Tire accounting principles
The main accounting parameters are: (click to expand)
- their number;
- model;
- tire brand;
- price;
- size.
Based on these indicators, accounting employees keep separate records of seasonal, summer and winter vehicle tires. At the same time, new and used spare parts are also taken into account separately. The purchase, their transfer into operation and other operations are reflected by the accounting service with account assignments (postings).
| Operation name | Accounting assignments |
| Buying a tire for a vehicle | DT 60, CT 51 (transfer of money for purchase), DT 10, subaccount “Spare parts” (“Spare tires”, “New tires”), KT 60 (financial obligations for purchased spare parts), DT 19, CT 60 (VAT on the cost of purchased goods), DT 68, CT 19 (VAT deductible) |
| Putting the tire into use | DT 10, sub-account “Spare parts” (“Tires in the sub-report”), KT 10, sub-account “Spare parts” and “Spare tires” |
| Disposal of a car tire due to its failure | DT 20 (26, 44), CT 10, subaccount “Spare parts”, “Tires in the sub-account” |
The cost of purchased vehicle tires for the purpose of replacing worn-out ones is displayed by the accounting service on account 10 “Materials”, subaccount “Spare parts”.
uchet_shin_v_buhgalterskom_uchete.jpg
Related publications
Like any company asset from the production inventory block, tires are taken into account according to the available parameters: model, brand, size. But their use involves a much wider range of operations than simply decommissioning into production. Let's look at how to ensure proper accounting of car tires in accounting.
Tax accounting of tires
When purchasing a car, the price of installed and spare tires is combined with the initial cost of the vehicle (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 257). These spare parts do not appear on the accounting accounts as separate objects. Tires purchased separately are not included in the purchased vehicle and are not added to its cost. Here, tax accounting of spare parts is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- Art. 254 (payer’s expenses for production and economic needs);
- Art. 260 (restoration of fixed assets);
- Art. 264 (maintenance and use of official transport).
So, for example, according to tax legislation, separately purchased spare parts can be taken into account as material expenses for the purchase of materials necessary for the maintenance of fixed assets. That is, tires in such cases are considered spare parts for a car, which are recorded at their cost among inventories. Expenses for their repair can be classified as other.
Expenses are considered for tax purposes in the tax period valid at that time. All expenses under the accrual method are recognized at the time the tires are assembled on the car. Spare parts removed from vehicles are not considered returnable waste or residual stock.
Write-off of tires that have become unusable.
The write-off of car tires may occur if their further use is inadmissible in accordance with current standards for the operation of vehicles (exceeding the permissible tread depth, the presence of cuts, other damage, etc.).
As a result of work to replace worn-out tires, documented in the appropriate acceptance certificate, the disposal of tires is reflected from off-balance sheet account 09 (paragraph 3, clause 349 of Instruction No. 157n). The decision to write off tires is made by the institution’s permanent commission on the receipt and disposal of assets.
The write-off procedure itself can be formalized by an act of write-off of inventories (form 0504230) or an accounting certificate (form 0504833). The corresponding document is established in the accounting policy of the institution.
Subsequently, tires that are not suitable for further use must be disposed of by a specialized organization. Until the moment of disposal, the specified components are recorded in off-balance sheet account 02 “Tangible assets accepted for storage” at the cost reflected in the write-off document, or in the conditional valuation: 1 tire - 1 rub. (clause 335 of Instruction No. 157n).
The capitalization of tires that are not suitable for further use is carried out at the estimated value as of the date they were accepted for accounting (clause 106 of Instruction No. 157n).
These transactions are reflected in accounting by the following accounting entries:
| State institution (Instruction No. 162n) | State-financed organization (Instruction No. 174n) | Autonomous institution (Instruction No. 183n) | |||
| Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit |
| Unusable tires were written off off-balance sheet | |||||
| Off-balance sheet account 09 | Off-balance sheet account 09 | Off-balance sheet account 09 | |||
| Discarded tires have been accepted for off-balance sheet accounting (until disposal) | |||||
| Off-balance sheet account 02 | Off-balance sheet account 02 | Off-balance sheet account 02 | |||
| Tires written off off-balance sheet | |||||
| Off-balance sheet account 02 | Off-balance sheet account 02 | Off-balance sheet account 02 | |||
| Unusable tires were capitalized at their estimated value | |||||
| 1 105 36 340 | 1 401 10 189 | 0 105 36 340 | 0 401 10 189 | 0 105 36 000 | 0 401 10 189 |
| Tires handed over for recycling | |||||
| 1 401 10 172 | 1 105 36 440 | 2 401 10 172 | 2 105 36 440 | 2 401 10 172 | 2 105 36 000 |
| Accrued income from recycling of unusable tires | |||||
| 1 205 74 560* | 1 401 10 172 | 2 209 89 560 | 2 401 10 172 | 2 209 89 000 | 2 401 10 172 |
* The institution has the right to provide in its accounting policy for the use of account 1,209,89,000.
Please note that the disposal of worn-out tires is one of the types of income-generating activities that government institutions can carry out if such a right is provided for in their constituent documents (Article 161 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation).
As for budgetary and autonomous institutions, they have the right to engage in other types of activities only insofar as this serves to achieve the goals for which they were created, and these types of activities correspond to these goals, provided that such activities are indicated in their constituent documents (charters) (Clause 4, Article 9.2 of the Federal Law of January 12, 1996 No. 7-FZ, Clause 7 of Article 4 of the Federal Law of November 3, 2006 No. 174-FZ).
State institutions are required to send funds received from such activities to the appropriate budget of the budget system of the Russian Federation (Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But budgetary and autonomous institutions have the right to dispose of them independently (clause 3 of article 298 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, clause 8 of article 2 of Federal Law No. 174-FZ).
The budgetary cultural institution wrote off 4 car tires that had become unusable from off-balance sheet accounting. in the amount of 6,000 rubles. As part of an agreement concluded with a specialized organization, these tires were handed over for recycling. The cost of recycled tires is equal to their current estimated value, determined by the commission on receipt and disposal of the institution’s assets in the amount of 1,200 rubles.
The accounting records reflect the following correspondence accounts:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | Primary document |
| Unusable tires were written off off-balance sheet | Off-balance sheet account 09 | 6 000 | Accounting certificate (f. 0504833) | |
| Discarded tires have been accepted for off-balance sheet accounting (until disposal) | Off-balance sheet account 02 | 4* | Accounting certificate (f. 0504833) | |
| Tires written off off-balance sheet | Off-balance sheet account 02 | 4* | Recycling act | |
| Unusable tires were capitalized at their estimated value | 2 105 36 340 | 2 401 10 189 | 1 200 | Receipt order for acceptance of material assets (non-financial assets) (f. 0504207) |
| Tires handed over for recycling | 2 401 10 172 | 2 105 36 440 | 1 200 | Invoice for the release of materials (material assets) to the third party (f. 0504205) |
| Accrued income from recycling of unusable tires | 2 209 89 560 | 2 401 10 172 | 1 200 | Agreement, accounting certificate (f. 0504833) |
* We proceed from the condition that the accounting policy of the institution provides for the acceptance of 02 components for the car into an off-balance sheet account until they are disposed of in a conditional valuation: 1 object - 1 rub.
Accounting documentation for tire operation
A specialized accounting form of the card is created by the technical service of the relevant division of the organization according to form No. 424-APK separately for each vehicle tire (new, used or refurbished).
The main purpose of the registration card is to document the movement of tires in use from the time they are assembled until they completely fail. The card contains the following information: (click to expand)
- date of manufacture, manufacturer, price, as well as the name of the wheels and serial number;
- technical condition (existing defects, damage);
- mileage (the previous one is for used tires, and the actual mileage for each month is for all types of tires);
- date of tire replacement, numbers of removed and reassembled tires;
- dismantling time, total mileage, tread pattern data, for what purpose and for what reason it was taken out of service (in case of deregistration of the tire).
The specified standard accounting forms are filled out completely and stored according to vehicle numbers, and are closed when the spare part is sent for disposal.
The reason for writing off or replacing a tire is not its mileage if its technical condition is satisfactory and requires modernization, reconstruction, repair, or further operation. After restoration, other cards are issued for vehicle spare parts. In isolated cases, when there are no such cards, you can get some information from the waybill, which is issued for the vehicle.
Organization of the accounting process.
In order to organize the accounting process for the operation of car tires, institutions should develop the necessary internal administrative documents establishing, in particular:
- forms of primary documents for acceptance, release, internal movement, write-off of tires and the procedure for filling them out, as well as document flow rules;
- the procedure for monitoring the rational use of tires;
- list of officials responsible for receiving and issuing tires.
When developing relevant documents, it is necessary to take into account the following provisions:
- Rules for the operation of automobile tires (AE 001‑04), approved by Order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2004 No. AK-9‑r (hereinafter referred to as Rules No. AE 001‑04), which can be followed to this day (see Letter from the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation dated 09/21/2009 No. 03‑2609);
- Temporary norms for the operational mileage of tires of motor vehicles (RD 3112199‑1085‑02), approved by the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation on 04.04.2002, which provides data on the average mileage of tires of various types of vehicles, as well as a formula for calculating the norm of operational mileage.
Please note that only when the service mileage has been reached, tires must be replaced or written off from the register. To track such mileage, as well as the technical condition of the tire, you should create a card to record its operation. The institution has the right to develop the form of this document independently or use the one given in Appendix 12 to Rules No. AE 001-04.
For a sample of the recommended form of a car tire performance record card (new, retreaded, resurfaced, used), see the end of the article.
These cards serve as the basis for the formation of primary accounting documents on the movement of car tires in the institution and the corresponding entries in the accounting accounts.
Operating mileage rate for write-off
Russian legislation does not establish specific standards for the write-off of vehicle tires. With regard to their operational mileage, the regulations of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation, set out in Letter No. 03-01/10-2830sh dated 08/24/2012, apply. Thus, according to the letter, the standards are determined by the manufacturer.
Accordingly, the head of the organization has the right to develop and approve standards by his own order based on the average mileage, using the available information:
- factory manufacturer;
- according to the method for determining mileage standards of the Temporary Standards (RD 3112199-1085-02) as amended on December 7, 2006 (in situations identical to the one under consideration, it can be used as a sample);
- experience in organizing transport operation.
Thus, according to the standards of RD 3112199-1085-02, the mileage rate established by the organization should not be less than 25% of the average mileage parameter.
| Manufacturer | Average tire mileage parameters (approximate figures), thousand km |
| Russian | 40–45 (passenger cars), up to 100 (trucks) |
| Foreign | 50—55 (passenger cars), up to 180 (trucks) |
In any case, independent development according to the standards must be financially justified and documented.
Enter the site
RSS Print
Category : Accounting Replies : 391
You can add a topic to your favorites list and subscribe to email notifications.
« First ← Prev. ...Next. → Last (40) »
| Anna (guest) [email protected] | |
| Please tell me, the organization shaved a set of car tires and immediately began using them, how to reflect these operations in accounting. accounting? Thank you all in advance | |
| I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because: Notification is being sent... |
| Tatiana (guest) | #2[9885] February 27, 2009, 5:48 pm |
Notification is being sent...
| Elena [email hidden] Belarus, Minsk Wrote 1805 messages Write a private message Reputation: 103 | #3[9892] February 27, 2009, 18:10 |
Notification is being sent...
| Andrej [email hidden] Belarus, Minsk Wrote 218 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #4[9894] February 27, 2009, 6:13 pm |
Notification is being sent...
| Andrej [email hidden] Belarus, Minsk Wrote 218 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #5[9898] February 27, 2009, 18:23 |
The cost of tires installed on vehicles involved in business activities is written off to replace worn-out ones.
cost of products (works, services) as the cost of repairing fixed assets
. I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:
Notification is being sent...
| Yaroslav [email hidden] Belarus, Minsk Wrote 1116 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #6[42997] October 23, 2009, 16:21 |
Notification is being sent...
Being a leader means not stopping good people from working. P. Kapitsa| Julie [email hidden] Belarus Wrote 636 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #7[76300] January 16, 2010, 5:02 pm |
Notification is being sent...
| Yaroslav [email hidden] Belarus, Minsk Wrote 1116 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #8[76326] January 16, 2010, 17:50 |
Juli wrote:
those. I bought tires this month and immediately put them on expenses?
Everything is correct, but taking into account the fact that they are supplied to the car, they may still lie in the warehouse.
I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:Notification is being sent...
Being a leader means not stopping good people from working. P. Kapitsa| Julie [email hidden] Belarus Wrote 636 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #9[76337] January 16, 2010, 18:22 |
Bronsi wrote:
Dct
Juli wrote:
those. I bought tires this month and immediately put them on expenses?
Everything is correct, but taking into account the fact that they are supplied to the car, they may still lie in the warehouse. Thanks a lot. In principle, I did just that, but I read a lot about write-offs based on mileage and was already scared, because... I've been writing off tires like this for a long time now.
I want to draw the moderator's attention to this message because:Notification is being sent...
| Julie [email hidden] Belarus Wrote 636 messages Write a private message Reputation: | #10[76345] January 16, 2010, 6:45 pm |
Notification is being sent...
« First ← Prev. ...Next. → Last (40) »
In order to reply to this topic, you must log in or register.
Accounting for wear and replacement of car tires
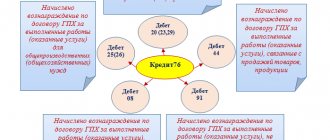
It is allowed to consider the replacement of unusable (worn out) specified spare parts as part of the repair. Then you should write off production costs and expenses for repairing the fixed asset. Costs associated with repairs are displayed by the accounting department using DT accounts for recording expenses for production (sales), CT accounts for accounting for expenses incurred. Thus, DT 20, 26, 44, KT 10, subaccount “Tire in the sub-account” reflects the inclusion of the price of seasonal vehicle spare parts in expenses for normal activities after their wear.
Worn-out automobile parts that are subject to modernization, repair, or reconstruction are included in the warehouse. Their accounting is kept in the subaccount “Tires subject to restoration”, “Materials sent for recycling”. The price is displayed as follows: DT 10, subaccount “Tire for restoration”, KT 91-1.
Changing seasonal vehicle tires is an integral part of the maintenance of a fixed asset, aimed at maintaining the characteristics of the vehicle in proper condition. The costs associated with this are recognized as expenses in the ordinary course of business. Their accounting department displays DT accounts for production (sales) expenses and CT accounts for production expenses (related to service costs).
But when replacing seasonal spare parts and sending them to the warehouse, their price is related to the reduction of expenses for current activities: DT 20 (26, 44), CT 10, subaccount “Tires in subaccount”. To display the replacement of summer and winter vehicle tires, account assignments are used for account 10. For example, when assembling winter tires, the price of vehicle tires put into use is displayed as follows: DT 10, subaccount “Tire in subaccount”, CT 10, subaccount “Spare tire”.
At the end of the season, winter parts are removed and summer parts are assembled. To display the price of the removed winter version, account assignment is used: DT 10, subaccount “Spare tire”, KT 10 “Tire in subaccount”. The price of the assembled summer version instead of the winter one will be displayed by account assignment: DT 10, subaccount “Tire in subaccount”, KT 10, subaccount “Spare tire”.
Example 1. Taking into account the cost of all-season car tires when purchasing them
Felix LLC purchased a set of all-season tires for a vehicle. Almost immediately, the worn-out parts were replaced with new ones, just purchased. The accounting service displayed all actions using account assignments.
| Operation name | Accounting assignments |
| Receipt of vehicle spare parts to the warehouse | DT 10, subaccount “Spare parts” and “Spare tires”, CT 60. |
Materials or fixed assets?
Despite the fact that the service life of car tires exceeds 12 months, they must be taken into account as part of inventory. Let's explain why.
Tangible assets, regardless of their value, with a useful life of more than 12 months, intended for use in the course of the institution’s activities, are taken into account as fixed assets (clause 38 of Instruction No. 157n[3]). In this case, an object of fixed assets is an object with all fixtures and accessories, or a separate structurally isolated object intended to perform certain independent functions, or a separate complex of structurally articulated objects that constitute a single whole and are intended to perform the corresponding work (clause 41 of the Instructions No. 157n).
A car tire cannot be used for its intended purpose separately from a vehicle; therefore, it does not form an independent fixed asset item. At their core, tires are close to components (spare parts), the accounting of which must be organized on account 1,105,36,000 “Other inventories - other movable property of the institution” (clauses 98, 99 of Instruction No. 157n, clause 21 of Instruction No. 162n [4]).
However, if tires are purchased along with a car, they are subject to reflection as part of an item of fixed assets and are not taken into account separately. In this case, the cost of tires participates in determining the cost of the car.
Average mileage of passenger car tires
The average lifespan of tires is about 5-10 years, depending on the season of their use.
In Russia, due to the mediocre condition of roads, this figure in practice is much lower. It is recommended to change tires every 3-4 years of operation.
Tire wear down to numbers
Tire wear can be calculated:
- According to the indicators on the tread, if the tread wears to this level, the tires require urgent replacement.
- Numbers may be printed on the surface of the tires to indicate the level of wear. Depending on the number, you can determine whether replacement is required.
- By measuring the tread with a depth gauge.
Note!
Also, weather and road factors can affect the average mileage of tires.
Primary documents
Accounting is carried out on the basis of the inter-industry primary form for MPZ, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 71a of October 30, 1997. This is a receipt order drawn up in form No. M-4, a special card drawn up in form No. M-8. The company can develop its own forms. However, they must comply with the provisions of Article 9 of the Accounting Law No. 402. If a company has developed its own forms, this should be reflected in its accounting policies.
An account card will be required. It describes the condition of the tire: main characteristics, defects, description of damage. If the items have already been in use, you must indicate the available mileage. It is also necessary to register the serial number, date of replacement, date of dismantling.
When disposing of components, it is necessary to issue an accounting card and a write-off report. The last paper is drawn up based on the decision of the commission. The report must indicate a defect that cannot be repaired. For example, it could be a break.
The most significant values to consider:
- Number of tires.
- Their model and brand.
- Price.
Accounting for elements of different types (summer, winter) is carried out separately. It is recommended to consider new and used tires separately.
Estimating the service life of car tires - should you trust the manufacturer?
In most cases, the manufacturer, indicating the period of use of tires in seasons or kilometers, provides a guarantee for these control figures. In such cases, this information about the period is more likely to be reliable, since if the tires wear out prematurely, the manufacturer undertakes to provide a new set or return the money. This rule only applies to original tires. Firstly, the manufacturer does not bear any responsibility if the tires were not purchased from an official dealer, and secondly, replicas are characterized by increased wear. Their wear resistance indicators have nothing to do with those of the original models.
Wear of tires to marks
Tire mileage before write-off according to technical regulations of the Ministry of Transport
The location of the lesion is on the sidewall of the tire
. According to the standards of the Russian Ministry of Transport, it is prohibited to operate a vehicle if there are types of technical faults that pose a threat to road safety. Among these are faults related directly to tires:
- the residual tread height of passenger car tires is less than 1.6 mm, for trucks - 1 mm, bus tires - 2 mm, motorcycle and moped tires - 0.8 mm;
- external damage to tires - such as punctures or tears, damage that exposes the cord, causes delamination of the carcass or peeling of the tire tread and its sidewall.
These damages are the full basis for the process of decommissioning tires and installing new tires instead.
As you can see, the mileage standards for tires for write-off are clearly regulated and can be used as a guide when calculating the service life of tires on your own car and when servicing the organization’s vehicle fleet. Thanks to the wear standards of car tires, it is possible to predict the wear and purchase of tires over time.