The transfer of children's New Year's gifts to employees is not related to the employee's work activity and is not remuneration for work depending on the employee's qualifications, complexity, quantity, quality and conditions of the work performed (paragraph 1 of article 129, article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
From a civil legal point of view, the gratuitous transfer of things into the ownership of another party is a donation (clause 1 of Article 572 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). If the donor is a legal entity and the value of the gift exceeds three thousand rubles, the gift agreement must be concluded in writing (clause 2 of Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
What is a gift
The Civil and Labor Codes of the Russian Federation establish the following definitions:
- A gift that is not related to the employee’s work activity. For example, issuing souvenirs for an employee’s anniversary or a holiday.
- Rewarding an employee for his labor merits. For example, for the fulfillment of a plan or for the successful execution of a transaction, the employer decided to reward subordinate employees with gift certificates, vouchers, equipment or other gifts.
According to Part 1 of Article 572 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a gift should be considered any thing (including money, electronic and paper gift certificates and even postcards) that the donor transfers to the recipient free of charge. In our case, the donor is the employer, and the recipient is one of the subordinate employees. In this case, a special document is drawn up - a gift agreement.
A gift agreement is required only if the souvenir being given has a value of more than 3,000 rubles, and the donor is a legal entity - the employing organization. If the price of the gift is lower than the specified amount, it is not necessary to draw up a gift agreement.
IMPORTANT!
For employees of budgetary institutions, and especially civil servants, it is recommended to draw up a gift agreement, regardless of the cost of the gift. This will protect the employer and employee from “corruption” problems and from claims from controllers from the Federal Tax Service.
What to do if there are many recipients? For example, for the New Year, the director of a manufacturing enterprise decided to give expensive souvenirs to 1,500 employees. Do not enter into a gift agreement with each of the employees of the enterprise. There is a way out of the situation. Draw up a multilateral gift agreement in which the donor is the same employer. And the recipients are all the company employees who were decided to be awarded with gifts. Such standards are enshrined in Article 154 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation determines that the employer has the right to reward a subordinate for achievements in his work. The cost of the gift is part of the recipient’s remuneration, which entails compliance with certain tax laws. Keep in mind that the transfer of such a souvenir is not formalized by a gift agreement, but is regulated in an employment contract (agreement, contract).
In essence, such a gift is a bonus, but not issued in cash, but transferred in kind, that is, in non-monetary form. Read about the features of bonuses for employees at the end of the year in the article “How to calculate and accrue the 13th salary.”
ConsultantPlus experts looked at how to arrange specific gifts:
- theater tickets;
- Gift certificates;
- for children;
- souvenirs for contractors.
Use these instructions and samples for free.
to read.
What about VAT?
It is better to pay VAT on the cost of gifts. And not only because this is the position of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation (Resolution No. 1001/13 dated June 25, 2013) and the regulatory authorities.
For more information, see our material “Do I need to pay VAT when giving gifts to employees?”
When giving gifts, including to children of employees, ownership of the goods is transferred free of charge. And by virtue of paragraph 1 of Art. 39 and paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, such transfer is subject to VAT. Consequently, the organization must calculate the tax on the market value of gifts (clause 2 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and pay it to the budget. You also need to draw up an invoice - in one copy, with dashes in lines 6-6b. One invoice is enough for all gifts.
If the gift seller also pays VAT, then there are no special problems here. By calculating the tax for this transaction, the purchasing organization receives the right to deduct the “input” tax (Clause 1, Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The market value of gifts, from which in this case VAT payable must be calculated, will be the price of their acquisition. Thus, the amount of tax accrued will be equal to the amount of the deduction. This means that the organization will not lose anything.
At the same time, failure to pay taxes may result in:
- claims from regulatory authorities;
- impossibility of deducting “input” VAT (clause 2 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the need for separate accounting (clause 4 of article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If gifts were purchased from a VAT evader (for example, from a “simplified person”), you will actually have to pay the tax at your own expense. If the amounts are significant, it is better to avoid such suppliers.
How to arrange gifts for employees
Encouraging employees is an initiative of the employer. If the manager decides to reward employees in the form of gifts, the gifts to employees must be properly executed. The employer will need:
- Order for the purchase and issuance of gift products.
- List of souvenirs issued to employees.
- Donation agreement, if necessary.
Let's start with the order for the delivery of presents. To purchase souvenirs and present gifts in a formal atmosphere, an official order from the manager is required. Formalize it with an organization order. It is permissible to use standardized forms T-11 or T-11a. It is allowed to use any form. Please fill out the order according to the general rules. Please provide a list of employees. It is permissible to separate it into a separate annex to the order.
The law makes it possible to divide orders: in the first order, a specific instruction is given to the responsible employee to purchase souvenirs, certificates, gifts, postcards, and in the second order, a list of employees who will be awarded awards is determined.
Then create a list of gifts for employees. Compose the document in any form. The most convenient way to do this is to use a table that will indicate the full name, position of the employee, the name of the gift and its value. We recommend that you provide separate columns for the signatures of the recipient employees and the date of delivery. Please note that the signature on the statement is a fact of receipt of the gift. The employee indicates the date of receipt personally.
Next, you will have to draw up a gift agreement. Let us remind you that the conclusion of this document is mandatory under the following conditions:
- The donor is a legal entity. That is, the employer encourages its employees and their children. Or the company decided to reward its customers, contractors or business partners.
- The price of the souvenir is more than 3000 rubles.
If both conditions are met, then the gift agreement is a mandatory document; only if it is available and properly executed is it possible to legally transfer the souvenir to the recipient.
Simplified form of gift agreement
The standard form is general, that is, it is suitable for different donation options. Therefore, it is not necessary to use the generalized form. The employer has the right to limit himself to drawing up a gift agreement in simple written form.
To simplify registration, please note the following mandatory details in the document:
- Title of the document.
- Date and place of compilation.
- Name of the parties: donor and donee employee.
- Subject of the agreement, its characteristics and cost.
- Signatures of the parties.
Gift decoration
Any decision of the employer in the organization is formalized by an administrative act - an order. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation specifies how to arrange gifts for employees for the New Year - the gift is formalized by an appropriate agreement. In accordance with Art. 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, written form is required only if the donation is made by a legal entity and the value of the gift exceeds 3,000 rubles. An essential condition of such an agreement is its subject matter (Article 572 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). If there are many employees being gifted, the agreement is made multilateral (Article 154 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Additionally, you will need to draw up a statement indicating that the issuance actually took place.
Registration consists of the following steps:
- Issuance of an order and familiarization with it to employees against signature.
- Preparing a statement and presenting gifts according to it.
- Conclusion of an agreement (if necessary).
For a simplified gift agreement, the following details are required:
- Title of the document;
- place and date of its compilation;
- information about the parties: employer and employee;
- subject of the agreement: description of the gift, its value, characteristics;
- signatures.
Income tax on gifts
After documenting the donation, accounting and taxation of New Year's gifts for the children of employees and the employees themselves are carried out. Personal income tax is calculated on all types of income of a citizen. There are no exceptions. There are rights to benefits and exemptions, but there are no exceptions. Even a gift to an employee or his child in kind (an item, equipment, dishes and even a vase) is subject to income tax.
IMPORTANT!
The tax base for calculating an employee’s personal income tax includes both tangible and intangible income (Clause 1, Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that all income received by a citizen is subject to taxation, including income received in the form of cash, tangible and intangible assets. Consequently, the present is the same income of the employee, and, accordingly, tax is withheld from it.
If the donor is the employer, then he charges personal income tax. Let us recall that the employer acts as a tax agent in relation to his subordinates. The organization maintains accounting and taxation of New Year's gifts according to the general rule: from all income that was received by an employee from a specific employer, the tax agent withholds and transfers it to the personal income tax budget.
If the total value of all gifts received for the reporting year by an individual employee is no more than 4,000 rubles, then this type of remuneration is not subject to personal income tax (clause 2, clause 2, article 211, clause 28, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03- 04-06/16327 dated 05/08/2013). This means that if during the calendar year you received from your employer, for example, a painting worth 1,500 rubles (regardless of the holiday), then personal income tax will not be withheld. But keep in mind that if you are given another valuable gift in the same year, for example, worth 5,000 rubles, then personal income tax will be withheld from 2,500 rubles (5,000 + 1,500 – 4,000).
Calculating the tax base for gifts is simple:
- Let's sum up the prices of all souvenirs received.
- We subtract the amount of the benefit due - 4000 rubles.
- From the positive difference we calculate personal income tax at the appropriate rate.
Income tax rates are determined in the generally accepted manner. Tax residents of Russia will be withheld 13%. And if the citizen is a non-resident, then the personal income tax rate is 30%. A tax resident of our country is considered to be those citizens who reside on the territory of the Russian Federation for at least 183 days in the reporting period, that is, in a calendar year.
New Year's gifts: how to take into account and correctly calculate taxes
For the New Year, many organizations purchase confectionery sets, gift certificates, household appliances and other goods to give to employees as New Year's gifts. When taxing, you should take into account the following nuances:
– in the application of income tax benefits;
– calculation of insurance premiums in Belgosstrakh from September 1, 2021;
– reflecting the gratuitous transfer of gifts in the income tax return, etc.
We'll look at the details in the material.
- Gift accounting
- When calculating income tax, do not forget about benefits
- Insurance premiums to the Social Security Fund and Belgosstrakh: there is a nuance
- When transferring gifts, pay VAT
- Income tax: gratuitous transfer is not reflected in the declaration
- Situation. Handing over New Year's gifts to employees
Gift accounting
Purchased goods are reflected in the debit of account 10 “Materials” as inventories at actual cost (clause 16 of the Instructions on the procedure for applying the standard chart of accounts, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated June 29, 2011 No. 50 (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 50), paragraphs. 2, 3, 6, 7 Instructions for accounting of inventories, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated November 12, 2010 No. 133 (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 133)).
Organizations have the right to clarify the contents of individual sub-accounts, excluding or merging them, as well as introduce additional sub-accounts, therefore, to account for acquired material assets as New Year's gifts, you can open a sub-account, for example 10-13 “New Year's gifts for employees” (part three of clause 3 of Instruction No. 50 ).
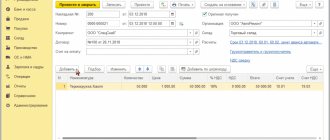
For the issuance of gifts, a statement of issue is drawn up, where each employee signs when receiving them. Next, a primary accounting document is drawn up - an act for writing off gifts, which serves as the basis for reflecting the transfer of gifts on accounting accounts (clause 1, article 10 of the Law of the Republic of Belarus dated July 12, 2013 No. 57-Z “On Accounting and Reporting”, clause 66 Instructions No. 133).
The transfer of New Year's gifts to employees is a gratuitous transfer and is reflected by entries in the debit of subaccount 90-10 “Other expenses for current activities” and the credit of account 10 (clause 16, part 19, clause 70 of Instruction No. 50, paragraph 4, clause 13, part two clause 32 of the Instructions for accounting of income and expenses, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated September 30, 2011 No. 102 (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 102)).
When calculating income tax, do not forget about benefits
When determining the tax base for income tax, all income of the payer received in cash and in kind is taken into account, incl. goods (clause 1 of article 199, subclause 2.2 of clause 2 of article 200 of the Tax Code of the Republic of Belarus; hereinafter referred to as the Tax Code).
The tax base is determined as the cost of gifts, including VAT (clause 1, article 200 of the Tax Code). However, a benefit can be applied: income that is not remuneration for the performance of labor or other duties is exempt from tax from each source during a calendar year in the amount (clause 23 of Article 208 of the Tax Code):
– 1,984 rub. – when receiving income from organizations that are the place of main work (including income of pensioners who previously worked for these employers);
– 131 rub. – when receiving income from other organizations.
Thus, if the value of transferred gifts including VAT, issued to an employee by an organization for which it is the main place of work, does not exceed 1,984 rubles, the object of income tax does not arise.
If the value of transferred gifts, including VAT, issued to a part-time employee, does not exceed 131 rubles, the object of taxation also does not arise. If the specified threshold is exceeded, the excess amount is subject to taxation in the month in which the excess occurred (subclause 1.2, clause 1, article 213 of the Tax Code).
The calculated amount of income tax is withheld by the organization from any funds paid to the employee (part two, paragraph 4, article 216 of the Tax Code).
Insurance premiums to the Social Security Fund and Belgosstrakh: there is a nuance
List No. 115* does not mention the social benefit in the form of issuing New Year's gifts, therefore their cost is an object for calculating insurance contributions to the Social Security Fund and Belgosstrakh. To calculate insurance premiums, the cost of gifts including VAT is taken into account.
For reference: the object for calculating mandatory insurance contributions to the Social Security Fund for employers and working citizens is payments of all types in cash and (or) in kind, accrued in favor of working citizens on all grounds, regardless of sources of financing, including remuneration under civil contracts, except provided for by List No. 115, but not higher than 5 times the average salary of workers in the republic for the month preceding the month for which mandatory insurance contributions are paid, unless otherwise established by the President of the Republic of Belarus (Article 2 of the Law of the Republic of Belarus dated 02.29.1996 No. 138-XIII “On mandatory insurance contributions to the budget of the state extra-budgetary fund for social protection of the population of the Republic of Belarus”).
The object for calculating insurance premiums in Belgosstrakh is payments of all types accrued in favor of persons subject to compulsory insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases, on all grounds, regardless of sources of financing, except for payments provided for in List No. 115 (clause 2 of the Regulations on the procedure for paying insurance premiums to the insurer for compulsory insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases, approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated October 10, 2003 No. 1297; hereinafter referred to as Regulation No. 1297).
Please note the nuance regarding the calculation of insurance premiums in Belgosstrakh: from September 1, 2021, payments made in favor of persons on vacation are not subject to their calculation:
– for pregnancy and childbirth;
– in connection with the adoption of a child under 3 months of age;
– child care up to 3 years old.
This rule does not apply to cases where such persons, during the period of these vacations, work under the terms of another employment agreement (contract), perform work under a civil contract (provide services, create intellectual property) with the insurer (part three, clause 2 of Regulation No. 1297).
Thus, if gifts are given to employees on maternity leave and childcare leave under 3 years of age, the object for calculating insurance premiums in Belgosstrakh does not arise.
Insurance contributions to the Social Security Fund, made at the expense of the organization, accrued on the value of the donated gifts, are reflected in the debit of those accounts that reflect the value of the donated gift, i.e. on the debit of subaccount 90-10 and the credit of account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” (clause 54 of Instruction No. 50, paragraph 4 of clause 13 of Instruction No. 102).
Insurance premiums in Belgosstrakh are reflected in the debit of subaccount 90-10 and the credit of subaccount 76-2 “Calculations for property and personal insurance” (clause 59 of Instruction No. 50, paragraph 4 of clause 13 of Instruction No. 102).
When transferring gifts, pay VAT
The issuance of New Year's gifts to employees is a gratuitous transfer, therefore an object of VAT taxation arises (subclause 1.1.3, clause 1, article 115 of the Tax Code).
Tax base for gratuitous transfer:
– purchased gifts – determined based on the price of their acquisition;
- goods produced by the organization itself - based on the cost of such goods (clause 14 of article 120 of the Tax Code).
The moment of actual implementation in case of gratuitous transfer is recognized as the day of such transfer (Clause 21, Article 121 of the Tax Code).
“Input” VAT on purchased gifts is deducted in the generally established manner. If desired, it can be attributed to an increase in their value, and in this case the tax base will increase by the amount of “input” VAT (clauses 5, 11 of Article 132 of the Tax Code).
If gift certificates are given as a New Year's gift, then there is no income from the transfer of property rights, therefore the VAT tax base is zero (subclause 16.1, clause 16, article 120 of the Tax Code; letter of the Ministry of Taxes of the Republic of Belarus dated September 30, 2011 No. 2-1-10 /10544 “On value added tax”).
For turnover on gratuitous transfers to individuals, the organization is obliged to create one final ESHF, which is sent to the Portal no later than the 20th day of the month following the expired reporting period.
For reference: the VAT tax period is a calendar year, the reporting period is a calendar month or quarter (Article 127 of the Tax Code).
Turnover on gratuitous gift transfers is reflected in the VAT return on page 1: in gr. 2 – cost of gifts including VAT, in gr. 4 – accrued VAT on gratuitous transfer.
For reference: in pp. 1–9 section. 1 of Part I of the VAT return reflects the tax base for operations for the sale of objects falling within the reporting period (paragraph 2 of part one, subclause 15.1, clause 15 of the Instructions on the procedure for filling out tax returns (calculations) for taxes (duties), the purchase book, approved Resolution of the Ministry of Taxes and Taxes of the Republic of Belarus dated January 3, 2019 No. 2).
Income tax: gratuitous transfer is not reflected in the declaration
Since the transfer of New Year's gifts is a gratuitous transfer, their cost is not included in revenue. The costs also do not include their cost and VAT calculated on such a transfer (part two, clause 1, article 168, subclause 1.19, clause 1, article 173 of the Tax Code). Accordingly, the turnover on the gratuitous transfer of New Year's gifts is not reflected in the income tax return and is not taken into account for the purpose of calculating income tax.
Situation. Handing over New Year's gifts to employees
The organization purchased 20 mixers for 96 rubles. (including VAT at a rate of 20% - 16 rubles), which were given to 20 employees as New Year's gifts.
The organization's accounting records the following entries (see table):
| Contents of operations | Debit | Credit | Sum, rub. |
| Funds were transferred to the seller for mixers | 60 | 51 | 1 920 (20 pcs. × 96 rub.) |
| The cost of purchased mixers is reflected | 10 | 60 | 1 600 |
| Input VAT on purchased mixers is reflected | 18 | 60 | 320 |
| Accepted for VAT deduction | 68-2 | 18 | 320 |
| The cost of donated mixers has been written off (excluding VAT) | 90-10 | 10 | 1 600 |
| VAT on gratuitous transfer is reflected | 90-8 | 68-2 | 320 (RUB 1,600 × 20%) |
| Insurance contributions to the Social Security Fund have been calculated | 90-10 | 69 | 652,8 (RUB 1,920 × 34%) |
| Insurance contributions to the Social Security Fund are withheld from employee income | 70 | 69 | 19,2 (RUB 1,920 × 1%) |
| Insurance premium charged in Belgosstrakh | 90-10 | 76-2 | 11,52 (RUB 1,920 × 0.6%) |
| For reference: employees will not be subject to income tax if during the calendar year the amount of payments not related to the performance of work duties does not exceed 1,984 rubles for employees and part-time workers. or 131 rub. accordingly (clause 23 of article 208 of the Tax Code) | |||
_________
* List of payments for which contributions for state social insurance are not charged, including professional pension insurance, to the budget of the state extra-budgetary fund for social protection of the population of the Republic of Belarus and for compulsory insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases to the Belarusian Republican Unitary Insurance Enterprise “Belgosstrakh”, approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated January 25, 1999 No. 115 (hereinafter referred to as List No. 115).
Natalya Borisenko, auditor
When to withhold personal income tax from a gift
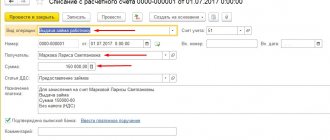
The withholding date and deadline for remitting income taxes on gifts received depend on the form in which the gift is given. Note:
- If money was gifted, then income tax is withheld on the day the money was transferred to the donee. For example, on the day of a New Year's corporate party. And the withheld personal income tax should be transferred to the budget no later than the day following the date of delivery of the money. For example, the day after a corporate event.
- If the incentive is made in material form, then how to withhold 13% or 30%? Tax will have to be withheld from wages or other amounts of remuneration for work. Moreover, withhold personal income tax from the next payment to the employee - advance payment for the first half of the month worked, wages for the remainder of the billing period. And the withheld tax must be transferred no later than the next day after the day of withholding.
Please note that if the company was unable to withhold personal income tax from the souvenir for any reason, then the Federal Tax Service should be notified about this in the appropriate manner. To do this, fill out a 2-NDFL certificate for the employee with taxpayer attribute “2” and submit the reporting document to the Federal Tax Service no later than March 1 of the year following the reporting year.
For example, in 2021, the institution gave an employee a gift worth 5,000 rubles. It was not possible to withhold personal income tax (the employee quit). Therefore, the organization is obliged to submit 2-NDFL for the employee before 03/01/2021.
In the report, reflect the cost of the souvenir under income code 2720. The income code should be indicated for all types of incentives, even with a cost of up to 4,000 rubles. Indicate the non-taxable value of the gift of 4,000 rubles (deduction) in the appropriate columns of the 2-NDFL certificate under deduction code 501.
The type of gift does not matter for personal income tax purposes. Income tax is withheld regardless of the relationship in which it is received. Therefore, calculate the tax on remuneration received under a gift agreement and under an employment agreement.
Product category
To correctly calculate the VAT base, the company must determine which category of goods the transferred gift belongs to. And then calculate the tax base for calculating VAT in relation to all gifts classified as intended for sale in one’s own capacity, the value of which exceeds 100 rubles.
At the same time, the company will not be able to deduct input VAT when purchasing gifts. Read about this in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 23, 2014 No. 03-07-11/53626.
The possibility of deducting VAT arises only in case of refusal of the benefit provided for in Article 149 of the Tax Code. Financial department specialists have repeatedly reported this in their letters (letter of the Russian Ministry of Finance dated June 14, 2021 No. 03-07-11/36977, letter of the Russian Ministry of Finance dated February 26, 2021 No. 03-07-07/10954).
Insurance premiums from gifts
The employer's obligations to accrue social insurance from gifts directly depend on their type. If gifts are issued within the framework of civil law relations, that is, under a gift agreement, then there is no need to charge insurance premiums. Please note that this condition applies only to employees of the institution.
If a gift is given to a citizen who is not in an employment relationship with the organization (a souvenir to a client), then there is no need to accrue insurance coverage. Moreover, the presence of a gift agreement does not play any role (clause 1, 4 of article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1 of article 20.1 of law No. 125-FZ, letters of the Ministry of Finance dated December 4, 2017 No. 03-15-06/80448, Ministry of Labor dated 27.10 .2014 No. 17-3/B-507).
When a gift is given as part of an employment contract as an employee’s remuneration for work, certain achievements and other working conditions, insurance premiums must be charged.
Therefore, in order to avoid additional costs for paying insurance premiums from gifts to employees, a gift agreement is concluded. Let us repeat that the cost of the gift is not important. The form of the gift does not matter, be it an item, a certificate or money. If there is a written gift agreement, then the employer does not pay contributions to the Federal Tax Service and Social Security. As a result, there is no basis for calculating insurance premiums.
IMPORTANT!
Check the gift agreement for content! No references or references to employment agreements are included in the document. Eliminate references to collective bargaining agreements. Remove labor law language and interpretations from the agreement. Do not allow the conditions for determining a gift to be fixed depending on the position or labor achievements or results. If the document contains such wording, then controllers will recognize the gift as one of the types of remuneration for work. And they will charge additional insurance premiums from the cost of gifts.
Recognition of implementation
In addition, VAT is charged on the value of gifts donated free of charge on the basis of subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code. If gifts are given as part of an advertising campaign, then VAT is charged only on the cost of the transferred goods over 100 rubles (clause 3, subclause 25, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Here it is necessary to immediately make a reservation that the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2014 No. 33 separates the concepts of advertising materials and goods intended for sale in their own capacity.
So, for example, the transfer of catalogues, leaflets and brochures distributed free of charge to potential buyers is not subject to VAT, regardless of the amount of expenses for the acquisition (creation) of these materials, since it belongs to the category of goods not intended for sale as goods.
As for gifts such as notebooks, umbrellas, sweets, etc., the cost per unit of which exceeds 100 rubles, their transfer to potential buyers is subject to VAT in accordance with the generally established procedure.
VAT on gifts
According to paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the opinion of experts from the Ministry of Finance (letter No. 03-07-11/16 dated January 22, 2009), a gift is a freely transferred value dedicated to a holiday or significant date, which is subject to value added tax. The organization that presented the souvenirs must charge VAT and deduct the amount of input tax (if there is an invoice). Based on the results of the transaction, the operating result is zero, since the accrued and written off amounts are similar to each other.
The tax base for calculating VAT is the cost of the souvenir, and the tax itself is calculated at an 18% rate (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT!
VAT on gifts given after 01/01/2019 is calculated at the new rate of 20%. Read about all changes in fiscal legislation in the article “All changes in taxes for 2021.”
If the gifted value is formalized as a reward for particularly distinguished employees, that is, the possibility of such reward is included in the provisions on remuneration and bonuses, then the gifts will not be salable and VAT will not be charged on them. Value added tax is not charged on the amount of a gift given to employees in the form of monetary incentives.
If the institution is on the simplified tax system and does not pay VAT, then the deduction does not apply, since input tax is not possible in the organization. On a simplified basis, in case of a gift, there is no need to pay VAT (Clause 2 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the organization has a general tax system or UTII, then VAT on themed souvenirs for employees is charged according to the general rules (clause 4 of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), since donation is not the activity in connection with which the organization was transferred to the UTII regime .
Accounting for New Year's gifts for employees' children
The procedure for reflecting in the accounting records New Year's gifts purchased by the organization for the children of employees is not established by law and should be enshrined in the accounting policies of the organization. In practice, several options are used:
- the cost of purchased New Year's gifts for the children of employees is charged at the time of purchase to the account of other expenses 91.2 “Other expenses” (clause 12 of PBU 10/99), and in order to control the movement of gifts, their accounting is organized on an off-balance sheet account;
- purchased gifts are accounted for as part of inventories on account 10 “Materials”;
- purchased gifts are recorded as goods on account 41 “Goods”.
If New Year's children's gifts, according to the accounting policy of the organization, are accounted for as inventories or goods and their cost was not taken into account in expenses earlier at the time of purchase, then their cost is included in other expenses when transferred to the employee (paragraph 5, paragraph 11, paragraph 16 of PBU 10/ 99).
The amount of VAT calculated on the gratuitous transfer of gifts is taken into account in other expenses (paragraph 5, clause 11, clause 16 of PBU 10/99) and is reflected in the accounting records as an entry in the debit of account 91.02 “Other expenses” and the credit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees" subaccount "Value Added Tax".
Income tax on a gift
Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03-04-06/6-329 dated November 22, 2012 and No. 03-03-06/1/653 dated October 19, 2010 establish that when taxing profits, the cost of gifts is not taken into account (clause 16 of Article 270 of the Tax Code RF), since they are considered gratuitously transferred property. Accounting for gifts to employees in accounting includes the amount of accrued VAT as part of the “Other expenses” account, while in the NU for gratuitous transfer the cost of the gift is not taken into account. The result is the resulting difference and the institution’s permanent tax obligations (PBU 18/02 “Accounting for calculations of corporate income tax”).
If gifts are equated to the cost of remuneration that stimulates employees based on the results of work, then these costs are taken into account in the income tax (clause 25 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The accountant must demonstrate certain evidence that the gift is an incentive for achieving high production results.
The taxpayer’s salary regulations must confirm the possibility of such operations, and incentive clauses must be included in the regulations and the collective agreement. The delivery is made as follows:
- An order or directive from the manager is being prepared to award bonuses to particularly distinguished employees. The order must refer to a specific clause in the bonus regulations.
- A list of awarded employees and a register with signatures of employees confirming receipt of remuneration are compiled.
IMPORTANT!
Gifts purchased through subsidies or LBO cannot be recognized as income tax expenses!
Taxation
Income tax
Personal income tax on gifts is paid, but only on amounts over 4,000 rubles. This is the opinion of law enforcers, based on the interpretation of the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2, clause 2, article 211, clause 28, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-06/16327 dated 05/08/2013). Not only material income, but also intangible income is subject to taxation.
Tax calculation:
- sum up the cost of all gifts and presents received during the reporting year;
- deduct a non-taxable amount of 4,000 rubles;
- We calculate the tax at a rate of 13% for residents and 30% for non-residents.
Withholding is made from cash payments on the day of issuance of the gift, transfer - no later than the next day, from intangible gifts - at the expense of the nearest cash payments, and the transfer is made no later than the day following the day of withholding.
Insurance premiums
Insurance premiums, regardless of the cost and type of gift, are not charged on gifts. This opinion of representatives of government agencies is based on clauses 1, 4 of Art. 420 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1, art. 20.1 of Law No. 125-FZ and set out in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated December 4, 2017 No. 03-15-06/80448 and the letter of the Ministry of Labor dated October 27, 2014 No. 17-3 / B-507.
Value added tax
VAT is charged on gifts; the opinion of representatives of government agencies is based on paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and set out in letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-11/16 dated January 22, 2009. Tax is calculated on the purchase price of the gift without VAT, and when donating the company’s own products - on its cost. The invoice is drawn up in a single copy for all gifts according to the statement. Input VAT can be deducted only if there is a supplier invoice (letter from the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-11/61750 dated 08/15/2019 and No. 03-07-09/6171 dated 02/08/2016).
Income tax
In accordance with paragraph 16 of Art. 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax is not charged on gifts. This statement also confirms the opinion of law enforcement officials. It is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03-04-06/6-329 dated November 22, 2012 and letter No. 03-03-06/1/653 dated October 19, 2010. Gifts are property transferred free of charge into the ownership of employees; their value should not be taken into account when calculating income tax.
Key points about paying taxes and fees on gifts
We offer an easy-to-use table reflecting the basic rules for paying taxes and fees when donating valuables to employees.
| Financial responsibility | Gift to an employee within the framework of labor relations |
| Personal income tax | The non-taxable amount of the gift is 4,000 rubles per year. Gifts in excess of 4,000 rubles (increasing amounts at the end of the year) are taxed at a rate of 13% for residents and 30% for non-residents. |
| Insurance contributions, including pensions, health insurance and others | Not credited. |
| VAT | Accrued on the purchase price excluding VAT or on the cost price. |
| Income tax | It is not accrued and is taken into account as expenses when calculating the tax base. |
Children's gifts
In almost every institution, children of employees are given sweet New Year's boxes. There are no exceptions for the design of such gifts - accounting and tax accounting of children's New Year's gifts to employees is carried out as follows:
- Calculate personal income tax if the amount of all gifts exceeds 4,000 rubles. Example: an employee received a souvenir for March 8 (500 rubles), a present for the company’s anniversary (3,000 rubles), and for the New Year she was given two bags (1,000 rubles each). Let's sum up the cost of all gifts for a calendar year: 500 + 3000 + 1000 + 1000 = 5500 rubles. Personal income tax will have to be withheld from the excess amount: 5500 – 4000 = 1500 rubles. Apply the rate depending on the taxpayer status: resident - 13%, non-resident - 30%.
- Insurance premiums are not charged for gifts to employees' children. Such gifts are not remuneration for work and have nothing to do with the labor relationship between the employer and the employee.
- When calculating income tax, do not take into account the costs of purchasing souvenirs for employees' children.
- Charge VAT on the purchase price of the gift without VAT, and if you give your own manufactured products, charge VAT on the cost of production.
Don't forget to decorate your children's gifts accordingly. Issue an order for the issuance of gifts, create a delivery list. Employees - parents of children who will receive gift boxes for the New Year - must sign for receipt.
Gift Tax Reminder
We offer a simple and convenient table for an accountant to use, which will allow you to quickly determine how to properly keep accounting for children's New Year's gifts and souvenirs for the organization's employees themselves.
| Type of tax burden | A gift given within the framework of civil legal relations | A gift given as part of an employment relationship (as remuneration for work) |
| Personal income tax | Withhold personal income tax at the appropriate tax rate on the cost of a souvenir exceeding 4,000 rubles. Remuneration worth up to 4,000 rubles is not taxed. | |
| Insurance coverage (compulsory insurance, compulsory medical insurance, VNIM, NS and PZ) | Don't charge. Conclude a gift agreement to avoid problems with controllers. | Charge the entire cost at the general insurance rates. |
| VAT | Charge VAT in the prescribed manner. | Exclude the cost of a gift given as part of an employment relationship from the VAT calculation base. |
| Income tax or simplified tax system | Do not include them in expenses when calculating the tax base. | Take into account expenses when calculating the tax base. |
Results
As you can see, keeping track of children's New Year's gifts is not so difficult. Follow our simple recommendations, and these pre-holiday chores will only be a joy for you.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n
- Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated June 25, 2013 No. 1001/13
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Accounting for gifts in non-profit organizations
Instructions on how to register gifts for employees for the New Year (including their children) in accounting:
- If the reward is in the form of a bonus for high performance results:
- accrual of employee incentives in the form of a bonus as part of salary expenses - Dt 20, 21, 23, 25, 26, 29, 44 Kt 70;
- calculation of insurance premiums - Dt 20, 21, 23, 25, 26, 29, 44 Kt 69;
- the employee received a bonus payment - Dt 70 Kt 91.1, 90.1;
- withholding of income tax - Dt 70 Kt 68;
- accounting for the amount of the bonus in the expenses of the institution - Dt 91.2, 90.2 Kt 10, 41;
- VAT calculation - Dt 91.2, 90.3 Kt 68.
- If an employee is given a New Year’s souvenir worth over 4,000 rubles:
- accounting for the purchase price as expenses - Dt 91.2 Kt 10, 41;
- VAT calculation - Dt 91.2 Kt 68;
- accrual of permanent tax liability - Dt 99 Kt 68;
- withholding personal income tax from an employee - Dt 70 Kt 68.
Gifts for clients
The transfer of something to third parties in itself is a gratuitous transfer subject to VAT and without reducing income tax on the cost of such transfer. If you want to take into account the costs of purchasing gifts for clients as part of other expenses (clause 49, paragraph 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), you need to justify such expenses, including with documentation. Establish in a local act general criteria for clients whose retention as partners is economically significant for the company. One of the methods of such retention is the periodic delivery of gifts of a certain value on holidays or dates specified in the local act.
Delivery of postcards to clients, costs for them (including envelopes) are taken into account as part of other expenses (clauses 24 and 25, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, FAS in case No. A40-22927/12-107-106).