The system of settlements with buyers, suppliers and contractors at any fairly large enterprise includes various types: non-cash and cash payments, offset of mutual claims, settlements with bills, etc. Most payments are made in non-cash form. However, transactions with bills of exchange, while sometimes not occupying a significant volume in the total cash flow of an enterprise, are distinguished by significant diversity, which requires the creation of an appropriate system for their accounting and control. At JSC STEKLONiT (Ufa), this accounting section was organized with the introduction at the plant of an automated sales management system, accounting and tax accounting, which was carried out on the basis of the “Accounting” configuration of the “1C: Enterprise 7.7” program system.
Bill payments
Payments by bill of exchange - 2021 - 2021 are one of the forms of non-monetary payments used in the economic market.
These types of transactions are regulated by special norms of bill of exchange legislation, however, in the absence of such special norms, the general norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) should be applied to them, taking into account their features (clause 1 of the resolution of December 4, 2000 of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation No. 33, Plenum Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 14, hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 33/14).
Thus, the main regulatory legal acts of bill of exchange legislation are:
- Law “On promissory notes and bills of exchange” dated March 11, 1997 No. 48-FZ (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 48-FZ);
- Resolution of the Central Executive Committee of the USSR and the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR “On the implementation of the Regulations...” dated 08/07/1937 No. 104/1341 (hereinafter referred to as Regulation No. 104/1341).
The general rules in relation to transactions with bills include Art. 143, 153–181, 307–419 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (from 06/01/2018, Articles 815–816 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation lost force).
Tax accounting of cambios issued as a future payment
The bill amount does not affect the procedure for calculating taxes and is not taken into account when calculating the tax base for income tax. The issued cambio does not affect VAT either. In general, the drawer accepts only the input VAT tax on the products received.
Expenses in the form of interest are considered non-operating. Accounting for expenses on discount and interest rates is the same and is carried out in compliance with the standards prescribed by Art. 269 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Since 2015, interest on promissory note loans has been included in expenses indefinitely. This innovation does not apply to controlled transactions.
Features of settlements using bills of exchange
These features include the following:
- the drawer and holder of the bill can be either a citizen or a legal entity (Article 2 of Law No. 48-FZ), including in cases established by law - an administrative-territorial unit;
- only a monetary obligation can be transferred under a bill of exchange;
- the bill of exchange can be executed exclusively on paper (Article 4 of Law No. 48-FZ, Clause 2 of Resolution No. 33/14);
- a bill of exchange can be simple (under which the drawer undertakes to pay the corresponding amount to the holder of the bill) or transferable (under which the drawer issues the bill to the holder of the bill, and payment for it is made by a third party who has assumed such an obligation by acceptance);
- the list of mandatory details of a promissory note is enshrined in clause 75 of regulation No. 104/1341, the details of a bill of exchange - in clause 1 of the said regulation.
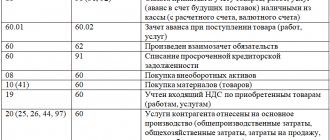
Key accounts used in cambio accounting
Key accounts are presented in the following list:
| Key account assignments and accounts for cambio accounting | Characteristic |
| Account 58, subaccount. "Cash equivalents" Account. 58, subaccount. "Cambio" | Liquid bills of exchange are taken into account, which are used as a means of payment or are repaid in 3 months. Cambios of a third party are displayed (they are also financial investments), for which income is possible in interest or in the form of a discount |
| Account 76 (Payment with lenders and debtors) DT 76, CT 62.1 (Payment with debtors and lenders) DT 76, KT 91.1 | Unprofitable cambios are shown Interest-free cambio transferred Selling third party cambio |
| Account 58 or 76, subaccount. “Discount, percentage” DT. 58 (Attachments), subaccount. “Discount”, KT 91 (Expenditures and income), subaccount. "Other income" | Interest is recorded separately from the cambio price Monthly discount |
| Account 60 (Payments with suppliers, etc.), subaccount. 60.3 (Cambio Issued) | Issued cambios are taken into account |
| DT 60 (Payments with suppliers, etc.), CT 91 (Expenditures and income), subaccount. "Profit" | Income at the time of transfer of cambio - the amount of debt for goods (services, work) |
| DT 76 (Debtors, lenders), CT 91, subaccount. "Profit" | Income at the time of issuance of the cambio - the contract price of the security |
| DT 51 (Current account), CT 76 (Lenders, debtors) | Paying off the debt at the time of crediting money via cambio |
General scheme of bill payments
The scheme for settlements with bills in the general case is as follows:
- When paying with simple bills:
- the buyer of goods/recipient of services (drawer) issues a bill of exchange to the seller/service provider (drawer) as confirmation of his obligation to pay for the goods/services in the future;
- the holder of the bill fulfills his obligation to the drawer, for example, through the sale of goods or the provision of services;
- the holder of the bill presents the bill for payment;
- repayment of a promissory note directly by the drawer, i.e. fulfillment of the obligation to pay for a good or service.
- When paying with bills of exchange:
- the buyer of goods / recipient of services (drawer, drawer) sends to the debtor (drawee) a bill of exchange (draft) issued in the name of the recipient of funds (remitee), for example, the seller;
- the drawee sends the accepted bill to the drawer (if the drawee does not accept the bill, the bill of exchange is subject to notarization);
- the drawer transfers such a bill to the remitter by means of an endorsement - an endorsement (Chapter II of Regulation No. 104/1341);
- the remitter presents the bill of exchange to the drawee for payment;
- the drawee carries out the cancellation of the bill, i.e. payment. IMPORTANT! When resolving disputes related to bill settlements, the following conclusions of the law enforcement officer may be useful (see the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated February 15, 2018 No. 305-ES17-17027 in case No. A40-90813/2016):
- if a promissory note is not presented, the holder loses his rights in relation to persons obligated under the bill, except the drawer;
- the drawer of a promissory note is obliged in the same way as the acceptor of a transferable bill;
- the claims of the holder of the bill against the drawer arising from the promissory note are extinguished upon the expiration of three years from the date of payment.
Automation
Automation of the sales management system, accounting and tax accounting was carried out in Ufa. The “Accounting” configuration of the “1C:Enterprise 7.7” program system was used as the initial one.
When automating plant operations to record settlements with customers, suppliers and contractors using promissory notes, special attention was paid to the following points:
- developed document flow and distribution of document processing functions among a large number of users;
- the requirement to reflect each separate business transaction in an electronic document in order to clearly differentiate access and maximize automation of information processing;
- automatic reflection of transactions for payment by bills in the purchase book and sales book.
- The absence in the basic standard configuration of 1C: Accounting of reference books and documents that fully reflect automated operations required the creation of new configuration objects.
To store information about bills of exchange, the “Bills of Exchange” directory was developed (Figure 1).
Picture 1
Unlike the standard “Securities” directory, the “Bills of Exchange” directory allows you to separately store information about the series, number, issuer, par value, date of issue and date of payment. These details are necessary for drawing up acts of acceptance and transfer of bills.
Transactions on the receipt of bank bills from buyers are registered using a specially designed document “Receipt of bills” (Figure 2).
Figure 2
The document allows you to select a buyer, a transaction (advance or against payment for supplies), generate and save a list of bills of exchange being transferred, as well as specify additional details necessary to draw up a bill of exchange acceptance certificate. The act can be printed directly from the document form. When posting a document, the transactions described above are generated.
Transactions involving the transfer to suppliers and contractors of own and bank bills previously received from buyers are recorded using a specially developed document “Expenditure of bills” (Figure 3).
Figure 3
The document allows you to select a supplier or contractor, an operation, generate and save a list of bills of exchange being transferred, and specify additional details necessary to prepare a printed form of the bill of exchange acceptance certificate. When posting a document, transactions are generated, the content of which is determined by the selected operation.
Figure 4 shows a printed form of the act of acceptance and transfer of bills.
Figure 4
Postings for accrual and offset of VAT are not generated directly in the documents “Receipt of bills of exchange” and “Expenditure of bills of exchange”. This is due to the general technology of VAT accounting in the developed program. All postings to account 68.2 “VAT (calculations with the VAT budget)” are generated only by the documents “Purchase book entry” and “Sales book entry”, which allows you to flexibly take into account the date of occurrence of obligations, simplify the verification of calculations and support the program.
| The work was performed by Soft-portal LLC, telephone: (3472) 747-746, fax, e-mail, www.soft-portal.ru |
Accounting for bills of exchange: selected key errors
Erroneous actions during transactions with cambio are often committed by both parties to transactions. The most common violations are committed during record keeping and registration of securities (for example, a purchase and sale agreement, which is incorrect, since the issuance of cambio is accompanied by the execution of a transfer and acceptance certificate).
A typical example from a series of similar violations is the incorrect accounting of profits under the simplified tax system, when cambio is used against a future payment. Thus, income is often shown at the time the security is received. This is not true. You need to be guided by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 346.17, paragraph 1. In accordance with this article, the seller on the simplified tax system, who received the cambio, takes into account the proceeds (income) on the date of their receipt according to this bill or on the day of its transfer to a third party.
Errors are also made when accounting for costs (for the simplified tax system) associated with the use of cambio, in relation to the incorrect determination of the date of accounting for expenses. The legal framework (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 346.17, clause 2, clause 5) obliges, when issuing a security, to take into account expenses on the date of transfer of money on the security. If the calculation is carried out by a third party cambio, then the date of its transfer is taken to account for expenses.
In order to eliminate or reduce the risk of erroneous actions, it is necessary, at a minimum, to analyze all transactions on securities, correctly organize their accounting, display and timely adjust all aspects of the accounting policy regarding transactions with cambio.
Bill of exchange - what is it? – Detailed analysis of the security in 2021
At the same time, he enters into a special register, which is maintained in the office, all the data on the protested bill, and on the front side of the bill itself he puts a note about the protest (the word “protested”, date, signature, seal).
Banks and enterprises are responsible for violating the rules for performing settlement transactions in accordance with current legislation. Property liability between the bank and its client is determined by regulations and agreements between the bank and its client. Regulatory acts include legislative acts, as well as rules issued by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. Penalties can only be applied if there is a contractual relationship between the bank that committed the violation and the client company. In accordance with clause 30 of the Law “On Banks and Banking Activities,” relations between the Bank of Russia, credit institutions and their clients are carried out on the basis of agreements, unless otherwise provided by federal law.
The agreement must indicate interest rates on loans and deposits, the cost of banking services and the timing of their implementation, including the processing time of payment documents, the property liability of the parties for violations of the agreement, including liability for violation of obligations regarding the timing of payments, as well as the procedure for its termination and other essential terms of the agreement.
The procedure for opening, maintaining and closing client accounts in rubles and foreign currency by the bank is established by the Bank of Russia in accordance with federal laws.
Participants in a credit organization do not have any advantages when considering the issue of obtaining a loan or providing them with other banking services, unless otherwise provided by federal law.
The enterprise bears direct responsibility for non-compliance with loan agreements and settlement discipline. An enterprise that systematically fails to fulfill its payment obligations may be declared insolvent. This is reported to the main suppliers of inventory items and to a higher authority.
M.A. Borovskaya Banking services for enterprises
Tutorial. Taganrog: TRTU Publishing House, 1999.
Special terms
There is hardly another financial paper such as a bill of exchange, with which so many different technical terms are used.
Allonge is an additional sheet that is attached to the bill. It is used when there is no longer room for notes on the back of the bill.
Aval is a guarantee of payment. It is carried out mainly in the form of a special inscription “per aval” next to the payer’s name, or without it. These data can be indicated on the front side of the document, on the back, and also on the allonge.
An avalist is someone who provides a guarantee of payment. Usually this is a bank.
Endorsement is a special entry on the back of the document, which contains an indication of the transfer of rights from one bill holder to another bill holder.
An endorser is a bill holder who transfers the right to claim a debt.
The endorser is the one who receives the right of claim and becomes the holder of the bill.
Draft is a bill of exchange.
Drawer - issues a bill of exchange.
Drawer - pays on a bill of exchange.
Remitter - the person in whose favor the bill of exchange is issued.
Prima bill is a document that the drawer issues to the holder of the bill.
A bill of exchange is a document issued by the drawer to the drawee.
Guest, have you already read it in the latest issue?
Is it worth investing in bills?
If an investor is faced with a choice of where to invest - in a deposit in a banking institution or in a bill of exchange, it is worth remembering that the security in question has an interest rate that is several percent lower than the deposit. It is also worth remembering that the bill has a high cost, is not covered by insurance, and also requires contributions to the tax office in the amount of 13%.
The advantages of investing in a bill include liquidity and ease of use. The security in question allows you to predict profit.
Thus, a bill is a security that is necessary to fulfill debt obligations. Many investors prefer this financial instrument because it allows them to get good profits. However, you should not forget about the shortcomings of the security in question.
why do you need a bill of exchange? an explanation in simple words of how to use a bill of exchange
What does a bill of exchange mean and why is it issued?
Payment by bills is carried out between sellers and buyers. The financial instrument provides deferred payment. The document has a strict form and filling rules. The signing involves the drawer (issuer, borrower) and the holder of the bill - creditor, recipient of the benefit.
The recipient can demand repayment of the loan from the debtor.
Characteristics of the bill:
- Indisputability. The debt is repaid in full in any situation.
- Unconditionality.
- Only monetary form.
- Appealability. Transferable without restriction from one owner to another by means of a deed of conveyance without the consent of the issuer.
- Independence and distraction from other transactions. It itself has value and legal status separately from additional conditions.
- Form of strict accountability
Main functions:
- Deferred payment for goods and services. A bill of exchange acts as security for a transaction.
- Obtaining and processing a loan. Bills of exchange are used to pay for material assets, services, repay loans, and issue loans. Lenders are comfortable with its strict form and ease of transfer, as well as the guarantee of debt repayment within the specified period.
The paper simultaneously ensures repayment of the debt and records its occurrence. The importance of this instrument is that it passes through several holders before maturity, extinguishes obligations with less money in circulation and speeds up settlements.
Who can write him out?
The right to draw up your own bill of exchange is called bill of exchange capacity. It can be produced by both companies and individuals. A person who can issue a credit ticket and be responsible for financial obligations must be an adult (over 18 years old) and mentally healthy.
Where and when can you use them?
The use of bill schemes is not limited to commodity turnover. Companies are attracting additional financial resources and restructuring accounts payable. The number of bills issued is not limited, so they are issued as an infusion of money is needed.
Types of operations:
- emission;
- sale to attract investment;
- accounting of issued and canceled forms to prevent “gray” schemes and counterfeits in the stock market;
- issuing or conducting mutual settlements;
- repayment.
Payment is possible at the end of the term or at the request of the lender. Without specifying the deadline, the receipt is considered invalid. Urgent bills require special care, since after the expiration of the term, payment of the debt is made only by agreement of the parties.
To be on the safe side before handing over the bill to the payer, I recommend making a copy of it.
When concluding a commodity transaction, the bill circulation scheme looks like this:
- After agreement, the goods are delivered to the buyer.
- The debtor's bank accepts (accepts for payment) the bill.
- The document is presented on the specified date.
- A payment order is made to the seller's account.
How to check
The issue of checking a security is especially acute if you did not receive it directly from the debtor. Banks conduct it in the presence and at the request of the client. When applying in writing, the registration of the document in the securities register is confirmed or refuted, the authenticity of the form and all marks made are verified.
To avoid being deceived, remember the following:
- The paper is considered invalid if the form prescribed by the regulations is violated.
- A document will be considered a forgery if some parts of it are falsified.
- There should be no errors or corrections in the content; information about the owner is genuine.
- The printing quality of counterfeit samples is revealed by blurry prints and excessively bright colors, glare on the main information, or poor paper quality.
The most reliable way to verify the authenticity of a debt obligation is to contact the issuer.
Is a bill of exchange a security?
Yes. According to Russian legislation, it meets this definition according to the following criteria:
- Established form of compilation and execution.
- Mandatory information about all participants.
- Contains and confirms a description of rights that are transferred only with the document and upon its presentation.
What does it look like
This is what a photo of the bill of exchange looks like. It can be downloaded online for free or purchased in the required quantity and design.
Required details
Very strict requirements are imposed on the form of the bill. It is drawn up on a regular sheet of paper or on letterhead, it depends on the drawer. The recipient of the payment may be indicated, but the document can be drawn up without this.
Required details include:
- A bill of exchange mark or designation of the type of document, such as "promissory note."
- Date and place of document preparation.
- An obligation to pay a debt amounting to a specified amount. It is indicated in numbers and words.
- Date and place of payment.
- Details of the payer and creditor. The order (to bearer) form does not indicate the recipient.
- Signature of the owner of the security (issuer).
- Details of the payer (for a bill of exchange).
It is very important to fill out the document without corrections, not to leave blank fields, and not to allow abbreviations. The receipt is invalid if errors are made in the design.
Acceptance
An accepted bill confirms the payer’s agreement to pay the debt specified in it. Until the acceptance is issued, the obligations lie with the issuer, after signing - with the drawee. This is the person indicated in the document as the payer).
The beneficiary can present a receipt for payment or transfer it to another person. For the operation, an endorsement (endorsement) on the back of the form is sufficient. The number of signatures on the transfer is not limited.
In addition to confirmation in circulation, a bill of exchange protest is often used. The act records the payer’s refusal to make the payment or indicate its exact date. Unaccepted papers go out of circulation and cannot be presented for payment or protested against non-payment.
Types of bills and their differences
Debt securities have several classifications depending on the changing characteristic:
- The organization that issued them.
- Reason for issue and purpose of issue.
- Payer of the obligation (drawer or third party).
- By payee.
Nominal
It differs in that it contains the details of the beneficiary.
If the recipient is not specified, any bearer will receive the payment.
Bank
Issued by the bank to accumulate investments or finance programs and projects. It can be compared to a deposit.
Treasury
Issued by the state to provide expenses in the necessary areas.
Commercial
Participates in transactions between sellers and buyers, providing the opportunity to defer payment. Helps you buy and sell goods on credit, without money.
Financial
Secures the occurrence of debt obligations when issuing a loan and guarantees its repayment. Enterprises purchase them from partners who have no debt.
Transfer of rights to a bill of exchange
The security in question can be transferred to another person, which is ensured by its mobility. Thus, one company, receiving a bill for goods and services from the issuer, in turn can pay for goods and services with a third organization. In order to do this, on the reverse side of the security in question, information about the new owner is written down, a seal and a signature are affixed. However, as mentioned above, the third party may not accept the bill for payment, demanding funds.
Advantages and disadvantages of using bills of exchange
With the help of bill circulation, commercial enterprises can receive or issue cash loans without involving the banking industry with its commissions and interest rates for services. In addition, having the status of a security, it is liquid and can either be sold or used as a mortgage.
Bill forms replace and save current assets; they are easy to fill out and convenient to use.
I will highlight the most important advantages:
- Undisputed repayment of obligations.
- Debt collection through court does not require argumentation.
- If necessary, it can be sold.
- Helps optimize tax payments.
- Used instead of money.
- Gives a deferred payment.
As you know, any coin has two sides, so issuing bills entails difficulties and inconveniences.
Main disadvantages:
- There is no guarantee of debt repayment or security.
- The procedure for compensation by court decision lasts several months.
- It may not be accepted as payment by a third party.
Additional classifications of bills
In addition to the fact that the security in question is divided into simple and transferable, it is also classified according to other criteria:
- personal We are talking about a registered bill of exchange if it contains information about who should receive funds under this document. If there is no information, every person who has the security in question can receive money;
- bank. Such a bill is issued by banking institutions to raise funds for some projects. A bank security can be compared to a deposit, only the rate is slightly higher;
- treasury. This type of securities is issued by government authorities in order to raise funds for the implementation of a program;
- A commercial bill is used when purchasing goods and services. With its help, the buyer takes out a loan, as it were;
- financial. Such a promissory note is used in cases where a company takes out a loan from another company and then pays it back with interest.