Author: Ivan Ivanov
The accounting department has a specific list, a purely professional chart of accounts, according to which specialists keep records of the movement of funds in the organization. Moreover, 99 of them reflect business operations at the enterprise, and therefore are called the main ones.
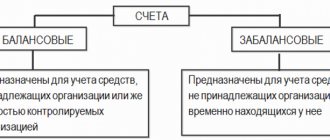
11 registers are used by financiers to convey additional information, a role that off-balance sheet accounts are intended to play. They cannot be seen in what financial condition the company or its production site is in; data from this instrument is not included in the formation of the balance sheet, which is why it is named behind the balance sheet.
Analysis of off-balance sheet accounts in the new chart of accounts
If the guarantee does not specify the amount, then for accounting purposes it is determined based on the terms of the contract.
The amounts of collateral recorded in account 009 “Collateral for obligations and payments issued” are written off as the debt is repaid.
Analytical accounting is maintained for each issued collateral (sub-account “Counterparties” and sub-account “Agreements”). Each recipient of a guarantee is an element of the “Counterparties” directory. Each guarantee is an element of the “Counterparty Agreements” directory.
Examples of ONA postings on account 09
To consider the features of accounting for transactions on account 09, we will analyze examples.
Posting for accrual of deferred tax asset
At the end of the 3rd quarter of 2015, 3 batches of materials (spare parts for electrical equipment) were delivered to the warehouse of Marker JSC for a total amount of 484,300 rubles, VAT 73,876 rubles. Payment for spare parts was made partially - in the amount of 232,500 rubles, VAT 35,466 rubles.
To reflect the amounts of IT in accounting, the accountant of Marker JSC made the following calculations:
Based on the above calculations, the following entries were made in the accounting of Marker JSC:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 10 | 60 | Spare parts have arrived at the Marker JSC warehouse (RUB 484,300 - RUB 73,876) | RUR 410,424 | Packing list |
| 19 | 60 | The amount of VAT on purchased spare parts is taken into account | RUR 73,876 | Invoice |
| 60 | 51 | Funds were transferred to the supplier to partially repay the debt for supplied spare parts | 232,500 rub. | Payment order |
| 60 | 60 Deductible temporary differences | The amount of the deductible temporary difference is reflected | RUR 213,390 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 09 | 68 Income tax | The increase in the amount of IT is taken into account (RUB 213,390 * 20%) | RUR 42,678 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
Write-off ONA
In April 2021, Bogatyr JSC sold a unit of production equipment. As of the date of sale, the amount of depreciation accrued on the equipment amounted to RUB 42,300. (accounting) and 39,800 rub. (tax accounting). The amount of IT for this object is 895 rubles.
When writing off equipment, the accountant of Bogatyr JSC will make the following entry:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 99 | 09 | The amount of ONA for sold equipment is written off | 895 rub. | OS write-off act |
Adjustment of the amount of ONA
From 01/01/2016 for Metropol JSC the income tax rate was reduced from 24% to 20%. The balance sheet of JSC Metropol as of December 31, 2015 on Dt 09 includes the amount of 64,900 rubles. The accountant recalculated the amount of ONA (64,900 rubles / 24% * 20% = 54,083 rubles) and made the following entry in accounting account 09:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 84 | 09 | The ONA has been adjusted (RUB 64,900 - RUB 54,083) | RUB 10,817 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
Reflection of ONA in case of loss received
The Profit and Loss Statement and Tax Return of JSC Sever contains the following information:
| Index | Data based on the results of 2015 | Data based on the results of the 1st quarter of 2021 | Data based on the results of the 2nd quarter of 2016 |
| Profit and loss statement (accounting) | Loss 181,300 rub. | Profit 211,400 rub. | Profit 53,200 rub. |
| Tax return (tax accounting) | Loss 181,300 rub. | Profit 211,400 rub. | Profit 53,200 rub. |
Based on the above information, the following entries were made in the accounting of JSC Sever to repay the deferred tax asset:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 68 Income tax | 99 Income from income tax (conditional) | The amount of conditional income at the end of 2015 is taken into account (RUB 181,300 * 20%) | RUR 36,260 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 09 | 68 Income tax | The amount of ONA from the resulting loss was taken into account at the end of 2015 | RUR 36,260 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 99 Income from income tax (conditional) | 68 Income tax | The amount of conditional income tax accrued for the 1st quarter of 2021 is reflected (RUB 211,400 * 20%) | RUB 42,280 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 68 Income tax | 09 | The amount of OTA from the loss was repaid | RUR 36,260 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 99 Income from income tax (conditional) | 68 Income tax | Reversal of conditional income tax accrued for the 1st quarter of 2016 | RUB 42,280 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 68 Income tax | 09 | The amount of ONA from the loss for 2015 was restored | RUR 36,260 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 99 Income from income tax (conditional) | 68 Income tax | The amount of conditional income tax accrued for the 1st half of 2021 is reflected (RUB 53,200 * 20%) | RUB 10,640 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 68 Income tax | 09 | The amount of OTA from the loss reducing taxable profit has been repaid | 10.640 | Accounting certificate-calculation |
Business operations:
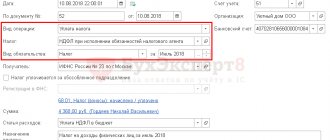
“Reflection of the amount of the deposit for returnable reusable packaging from the buyer (pledgor) on off-balance sheet accounting”
Debit 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued” Credit ““
What document is used in 1c:Accounting 2.0/1c:Accounting 3.0
: —
Operation (accounting and tax accounting)
in the menu “Operations — Operations entered manually”
“Transfer of a bill of exchange secured by a loan secured off-balance sheet”
Debit 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued” Credit ““
What document is used in 1c:Accounting 2.0/1c:Accounting 3.0
: —
Operation (accounting and tax accounting)
in the menu “Operations — Operations entered manually”
“Write-off from off-balance sheet accounting the amount of the deposit for returnable reusable packaging from the supplier (pledger)”
Debit "" Credit 009 "Securities for obligations and payments issued"
What document is used in 1c:Accounting 2.0/1c:Accounting 3.0
: —
Operation (accounting and tax accounting)
in the menu “Operations — Operations entered manually”
“Write-off from off-balance sheet accounting the value of a bill of exchange previously pledged to secure a loan upon receipt of notice of payment of the bill of exchange”
Debit "" Credit 009 "Securities for obligations and payments issued"
What document is used in 1c:Accounting 2.0/1c:Accounting 3.0
: —
Operation (accounting and tax accounting)
in the menu “Operations — Operations entered manually”
“Entering initial balances: collateral for obligations and payments issued (off-balance sheet accounting)”
Debit "" Credit 009 "Securities for obligations and payments issued"
What document is used in 1c:Accounting 2.0/1c:Accounting 3.0
: —
Entering initial balances
in the “Enterprise” menu, type of operation: “
Other accounting accounts”
Formation of deferred tax assets when carrying forward annual losses to future periods
The loss identified based on the results of work within 12 months must be taken into account in the accounting department on the last day of the 12th month of the year. For purposes of calculating income tax, this type of expense must be recognized gradually as profits are calculated. In this case, the company is faced with the formation of a deferred asset, which must be reflected on account 09 on the last day of the year and gradually written off in future periods upon receipt of profit. The write-off is carried out on the last day of each period until it is repaid in full.
Example:
At the end of 2021 the organization summed up the results of its activities and established its negative value - the loss amounted to 800,000 rubles. This loss in accounting will be shown through appropriate entries upon detection (December 31), and in taxation it will be transferred to future periods. Due to such differences, ONA is formed.
Amount of deferred asset:
SHE = 800,000 * 20% = 160,000 rub.
The calculated value is shown as ONA on the last day of 2015.
Profit according to tax information for the first quarter. – 450,000 rubles, for 6 months. – 1,280,000 rub.
The company recognized this tax loss as follows:
- for the first quarter 2021 – share of loss for 2015 RUB 450,000;
- in 6 months 2021 – the entire amount of loss for 2015. 800,000 rub.
On the last day of each period, a double entry was made to repay the deferred asset:
- For the first quarter – 450,000 * 20% = 90,000 rub.;
- In 6 months – (800,000 – 450,000) * 20% = 70,000 rub.
Postings for this example: (click to expand)
| date | Operation | Sum | Debit | Credit |
| 31.12.15 | The deferred asset was taken into account in the form of an expense not taken into account for taxation | 160000 | 09 | 68 |
| 31.03.16 | The deferred asset is partially repaid | 100000 | 68 | 09 |
| 30.06.16 | The asset is fully repaid | 60000 | 68 | 09 |
The sale of an object (if this is not the main activity) is carried out through 91 accounts, on the debit of which expenses are recorded in the form of the residual value of the object (the original cost, reduced by the amount of depreciation charges made), on the credit - income in the form of receipts from the buyer. If the debit indicator exceeds the credit indicator, then the result from the sale of the fixed assets will be negative - the company will incur a loss.
This type of expense can be taken into account immediately in accounting, but in tax accounting it must be gradually written off in equal parts monthly over a time period determined by the formula:
Term (in months) = Useful life (in months) – In fact, the period of use of the OS (in months)
The last indicator is calculated starting from the 1st month after the asset was taken into account and ending with the month of sale.
Example:
The company purchased an OS, the period of use of which is set at 60 months. Month of start of operation – January 2013. In May 2021 The OS is for sale.
Actual period of use = 40 months. (from February 2013 to May 2016).
The transaction for the sale of fixed assets was unprofitable, the amount of loss = 50,000 rubles.
The period during which this expense will be recognized in tax accounting = 60 – 40 = 20 months.
Amount subject to monthly accounting in other expenses = 50,000 / 20 = 2,500 rubles.
Accordingly, an amount of 2500 * 20% = 500 rubles will be debited from ONA every month.
09 accounting account is used in organizations to reflect deferred tax assets (DTA), the indicator of which affects the amount of income tax payable to the budget. From our article you will learn how to determine the amount of IT and what transactions to reflect it in accounting.
Off-balance sheet account 009 in accounting
Description of account 83.09 Other sources
Account 83.09 Other sources is intended for accounting for transactions related to other sources of formation of additional capital (except for share premium from the sale of shares). Account 83.09 reflects the amounts of exchange rate differences associated with the formation of the authorized capital of the joint-stock company, retained earnings aimed at covering the costs of capital investments, as well as funds received from the state budget to finance long-term capital investments.
Score 83.09 Other sources is Passive .
Passive accounts
— accounting accounts designed to record the status, movement and changes in the sources of funds of the enterprise.
Passive accounts display transactions that change the amount of the company's funds (company assets), as well as transactions that change the composition of debts (moving funds between two passive accounts, for example, withholding taxes from payroll). They are designed to take into account the company's obligations to partners, employees or the state.
Analytics on account 83.09 Other sources
Analytical accounting of account 83.09 is organized in the context of each individual source of income to the authorized capital.
Use of account 83.09 Other sources. Postings
Dt 83.09 Kt 01.01 Additional capital is reduced by the amount of the markdown equal to the amount of the previous revaluation of the object Dt 83.09 Kt 02.01 Additional capital is reduced by the amount of the increase in depreciation, which exceeds the amount of its decrease during the previous markdown of the object Dt 83.09 Kt 75.02 Additional capital is distributed among the founders (participants) of the organization Dt 83.09 Kt 80 Additional capital is aimed at increasing the authorized capital (after making changes to the constituent documents) Dt 83.09 Kt 84 Additional capital is written off upon disposal of fixed assets that were subject to revaluation Dt 83.09 Kt 84 Additional capital funds are used to pay off losses Dt 01.01 Kt 83.09 Additional capital is increased capital by the amount of the excess of the revaluation over the previously received markdown of the object Dt 02.01 Kt 83.09 Additional capital is increased by the amount of the markdown of the depreciation of the object in the amount of its increase during the previous revaluation Dt 75 Kt 83.09 Income from the placement of own shares at a price above par (share premium) is aimed at increasing the additional capital Dt 84 Kt 83.09 Net profit is aimed at forming (increasing) additional capital Dt 86.01 Kt 83.09 Actually used target investment funds are included in additional capital (in a non-profit organization)
Why do deferred tax assets arise?
Sometimes the indicators reflected for the same transaction differ in tax and accounting; in particular, this can be observed in the order of reflecting expenses and income for individual objects, for the purpose of accounting and calculating profit tax.
The tax calculated according to accounting data is called conditional, according to tax data - current. It is the latter that needs to be listed based on the results of each period. When calculating these indicators at the end of the period, a difference arises, entailing the formation of a deferred asset and the need for its future reduction in future periods.
Deferred tax assets appear if expenses for specific transactions are shown in accounting in the current period (upon the fact of their establishment), and in tax - in future periods.
Similarly, deferred tax assets are created if income is recorded for income tax purposes before it is shown in the books.
Some examples of when this can happen: (click to expand)
- When a loss is established at the time of disposal of the fixed assets upon sale;
- When creating only in accounting a reserve for paying vacation pay to staff;
- When identifying a loss based on the results of annual activities and transferring it to future periods in order to determine the tax burden;
- With different methods for calculating depreciation charges;
- In case of excessive tax transfer and non-refund;
- When forming accounts payable for purchased assets, if income and expense indicators are recognized on a cash basis;
- In other cases where there is a temporary difference in cost recognition.
In the cases under consideration, the accounting profit is less than the tax profit, as a result of which the conditional tax in accounting turns out to be less than the actual tax payable (the conditional tax is less than the current one) - as a result of this phenomenon, a deferred tax asset arises.
Formula for calculating deferred tax assets (DTA):
SHE = expenses recorded in accounting. accounting in the current period, and in cash. accounting in subsequent periods (or income recorded in cash accounting in the current period, and in accounting in subsequent periods) * rate
Subsequently, when accounting expenses are recognized in taxation, the opposite situation will form - tax profit and current tax will be less than accounting profit and conditional tax, as a result of which IT is repaid. A similar reduction in the deferred asset is observed with the subsequent recognition of tax income in accounting.
The formula for calculating the amount to reduce deferred tax assets (DTA):
Amount to be repaid = expenses written off in accounting. accounting in the previous period, and cash. accounting in the current period) (or income shown in cash accounting in the previous period, and in accounting in the current period) * rate
IT is a type of asset, the value of which in future periods gradually reduces the current tax payable, while the conditional tax according to accounting data increases.
In the video lesson, expert teacher of the site Gandeva N.V. (chief accountant) explains how the organization’s deferred tax assets are formed and accounted for. To view the video, click below ⇓
You can follow the link for slides and presentation for the lesson.
Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued
Credit of account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued (there is no entry in the debit of the account).
When issuing an uncovered letter of credit, subaccount 55-1 Letters of credit is not used. All entries are made in off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued.
The issuance of your own bill of exchange to the supplier can be reflected in off-balance sheet account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued,” which is intended to summarize information about the availability and movement of guarantees issued to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments. The collateral amounts recorded in account 009 are written off as the debt is repaid. Analytical accounting for account 009 is maintained for each issued collateral.
Such requirements are contained in paragraph 4 of Art. 167 and in paragraph 2 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The payer becomes the principal debtor on the bill of exchange only after its acceptance. If payment or acceptance is refused, the drawer bears responsibility for paying the bill on time. Therefore, until the moment of payment, the amount of the issued bill must be reflected by the drawer in off-balance sheet account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued.”
At the same time, account 009 “Security for obligations and payments issued” is debited.
The company must record issued awali (guarantees for bills) in off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued. I
Transactions on discounting bills of exchange can be considered and reflected in accounting as a purchase of a bill of exchange by a bank, and not as a receipt of a loan secured by a bill of exchange. When a bank purchases a bill of exchange, the enterprise transfers its bill of exchange to it by endorsement (endowment note) and removes this bill from the register. In this case, the enterprise retains only conditional obligations, namely, that if the bank cannot receive the bill, it has the right to present it to any endorser, including the mentioned enterprise, and is obliged to pay this bill. Accounting for contingent rights and obligations is carried out on off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued.
Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued
Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of guarantees issued to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments. If the guarantee does not specify the amount, then for accounting purposes it is determined based on the terms of the contract.
The amounts of collateral recorded in account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued are written off as the debt is repaid.
Analytical accounting for account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued is maintained for each security issued.
ACCOUNT 009 SECURITY FOR OBLIGATIONS AND PAYMENTS ISSUED
To control endorsed bills of exchange, off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued is used.
Obtaining a guarantee of the buyer's solvency
An example will show what postings you should make in this situation.
EXAMPLE
JSC Aktiv entered into an agreement for the supply of goods with LLC Passiv. The cost of goods is 236,000 rubles. (including VAT - 36,000 rubles), cost - 120,000 rubles. JSC Aktiv (supplier) demanded that the buyer, LLC Passiv, provide a bank guarantee to ensure payment for the goods. Passiv LLC provided a bank guarantee. After this, Aktiv JSC shipped the goods.
The Aktiva accountant must make the following entries:
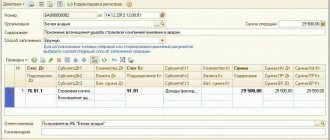
DEBIT 008 – 236,000 rub. – reflects the amount of the received bank guarantee;
DEBIT 62 CREDIT 90-1 – 236,000 rub. – revenue from the sale of goods is reflected;
DEBIT 90-2 CREDIT 41 – 120,000 rub. – the cost of goods sold is written off;
DEBIT 90-3 CREDIT 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” – 36,000 rubles. – VAT is charged;
DEBIT 51 CREDIT 62 – 236,000 rub. – funds were received from the buyer – Passiv LLC;
LOAN 008 – 236,000 rub. – the amount of the bank guarantee has been written off.
At the end of the month, the Aktiva accountant must determine the financial result from the sale of goods:
DEBIT 90-9 CREDIT 99 – 80,000 rub. (236,000 – 120,000 – 36,000) – profit from the sale is reflected.
Off-balance sheet accounting of collateral for issued obligations
In this off-balance sheet account, endorsed bills of exchange are listed until the expiration of the deadline for filing claims on these bills in accordance with the established procedure, receiving notification of their payment or payment by their organization (as amended by the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 16, 1996 No. 62)
The organization that issued the aval (guarantee for the bill) reflects it on the off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued, (as amended by the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 16, 1996 No. 62) t
The section indicators can be expanded if there are other types of assets accounted for in off-balance sheet accounts not specified in the list (in particular, account 008 “Security for obligations and payments received”, account 009 “Security for obligations and payments issued”).
Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of guarantees issued to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments.
At the same time, as noted above, acceptance of the bill for payment by the drawee does not relieve the drawer of responsibility for timely and full repayment of the bill. This fact is reflected in the accounting of the drawer in the off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued as a conditional obligation to the remittor in the amount of the face value of the bill and the interest due for payment on it (if the accrual of such is possible and conditional). The amount of this obligation continues to be listed in account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued until the payer repays the bill.
Based on the foregoing, the fact of acceptance of a bill of exchange through mediation should be reflected in the accounting of the person who made it in the off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued.
The transfer of a bill of exchange as security for a received loan is accounted for by the bill holder in the off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued. The amounts of such collateral are written off from this account as the debt to the bank for the loan received is repaid.
The endorser's accounting records reflect the occurrence of a contingent liability under the bill in case of failure to repay it on time Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued Amount payable under the bill at the time the obligation is reflected
The issuance of a bill of exchange is reflected in the accounting records of the avalist Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued Amount of the aval issued
In the mortgagor’s accounting, the amounts of inventory pledged are reflected in off-balance sheet account 009 “Security for obligations and payments issued” in the amount specified in the agreement.
At the same time, bills of exchange transferred to the bank are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued.
The company that issued the aval (guarantee on the bill) reflects it on the off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued.
Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of issued
Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of guarantees issued to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments. If the guarantee does not specify the amount, then for accounting purposes it is determined based on the terms of the contract. The amounts of collateral recorded in account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued are written off as the debt is repaid.
At the same time, to control endorsed bills, an entry is made in the debit of off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued, where they are listed until the expiration of the deadline for filing claims on these bills, receiving notice of their payment or payment by the enterprise itself, after which an entry is made in the credit of account 009 .
If an organization gives an aval for a bill of exchange to another organization, a corresponding entry is made in the debit of off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued.
To secure borrowed funds, an organization can issue bills or bonds to the lender (creditor). Accounting for interest and discount on such bills and bonds is discussed in paragraph 18 of PBU 15/01. At the time of issuance of the bill of exchange, the borrower must reflect the amount specified in it as accounts payable. Bills of exchange issued against borrowed funds are recorded in off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued (according to the new Chart of Accounts). And interest and discount on the bill are included in the operating income of the organization. PBU 15/01 provides two ways to write them off. They can either be charged to operating expenses immediately after accrual, or pre-accounted for as deferred expenses. The second method allows you to evenly write off the costs of loans and credits.
When reflecting the issuance of a bill of exchange guarantee in the accounting records of an avalist, one should take into account the nature of the latter’s obligation to pay the bill of exchange (provided that the obligation is in fact guaranteed), which arises in the event of non-payment of the bill of exchange (claim on the bill of exchange) by the person for whom the aval was issued. Based on this, the fact of avalization of a bill before the occurrence of an unconditional debt to the bill holder or termination of the guarantee should be reflected in the avalist’s accounting in the off-balance sheet account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued by an entry in the amount of this guarantee.
See pages where the term Account 009 is mentioned Security for obligations and payments issued
:
View chapters in:
Chart of accounts for financial and economic activities of organizations and instructions for its use -> Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued
To help accountants and auditors Handbook Volume 2 Issue 11 -> Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued
Chart of accounts -> Account 009 Security for obligations and payments issued
What are off-balance sheet accounts?
Accounting provides for a certain professional chart of accounts, using which specialists maintain accounting of the company’s funds. 99 of the accounts presented in the chart are basic, since with their help business transactions in the organization are reflected. 11 registers are off-balance sheet accounts; they are necessary to reflect additional information. These accounts do not reflect the financial condition of the company or a separate production site. Indicators from these accounts are not taken into account when preparing the balance sheet, hence the corresponding name for such accounts - off-balance sheet (
Accounting on off-balance sheet account 008 “Securities for obligations and payments received”
⇐ PreviousPage 37 of 37
To summarize information on the availability and movement of guarantees received to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments, as well as collateral received for goods transferred to other organizations (individuals), off-balance sheet account 008 “Collateral for obligations and payments received” is used.
Security (guarantee) is a document in which one organization guarantees another to fulfill obligations within a certain period of time for a certain amount and confirms that it is ready to repay the debt if it arises as a result of failure to fulfill obligations.
Accounting for received obligations is carried out at the value of the obligation or the value established by the contract. If the guarantee does not indicate the exact amount, then in accounting it is accepted based on the terms of the contract.
Bonds, bills of exchange, other securities and types of property are used as collateral for loans received, goods shipped, work performed, and services provided.
The value of received liabilities at their estimated value is accounted for as a debit to off-balance sheet account 008 “Securities for obligations and payments received.” Analytical accounting for account 008 “Securities for obligations and payments received” is maintained for each security received.
In the mortgagee's accounting, the amounts of collateral recorded in account 008 “Securities for obligations and payments received” are written off as the debt is repaid from the credit of the named off-balance sheet account. A credit entry on the specified account means, in particular, the end of the property pledge agreement due to the full repayment of the loan (loan) received by the pledgor secured by the property, as well as the restoration of the property as part of one’s own after the expiration of the property pledge agreement and the full repayment of the pledged debt to the pledgee.
Accounting on off-balance sheet account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued”
To summarize information on the availability and movement of guarantees issued to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments, off-balance sheet account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued” is used.
Accounting for issued obligations is carried out at the value of the obligation or the value established by the contract.
If the guarantee does not indicate the exact amount, then in accounting it is accepted based on the terms of the contract.
The issuance of guarantees is reflected in the debit of account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued”
As obligations are repaid or the period of issued guarantees expires, their value is written off from the credit of account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued.”
Accounting on off-balance sheet account 010 “Depreciation of fixed assets”
Account 010 “Depreciation of fixed assets” is intended to summarize information on the movement of depreciation amounts for housing facilities, external improvement facilities and other similar objects (forestry, road management, specialized shipping facilities, etc.), as well as for non-profit organizations for fixed assets.
Depreciation on these objects is accrued at a time at the end of the year according to established depreciation rates, reflecting the amount of depreciation in the debit of account 010 “Depreciation of fixed assets.”
When these objects are disposed of, the write-off of accrued depreciation is reflected in the credit of account 010 “Depreciation of fixed assets.”
Analytical accounting must be organized for each existing object.
Accounting on off-balance sheet account 011 “Fixed assets leased”
Account 011 “Fixed assets leased” is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of fixed assets by the organization that leased fixed assets under the lease agreement. Leased fixed assets are reflected in the debit of account 011 “Fixed assets leased” in the valuation specified in the agreement, on the basis of an acceptance certificate, invoice or other document certifying the fact of transfer of fixed assets to the tenant.
If the contract does not provide for the transfer of ownership rights to the leased fixed assets to the tenant, then upon termination of the lease agreement and the return of all leased fixed assets to the owner, account 011 “Fixed assets leased” is closed with a credit entry to account 011 “Fixed assets”. funds leased” and has no balance. A similar entry is made when transferring ownership of fixed assets to the tenant.
TOPIC 18. CONTENT AND PROCEDURE FOR PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Contents of financial statements
The purpose of financial statements is to provide useful and transparent information about the financial position, results of operations and changes in the financial position of the organization. This information is needed by a wide range of users when making economic decisions.
Financial statements prepared for these purposes satisfy the general needs of most users. However, financial statements do not provide all the information that users will need to make economic decisions because they primarily reflect the financial results of past events and do not necessarily contain non-financial information. Those users who want to evaluate an organization's performance do so in order to make economic decisions; These decisions may include, for example, the decision to retain or sell an entity's investments.
For the correct formation of financial reporting indicators, it is impossible to apply the norms of each individual accounting standard in isolation from other regulatory documents and accounting provisions! Only this approach will allow the accountant to develop a professional judgment about how each specific indicator will be recognized in accounting and presented in the financial statements.
Knowledge and interconnected application of the norms of all Accounting Regulations as a single block of documents normative regulation of accounting will allow the accountant to correctly recognize the accounting object, understand its economic content, and then (according to this economic content) determine on which specific account to technically reflect this accounting object .
The main task of generating an organization’s accounting report is to ensure the timeliness, completeness and reliability of the accounting data presented to interested users. The obligation of organizations to prepare financial statements for the month, quarter and year is established by clause 29 of the Accounting Regulations.
Correspondence
009 account can be represented by various information. For example, that third parties who vouch for the company in front of contractors guarantee the reliability of the company. This register reflects information about the property issued as collateral.
A guarantee from a third-party company is registered in the debit of account 009. This will indicate that in the event of financial problems in the company, the partner will receive insurance for the return of amounts. These actions can also emphasize the business reputation of the company, as well as its importance in the business sphere.
If property is transferred in the form of money, then the entries should be as follows:
- debited to accounts that reflect settlements with partners;
- credited to accounts 51 and 52;
- The debit of account 009 reflects the amount of the transaction.
Important! When real estate or other property is pledged, regardless of where it is located, it does not disappear from the company’s balance sheet. This fact must be simultaneously indicated in the debit of account 009, from which, after the return of funds, the debit will be made.
The entry for the loan received under the pledge certificate or warrant will be as follows:
- 51 (66) – a loan issued by a bank or received by a borrower, as collateral was recorded in the company’s warehouse;
- loan 008 – the amount indicated in the receipt for acceptance of the value for storage is reflected (the information is transferred to the lender, documented and serves as security for the return of funds);
- debit 009 – indicates the amount that was provided to the financial organization as collateral along with the warrant.
If the loan has not yet been repaid, but the pledged goods have already been sold, then the postings will be as follows:
62(90.1) – revenue from sales is reflected;
90.3(68) – accrual of VAT on income from sold property;
90.2(41.1) – write-off of products at actual cost;
66(62) – transfer of debt obligations secured by security;
Credit 009 – reflects the warehouse receipt that was transferred to the new owner.
Service Temporarily Unavailable
The indicators of the organization's financial statements according to the standard version must be formed in accordance with the accounting methods approved by the order on the accounting policy, subject to the requirements established by the Russian accounting rules. When disclosing information in financial statements, it should be taken into account that there will be constant improvement of previously adopted and approval of new accounting provisions. The formation of accounting reporting indicators must be carried out in accordance with the general requirements set out in PBU 4/99 “Accounting reporting of an organization”, and the rules of information disclosure given in each accounting regulation, as well as taking into account the characteristics of small businesses and non-profit organizations, medium-sized and large organizations, largest organizations.
That is why, according to currently valid regulatory documents, there are four options for generating financial statements in accordance with Russian accounting rules - simplified, standard, multiple and in full compliance with international financial reporting standards.
The provision of transparent and useful information about business participants and their transactions is a necessary condition for an organized and efficient market. This is one of the most important prerequisites for running a market economy.
The purpose of financial (accounting) reporting is to provide the necessary useful information to all potential users interested in obtaining information about the financial position of an organization or a consolidated group of enterprises and its changes, the results of economic activities, management efficiency and the degree of responsibility of managers for the assigned work. In the absence of comprehensive useful information, even the leaders of an organization may not know its real financial situation, and other market participants may even more so be misled, which interferes with the functioning of the market.
In world practice, when constructing reporting forms (formats), there is no single approach both in structure and content. Thus, the form (format) of the balance sheet provides for a horizontal or vertical arrangement of balance sheet items; the form (format) of the profit and loss statement has different contents of the items depending on the method of determining the financial result (by functions and characteristics).
In accordance with the Federal Law “On Accounting” No. 129-FZ dated November 21, 1996 and the accounting regulations “Accounting statements of an organization” PBU 4/99, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 43 dated July 6, 1999, legal persons prepare uniform forms of annual and interim (month, quarter) reporting. Forms of accounting (financial) statements are approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On forms of accounting statements of an organization” No. 67n dated July 22, 2003.
The annual volume of accounting reporting forms includes:
Balance sheet (form No. 1);
Profit and loss statement (form No. 2);
Statement of changes in capital (form No. 3);
Cash flow statement (form No. 4);
Appendixes to the balance sheet (form No. 5);
Report on the intended use of funds received (form No. 6);
Explanatory note;
Audit report.
The intermediate volume of accounting reporting forms includes:
Balance sheet (form No. 1);
Profit and loss statement (form No. 2).
Monthly, quarterly and annual financial statements (individual statements) prepared by the organization reflect the composition of the property and the sources of its formation, including the property of production facilities, branches, representative offices and other divisions allocated to a separate balance sheet. Associations that include organizations that form an independent balance sheet, and centralized accounting that serves the organization - accounting statements that reflect the results of economic activities, the property of these organizations, and the sources of its formation are reflected in the consolidated financial statements.
In related companies, in addition to annual individual reporting prepared by subsidiaries, the parent company prepares individual and consolidated reporting
Financial reporting indicators are formed on the basis of financial accounting data.
⇐ Previous28293031323334353637
Regulatory acts
Off-balance sheet accounts are regulated by the following legislative acts:
- Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”, which contains the basic requirements for the documentation compiled. The law determines that a company’s own property should be taken into account separately from non-own material assets. For the latter, off-balance sheet accounting must be maintained.
- Article 275 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates the taxation procedure.
- Article 329 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, according to which obligations must be secured by penalties, pledges, deposits, guarantees and other means that do not contradict current legislation. In addition, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation specifies the rights and obligations of the parties that are bound by a lease agreement or a commission under it.
- Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 34n as amended in 2021, which explains the procedure for accounting for off-balance sheet accounts.