- details of the parties to the transaction;
- other data provided for by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated November 28, 1997 No. 78.
Algorithm of actions
The process of preparing a draft agreement can be divided into several stages:
- verification of the counterparty;
- determination of the subject of the transaction and the procedure for fulfilling the obligations assumed by the parties;
- compiling a list of related services ;
- establishing deadlines for the execution of the contract;
- determining the cost of services and the procedure for making payments;
- determination of conditions regarding the parties’ liability for improper fulfillment of obligations under the contract and the procedure for compensation for damage caused;
- determining the conditions and procedure for terminating the contract;
- establishing a procedure for resolving disputes that may arise between the parties during the execution of the transaction;
- application approval ;
- signing the contract.
What documents can justify the transportation of goods by the supplier?
The transportation of goods by the supplier can be understood as 2 delivery options:
- The supplier independently delivers the goods to the buyer.
- The supplier enters into an agreement with the carrier, who transports the goods to the destination.
If the supplier, when drawing up an agreement with the buyer, provides for the supply of goods on its own, then delivery can be made taking into account the following features:
- The supplier may not separately highlight the cost of delivery in the contract, but include it in the price of the goods (the first case).
- The supplier has the right to specify the delivery cost in the contract (second case).
Depending on the above conditions, the documentation of delivery services changes:
- In the first case, the supplier draws up only a waybill, which will confirm the fact of delivery and the costs of it.
- In the second case, he needs to issue a bill of lading (Bill of Lading) or a bill of lading (BW) to the buyer.
If the supplier has engaged an intermediary to transport goods, the document flow will be as follows:
- The supplier can issue a TTN in 4 copies. In this case, one copy remains with the supplier, the other three are transferred to the intermediary carrying out transportation. The intermediary, having completed delivery, transfers 3 copies of the TTN to the buyer, who puts his signature on them. One copy remains with the buyer. Based on the remaining 2, the intermediary draws up an act of services rendered. In this case, one of the copies of the TTN, signed by the buyer, is returned to the seller along with the act.
- If the supplier, instead of the TTN, decides to issue a TTN, three copies of this document will need to be made: one is intended for the carrier, the second for the seller, and the third for the buyer. The fact of provision of transport services for the supplier can be confirmed by the TN signed by the buyer and the carrier.
To learn about filling out a bill of lading using online services, read the article “Online filling out a bill of lading: what services are there?”
Cost and payment procedure
The cost of services is determined directly in the text of the contract or is established separately for each client’s application. In the second case, you can draw up an appendix to the contract with a list of carrier prices. In this case, it is advisable to indicate in the document a possible procedure for changing such a price list.
Payments under the contract are made in a lump sum or divided into stages. The parties have the right to provide for an advance payment condition .
Payment terms are set as a fixed date , if one can be determined, or tied to some event . For example, the customer can make payments within 5 banking days from the moment the cargo is accepted at the destination or after the carrier issues an invoice.
The text of the agreement also establishes the form of payment : cash or bank transfer. In addition, if the parties work on a common taxation system, it is necessary to indicate the inclusion of VAT in the cost of services.
How to justify the transportation made by the buyer?
It should be noted that when the buyer independently transports the goods from the seller’s warehouse, TN and TTN are not drawn up. And the justification for the expenses incurred by the buyer will be the travel documents issued by him (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 22, 2011 No. 03-03-10/123).
If the buyer enters into an agreement with an intermediary, then his actions must be as follows:
- You can issue a TTN in 4 copies, where the buyer fills out only the transport section. After this, the specified documents are transferred to the carrier for completion by the supplier of the goods section. Having filled out the TTN, the supplier hands over 3 copies to the carrier. Having accepted the cargo, the buyer keeps one copy for himself, and hands the remaining 2 copies to the carrier, on the basis of which he draws up an act.
- If the buyer draws up a TN, he must indicate himself as the consignee and consignor. This TN is drawn up in 2 copies - one remains with the buyer, the other is transferred to the transport organization.
Termination
According to the norms of civil law, the parties to a contract for the provision of paid services have the right to terminate the transaction at any time by mutual agreement or unilaterally.
It should be borne in mind that the initiator of unilateral termination of the transaction is obliged to compensate the counterparty for damage caused by the early termination of the contractual relationship.
To avoid conflicts , the text of the contract must indicate :
- how many days in advance and in what form must the initiator of termination of the contract notify the counterparty of his decision;
- final payments for services rendered should be made ;
- in what order is a claim for compensation for damage caused by early termination of the contract made?
- within what time period this damage must be compensated.
If it was not possible to terminate the contract voluntarily , this can be done in court.
We discuss the nuances of concluding contracts for the provision of cleaning, accounting, educational, consulting, marketing, repair, real estate, medical and legal services in separate articles.
Results
Transportation costs occur in almost any business activity. Having all the necessary supporting documents is of great importance for both suppliers and buyers, as it allows them to reduce the cost of paying income taxes.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 15, 2011 No. 272
- Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated November 28, 1997 No. 78
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.