From May 1, 2021, the minimum wage will be 11,163 rubles (+17.6%), i.e. will be equal to the federal cost of living for workers. Vladimir Putin announced this at a meeting with workers of the Tver Carriage Plant.
From January 1, 2021, the minimum wage is 9,489 rubles.
Also read the article: Living wage.
Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a law on increasing the minimum wage (minimum wage). According to it, the minimum wage will be increased by 4% from July 1, 2021, from 7,500 rubles. up to 7800 rub. per month.
From July 1, 2021, the federal minimum wage will be raised from 7,500 to 7,800 rubles.
Table of the regional minimum wage 2021 for the constituent entities of Russia. More precisely, it is called the Minimum Wage in the Regions (MW). Not all regions have raised the minimum wage bar above the federal one.
In fact, the employee’s salary paid in person may be lower than the regional minimum wage, since the minimum wage is calculated from the accrued salary, i.e. before personal income tax is withheld. Accordingly, with an accrued salary of 1 minimum wage (7,800 rubles), the amount of payment to the employee in person is reduced by the amount of personal income tax. Also, the calculation of sick leave may not be lower than the calculation based on the local minimum wage.
Let us remind you that as of July 1, 2021, the Federal minimum wage will be 7,800 rubles.
| Region code | Region of the Russian Federation | Minimum wage from July 1, 2021, rubles |
| 1 | Republic of Adygea | 7 800 |
| 2 | Republic of Bashkortostan | 8,900, including allowances for work in special climatic conditions 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 3 | The Republic of Buryatia | 7 800 |
| 4 | Altai Republic | 8751 – for employees of extra-budgetary organizations, except for organizations and individual entrepreneurs operating in the field of agriculture and education 7800 – for employees of organizations operating in the field of agriculture 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 5 | The Republic of Dagestan | 7 800 |
| 6 | The Republic of Ingushetia | 7 800 |
| 7 | Kabardino-Balkarian Republic | The cost of living of the working population for the fourth quarter of the previous year, with quarterly indexation throughout the year 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 8 | Republic of Kalmykia | 7 800 |
| 9 | Karachay-Cherkess Republic | 7 800 |
| 10 | Republic of Karelia | The living wage for the working population, established for the third quarter of the previous year, is 8,900 rubles. – for employees employed by agricultural producers in the northern part of the Republic of Karelia (Belomorsky, Kalevalsky, Kemsky, Loukhsky districts, Kostomuksha) 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 11 | Komi Republic | 8100 rub. – for employees who work in the southern climatic zone: the cities of Vuktyl, Sosnogorsk, Syktyvkar, Ukhta with their subordinate territories, Koygorodsky district, Kortkerossky district, Knyazhpogostsky district, Priluzsky district, Syktyvdinsky district, Sysolsky district, Troitsko-Pechorsky district, Udorsky district, Ust-Vymsky district, Ust-Kulomsky district 9300 rub. – for employees who work in the northern climatic zone: the cities of Vorkuta, Inta, Pechora and Usinsk with their subordinate territories, Izhemsky district, Ust-Tsilemsky district 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 12 | Mari El Republic | 9251 7 800 (for public sector employees) |
| 13 | The Republic of Mordovia | 7 800 |
| 14 | The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | 16 824 7 800 (for public sector employees) |
| 15 | Republic of North Ossetia–Alania | 7 800 |
| 16 | Republic of Tatarstan | 8252 7 800 (for public sector employees) |
| 17 | Tyva Republic | 7 800 |
| 18 | Udmurt republic | 7,800 (taking into account the regional coefficient of 8970) 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 19 | The Republic of Khakassia | 7 800 |
| 20 | Chechen Republic | 9274 7 800 (for public sector employees) |
| 21 | Chuvash Republic | 7 800 |
| 22 | Altai region | 9400 rub. – for employees of non-budgetary organizations. With the exception of employees who participate in public works or are temporarily employed under contracts between employers and employment services. As well as disabled employees employed under the established quota in public organizations of disabled people 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 23 | Krasnodar region | The monthly subsistence minimum for the working-age population is 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 24 | Krasnoyarsk region | RUB 16,130 – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in Norilsk 15,515 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in the North-Yenisei region 17,687 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in the Taimyr Dolgano-Nenets municipal district (except for the rural settlement of Khatanga) 26,376 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in the rural settlement of Khatanga 20,991 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in the Turukhansky district 19,704 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in the Evenki municipal district 15,918 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in Yeniseisk 12,436 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in Lesosibirsk 15,545 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in the Boguchansky district 16,042 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in the Yenisei region 15,048 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in the Kezhemsky district 15,918 rubles. – for employees of organizations carrying out labor activities in the Motyginsky district 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 25 | Primorsky Krai | 7 800 |
| 26 | Stavropol region | The cost of living of the working-age population for the first quarter of the current year, starting from the next month after its establishment. Until such a value is established, the cost of living of the working-age population for the first quarter of the previous year is used: 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 27 | Khabarovsk region | RUB 11,414 – for employees working in Bikinsky, Vyazemsky, Lazo, Nanaisky, Khabarovsk districts and the city of Khabarovsk 12,408 rubles. – for employees working in the Amursky, Vaninsky, Verkhnebureinsky, Komsomolsky, Nikolaevsky, named after Polina Osipenko, Sovetsko-Gavansky, Solnechny, Tuguro-Chumikansky, Ulchsky districts and the city of Komsomolsk-on-Amur 14,269 rubles. – for employees working in the Ayano-Maysky district 15,510 rubles. – for employees working in the Okhotsk region 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 28 | Amur region | 7 800 |
| 29 | Arhangelsk region | 7 800 |
| 30 | Astrakhan region | 7 800 |
| 31 | Belgorod region | 7 800 |
| 32 | Bryansk region | 8 500 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 33 | Vladimir region | 8500 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 34 | Volgograd region | 1.2 times the subsistence level of the working-age population 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 35 | Vologda Region | 7 800 |
| 36 | Voronezh region | The cost of living of the working-age population is 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 37 | Ivanovo region | The cost of living of the working-age population determined for the third quarter of the previous year is 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 38 | Irkutsk region | 7,800 rub. – for employees of agricultural organizations in the Irkutsk region 8259 rubles. – for employees of state and municipal institutions operating in other areas of the Irkutsk region 9,717 rubles. – for employees of other organizations operating in other areas of the Irkutsk region 10,754 rubles. – for employees of state and municipal institutions operating in regions of the Far North and areas equated to regions of the Far North RUB 12,652. – for employees of other organizations operating in regions of the Far North and areas equated to regions of the Far North, Irkutsk region |
| 39 | Kaliningrad region | 10,000 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 40 | Kaluga region | The monthly subsistence minimum for the working-age population is 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 41 | Kamchatka Krai | RUB 18,210 – for employees working in organizations located on the territory of the Koryak District 19,510 rubles. – for employees working in organizations located on the territory of the Aleutian municipal district 16,910 rubles. – for employees working in organizations located in the rest of the Kamchatka Territory 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 42 | Kemerovo region | One and a half times the subsistence level of the working population for the fourth quarter of 2015 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 43 | Kirov region | 7 800 |
| 44 | Kostroma region | The cost of living of the working-age population is 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 45 | Kurgan region | 8770 7 800 (for public sector employees) |
| 46 | Kursk region | 9804 7 800 (for public sector employees) |
| 47 | Leningrad region | 10 850 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 48 | Lipetsk region | 1.2 subsistence level of the working population for the fourth quarter of the previous year 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 49 | Magadan Region | RUB 18,750 – for employees of non-budgetary organizations of the Magadan region, with the exception of the North-Evensky urban district 20,250 rubles. – for employees of non-budgetary organizations in the North-Evensky urban district of the Magadan region 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 50 | Moscow region | 13 750 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 51 | Murmansk region | 14 281 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 52 | Nizhny Novgorod Region | 9000 rub. – for employees of organizations in the small business sector of the economy with an average number of employees of no more than 50 people, 9,500 rubles. – for employees of organizations in the non-budgetary sector of the economy 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 53 | Novgorod region | The monthly subsistence minimum for the working-age population is 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 54 | Novosibirsk region | 7,800 rub. – for employees of agricultural organizations 9030 rubles. – for employees of public sector organizations, except for organizations financed from the federal budget, 10,000 rubles. – for employees of non-budgetary organizations, except agriculture 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 55 | Omsk region | 7,800 – for employees of organizations and individual entrepreneurs carrying out “agriculture, hunting and forestry” as their main economic activity, and organizations financed from the regional and local budgets of the Omsk region 8,625 – for employees of extra-budgetary organizations, except for organizations and individual entrepreneurs carrying out “agriculture, hunting and forestry” as their main economic activity 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 56 | Orenburg region | 7 800 |
| 57 | Oryol Region | 10,000 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 58 | Penza region | 7 800 |
| 59 | Perm region | The cost of living of the working-age population |
| 60 | Pskov region | 7,800 rub. – for employees of: state, municipal institutions, as well as municipal unitary enterprises, socially oriented non-profit organizations, small businesses and other organizations that are classified as support staff RUB 11,450. – for employees of other organizations who are classified as core personnel. |
| 61 | Rostov region | 7 800 |
| 62 | Ryazan Oblast | 8500 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 63 | Samara Region | 7 800 |
| 64 | Saratov region | 7900 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 65 | Sakhalin region | RUB 15,150 – for persons working in Aleksandrovsk-Sakhalinsky, Anivsky, Dolinsky, Korsakovsky, Makarovsky, Nevelsky, Poronaisky, Smirnykhovsky, Tomarinsky, Tymovsky, Uglegorsky, Kholmsky districts, the city of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk 18,757 rubles. – for persons working in Nogliki and Okha districts 20,200 rubles. – for persons working in the Kuril, North Kuril and South Kuril regions 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 66 | Sverdlovsk region | 8862 |
| 67 | Smolensk region | 7 800 |
| 68 | Tambov Region | 8500 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 69 | Tver region | 7 800 |
| 70 | Tomsk region | 16,500 rub. – for employees of organizations financed from the regional and local budgets, territorial state extra-budgetary funds of the Tomsk region, other employers in the Alexandrovsky district, the urban district of Strezhevoy 15,000 rubles. – for employees of organizations financed from the regional and local budgets, territorial state extra-budgetary funds of the Tomsk region, other employers in the Verkhneketsky district, Kargasoksky district, Kedrovy, Kolpashevo district, Parabelsky district, Chainsky district 13,500 rubles. – for employees of organizations financed from the regional and local budgets, territorial state extra-budgetary funds of the Tomsk region, other employers in the Teguldetsky district, Molchanovsky district, Bakcharsky district, Krivosheinsky district 11,250 rubles. – for employees of organizations financed from the regional and local budgets, territorial state extra-budgetary funds of the Tomsk region, other employers in the urban district – closed administrative-territorial entity Seversk, Tomsk region 9,750 rubles. – for employees of organizations financed from regional and local budgets, territorial state extra-budgetary funds of the Tomsk region, other employers in Tomsk, Asinovsky district, Zyryansky district, Kozhevnikovsky district, Pervomaisky district, Tomsk district, Shegarsky district 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 71 | Tula region | 13,000 (11,000 for state and municipal institutions) 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 72 | Tyumen region | 8500 rub. – for employees of budgetary, state-owned, autonomous institutions and autonomous non-profit organizations established by the Tyumen region or municipalities of the Tyumen region 9950 rubles. – for an employee of the non-budgetary sector of the economy 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 73 | Ulyanovsk region | 10,000 rub. – for employees of main production facilities of the non-budgetary sector of the economy 7,800 rubles. – for employees of organizations established by the Ulyanovsk region or municipalities of the Ulyanovsk region, as well as for employees of small and medium-sized businesses |
| 74 | Chelyabinsk region | 9700 rub. – for employees of organizations in the non-budgetary sector of the economy 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 75 | Transbaikal region | for employees of organizations financed from the regional and local budgets and the compulsory health insurance fund, who work in the Far North and equivalent areas - 10,960 rubles. – in the Kalarsky district 9499 rubles. – in Tungiro-Olekminsky and Tungochensky districts 8647 rubles. – for employees of organizations in the non-budgetary sector of the economy (except for agriculture) for employees of organizations in the non-budgetary sector of the economy (except for agriculture) working in the Far North and equivalent areas RUB 11,190. – in the Kalarsky district 10,172 rubles. – in Tungiro-Olekminsky and Tungochensky districts 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 76 | Yaroslavl region | 10,002 rub. – for employees of non-budgetary organizations, with the exception of employees of small and medium-sized enterprises, 9,640 rubles. – for employees of small and medium-sized enterprises 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 77 | Moscow | 17,561/18,742 rubles (decision of the Moscow Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations dated December 15, 2015) |
| 78 | Saint Petersburg | 16,000 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 79 | Jewish Autonomous Region | 7,800 with the addition of a regional coefficient and a percentage bonus for work experience in the southern regions of the Far East 7,800 (for state employees) |
| 83 | Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 12 420 7 800 (for state employees) |
| 86 | Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug – Ugra | 7,800 taking into account the regional coefficient and the percentage increase in salary for work experience in the Far North and equivalent areas (but not lower than the subsistence level of the working-age population established in the district) |
| 87 | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug | 7 800 |
| 89 | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 12,431 taking into account additional payments and allowances of a compensatory and incentive nature 7,800 (for public sector employees) |
| 91 | Republic of Crimea | 7 800 |
| 92 | Sevastopol | 8000 7 800 (for state employees) |
Minimum wage - Minimum wage . Its size is set by the government. At the same time, this figure increases almost every year. The minimum wage for 2021 does not increase from January 1 and remains at 7,500 rubles . It will be increased from July 1, 2021 to 7,800 rubles. This figure is generalized for all of Russia. In individual regions, depending on their development, the size of the minimum wage is different, so we provide a forecast list of the minimum wage 2021 for the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (regions). However, regions cannot set the minimum wage lower than the national average.
Minimum wage from January 1: size
The minimum wage will not be increased in Russia from January 1, 2021. Officials considered that there was no need to change the minimum wage from the beginning of the year. Note that many accountants are accustomed to the fact that the minimum wage increases from the beginning of the year. So, for example, in 2021 the minimum wage will increase from January 1 and amounted to 6,204 rubles (Article 1 of the Federal Law of December 14, 2015 No. 376-FZ). However, from 2021 there will be no increase.
The last time the minimum wage was increased from July 1, 2021 to 7,500 rubles (Federal Law, Article 1 of Federal Law dated June 2, 2016 No. 164-FZ). In this regard, in particular, the amounts of benefits have changed. See "Benefits from July 1, 2021: How the sizes have changed."
From January 1, 2021, the minimum wage (minimum wage) has not changed. Therefore, the amount of benefits will remain at the same level.
Keep in mind that from July 1, 2021, the minimum wage will increase by 300 rubles and its amount will be 7,800 rubles. Indexation of the minimum wage by 4% is due to forecast inflation rates, which should be 4% in 2017. This is provided for by the relevant bill.
It was initially planned that the minimum wage from January 1, 2021 would be 8,800 rubles. However, later officials abandoned the new minimum wage and left it at the same level. See “Will the minimum wage increase in 2021?”
Regional minimum wage
In addition to the federal minimum wage, which is valid throughout Russia, some regions determine their own minimum wage or regional minimum wage. If the authorities of your region have established their own minimum wage, be guided by it when issuing wages. It doesn't affect anything anymore.
If the regional minimum wage is less than the federal one, use the federal amount.
We found the minimum wage for some regions. If yours is not on the list, write in the comments, we will try to help.
To make sure that the minimum wage is up to date, follow the link in the table.
| Region | Minimum wage size, ₽ |
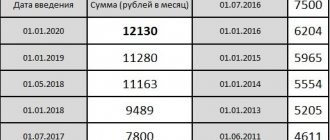
| Moscow | 20,589 from January 1, 2021, 20,361 in 2020 |
| Saint Petersburg | 19,000 from January 1, 2021 |
| Sevastopol | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 ₽ in 2020 |
| Altai region | 13,000 from January 1, 2021 (x district coefficient) |
| Bashkortostan | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2021 (x regional coefficient) |
| Volgograd region | 14,032 from January 1, 2021 |
| Irkutsk region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2021 (x district coefficient) |
| Kabardino-Balkaria | 12,834 since August 30, 2019 |
| Karelia, Republic | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2021 (x regional coefficient) |
| Kemerovo region | 21,471 from January 1, 2021, 16,516.50 in 2021 (x district coefficient) |
| Krasnodar region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2020 |
| Crimea, Republic | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2020 |
| Kursk region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2020 |
| Leningrad region | 12,800 from January 1, 2020 |
| Moscow region | 15,000 from November 1, 2019 |
| Nizhny Novgorod Region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 ₽ in 2020 |
| Novgorod region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 ₽ in 2020 |
| Novosibirsk region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 from January 1, 2021 (x regional coefficient 1.2) |
| Perm region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2021 (x regional coefficient) |
| Pskov region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2020 |
| Rostov region | 14,556 from January 1, 2020 |
| Sverdlovsk region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 ₽ in 2021 (x regional coefficient) |
| Stavropol region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2021 (x regional coefficient) |
| Tomsk region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2021 (x regional coefficient) |
| Tula region | 14,100 ₽ — from October 1, 2019 |
| Tyumen region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 13,200 in 202 (x regional coefficient) |
| Khabarovsk region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2021 (x regional coefficient) |
| Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 ₽ in 2021 (x regional coefficient) |
| Chelyabinsk region | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 in 2020 |
| Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 12,792 from January 1, 2021, 12,130 ₽ in 2021 (x regional coefficient) |
Minimum wage from January 1, 2021 and salary
The minimum wage is the minimum wage that an organization or individual entrepreneur (employer) must accrue to employees for the month they have fully worked (Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, keep in mind that an employee may receive less than the minimum wage in person - minus personal income tax and other deductions, such as alimony. Accordingly, from January 1, 2017, I cannot pay less than 7,500 rubles.
From January 1, 2021, employees’ salaries may be less than the minimum wage.
After all, the total salary, which includes (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) cannot be less than the minimum wage:
- remuneration for work;
- compensation payments, including additional payments and allowances;
- incentive payments (bonuses).
The total amount of all such payments from January 1, 2021 must be at least 7,500 rubles.
What is the minimum wage?
Minimum wage (also widely used as the abbreviation “MROT”: minimum wage) is a payment threshold below which an employer cannot pay its employee. It can be set in an hour, a month or a year.
Please note: the minimum wage is not a “bare” salary. This is the total salary, which includes the base rate, bonuses and other types of allowances (according to Article No. 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). That is, an employee’s net salary may be lower than the regional minimum wage. Also, the minimum wage is not a living wage.
This regulatory system was proposed and is still used as a means of “protecting” low-wage workers from wage undercutting. In the past, many businesses charged unfairly low prices for hard work. First of all, this concerned physical labor.
In addition, the installation and regular recalculation of the minimum wage is one of the state’s methods of combating poverty. Of course, it is very difficult to live on the actual minimum wage in the Russian Federation, but it is still possible. By the way, citizens must pay taxes on the minimum wage in full.
Most countries of the world have their own minimum wage (established by law). At the international level, it is regulated by the UN International Labor Organization Convention No. 131 (“On Minimum Wages”), adopted on June 3, 1970.
Not all states comply with it: as of the summer of 2021, only 53 countries (out of 251) have ratified the agreement. Moreover, it is not the third world countries that are abandoning the “standard” method of regulation; they are not accepting such a system:
- Japan: here the minimum wage is not set for the entire country or region, but separately for each industry;
- Switzerland, Italy, some Scandinavian countries: do not set a minimum rate at all.
Basic provisions
- Do laws regulate the minimum wage? Yes, in Russia this is law No. 82-FZ.
- Who adjusts the minimum wage? In the Russian Federation, this is done at two levels of government: federal (a single value is established for the entire country) and regional (a value is established for a particular region, depending on a number of factors).
- Does the minimum wage depend on the number of working hours actually worked? When calculating the size, a standard work week of 40 hours is used.
The regional-level administration can change the minimum wage, but only upward (that is, the official salary in the regions cannot be lower than the established minimum in the country).
The minimum wage changes regularly and depends on annual inflation. In fact, it should not be lower than the cost of living in the region (for able-bodied citizens).
The main resource for payments is the employer's funds. For government organizations, these are budget funds (local or federal budget).
Why is a minimum wage needed?
This value is used by the state for the following purposes:
- For financial protection of citizens who work in low-paid positions (as mentioned above).
- As a basis for calculating benefits (unemployment, temporary disability).
Salary below the minimum wage: responsibility in 2017
If, from January 1, 2021, the employee’s salary is less than the minimum wage (7,500 rubles), then the employer may be held accountable in the form of fines. The fine for an organization can range from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles, and if detected again - from 50,000 to 70,000 rubles. For a director or chief accountant, the liability may be as follows: for a primary violation, they may issue a warning or a fine of 1,000 to 5,000 rubles, for a repeated violation, a fine of 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. Moreover, they can be disqualified for a period of one to three years (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Read also
14.09.2016
How is the minimum wage related to the cost of living?
The minimum wage in Moscow is tied to the subsistence level. If the cost of living becomes higher, then from the next month the minimum wage will also increase (clauses 3.1.1, 3.1.2 of the Moscow Government Decree dated December 15, 2015 No. 858-PP). The cost of living in the second quarter of 2021 in Moscow was equal to 18,742 rubles - Moscow Government Decree No. 663-PP dated September 12, 2017. In this regard, from October 1, 2021, the minimum wage is 18,742 rubles.
Refusal to apply the new minimum wage in Moscow
If no action is taken after the new minimum wage has been announced, the employer will be deemed to have accepted the provisions of the tripartite agreement and undertakes to base its employees' wages on the current minimum wage.
If you decide to try to get permission to set wages below the minimum wage, you must first justify the reasons for disagreement with the value of the new minimum wage. The following will be accepted as valid arguments:
- significant impact of the economic crisis in the country on the company's activities;
- the number of orders from the company’s clients is insufficient to obtain the opportunity to increase employees’ salaries;
- the risk, due to an increase in wages, of the need to fire a large number of employees.
It is necessary to formalize the employer’s refusal to follow the new minimum wage in writing and send it to the Committee on Labor and Employment within a month from the date of publication of the text of the agreement on recalculation of the minimum wage in the regions.
Regional minimum wage for Moscow and the Moscow region
Currently, in the Russian Federation two concepts of minimum wage (minimum wage) are legally established:
- federal minimum wage and
- regional minimum wage.
Articles 133 and 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (as amended on June 18, 2017) establish two concepts:
- the minimum wage, which is established by federal law throughout the Russian Federation (federal minimum wage), and
- minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation (regional minimum wage).
From July 1, 2021, the federal minimum wage was increased. Now the federal minimum wage is 7,800 rubles.
The increase in the minimum wage by 300 rubles (from 7,500 to 7,800 rubles) occurred in accordance with the Federal Law of December 19, 2016 N 460-FZ “On Amendments to Article 1 of the Federal Law of June 19, 2000 N 82-FZ “On the Minimum amount of remuneration."
“Article 1. Establish the minimum wage from July 1, 2017 in the amount of 7,800 rubles per month”
The federal minimum wage is established by Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 133. “Establishing the minimum wage”:
- The minimum wage is established simultaneously throughout the entire territory of the Russian Federation by federal law and cannot be lower than the subsistence level of the working population.
- The minimum wage established by federal law is ensured by:
- organizations financed from the federal budget - at the expense of the federal budget, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from business and other income-generating activities;
- organizations financed from the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - at the expense of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from entrepreneurial and other income-generating activities;
- organizations financed from local budgets - at the expense of local budgets, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from business and other income-generating activities;
- other employers - at their own expense.
The features of the regional minimum wage are established by Article 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 133.1. “Establishing the minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation”:
- In a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, a regional agreement on the minimum wage may establish the amount of the minimum wage in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
- The minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation may be established for employees working in the territory of the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation, with the exception of employees of organizations financed from the federal budget.
- The size of the minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation is established taking into account socio-economic conditions and the cost of living of the working population in the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
- The minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation cannot be lower than the minimum wage established by federal law.
- The minimum wage in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation is ensured by:
- organizations financed from the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - at the expense of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from entrepreneurial and other income-generating activities;
- organizations financed from local budgets - at the expense of local budgets, extra-budgetary funds, as well as funds received from business and other income-generating activities;
- other employers - at their own expense.
Based on the above federal legislative norms (Articles 133 and 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), most constituent entities of the Russian Federation in their territories introduce their own regional minimum wage, which exceeds the minimum wage established at the federal level (federal minimum wage).
The minimum wage in Moscow and the Moscow region depends on:
- from the subsistence level in the region,
- as well as from the federal minimum wage.
Since the cost of living in these regions is revised quarterly, and since July 1, the federal minimum wage has been increased, the minimum wage in Moscow and the Moscow region has also changed since July 1, 2021.
Minimum wage (minimum wage) from July 1, 2021 in Moscow
In Moscow, the minimum wage depends on the subsistence level of the working population.
Moscow tripartite agreement for 2016-2018. dated 12/15/2015.
The cost of living is approved once every three months. As the cost of living increases, the regional minimum wage also increases. The new minimum wage in Moscow begins to operate on the 1st day of the month following the month in which the next decree on the subsistence minimum comes into force. But if the cost of living has not changed or even decreased, then the minimum wage in Moscow remains the same.
In the 4th quarter of last year, the cost of living in Moscow was reduced to 17,487 rubles from 17,561 rubles in the 3rd quarter (?). Therefore, the minimum wage in Moscow did not change and amounted to 17,561 rubles from January 1, 2021.
From July 1, 2021, it increased to 17,624 rubles per month (with bonuses and allowances). This living wage for the working population was established by the Moscow Government.
Decree of the Moscow Government of June 13, 2021 N 355-PP “On establishing the cost of living in the city of Moscow for the first quarter of 2021”
The new minimum wage in Moscow in the amount of 17,624 rubles has been in effect since July 1, 2017.
Salaries of employees with bonuses and allowances must not be lower than this minimum wage level. Therefore, companies in the capital need to raise employee salaries to 17,624 rubles per month, if they are lower.
You can refuse the regional minimum wage and adhere to the federal minimum wage. Reasoned refusals must be sent within 30 calendar days from the official publication of the Moscow government decree on the new living wage. The refusal must be sent to the Moscow Tripartite Commission.
If the company has not officially renounced the regional minimum wage and does not comply with it, then the employer may be held liable in the form of fines:
- penalty for the organization:
- can range from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles,
- and if this violation is repeatedly detected - from 50,000 to 70,000 rubles;
- in case of a primary violation, they may issue a warning or issue a fine from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles,
- if repeated - a fine of 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. Moreover, they can be disqualified for a period of one to three years.
Part 6 of Article 5.27 “Violation of labor legislation and other normative legal acts containing labor law norms” of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses (CAO RF)
Minimum wage (minimum wage) from July 1, 2021 in the Moscow region
From January 1, 2021, the minimum wage in the Moscow region is 13,750 rubles.
Agreement dated November 30, 2021 N 118 “On the minimum wage in the Moscow region between the Government of the Moscow Region, the Union “Moscow Regional Association of Trade Union Organizations” and employers’ associations of the Moscow Region”
In 2021, the minimum wage was changed only once, so it is possible that from July 1, 2021, the minimum wage in the Moscow region will be revised. For now, the current minimum wage in the Moscow region - 13,750 rubles - is used by all employers in the Moscow region who did not switch to the federal minimum wage in January 2017.
For all employers who promptly abandoned the regional minimum wage and switched to the federal minimum wage, in Moscow and the Moscow region, from July 1, 2021, the minimum wage will be 7,800 rubles.
Employees' wages cannot be lower. Otherwise, the employer will be held accountable for violating the labor rights of employees.
How salaries have changed in Moscow and the Moscow region
Moscow employers have a reason to raise wages. Over the past year, Moscow showed growth in all sectors:
- the maximum increase for financial companies is plus 18.5 thousand rubles,
- Average salaries increased the least in the “Hotels and Restaurants” industry - plus 906 rubles.
Companies located near Moscow can afford to reduce wages for their employees.
In the Moscow region in 2021, average wages decreased in most industries:
- the largest increase occurred in public administration - plus 2.3 thousand rubles,
- Trade workers lost the most - minus 9.2 thousand rubles.
If you have any questions about the violation of your rights, or you find yourself in a difficult life situation, then an online duty lawyer is ready to advise you on this issue for free.
STATE SOCIAL ASSISTANCE
How to apply the new minimum wage
Any subject of the Russian Federation (including Moscow) can set its own minimum wage. But it cannot be lower than the minimum wage approved by federal law (Article 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). From July 1, 2021, the federal minimum wage is 7,800 rubles.
If the salary in Moscow to be calculated for October, November and December 2017 is lower than the minimum wage (18,742 rubles), then the employee must be paid extra. And from October 1, 2021. You can set the surcharge in two ways:
- increase salary;
- establish in a local act (for example, a separate order or Regulation on remuneration) an additional payment up to the minimum wage. That is, it should be directly stated that employees are given an additional payment up to the regional minimum wage. Then there will be no need to review salaries or change employment contracts.
An employee whose salary in Moscow is less than the new minimum wage may demand:
- additional payment for the period of validity of the new minimum wage from October 1, 2017;
- compensation for delayed payment from October 1, 2021 (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The minimum wage in Moscow from October 1, 2021 does not affect the amount of benefits. Benefits are calculated based on the federal, not regional minimum wage.
Can a salary or salary be less than the minimum wage?
The salary for a month of work of an employee should not be lower than the federal level. Minimum wage, if:
- he worked full time and worked all the required hours;
- he did not violate his work duties.
It is also possible to approve a different minimum wage indicator for the regions through the adoption of a regional agreement. And when calculating payments to employees, you need to take into account regional coefficients and allowances for work in unusual conditions.
As a result, when calculating employee salaries, three factors are taken into account:
- minimum wage indicator;
- increasing coefficient of the subject of the Russian Federation;
- the presence of allowances for employee work in special conditions.
However, it happens that the salary turns out to be below the minimum wage level, but this can happen if there is only one legal basis - the employee receives some amounts of money every month as an incentive to work, these could be bonuses, for example. Therefore, if the total amount of payments for bonuses and basic salary is equal to or exceeds the minimum wage, the requirements of the law are not violated.
But employee salaries may be lower than the established minimum wage for three reasons:
- The salary is actually not lower than the minimum wage, but monthly payments are less than the minimum wage due to the personal income tax withheld by the employer and transferred to the budget.
- The salary actually turned out to be less than the minimum wage, since the employee was hired on a part-time basis.
- Finally, wages may not reach the minimum wage due to the fact that the employee combines several jobs at once.
What does the capital's minimum wage include?
The new minimum wage from October 1 (18,742 rubles) should already include all types of bonuses and additional payments to employees, except for additional payments:
- for working in harmful and dangerous working conditions
- for overtime work;
- for night work;
- for working on weekends or holidays;
- for combining professions.
It is also important that with the new Moscow minimum wage from October 1, 2021, you need to compare the amount before deduction of personal income tax. That is, if the employee worked the full working time for October. This means that he will receive at least 16,305.54 rubles in his hands. (RUB 18,742 – (RUB 18,742 x 13%).
Minimum wage and taxes
Some employers set the employee's salary strictly in accordance with the minimum wage (no more and no less). However, if an employee’s salary is equal to the minimum wage, personal income tax and insurance premiums, including “for injuries,” should still be withheld from it. This is confirmed by legal norms:
- Personal income tax – articles 210 and 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- insurance contributions for compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance - Articles 420 and 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- insurance premiums for insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases (“injuries”) - Articles 20.1 and 20.2 of the Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ.
Moscow minimum wage table for wages by year
The minimum wage by region is approved on the basis of an agreement between representatives of employers and government executive bodies. authorities and employees of organizations, starting from the beginning of September 2007. This does not apply to employees of those institutions whose source of funding is the federal budget.
The minimum wage in the regions should not be lower than the minimum wage level approved at the federal level.
The table shows the minimum wage:
| Minimum wage approval date | Type of enterprises | Value (rub/month) | ||
| day | month | year | ||
| 1 | October | 2016 | Moscow employers | 17561 |
| 1 | November | 2015 | 17300 | |
| 1 | June | 16500 | ||
| 1 | April | 15000 | ||
| 1 | January | 14500 | ||
| 1 | June | 2014 | 14000 | |
| 1 | January | 12600 | ||
| 1 | July | 2013 | 12200 | |
| 1 | January | 11700 | ||
| 1 | January | 2012 | 11300 | |
| 1 | July | 2011 | 11100 | |
| 1 | January | 10400 | ||
| 1 | May | 2010 | Commercial enterprises and budgetary institutions (except for those that receive funding from the federal budget) | 10100 |
| 1 | January | 9500 | ||
| 1 | September | 2009 | Commercial/budgetary, receiving funding from the Moscow budget | 8700/6325 |
| 1 | May | 8500/5855 | ||
| 1 | January | 8300/5420 | ||
| 1 | September | 2008 | 7500/5020 | |
If the salary is less than the minimum wage in Moscow and the Moscow region
Rostrud has always strictly monitored violations regarding payments to employees of enterprises, but previously the low level of salaries in the organization provoked only an unscheduled documentary inspection. Not all inspectors received approval for an on-site inspection from the prosecutor's office - they had to limit themselves to reviewing papers. According to the new rules, coordination with the prosecutor's office of intentions to conduct on-site control of organizations is not required. Therefore, as soon as the labor inspector receives information about a deliberate understatement of payments to employees of a company (information can come from tax authorities, funds, articles in the media, employee complaints), he has the right to organize an on-site inspection.
In order not to bring trouble to your company, you should always check the regional minimum wage and adjust salaries and other employee benefits in accordance with it. Reduced salaries and not paid salaries and benefits on time will be the basis for a visit from Rostrud inspectors. It is worth noting that more than 3/4 of all inspections they conducted resulted in the discovery of violations and the imposition of fines.
For non-compliance with minimum wage requirements, officials can not only impose a fine, but also bring the head of the company to criminal liability if it is discovered that the salary in his company was underestimated for more than 2 months. For repeated violations, regulatory authorities have the right to disqualify an official for up to 3 years.
In addition, if payments to employees are below the minimum wage, this is recognized as a violation or failure to comply with the terms of the collective agreement, for which it is necessary to first issue a warning and then impose a fine (3-5 thousand rubles).
The amount of fines for paying employees below the minimum wage
The table shows the amounts of fines:
| Officials | OOO | IP |
| First violation | ||
| 10-20 thousand | 30-50 thousand | 1-5 thousand |
| Repeated violation | ||
| 20-30 thousand | 50-100 thousand | 10-30 thousand |
Fines can be imposed not only by the labor inspector, but also by court decision. Companies that pay their employees salaries less than the minimum wage will not have to make additional payments to the budget for taxes and contributions, however, tax authorities have the right to report violations to Rostrud.
But underpaid amounts of wages, as well as compensation under the law, can be requested by employees of enterprises. And the organization will need to pay additional amounts of funds for the full period of work of employees, plus compensation for money not paid on time.
About the growth rate
Minister of Labor and Social Development Maxim Topilin told what the minimum wage will be in 2021. Its size should not be less than 11 thousand rubles, and this, according to the head of the department, is not such a significant amount that requires lengthy discussions.
Minimum wages are tied to the subsistence level, but for several years now trade unions, business and the government have been unable to agree on the rate of growth of the minimum wage and the conditions under which this increase will be possible. Presumably, it will be possible to reach a final decision within three years, so it will be possible to equalize the minimum wage and the subsistence minimum only by 2021. But, the minister believes, it is no longer possible to turn a blind eye to the problem.
On a note! According to the head of the Ministry of Labor, 4.9 million Russians today receive wages below the subsistence level.
Deputy Prime Minister Olga Golodets also spoke about the need to equalize the minimum indicators. In her opinion, this “will give a serious gain” and will stop slowing down the development of production. A unique situation has developed in Russia in which working people are the poor. At the same time, cheap labor is downright the scourge of our time, because business does not want to invest in the modernization of production when it is possible to attract free workers.
This might also be useful:
- Taxes are urgent: you must pay before December 1
- Property tax and assessment quality
- From 2021, income limits for switching to the simplified tax system will be increased
- UST in 2021
- What will the minimum wage be in 2021?
- Tax calendar for 2021
Is the information useful? Tell your friends and colleagues
Dear readers! The materials on the TBis.ru website are devoted to typical ways to resolve tax and legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific issue, please contact the online consultant form. It's fast and free!
Common mistakes
Error No. 1: The company received a notice of payment of a fine in the amount of 10 minimum wages, the accountant transferred 75,000 rubles to the budget on the basis that the current minimum wage is 7,500 rubles.
Comment : To calculate penalties, fines and taxes, the minimum wage value is taken to be one hundred rubles, that is, a fine of 10 minimum wages is 1000 rubles.
Error No. 2: Accrual of cash benefits for temporary disability below the level of the current minimum wage due to the fact that the employee’s work experience has not reached six months.
Comment : In cases where the monthly benefit is less than the minimum wage due to the employee’s short work experience, sick leave payments should be equal to the minimum wage.